项目中 SimpleDateFormat 的正确使用
日常开发中,我们经常需要使用时间相关类,说到时间相关类,想必大家对 SimpleDateFormat 并不陌生。主要是用它进行时间的格式化输出和解析,挺方便快捷的,但是 SimpleDateFormat 并不是一个线程安全 的类。在多线程情况下,会出现异常,想必有经验的小伙伴也遇到过。下面我们就来分析分析SimpleDateFormat为什么不安全?是怎么引发的?以及多线程下有那些SimpleDateFormat的解决方案?
先看看《阿里巴巴开发手册》对于 SimpleDateFormat 是怎么看待的:
一、问题场景重现
一般我们使用SimpleDateFormat的时候会把它定义为一个静态变量,避免频繁创建它的对象实例,如下代码:
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {
/** 日期格式化类. */
private static final SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static String formatDate(Date date) throws ParseException {
return sdf.format(date);
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException {
return sdf.parse(strDate);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/** 单线程下测试. */
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()));
}
}
是不是感觉没什么毛病?单线程下自然没毛病了,都是运用到多线程下就有大问题了。 测试下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/** 单线程下测试. */
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()));
/** 多线程下测试. */
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
try {
System.out.println(parse("2018-01-02 09:45:59"));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
// 等待上述的线程执行完后
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
控制台打印结果:
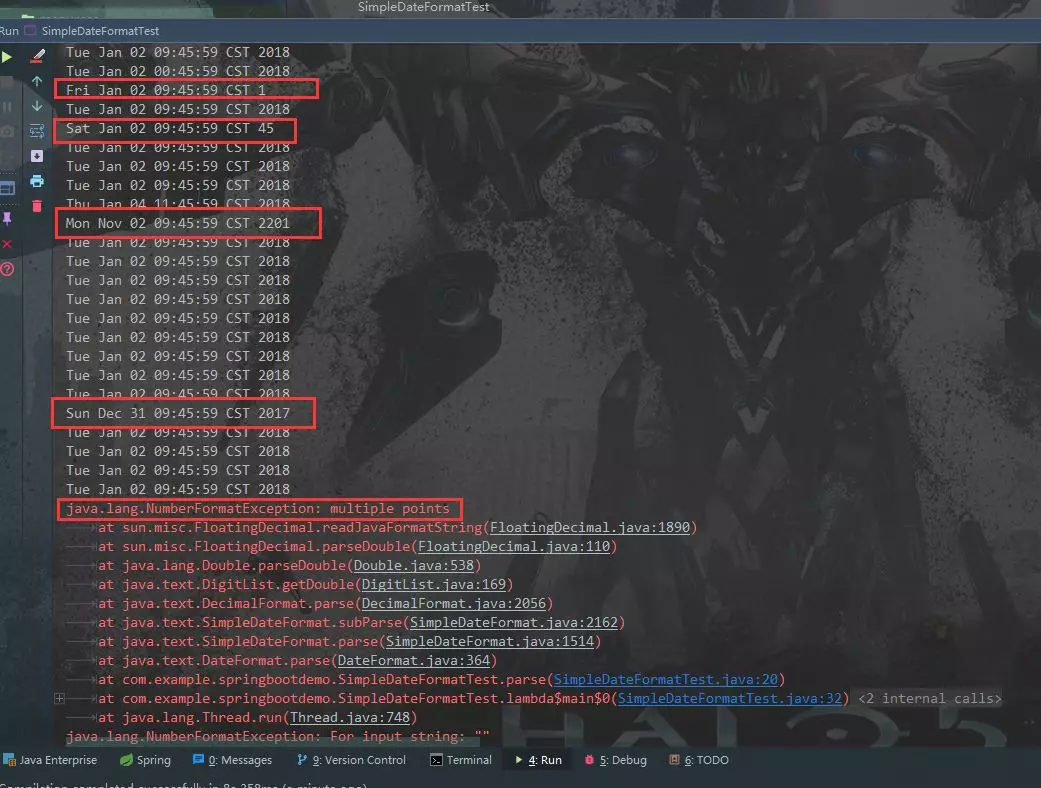
部分线程获取的时间不对,部分线程直接报 java.lang.NumberFormatException:multiple points 错,线程直接挂死了。
二、多线程不安全原因
因为我们把 SimpleDateFormat 定义为静态变量,那么多线程下SimpleDateFormat的实例就会被多个线程共享+,B线程会读取到A线程的时间,就会出现时间差异和其它各种问题。SimpleDateFormat和它继承的DateFormat类也不是线程安全的
来看看SimpleDateFormat的format()方法的源码
// Called from Format after creating a FieldDelegate
private StringBuffer format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo,
FieldDelegate delegate) {
// Convert input date to time field list
calendar.setTime(date);
boolean useDateFormatSymbols = useDateFormatSymbols();
for (int i = 0; i < compiledPattern.length; ) {
int tag = compiledPattern[i] >>> 8;
int count = compiledPattern[i++] & 0xff;
if (count == 255) {
count = compiledPattern[i++] << 16;
count |= compiledPattern[i++];
}
switch (tag) {
case TAG_QUOTE_ASCII_CHAR:
toAppendTo.append((char)count);
break;
case TAG_QUOTE_CHARS:
toAppendTo.append(compiledPattern, i, count);
i += count;
break;
default:
subFormat(tag, count, delegate, toAppendTo, useDateFormatSymbols);
break;
}
}
return toAppendTo;
}
【注意】:calendar.setTime(date),SimpleDateFormat的format方法实际操作的就是 Calendar。
因为我们声明SimpleDateFormat为static变量,那么它的Calendar变量也就是一个共享变量,可以被多个线程访问。
假设线程A执行完calendar.setTime(date),把时间设置成2019-01-02,这时候被挂起,线程B获得CPU执行权。线程B也执行到了calendar.setTime(date),把时间设置为2019-01-03。线程挂起,线程A继续走,calendar还会被继续使用(subFormat方法),而这时calendar用的是线程B设置的值了,而这就是引发问题的根源,出现时间不对,线程挂死等等。
其实SimpleDateFormat源码上作者也给过我们提示:
* Date formats are not synchronized.
* It is recommended to create separate format instances for each thread.
* If multiple threads access a format concurrently, it must be synchronized
* externally.
日期格式不同步。建议为每个线程创建单独的格式实例。 如果多个线程同时访问一种格式,则必须在外部同步该格式。
三、解决方案
只在需要的时候创建新实例,不用static修饰
public static String formatDate(Date date) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(date);
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.parse(strDate);
}
如上代码,仅在需要用到的地方创建一个新的实例,就没有线程安全问题,不过也加重了创建对象的负担,会 频繁地创建和销毁对象,效率较低。
synchronized 大法好
public static String formatDate(Date date) throws ParseException {
//return sdf.format(date);
synchronized (sdf) {
return sdf.format(date);
}
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException {
//return sdf.parse(strDate);
synchronized (sdf) {
return sdf.parse(strDate);
}
}
简单粗暴,synchronized往上一套也可以解决线程安全问题,缺点自然就是并发量大的时候会对性能有影响,线程阻塞。
ThreadLocal
/* ThreadLocal */
private static ThreadLocal<DateFormat> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<DateFormat>() {
@Override
protected DateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
};
public static String formatDate(Date date) throws ParseException {
//return sdf.format(date);
/*synchronized (sdf) {
return sdf.format(date);
}*/
return threadLocal.get().format(date);
}
public static Date parse(String strDate) throws ParseException {
//return sdf.parse(strDate);
/*synchronized (sdf) {
return sdf.parse(strDate);
}*/
return threadLocal.get().parse(strDate);
}
ThreadLocal 可以确保每个线程都可以得到单独的一个 SimpleDateFormat 的对象,那么自然也就不存在竞争问题了。
基于JDK1.8的DateTimeFormatter
也是《阿里巴巴开发手册》给我们的解决方案,对之前的代码进行改造:
public class SimpleDateFormatTest8 {
// 新建 DateTimeFormatter 类
private static final DateTimeFormatter FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private static String formatDate(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
return FORMATTER.format(dateTime);
}
private static LocalDateTime parse(String dateNow) {
return LocalDateTime.parse(dateNow, FORMATTER);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
try {
System.out.println(parse(formatDate(LocalDateTime.now())));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
// 等待上述的线程执行完后
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
}
DateTimeFormatter源码上作者也加注释说明了,他的类是不可变的,并且是线程安全的。