location对象
location.href url地址
location.hash 锚点
location.hostname 主机名(需要放到服务器上)
location.host 主机名+端口号(需要放到服务器上)
location.pathname 目录或者文件
location.port 端口
location.protocol 协议
location.search ?后面的内容
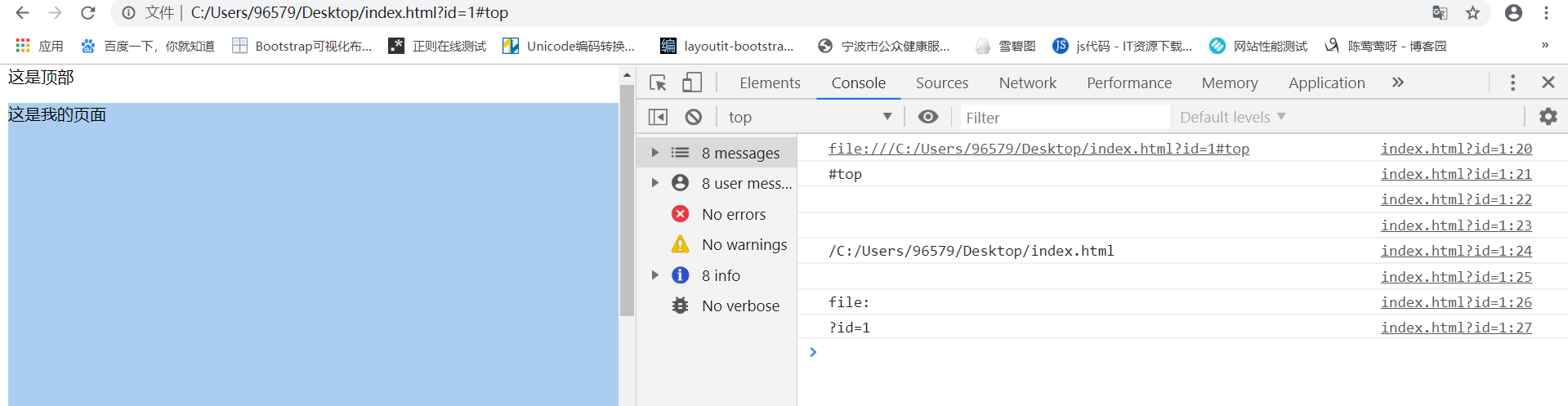
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } p{ height:100%; height:2000px; background:#abcdef; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ console.log(location.href);//file:///C:/Users/96579/Desktop/index.html console.log(location.hash);//#top console.log(location.host); console.log(location.hostname); console.log(location.pathname);///C:/Users/96579/Desktop/index.html console.log(location.port); console.log(location.protocol);//file: console.log(location.search);//?id=1 } </script> </head> <body> <a id="top">这是顶部</a> <p>这是我的页面</p> <a href="#top"><button>回到顶部</button></a> </body> </html>
利用js控制location.hash ,跳转到某个锚点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } p{ height:100%; height:2000px; background:#abcdef; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ var btn=document.getElementById("btn"); btn.onclick=function(){ location.hash="#top"; } } </script> </head> <body> <a id="top">这是顶部</a> <p>这是我的页面</p> <button id="btn">回到顶部</button> </body> </html>
location.href=url 切换页面url,会有历史记录
window.location=url 切换页面url,会有历史记录
location.replace(url) 切换页面url,没有历史记录
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } p{ height:100%; height:2000px; background:#abcdef; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ setTimeout(function(){ location.href="new.html"; },1000); } </script> </head> <body> <p>这是我的页面</p> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } p{ height:100%; height:2000px; background:#abcdef; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ setTimeout(function(){ location.replace("new.html"); },1000); } </script> </head> <body> <p>这是我的页面</p> </body> </html>
location.reload() 重新加载页面(有可能从缓存中加载)
location.reload(true) 重新加载页面(强制从服务器重新加载)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ var reload=document.getElementById("reload"); reload.onclick=function(){ location.reload();//有可能从缓存中刷新 location.reload(true);//强制从服务器重新加载 } } </script> </head> <body> <button id="reload">刷新</button> </body> </html>
history对象
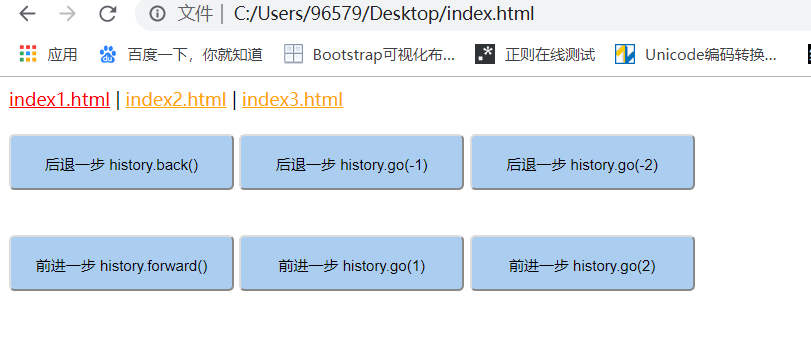
history.back() 后退一步
history.go(-1) 后退一步
history.go(-n) 后退n步
history.forward() 前进一步
history.go(1) 前进一步
history.go(n) 前进n步
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } a{ color:orange; } a.active{ color:red; } button{ background:#abcdef; width:200px; height:50px; line-height:50px; text-align: center; border-radius:5px; cursor:pointer; margin:20px 0; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ var back=document.getElementById("back"); var back1=document.getElementById("back1"); var back2=document.getElementById("back2"); back.onclick=function(){ history.back(); } back1.onclick=function(){ history.go(-1); } back2.onclick=function(){ history.go(-2); } } </script> </head> <body> <div> <a href="index1.html" class="active">index1.html</a> | <a href="index2.html">index2.html</a> | <a href="index3.html">index3.html</a> </div> <button id="back">后退一步 history.back()</button> <button id="back1">后退一步 history.go(-1)</button> <button id="back2">后退两步 history.go(-2)</button> <br> <button id="forward">前进一步 history.forward()</button> <button id="forward1">前进一步 history.go(1)</button> <button id="forward2">前进两步 history.go(2)</button> </body> </html>
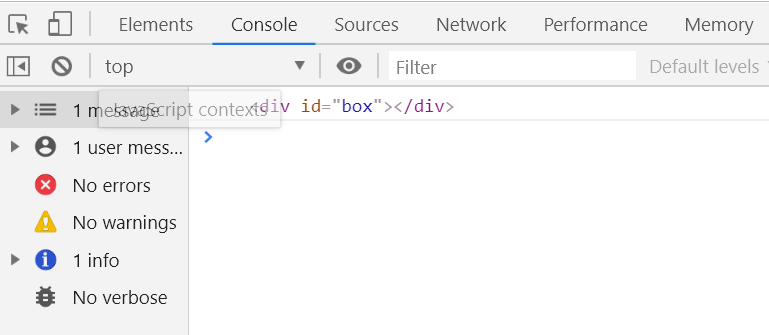
补充,在原生js中,可以直接使用id获取元素
如:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>new</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ console.log(box); } </script> </head> <body> <div id="box"></div> </body> </html>
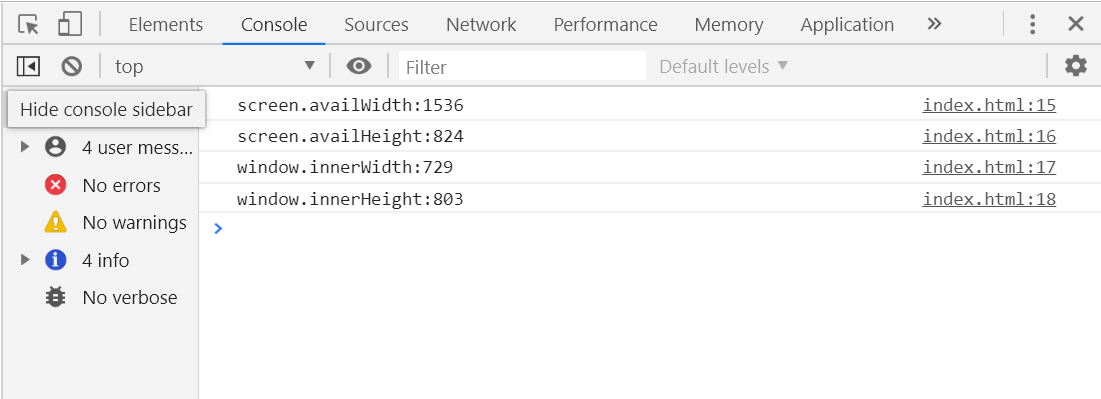
screen 对象
screen.availWidth 屏幕可用宽度
screen.availHeight 屏幕可用高度(去除底部任务栏)
window.innerWidth 窗口可见宽度
window.innerHeight 窗口可见高度
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ console.log("screen.availWidth:"+screen.availWidth); console.log("screen.availHeight:"+screen.availHeight); console.log("window.innerWidth:"+window.innerWidth); console.log("window.innerHeight:"+window.innerHeight); } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
IE浏览器不支持console.log
navigator 对象
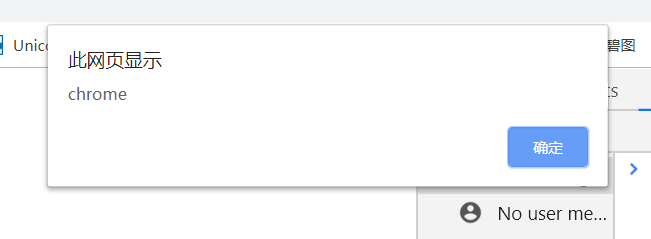
navigator.userAgent 获取浏览器相关信息
控制台的移动端设备可以编辑新增
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ width:100%; height:100%; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ function getBrowser(){ var explorer=navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase(); if(explorer.indexOf("msie")>-1){ return "IE8~10(低版本IE)"; }else if(explorer.indexOf("trident")>-1){ return "高版本IE或者edge浏览器"; }else if(explorer.indexOf("chrome")>-1){ return "chrome"; }else if(explorer.indexOf("firefox")>-1){ return "firefox"; }else if(explorer.indexOf("opera")>-1){ return "opera"; }else if(explorer.indexOf("safari")>-1){ return "safari"; }else{ return "未知浏览器"; } } var myBrowser=getBrowser(); alert(myBrowser); } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>