前言
我们知道在使用SpringMVC的时候,我们会在web.xml中配置如下内容,DispatcherServlet会拦截住所有的请求然后处理。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:application-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
首先我们先看下DispatcherServlet的继承关系,然后我们再来逐步分析。
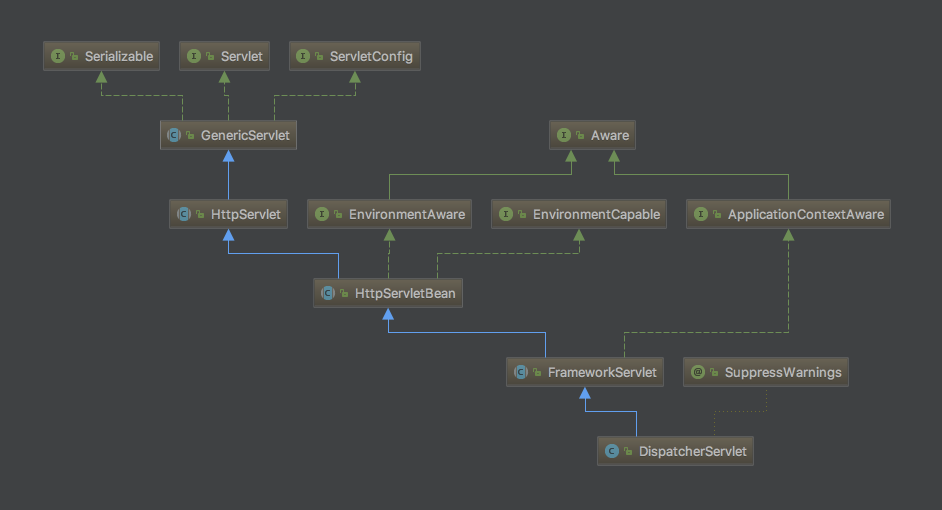
DispatcherServlet继承关系
Servlet
public interface Servlet {
/**
* 容器启动时被调用(当load-on-startup为负数或者不设置时,会在第一次被使用时才调用),只会调用一次
* 它有一个参数ServletConfig,是容器传进来的,表示的是这个Servlet的一些配置,比如DispatcherServlet配置的<init-param>
*/
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
/**
* 获取Servlet的配置
*/
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* 最重要的一个方法,是具体处理请求的地方
*/
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* 获取Servlet的一些信息,比如作者、版本、版权等,需要子类实现
*/
public String getServletInfo();
/**
* 用于Servlet销毁(主要指关闭容器)时释放一些资源,只会调用一次
*/
public void destroy();
}
ServletConfig
public interface ServletConfig {
/**
* 返回Servlet的名字,就是<servlet-name>中配置的名字
*/
public String getServletName();
/**
* 返回应用本身的一些配置
*/
public ServletContext getServletContext();
/**
* 返回<init-param>配置的参数
*/
public String getInitParameter(String name);
/**
* 返回<init-param>配置的参数的名字
*/
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames();
}
GenericServlet
GenericServlet是Servlet的默认实现,主要做了如下几件事
- 提供了无参的init方法,init()是一个模板方法,留给子类实现
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
- 实现了ServletConfig的接口,可以直接调用ServletConfig中的方法,这样做的好处是如果我们想获取ServletConfig中的内容,不必先调用getServletConfig()了,比如获取ServletContext的代码
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
ServletConfig sc = getServletConfig();
if (sc == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized"));
}
return sc.getServletContext();
}
HttpServlet
HttpServlet是用HTTP协议实现的Servlet的基类,一般我们写的Servlet就是继承于它,我们注意到HttpServlet并没有实现init方法
HttpServletBean
从HttpServletBean开始我们就进入Spring的范围了,HttpServletBean重写了init方法
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// 从ServletConfig中获取初始配置,比如contextConfigLocation
PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
// 模板方法,做一些初始化的工作,bw代表DispatcherServlet,但是没有子类重写
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 把初始配置设置给DispatcherServlet,比如contextConfigLocation
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 模板方法,子类重写,做进一步初始化的工作
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
FrameworkServlet
FrameworkServlet实现了initServletBean方法,其简化代码如下
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
try {
// 初始化WebApplicationContext
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 初始化FrameworkServlet,模板方法,并没有子类实现
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
}
我们可以看到最重要的代码只有两句,而这两句之中最主要的是initWebApplicationContext(),下面我们就来看下initWebApplicationContext的简化代码
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取父WebApplicationContext,如果我们在web.xml中配置了ContextLoaderListener,那么它加载的就是父WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 如果通过构造方法传入了webApplicationContext,就使用它
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 从ServletContext中获取webApplicationContext,一般情况下是没有的
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 自己创建一个webApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// 当ContextRefreshedEvent事件没有触发时调用此方法,模板方法,子类实现,是DispatcherServlet中重要的方法
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// 把webApplicationContext保存到ServletContext中
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
正常情况下都是自己创建一个webApplicationContext,我们看下创建的过程
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
// 获取创建类型
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
// 具体创建
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
// 将设置的contextConfigLocation参数传给wac,默认传入WEB-INFO/[ServletName]-Servlet.xml
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
// 配置和刷新wac
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new FrameworkServlet.ContextRefreshListener()));
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// 根据contextConfigLocation的值刷新webApplicationContext
wac.refresh();
}
DispatcherServlet
从上面的分析可以知道DispactcherServlet初始化的入口方法是onRefresh(wac),下面我们来具体看下
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
我们可以看到onRefresh方法只是调用了initStrategies方法,而initStrategies方法内部调用了九个初始化SpringMVC组件的方法,这九个组件的初始化过程类似,我们就以initHandlerMappings为例分析下
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
// detectAllHandlerMappings默认是true
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 从ApplicationContext中找到所有的HandlerMapping
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
} else {
try {
// 从ApplicationContext中获取名称为handlerMapping的Bean
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
// 如果没有HandlerMapping,则使用默认策略
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
}
}
默认策略其实就是根据DispatcherServlet.properties中的配置加载对应的组件,下面就是文件中具体的内容,我要说的是默认配置并不是SpringMVC的推荐配置,比如DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping现在已经是废弃状态。
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
总结
下面用表格的形式简要总结下DispatcherServlet初始化过程
| 类或接口 | 初始化入口方法 | 具体作用 |
|---|---|---|
| Servlet | init(ServletConfig config) | 接口定义,由Web容器调用 |
| GenericServlet | init(ServletConfig config) | 保存ServletConfig,内部调用无参的init方法 |
| HttpServlet | - | - |
| HttpServletBean | init() | 设置contextConfigLocation的值,内部调用initServletBean() |
| FrameworkServlet | initServletBean() | 初始化webApplicationContext,内部调用onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) |
| DispatcherServlet | onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) | 初始化九大组件 |
文章转载自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/be981b92f1d2