一、Redis单线程
在Redis6.0版本之前,Redis可以被认为是单线程服务(除少量的后台定时任务、文件异步操作、惰性删除外),它的处理过程主要包括:
1接收命令。通过TCP或者UDP接收到命令
2解析命令。将命令取出来
3执行命令。到对应的地方将value读出来
4返回结果。将结果返回给客户端
Redis在启动后会产生一个死循环aeMain,在这个循环里通过IO多路复用(linux系统采用epoll方式)等待事件发生。
事件分为IO事件和timer事件,timer事件即开头提到的后台定时任务,如expire key等。IO事件即来自客户端的命令转化的事件,由epoll处理。
epoll多路复用的处理结构如下图所示
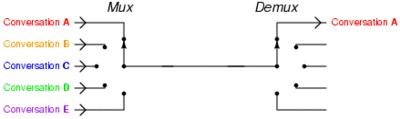
即多个网络连接复用一个IO线程。由于单个线程可以记录每个socket的状态来同时管理多个IO流,所以能够提高服务的吞吐能力。
二、单线程IO的瓶颈
前面简单的介绍了单线程IO的处理过程以及高性能的原因,官方压测的结果是10万QPS,我们现网使用经验在3~4万QPS。
虽然这个性能指标已经挺高了,但是单线程IO模型有几个明显的缺陷:
1、只能使用一个CPU核(忽略后台线程和子线程)
2、如果涉及到大key,Redis的QPS会下降的厉害
3、由于解析和返回的限制,QPS难以进一步提高
针对以上的缺陷,又为了避免多线程执行命令带来的控制key、lua脚本、事务等并发复杂问题,Redis作者选择了多线程IO模型,即执行命令仍采用单线程,解析和返回等步骤采用多线程。
三、多线程IO
多线程IO的设计思路大体如下图
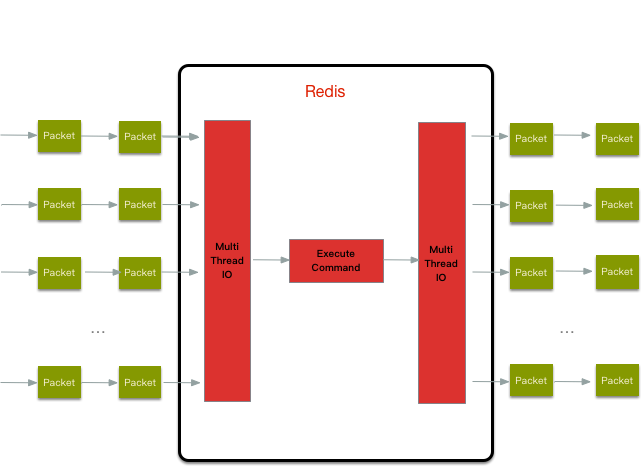
整体的读流程包括:
1、主线程负责接收建连请求,读事件到来(收到请求)则放到一个全局等待读处理队列
2、主线程处理完读事件之后,通过轮询将这些连接分配给这些 IO 线程,然后主线程忙等待(spinlock 的效果)状态
3、IO 线程将请求数据读取并解析完成(这里只是读数据和解析并不执行)
4、主线程执行所有命令并清空整个请求等待读处理队列(执行部分串行)
readQueryFromClient 函数: void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) { /* Check if we want to read from the client later when exiting from * the event loop. This is the case if threaded I/O is enabled. */ if (postponeClientRead(c)) return; ... }
readQueryFromClient 之前的实现是负责读取和解析请求并执行命令,加入多线程 IO 之后加入了postponeClientRead 函数,它的实现逻辑如下:
int postponeClientRead(client *c) { if (io_threads_active && // 多线程IO是否在开启状态,在待处理请求较少时会停止IO多线程 server.io_threads_do_reads && // 读是否开启多线程 IO !(c->flags & (CLIENT_MASTER|CLIENT_SLAVE|CLIENT_PENDING_READ))) // 主从库复制请求不使用多线程 IO { // 连接标识为 CLIENT_PENDING_READ 来控制不会反复被加队列, // 这个标识作用在后面会再次提到 c->flags |= CLIENT_PENDING_READ; // 连接加入到等待读处理队列 listAddNodeHead(server.clients_pending_read,c); return 1; } else { return 0; } }
postponeClientRead 判断如果开启多线程 IO 且不是主从复制连接的话就放到队列然后返回 1,在 readQueryFromClient 函数会直接返回不进行命令解析和执行。int handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads(void) { ... // 将等待处理队列的连接按照 RR 的方式分配给多个 IO 线程 listRewind(server.clients_pending_read,&li); int item_id = 0; while((ln = listNext(&li))) { client *c = listNodeValue(ln); int target_id = item_id % server.io_threads_num; listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[target_id],c); item_id++; } ... // 一直忙等待直到所有的连接请求都被 IO 线程处理完 while(1) { unsigned long pending = 0; for (int j = 0; j < server.io_threads_num; j++) pending += io_threads_pending[j]; if (pending == 0) break; }
代码里面的 io_threads_list 用来存储每个 IO 线程对应需要处理的连接,然后主线程将这些连接分配给这些 IO 线程后进入忙等待状态(相当于主线程 blocking 住)。
IO 处理线程入口是 IOThreadMain 函数:
void *IOThreadMain(void *myid) { while(1) { // 遍历线程 id 获取线程对应的待处理连接列表 listRewind(io_threads_list[id],&li); while((ln = listNext(&li))) { client *c = listNodeValue(ln); // 通过 io_threads_op 控制线程要处理的是读还是写请求 if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE) { writeToClient(c->fd,c,0); } else if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_READ) { readQueryFromClient(NULL,c->fd,c,0); } else { serverPanic("io_threads_op value is unknown"); } } listEmpty(io_threads_list[id]); io_threads_pending[id] = 0; } }
IO 线程处理根据全局 io_threads_op 状态来控制当前 IO 线程应该处理读还是写事件,这也是上面提到的全部 IO 线程同一时刻只会执行读或者写。另外,已经加到等待处理队列的连接会被设置 CLIENT_PENDING_READ 标识。postponeClientRead 函数不会把连接再次加到队列,readQueryFromClient 会继续执行读取和解析请求。readQueryFromClient 函数读取请求数据并调用 processInputBuffer 函数进行解析命令,processInputBuffer 会判断当前连接是否来自 IO 线程,如果是的话就只解析不执行命令。IOThreadMain 线程是没有任何 sleep 机制,在空闲状态也会导致每个线程的 CPU 跑到 100%,但简单 sleep 则会导致读写处理不及时而导致性能更差。Redis 当前的解决方式是通过在等待处理连接比较少的时候关闭这些 IO 线程来避免长期CPU跑满。
四、性能对比
本次性能压测采用了控制单变量法多次测试,变量包括线程数、request请求数、客户端连接数。一共测试了set、get、incr、hset4种命令。每组参数测试5次取平均值为最终测试结果。详细测试数据见附件Excel
由于压测结果显示QPS与客户端连接数关系不大。故作图数据采用get命令,50个客户端为例,绘制了QPS与线程数及请求数的关系。

结论:
1、随着IO线程数增多,每个IO线程可支持约4.5万QPS,呈线性关系,4IO线程时,可达到20万QPS。但是从4线程IO之后,线程数对QPS的提升效果逐渐降低。
2、随着IO线程数增多,QPS随着request的增加有一定的增加,但是差距不明显。
五、建议
由于Redis6支持绑定IO线程、持久化子线程及后台线程,对于QPS高的业务线,可通过Redis配置文件绑定多核开启多线程IO提高CPU利用率来提高QPS。
相关配置参数如下
io-threads 4 # Setting io-threads to 1 will just use the main thread as usually. # When I/O threads are enabled, we only use threads for writes, that is # to thread the write(2) syscall and transfer the client buffers to the # socket. However it is also possible to enable threading of reads and # protocol parsing using the following configuration directive, by setting # it to yes: io-threads-do-reads yes
# Jemalloc background thread for purging will be enabled by default jemalloc-bg-thread yes # It is possible to pin different threads and processes of Redis to specific # CPUs in your system, in order to maximize the performances of the server. # This is useful both in order to pin different Redis threads in different # CPUs, but also in order to make sure that multiple Redis instances running # in the same host will be pinned to different CPUs. # # Normally you can do this using the "taskset" command, however it is also # possible to this via Redis configuration directly, both in Linux and FreeBSD. # # You can pin the server/IO threads, bio threads, aof rewrite child process, and # the bgsave child process. The syntax to specify the cpu list is the same as # the taskset command: # # Set redis server/io threads to cpu affinity 0,2,4,6: server_cpulist 7-15 # # Set bio threads to cpu affinity 1,3: # bio_cpulist 1,3 # # Set aof rewrite child process to cpu affinity 8,9,10,11: # aof_rewrite_cpulist 8-11 # # Set bgsave child process to cpu affinity 1,10,11 # bgsave_cpulist 1,10-11