1. 概述
1.1 简介
- ArrayList是一种以动态数组实现的List,能在常数时间内随机访问元素,但非尾部的插入和删除需要线性时间,需要移动元素
- 同时数组元素的存储在物理上是连续的,因此其存取可能极大得益于CPU缓存
1.2 继承体系
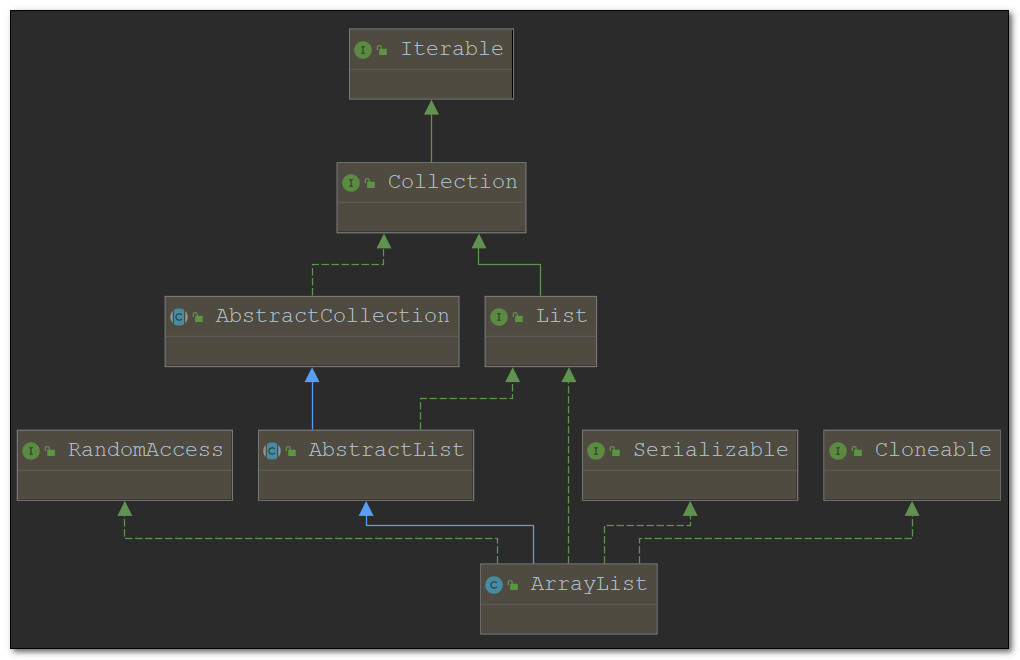
- ArrayList实现了List,提供了基础的基于索引的添加、删除、遍历等操作
- ArrayList实现了RandomAccess,提供了随机访问的能力
- ArrayList实现了Cloneable,可以被克隆
- ArrayList实现了Serializable,可以被序列化
2. 源码解析
2.1 属性
1 // 默认容量 2 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 3 // new ArrayList(0)或0个元素集合初始化时使用 4 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 5 // new ArrayList()使用 6 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 7 // 存储元素的数组 8 transient Object[] elementData; 9 // 元素个数 10 private int size;
2.2 构造函数
1 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 2 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 3 // 构造函数中分配空间 4 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 5 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 6 // 7 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 8 } else { 9 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ 10 initialCapacity); 11 } 12 }
1 public ArrayList() { 2 // 默认容量, 并不立即开辟空间 3 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 4 }
1 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 elementData = c.toArray(); 3 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 4 // 以前的一个bug, 以前的Arrays.asList返回的List#toArray返回的不一定是Object[]类型 5 // elementData原来是Object[]类型, elementData[i]可以存储任意引用类型 6 // 当String[]赋予elementData后, elementData[i]就只能存储String类型了 7 // 而ArrayList代码内是将element[i]当作Object操作的, 可能就会出问题 8 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 9 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 10 } else { 11 // 集合没有元素, 带参构造函数的空容器就是EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 12 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 13 } 14 }
2.3 常规操作
public boolean add(E e)
将元素添加到末尾,平均时间复杂度O(1)
1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 // add操作是一个Structural modification 3 modCount++; 4 // 末尾添加 5 add(e, elementData, size); 6 // 一定成功, 失败那就是OOM了 7 return true; 8 } 9 10 11 private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) { 12 // 实际插入前扩容检查 13 if (s == elementData.length) 14 elementData = grow(); 15 elementData[s] = e; 16 // ?, 指定索引插入调用的不是这个插入方法, 这个插入方法是尾插特有的 17 size = s + 1; 18 }
public void add(int index, E element)
// 指定索引插入 public void add(int index, E element) { // index有效性检查 rangeCheckForAdd(index); // 实际插入是一个Structural modification操作 modCount++; // 保存size的temp变量 final int s; Object[] elementData; // 扩容检查 if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length) elementData = grow(); // 元素后移 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, s - index); elementData[index] = element; size = s + 1; }
1 public E get(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 return elementData(index); 4 }
1 public E set(int index, E element) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 E oldValue = elementData(index); 5 elementData[index] = element; 6 return oldValue; 7 }
public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); // remove也是一个 Structural modification操作 modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); // 需要前移的元素个数 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
1 public boolean remove(Object o) { 2 // 分为null和非null查找, 找到index然后进行index的shanc 3 // 相等性比较使用的是equals 4 if (o == null) { 5 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 6 if (elementData[index] == null) { 7 fastRemove(index); 8 return true; 9 } 10 } else { 11 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 12 // equals进行相等性比较 13 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 14 fastRemove(index); 15 return true; 16 } 17 } 18 19 // 未删除任何元素, 返回false 20 return false; 21 } 22 23 // 快速删除: 不进行index检查, 不返回删除元素 24 private void fastRemove(int index) { 25 // 插入是一个Structural modification操作 26 modCount++; 27 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 28 if (numMoved > 0) 29 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 30 numMoved); 31 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 32 }
2.4 参数为集合的操作
1 // 尾插一个集合 2 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 3 // 转数组后再对数组进行操作 4 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 5 // 插入是一个Structural modification操作 6 modCount++; 7 int numNew = a.length; 8 // 无需要插入的元素 9 if (numNew == 0) 10 return false; 11 Object[] elementData; 12 final int s; 13 // 空闲位置不够插入, 进行扩容 14 if (numNew > (elementData = this.elementData).length - (s = size)) 15 elementData = grow(s + numNew); 16 // 复制 17 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, s, numNew); 18 size = s + numNew; 19 return true; 20 }
// 范围内批量删除操作, complement为false表示删除c中存在的元素, true删除c不存在的元素 // 以下以删除为例 boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement, final int from, final int end) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); final Object[] es = elementData; int r; // Optimize for initial run of survivors // 如果传入集合不含本集合返回内元素, 返回 for (r = from;; r++) { if (r == end) return false; if (c.contains(es[r]) != complement) break; } // elementData[r]是第一个双方都存在的元素 // r读指针, w写指针, w指向第一个双方都存在的元素索引, r指向后一个元素 int w = r++; try { for (Object e; r < end; r++) // complement == false, 不包含则向elementData[w]写入 // 初始[w]指向相等元素, 第一次写入的是es存在而c不存在的【不需要删除的】, 相当于[w]被删除了 // 可使用循环不变式的思想思考其正确性 if (c.contains(e = es[r]) == complement) es[w++] = e; } catch (Throwable ex) { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. // 将未读元素复制到写指针之后, 即删除的就删除的, 其它的元素继续保存 System.arraycopy(es, r, es, w, end - r); // 保证[w, end)内元素是无效的, 即应该被删除的 w += end - r; throw ex; } finally { // modCount += end - w ===> modCount += (end - w); modCount += end - w; // 删除无效元素 shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end); } return true; } /** Erases the gap from lo to hi, by sliding down following elements. */ // elementData内元素分为: [0, low)有效, [low, hight)无效, [hight, size)有效 private void shiftTailOverGap(Object[] es, int lo, int hi) { // 将[hight, size)前移变为[low, ?) System.arraycopy(es, hi, es, lo, size - hi); // 无效位置置null, i = (size -= hi - lo) ===> i = (size -= (hi - lo)) for (int to = size, i = (size -= hi - lo); i < to; i++) es[i] = null; }
1 // 保留双方都存在的元素, 求交集 2 public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { 3 // 4 return batchRemove(c, true, 0, size); 5 }
2.5 JDK8及以后的操作(基本涉及函数式接口及Lambda表达式)
1 public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { 2 return removeIf(filter, 0, size); 3 } 4 5 // 删除满条件的元素, Predicate 谓词 6 boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter, int i, final int end) { 7 Objects.requireNonNull(filter); 8 int expectedModCount = modCount; 9 final Object[] es = elementData; 10 // 找到第一个满足的 11 for (; i < end && !filter.test(elementAt(es, i)); i++) 12 ; 13 // Tolerate predicates that reentrantly access the collection for 14 // read (but writers still get CME), so traverse once to find 15 // elements to delete, a second pass to physically expunge. 16 if (i < end) { 17 final int beg = i; 18 // 使用bitmap算法保存无效内容, 使用long型保存 19 // 每一个位标记一个位置, long可标记64个元素 20 // long[] nBits(int n) -> new long[((n - 1) >> 6) + 1] 21 final long[] deathRow = nBits(end - beg); 22 // 第一个元元素必然是无效的 23 deathRow[0] = 1L; 24 // 先找出全部无效元素 25 for (i = beg + 1; i < end; i++) 26 if (filter.test(elementAt(es, i))) 27 // 此位置元素无效, 1L << num, 当num=63时移到最高位, num=64时绕回来了, 移位数0, 65移一位, ... 28 // setBit(long[] bits, int i) -> bits[i >> 6] |= (1L << i) 29 setBit(deathRow, i - beg); 30 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 31 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 32 modCount++; 33 // 开始写了, 将有效元素全部往前写 34 int w = beg; 35 for (i = beg; i < end; i++) 36 // 为0表示有效, 无效的都被标记了 37 // boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) -> (bits[i >> 6] & (1L << i)) == 0 38 if (isClear(deathRow, i - beg)) 39 es[w++] = es[i]; 40 // 有效数据[end, size)前移到从w开始, 无效数据赋值null删除 41 shiftTailOverGap(es, w, end); 42 return true; 43 } else { 44 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 45 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 46 return false; 47 } 48 }
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action)
2.6 扩容策略(基本add之前都要先判断)
1 // 这个一般是使用者调用, 用来避免频繁扩容的 2 public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { 3 // 未使用过(调用的是默认构造函数) 若请求容量小于10不做处理, 大于等于则扩容请求容量 4 // 其它 若请求容量不到elementData.length不做处理, 否则扩容max(1.5倍, 请求容量) 5 if (minCapacity > elementData.length 6 && !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 7 && minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) { 8 modCount++; 9 grow(minCapacity); 10 } 11 } 12 13 14 // new ArrayList()扩容DEFAULT_CAPACITY 15 // new ArrayList(initCapacity)或存在元素扩容1.5倍 16 private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) { 17 // 18 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 19 // 不是new ArrayList()默认构造后立即添加元素导致的grow()扩容 20 if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 21 // 默认扩容 max(1.5倍, 请求容量), 请求容量一般为1 22 int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity, 23 minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */ 24 oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */); 25 return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 26 } else { 27 // new ArrayList()后立即添加元素导致grow()扩容为 max(默认容量10, 请求容量) 28 // 请求容量大于1的情况是批量添加时 29 // 即保证容量大于等于默认容量, 避免频繁扩容 30 return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)]; 31 } 32 } 33 34 // 默认扩容 max(1.5倍, 请求容量) 35 public static int newLength(int oldLength, int minGrowth, int prefGrowth) { 36 int newLength = Math.max(minGrowth, prefGrowth) + oldLength; 37 if (newLength - MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH <= 0) { 38 return newLength; 39 } 40 return hugeLength(oldLength, minGrowth); 41 } 42 43 // 44 private static int hugeLength(int oldLength, int minGrowth) { 45 // 请求容量太大, OOM 46 int minLength = oldLength + minGrowth; 47 if (minLength < 0) { // overflow 48 throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array length too large"); 49 } 50 // 小于等于MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH(Integer.MAX_VALUE-8) 51 if (minLength <= MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH) { 52 return MAX_ARRAY_LENGTH; 53 } 54 return Integer.MAX_VALUE; 55 }
- 默认容量10
- 默认构造函数扩容后一般扩容为0,若是批量添加元素,则扩容为 max(10,批量添加的元素数量)
- 非默认构造函数扩容一般扩容为 原来的1.5倍
2.7 重要的工具方法
Arrays#
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { // new 一个指定长度的 newType.getComponentType()数组 // ArrayList需要的Object[] T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); // 元素复制 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }
System.arraycopy
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
1 // 元素赋值(这是最终调用的,中间检查环境省略了) 2 // 不会创建temp数组, 赋值效率还是很高的 3 static void pd_conjoint_jints_atomic(jint* from, jint* to, size_t count) { 4 // 从前往后复制 5 if (from > to) { 6 while (count-- > 0) { 7 // Copy forwards 8 *to++ = *from++; 9 } 10 } else { 11 // 从后往前复制 12 from += count - 1; 13 to += count - 1; 14 while (count-- > 0) { 15 // Copy backwards 16 *to-- = *from--; 17 } 18 } 19 }
4. JDK序列化方式
// 使用了transient修饰,不会被默认序列化,需要自己处理其序列化 transient Object[] elementData;
// 使用了 transient 修饰, 不会被默认序列化, 需要手动处理 // elementData 使用 transient 修饰的原因是一般而言数组空间是不会被刚好用尽的 // 而序列化会保存整个数组内元素, 而没有使用的空间序列化是没有意义的, 还占空间 transient Object[] elementData; // 不会被序列化, 即最后反序列化后默认0值,可能是反序列化后还保存这个值没有啥意义 protected transient int modCount = 0;
// 序列化 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { int expectedModCount = modCount; // 写入默认要序列化的字段(没有被static和transient修饰的字段) s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size as capacity for behavioral compatibility with clone() // 写入元素数量 ? s.writeInt(size); // 写入有效元素 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } // 反序列化 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // 反序列化默认字段 s.defaultReadObject(); // 反序列化size, 只是因为序列化时还重复序列化了这个字段 s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { // 开辟size数量的空间存储元素 SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, size); Object[] elements = new Object[size]; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { elements[i] = s.readObject(); } elementData = elements; } else if (size == 0) { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Invalid size: " + size); } }
3. 总结
- ArrayList内部使用数组存储元素,当数组长度不够时进行扩容,每次加一半的空间,ArrayList不会主动进行缩容;
- ArrayList支持随机访问,通过索引访问元素极快,时间复杂度为O(1);
- ArrayList添加元素到尾部极快,平均时间复杂度为O(1);
- ArrayList添加元素到中间比较慢,因为要搬移元素,平均时间复杂度为O(n);
- ArrayList从尾部删除元素极快,时间复杂度为O(1);
- ArrayList从中间删除元素比较慢,因为要搬移元素,平均时间复杂度为O(n);
- ArrayList支持求并集,调用addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可
- ArrayList支持求交集,调用retainAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可
- ArrayList支持求单向差集,调用removeAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可