反射,在Java常用框架中屡见不鲜。它存在于java.lang.reflact包中,就我的认识,它可以拿到类的字段和方法,及构造方法,还可以生成对象实例等。对深入的机制我暂时还不了解,本篇文章着重在使用方面,并附上一个本人应用到项目中的案例。
- 基础姿势
拿到类,反射是以类为基础的基础,首先拿到项目中的类,既可以这样拿
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(类路径);
也可以这样拿
Class<?> clazz = 类名.getClass();
在一般意义的JavaBean中,存在构造函数、字段、一般函数三中不同元素,只要拿到了类,接着拿到它们就是水到渠成
Constructor constructors = clazz.getConstructor(null);//拿到构造函数 Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();//拿到它定义的所有字段 Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();//拿到它定义的所有方法
注意,拿到无参的构造函数传入的是null,拿到有参构造函数,则按照构造函数的参数位置传入对应的类型class就行,比如
Constructor constructors = clazz.getConstructor(String.class,Integer.class,Double.class);//拿到有参构造函数
拿到他们有什么用?拿到构造函数还好可以新建对象,拿到字段呢?这时候就得配合自定义注解来使用了?
定义一个自定义标签
import java.lang.annotation.*; @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //@Documented public @interface AnnotationDemo { public String name(); public String value(); }
ElementType是作为标志存在的,而这个RetentionPolicy则是对功能上有影响的,它里面有三种策略。从源码上看它存在CLASS,RUNTIME,SOURCE三种方式。这个Documented是生成java文档时候是否带上的意思。
package java.lang.annotation; /** * Annotation retention policy. The constants of this enumerated type * describe the various policies for retaining annotations. They are used * in conjunction with the {@link Retention} meta-annotation type to specify * how long annotations are to be retained. * * @author Joshua Bloch * @since 1.5 */ public enum RetentionPolicy { /** * Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler. */ SOURCE, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler * but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default * behavior. */ CLASS, /** * Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and * retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively. * * @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement */ RUNTIME }
官方解释是,这个注解会留在编译器,class文件,和VM中,我理解为作用范围。一般使用RUNTIME。
接着造一个bean。
public class DemoBean { public String pubField; protected String protectField; String defaultField; @AnnotationDemo(name="test",value="123") private String priField; public DemoBean(){ this("pub","protect","default","pri"); } public DemoBean(String pubField,String protectField,String defaultField,String priField){ this.pubField = pubField; this.protectField = protectField; this.defaultField = defaultField; this.priField = priField; } public void function1(){ System.out.println("public function"); } protected void function2(){ System.out.println("protect function"); } void function3(){ System.out.println("default function"); } private void function4(){ System.out.println("private function"); } }
在拿到class之后,遍历它的field寻找注解,当然了,对method也可以这样。
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();//拿到它定义的所有字段 for(Field field:fields){ if(field.isAnnotationPresent(AnnotationDemo.class)){ System.out.println("有注解"); } AnnotationDemo annotationDemo = field.getAnnotation(AnnotationDemo.class); if(annotationDemo != null){ System.out.println("注解 name:"+annotationDemo.name()); System.out.println("注解 value:"+annotationDemo.value()); } System.out.println("属性:"+field.getName()+" "+field.getModifiers()); }
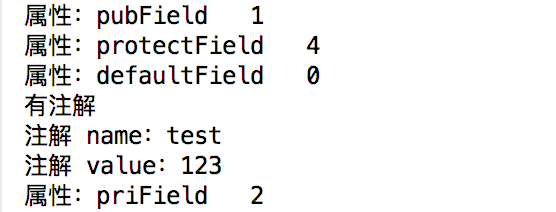
这种方式是不是很眼熟啊?没错,Spring里面到处都是。
- 实际应用

在给字段和方法打上标签之后,繁琐的,重复性的行为都让框架为你处理,这种开发方式节省了很多代码,加强了阅读性,是非常提升效率的。
反射有种方式是绕过编译器对字段封装性的限制的,也就是无论是public还是private的字段,在反射的程序中都是可以拿到并且改变它的值的。我们知道Spring框架对bean的注入,有好几种方式。最让人想的清楚的是构造方法注入和setter注入。而@autowired呢?即使不提供暴露接口一样可以设置,这就是利用了反射的方式。
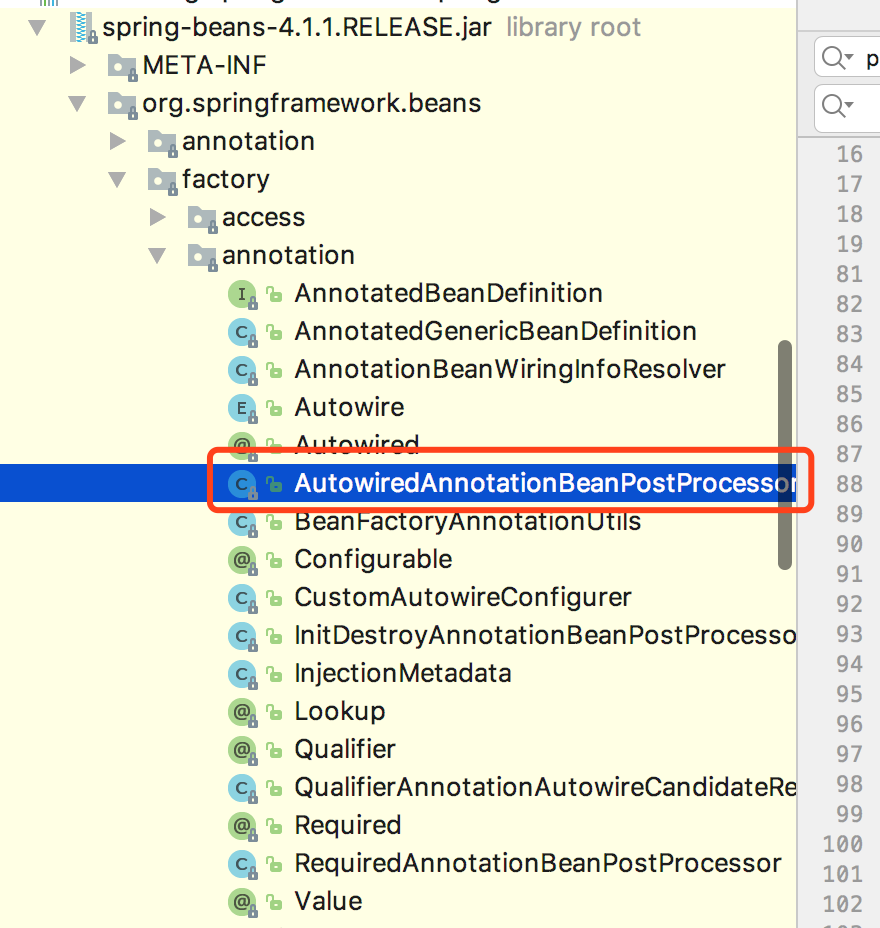
经过查阅资料,阅读源码,在Spring-bean中寻找到这两个类,因为设计图太过复杂,本人只能在细小之处分析了。

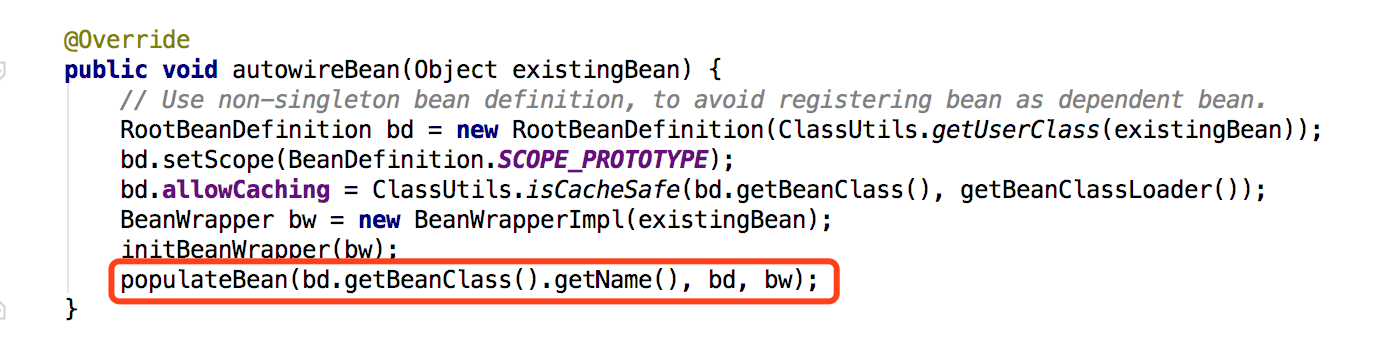
/** * Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values * from the bean definition. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param mbd the bean definition for the bean * @param bw BeanWrapper with bean instance */ protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) { PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); if (bw == null) { if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance"); } else { // Skip property population phase for null instance. return; } } // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the // state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, // to support styles of field injection. boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { continueWithPropertyPopulation = false; break; } } } } if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) { return; } if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } pvs = newPvs; } boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(); boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE); if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) { PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); if (hasInstAwareBpps) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvs == null) { return; } } } } if (needsDepCheck) { checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs); } } applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); }
经过一系列前置验证(看得迷迷糊糊)然后进行bean注入,调用的是postProcessPropertyValues方法,点进去是个接口(多态性是挺坑的)。找了一下,最后找到AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类,里面有个内部类AutowiredMethodElement,其中有个Inject方法是实施注入的。
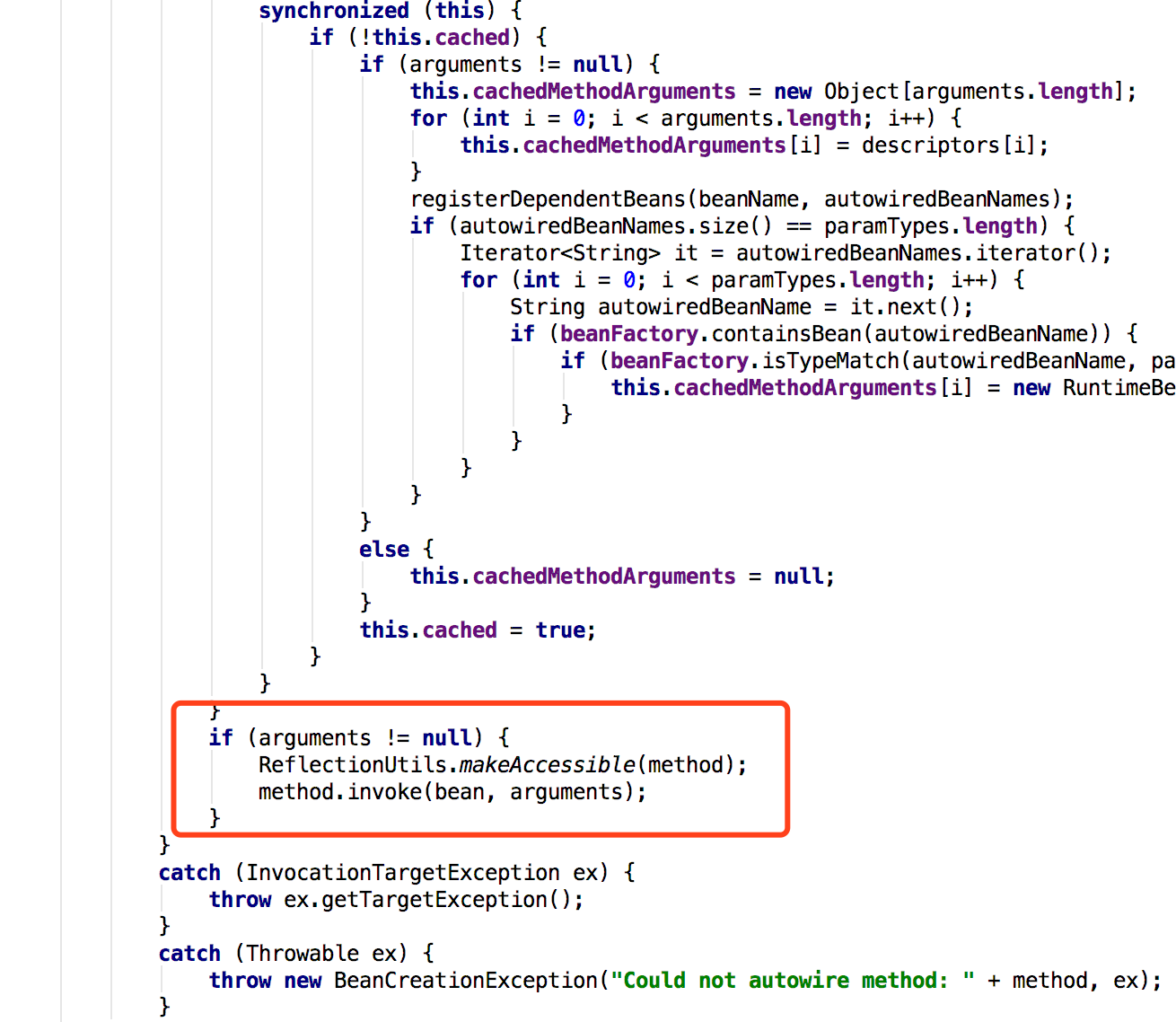
public static void makeAccessible(Field field) { if((!Modifier.isPublic(field.getModifiers()) || !Modifier.isPublic(field.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()) || Modifier.isFinal(field.getModifiers())) && !field.isAccessible()) { field.setAccessible(true); } }
@CallerSensitive public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { if (!override) { if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers); } } MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile if (ma == null) { ma = acquireMethodAccessor(); } return ma.invoke(obj, args); }
前一个是打开权限,后一个粗略看了下,就是注入了。
大概的思路就是使用反射打开权限,然后从对象池中拿取对象并设置到该字段中。如果对象池没有,大概就是放个空进去了,最后调用的时候就是空指针了。
- 实践案例
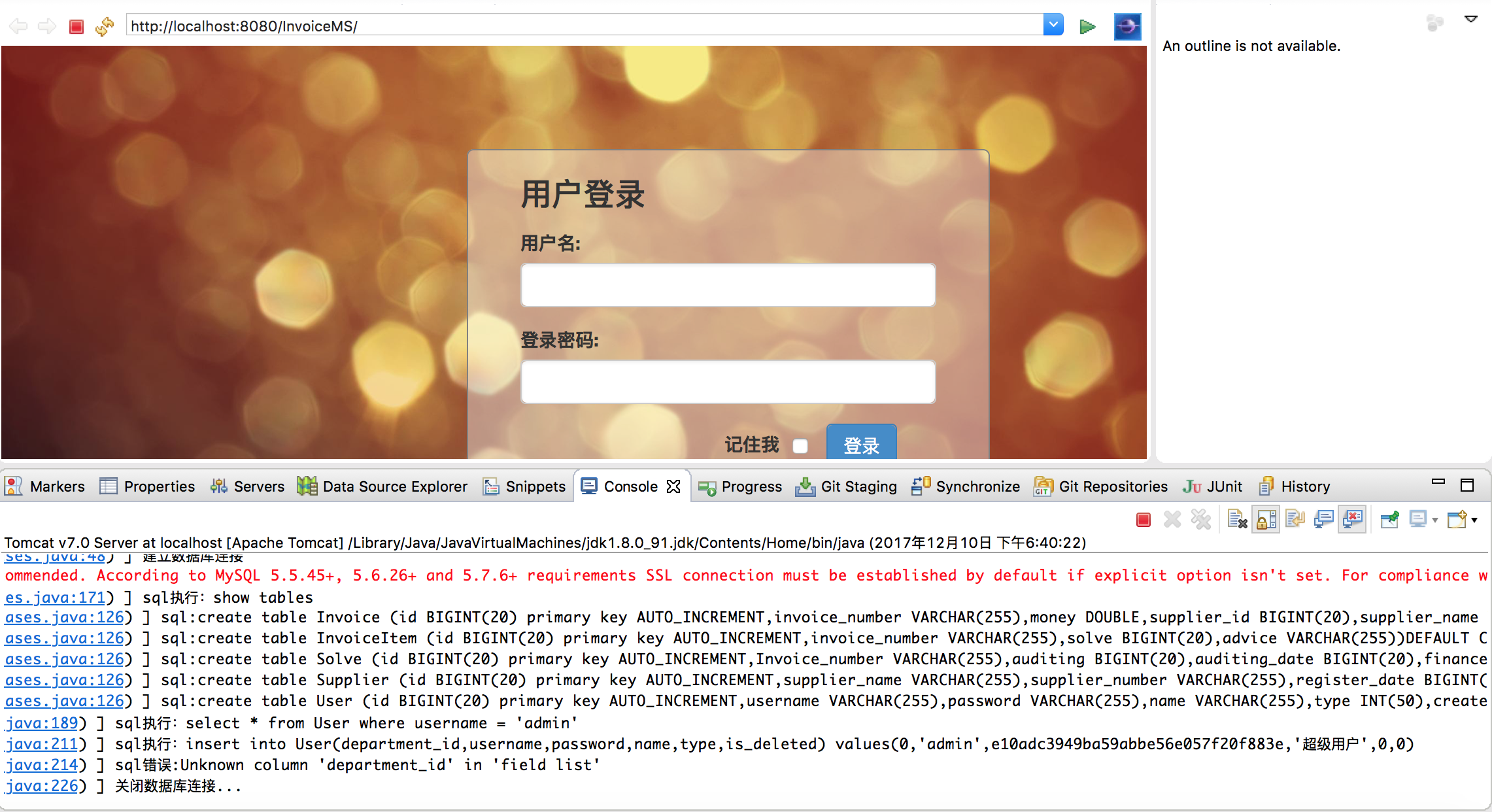
未能吸取Spring优秀框架的思想,但是自己在项目中应用了一下这种技术。小型项目对建表的要求就是,新建一个bean自动生成一个表。是不是很像某ORM?是的,仅仅使用几百行代码就可以实现这个功能了,采用的就是以反射、Annotation为基础的技术。
package Common; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import Common.Annotation.ATable; import Common.Annotation.AutoIncrement; import Common.Annotation.Column; import Common.Annotation.PrimaryKey; /** * 初始化数据库 按照Model包下的类及字段创建 * @author ctk * */ public class InitDataBases { private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(InitDataBases.class); private Connection conn = null; private Set<String> tables; //单例 private static InitDataBases instance = new InitDataBases(); private InitDataBases(){ conn = getConnection(); tables = new HashSet<>(); searchTables(); } /** * 读取数据库资源文件 * 获得数据库链接 * @return */ private Connection getConnection(){ logger.debug("建立数据库连接"); String driver = ""; String url = ""; String username = ""; String password = ""; File f = new File(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/").getPath()+"jdbc.properties"); Properties pro = new Properties(); InputStream in = null; try { in = new FileInputStream(f); pro.load(in); driver = pro.getProperty("jdbc.driverClass"); url = pro.getProperty("jdbc.url"); username = pro.getProperty("jdbc.username"); password = pro.getProperty("jdbc.password"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { logger.error("资源文件未找到,请命名为jdbc.properties,并置于src下"); System.err.println("资源文件未找到,请命名为jdbc.properties,并置于src下"); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("资源文件读写异常"); System.err.println("资源文件读写异常"); } Connection conn = null; try { Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { logger.error("加载驱动不成功,请检查是否添加了jdbc的必要包"); System.err.println("加载驱动不成功,请检查是否添加了jdbc的必要包"); } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("数据库连接错误,检查账号密码和数据库地址"); System.err.println("数据库连接错误,检查账号密码和数据库地址"); } return conn; } /** * 自动建表 * @param clazz */ public void checkAndCreate(Class<?> clazz){ String tableName = getTableName(clazz); if(tableExist(tableName)) { logger.debug(tableName+"表已存在"); return; } Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("create table "); sb.append(tableName); sb.append(" ("); for(int i=0;i<fields.length;i++){ PrimaryKey pk = fields[i].getAnnotation(PrimaryKey.class); sb.append(getColumnName(fields[i])); sb.append(" "); Class<?> type = fields[i].getType(); if(type == String.class) sb.append("VARCHAR(255)"); else if(type == int.class) sb.append("INT(50)"); else if(type == long.class) sb.append("BIGINT(20)"); else if(type == double.class || type == float.class) sb.append("DOUBLE"); //如果是主键字段 if(pk != null){ sb.append(" primary key"); AutoIncrement ai = fields[i].getAnnotation(AutoIncrement.class); //判断是否自增 if(ai != null){ sb.append(" AUTO_INCREMENT"); } } if(i != (fields.length-1)) sb.append(","); } sb.append(")DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8"); logger.debug("sql:"+sb.toString()); try { PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sb.toString()); pst.execute(); } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("建表错误:"+e.getMessage()); } } /** * 获得表名字 * @param clazz * @return */ public String getTableName(Class<?> clazz){ //获得表别名 ATable table = clazz.getAnnotation(ATable.class); if(table != null && "".equals(table.name())) return table.name(); else { return clazz.getSimpleName(); } } /** * 获取列名称 * @param field * @return */ public String getColumnName(Field field){ Column column = field.getAnnotation(Column.class); if(column != null){ return column.value(); }else{ return field.getName(); } } /** * 查询表是否存在 * @return */ private void searchTables(){ String sql = "show tables"; try { PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql); logger.debug("sql执行:"+sql); ResultSet rset = pst.executeQuery(); while(rset.next()){ String tname = rset.getString(1); tables.add(tname); } } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("sql错误:"+e.getMessage()); } } /** * 判断是否存在某数据 * @param sql * @return */ public boolean dataExist(String sql){ try { PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql); logger.debug("sql执行:"+sql); ResultSet rset = pst.executeQuery(); long id = 0; while(rset.next()){ id = rset.getLong("id"); } if(id == 0) return false; else return true; } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("sql错误:"+e.getMessage()); return false; } } /** * 插入数据sql * @param sql */ public void insertSql(String sql){ try { PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql); logger.debug("sql执行:"+sql); pst.execute(); } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("sql错误:"+e.getMessage()); } } //获得单例 public static InitDataBases getInstance(){ return instance; } public boolean tableExist(String table) { return tables.contains(table); } //关闭链接 public void closeConn(){ logger.debug("关闭数据库连接..."); try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { logger.error("关闭数据库连接失败:"+e.getMessage()); } } }
然后在启动的Listener中加入。
CommonInfo.FilePackage = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/").getPath()+"/WEB-INF/fildDownload"; File pkg = new File(CommonInfo.FilePackage); if(!pkg.exists()) pkg.mkdirs(); File f = new File(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/").getPath()+"/Model"); File[] fs = f.listFiles(); List<String> tables = new ArrayList<>(); for(File fl:fs){ String fname = fl.getName(); fname = fname.substring(0,fname.length()-6); tables.add(fname); } InitDataBases initDB = InitDataBases.getInstance(); try { for (String table : tables) { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("Model." + table); initDB.checkAndCreate(clazz); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { logger.error("找不到bean:"+e.getMessage());;
大概的思路就是,检查bean文件夹下是否存在bean并且bean中是否有Annotation修饰,并拼凑建表语句,最后新建表,别忘了关闭数据库连接。