ButterKnife在实际开发中有着大量运用,其强大的view绑定和click事件处理,使得开发效率大大提高,同时增加了代码的阅读性又不影响其执行效率
注解的分类
注解主要有两种分类,一个是运行时,一个是编译时
运行时注解:由于会影响性能,不是很推荐使用
编译时注解:编译时注解的核心原理依赖APT(Annotation Processing Tools)实现
编译时注解说明
使用了编译时注解的第三方框架主要有
ButterKnife:这个库是针对View,资源ID,部分事件等进行注解的开源库,它能够去除掉一些不怎么雅观的样板式代码,使得我们的代码更加简洁,易于维护,同事给予APT也能使得它的效率得到保证。ButterKnife是针对View等进行注解的开源库DraggerRetrofit
核心原理:APT(Annotation Processing Tools)实现
编译时Annotation解析的基本原理是,在某些代码元素上(如类型、函数、字段等)添加注解,在编译时javac编译器会检查AbstractProcessor的子类,并且调用该类型的process函数,然后将添加了注解的所有元素都传递到process函数中,使得开发人员可以在编译器进行相应的处理,例如,根据注解生成新的Java类,这也就是ButterKnife Dragger等开源库的基本原理
APT工具
APT(Annotation Processing Tool)是一种处理注释的工具,它对源代码文件进行检测找出其中的Annotation,使用Annotation进行额外的处理。Annotation处理器在处理Annotation时可以根据源文件中的Annotation生成额外的源文件和其它的文件(文件具体内容由Annotation处理器的编写者决定),APT还会编译生成的源文件和原来的源文件,将它们一起生成class文件
Java源文件编译成Class文件
工具是javac工具,注解处理器是一个在javac中的,用来编译时扫描和处理的注解的工具。你可以为特定的注解,注册你自己的注解处理器
怎样注册注解处理器
MyProcessor到javac中。你必须提供一个.jar文件。就像其他.jar文件一样,你打包你的注解处理器到此文件中。并且,在你的jar中,你需要打包一个特定的文件javax.annotation.processing.Processor到META-INF/services路径下
依赖准备
需要一个注入模块,也就是一个依赖库,这是一个Android Library
新建Android依赖库
项目右键 -> New -> Module -> Android Library
需要一个Java Library,用来包含注解,注解库
新建Java依赖库
项目右键 -> New -> Module -> Java Library
同时就需要一个注解处理器,这也是一个Java Library,编译库
新建Java依赖库
项目右键 -> New -> Module -> Java Library
至此,主项目,Android依赖库,Java依赖库新建完成
添加依赖
工程gradle增加maven库和apt插件
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
//maven库
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.3'
//apt插件,如果报错则不使用apt,不添加这行
//classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
//maven库
mavenCentral()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}
主工程gradle下引入apt
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
//引入apt,如果报错则不使用apt,不添加这行
//apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
android {
compileSdkVersion 25
···
配置主项目,Android依赖和Java依赖之间的关系
项目右键 -> Open Module Settings -> ···
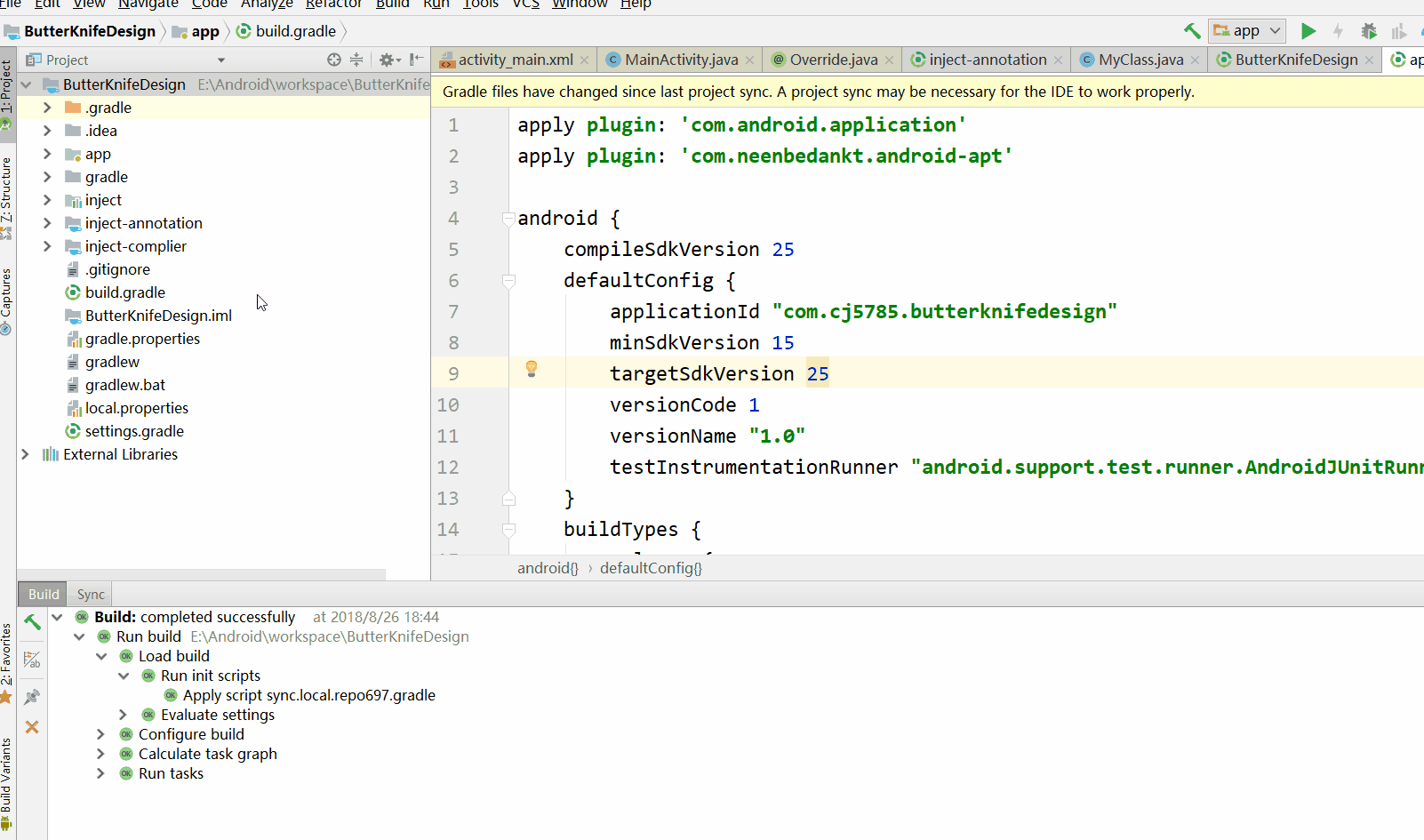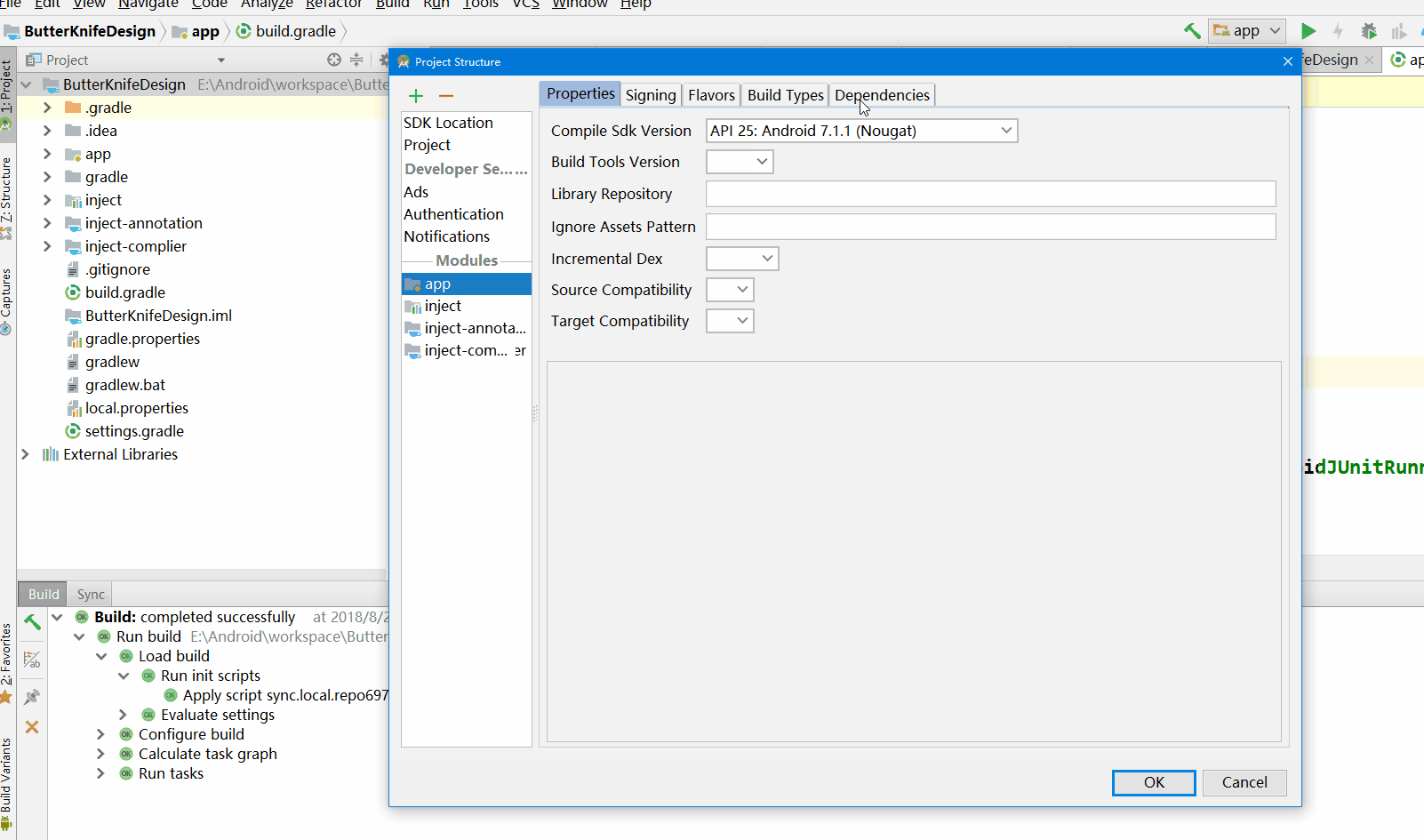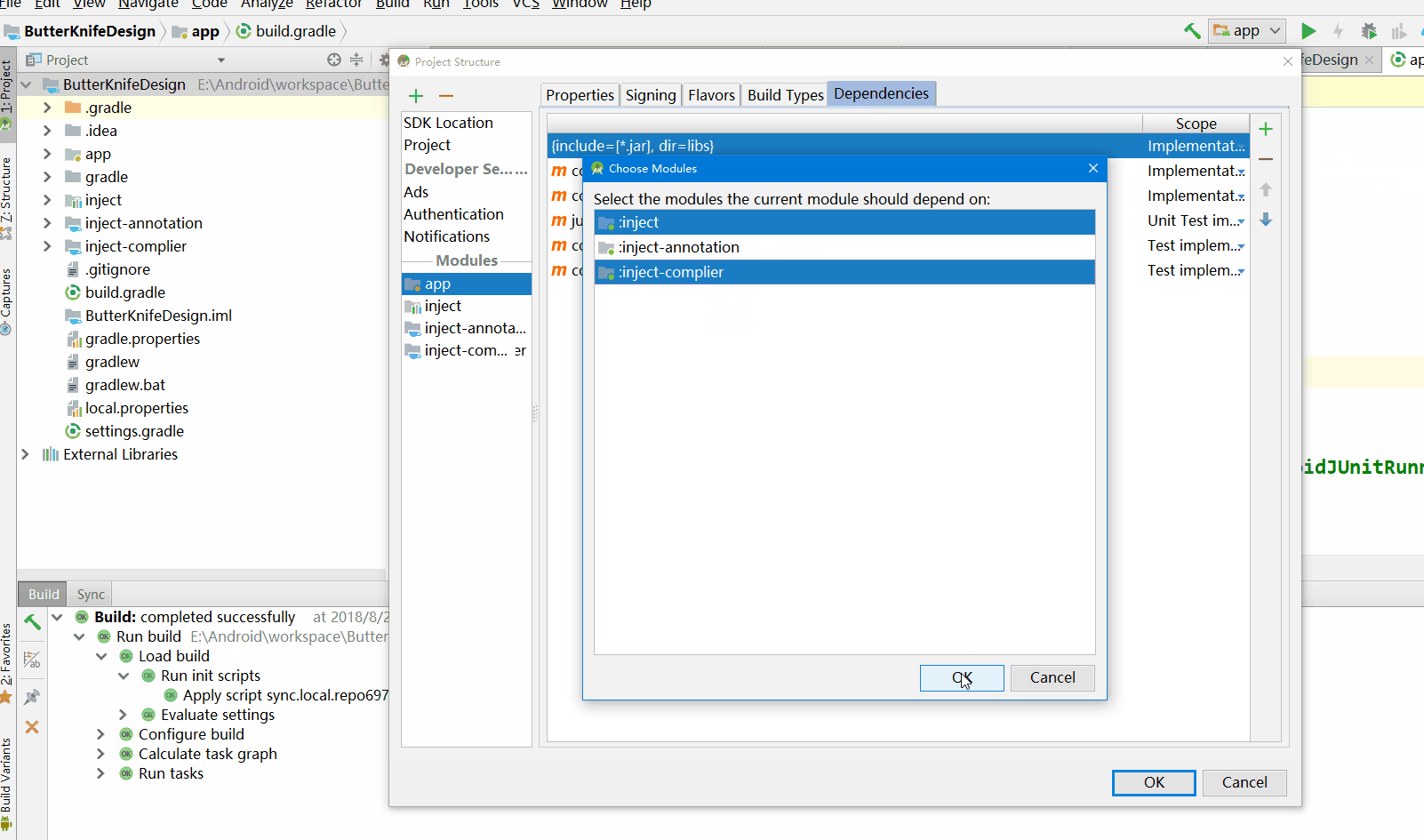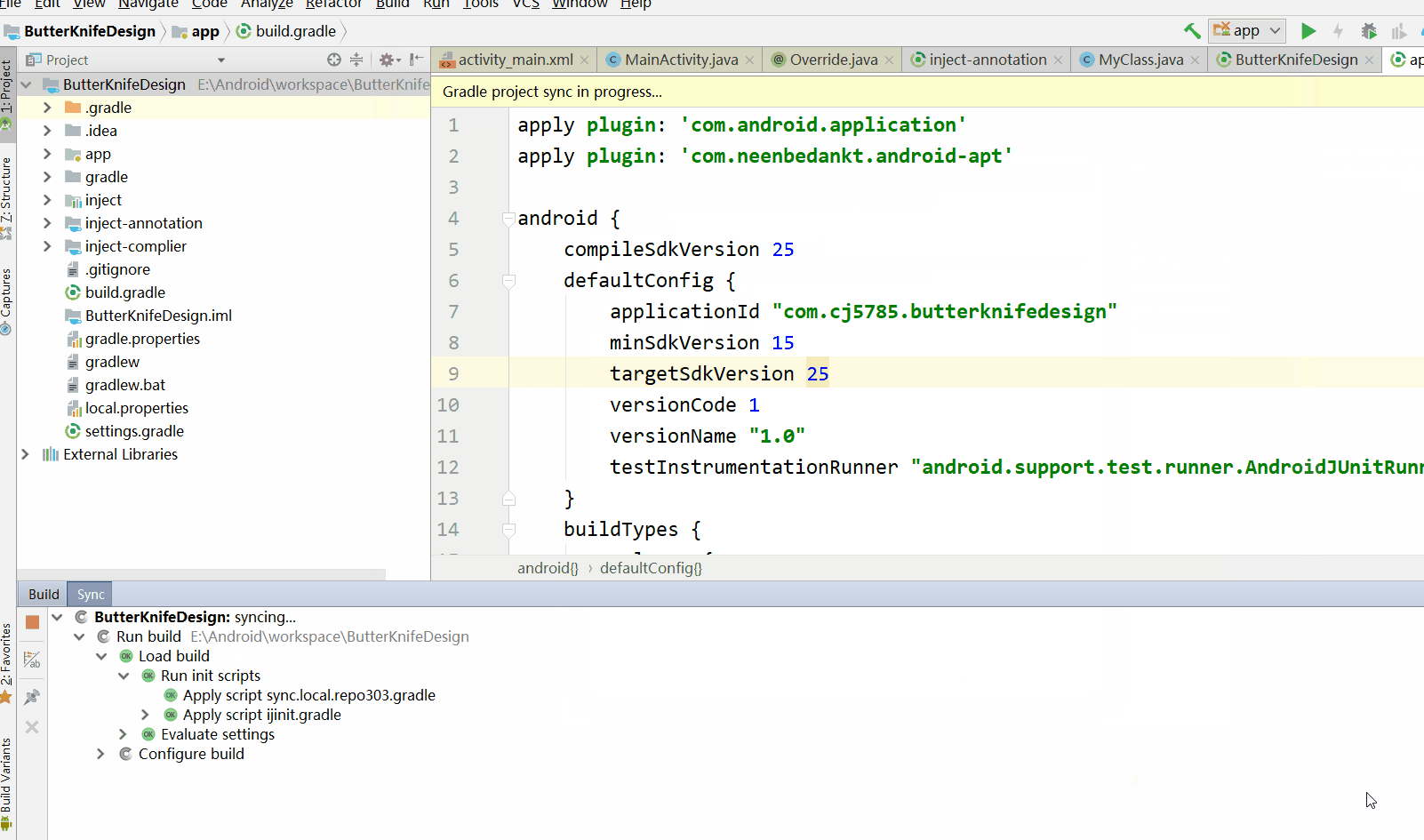
如果配置完成报错,那么就不添加apt,而使用annotationProcessor
android-apt plugin is incompatible with the Android Gradle plugin. Please use 'annotationProcessor' configuration instead.
此时再主项目gradle中会生成
dependencies {
···
implementation project(':inject')
implementation project(':inject-complier')
}
将其修改为,apt和annotationProcessor两种形式
dependencies {
···
implementation project(':inject')
//apt project(':inject-complier')
annotationProcessor project(':inject-complier')
}
否则编译器不知道由谁去负责apt
添加inject-complier的依赖inject-annotation
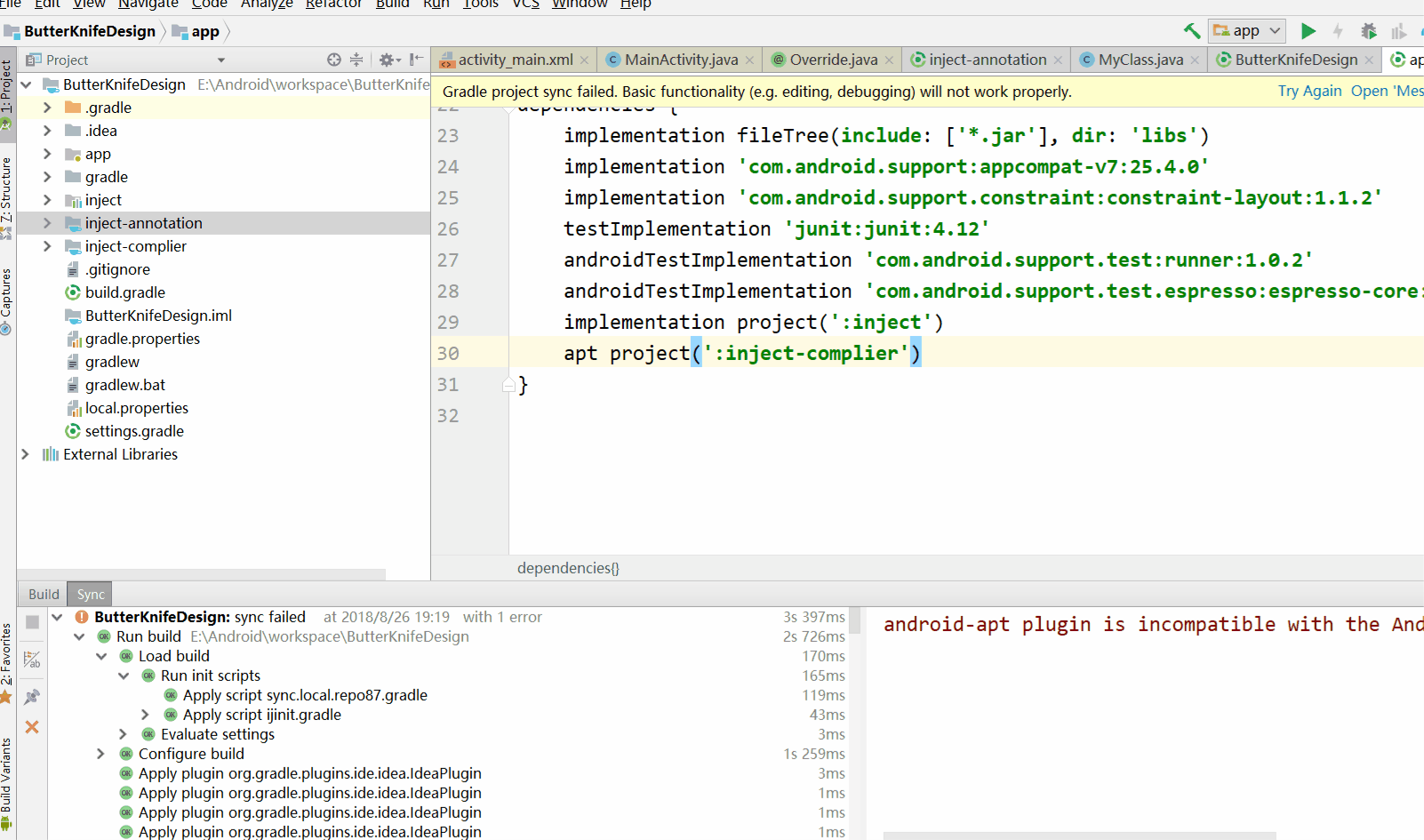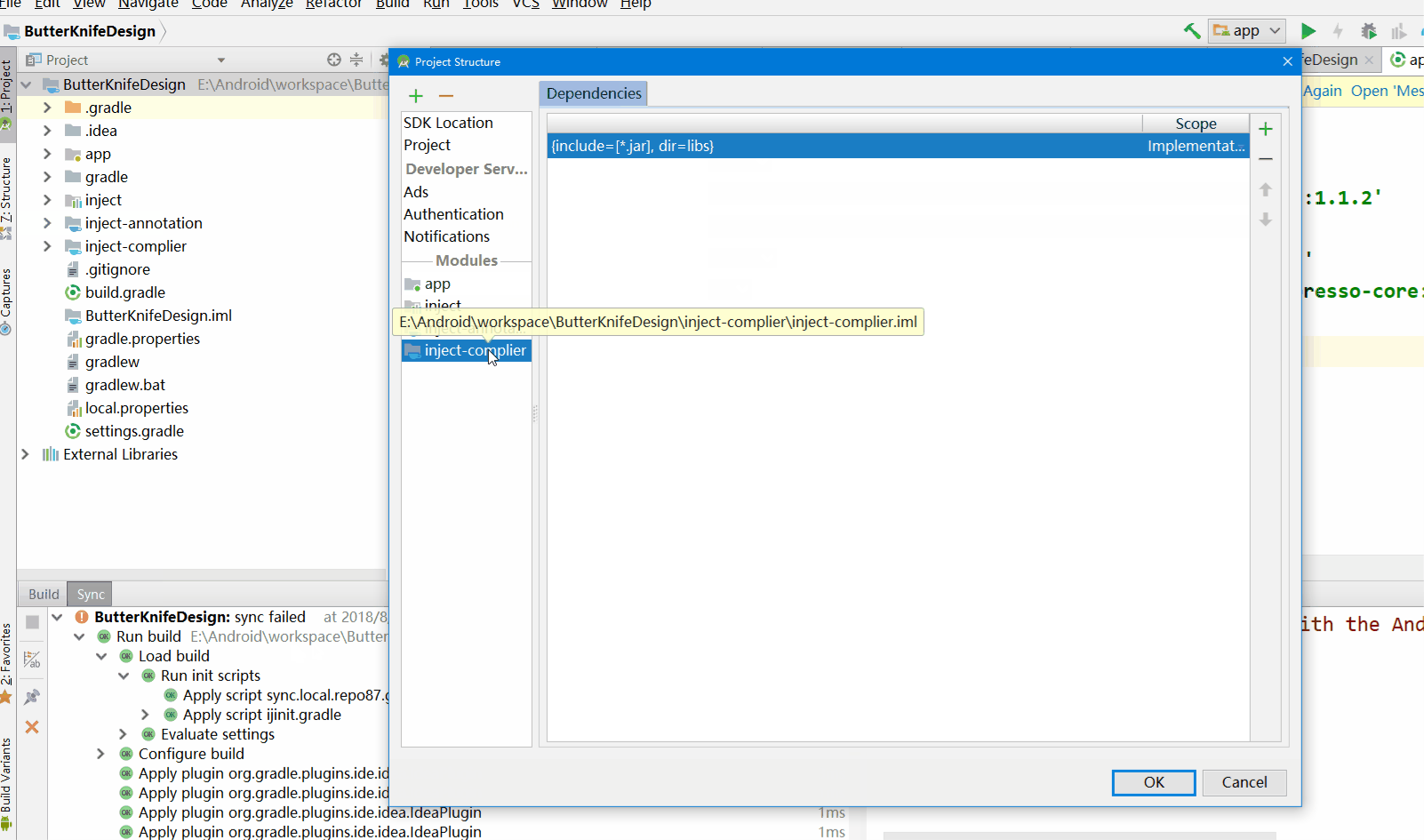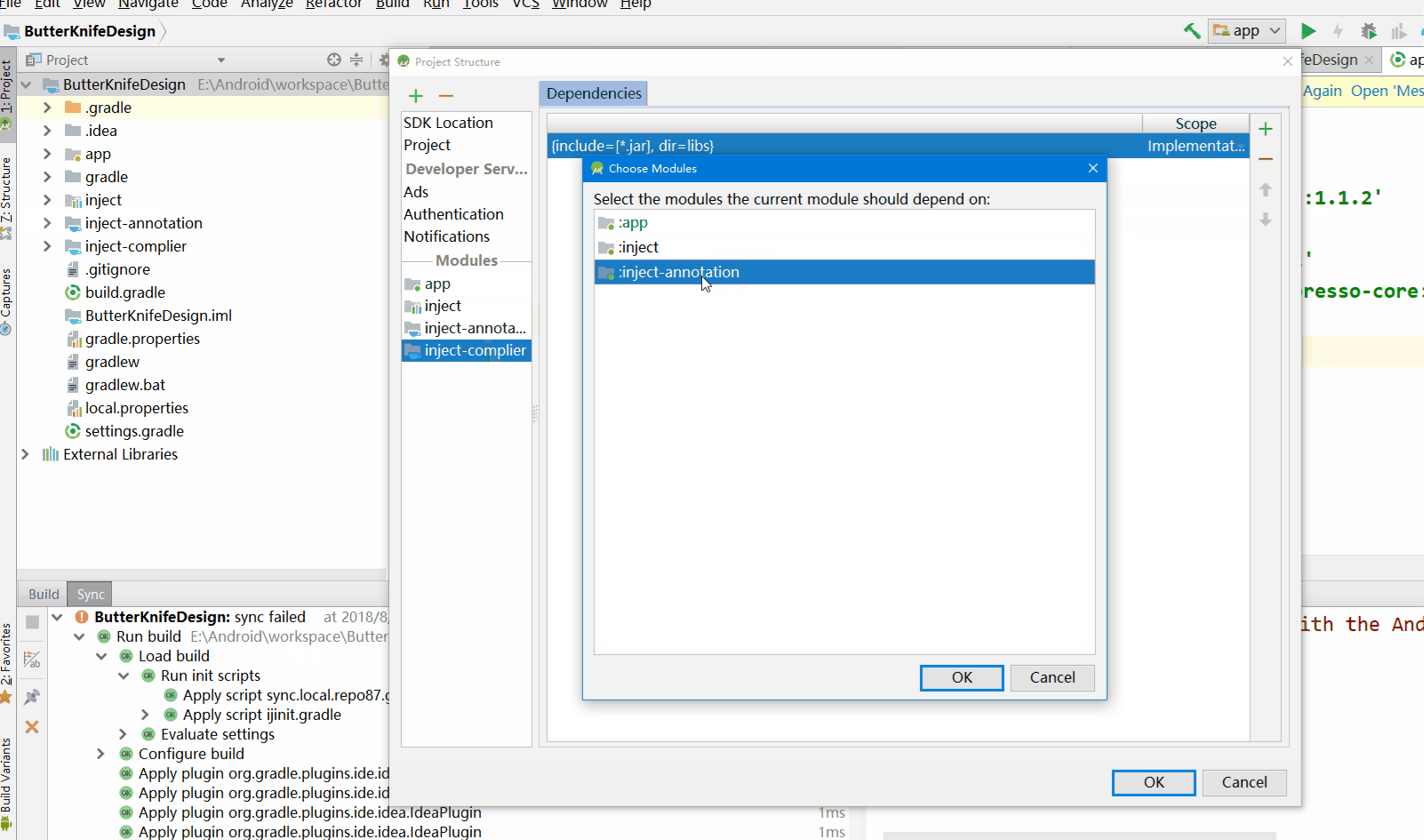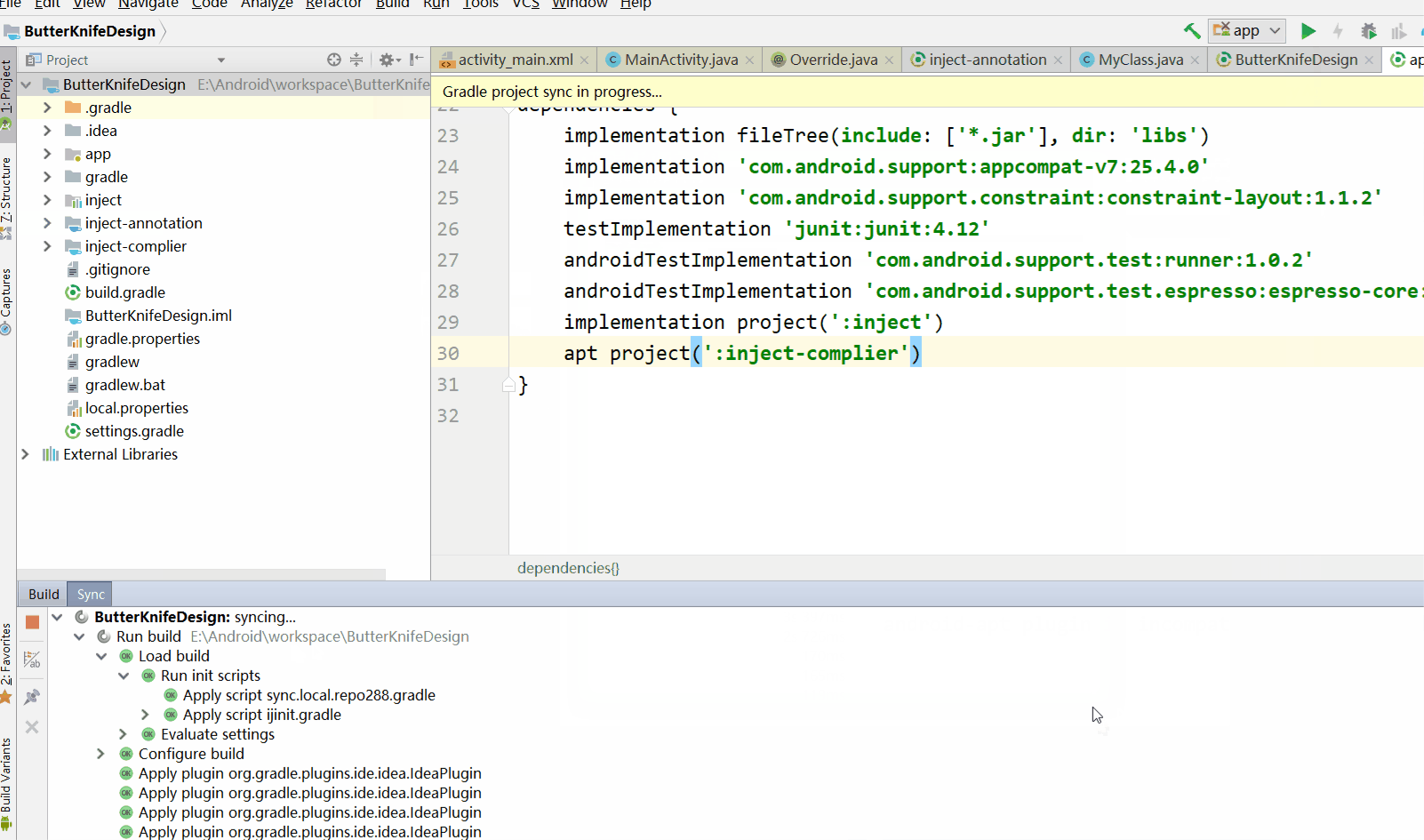
同样的做法,inject添加inject-annotation依赖
在inject-complie添加生成源代码的com.google.auto:auto-common``com.google.auto.service:auto-service库和生成Java源文件的com.squareup:javapoet库
配置完成gradle如下
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
implementation project(':inject-annotation')
implementation 'com.google.auto:auto-common:0.10'
implementation 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4'
implementation 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.11.1'
}
最终生成的各个gradle依赖如下
主项目gradle
dependencies {
···
implementation project(':inject')
//apt project(':inject-complier')
annotationProcessor project(':inject-complier')
implementation project(':inject-annotation')
}
Android Library
dependencies {
···
implementation project(':inject-annotation')
}
注解库依赖没有添加任何依赖
编译库依赖
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
implementation project(':inject-annotation')
implementation 'com.google.auto:auto-common:0.10'
implementation 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc4'
implementation 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.11.1'
}
代码实现
主项目代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@BindView(R.id.text_view)
TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
InjectView.bind(this);
Toast.makeText(this, "textView=" + textView, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
textView.setText("改写成功");
}
}
Android依赖库代码
public interface ViewBinder<T> {
void bind(T tartget);
}
public class InjectView {
//绑定Activity
public static void bind(Activity activity) {
//通过反射拿到编译后生成的绑定内部类
String className = activity.getClass().getName();
try {
Class<?> viewBindClass = Class.forName(className + "$$ViewBinder");
ViewBinder viewBinder = (ViewBinder) viewBindClass.newInstance();
viewBinder.bind(activity);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注解库代码
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface BindView {
int value();
}
编译库代码
public class FieldViewBinding {
private String name;
private TypeMirror typeMirror;
private int resId;
public FieldViewBinding(String name, TypeMirror typeMirror, int resId) {
this.name = name;
this.typeMirror = typeMirror;
this.resId = resId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public TypeMirror getTypeMirror() {
return typeMirror;
}
public int getResId() {
return resId;
}
}
@AutoService(Processor.class)
public class BindViewProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
private Elements elementUtils;
private Types typeUtils;
private Filer filer;
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
super.init(processingEnvironment);
elementUtils = processingEnvironment.getElementUtils();
typeUtils = processingEnvironment.getTypeUtils();
filer = processingEnvironment.getFiler();
}
@Override
public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() {
Set<String> stringSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
stringSet.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName());
return stringSet;
}
@Override
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
return SourceVersion.latestSupported();
}
@Override
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
Map<TypeElement, List<FieldViewBinding>> targetMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Element element : roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class)) {
TypeElement enclosingElement = (TypeElement) element.getEnclosingElement();
List<FieldViewBinding> list = targetMap.get(enclosingElement);
if (list == null) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
targetMap.put(enclosingElement, list);
}
String packageName = getPackageName(enclosingElement);
int id = element.getAnnotation(BindView.class).value();
String fieldName = element.getSimpleName().toString();
TypeMirror typeMirror = element.asType();
FieldViewBinding fieldViewBinding = new FieldViewBinding(fieldName, typeMirror, id);
list.add(fieldViewBinding);
}
for (Map.Entry<TypeElement, List<FieldViewBinding>> item : targetMap.entrySet()) {
List<FieldViewBinding> list = item.getValue();
if (list == null || list.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
TypeElement enclosingElement = item.getKey();
String packageName = getPackageName(enclosingElement);
String complite = getClassName(enclosingElement, packageName);
ClassName className = ClassName.bestGuess(complite);
ClassName viewBinder = ClassName.get("com.cj5785.inject", "ViewBinder");
TypeSpec.Builder result = TypeSpec.classBuilder(complite + "$$ViewBinder")
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.addTypeVariable(TypeVariableName.get("T", className))
.addSuperinterface(ParameterizedTypeName.get(viewBinder, className));
MethodSpec.Builder methodBuilder = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("bind")
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.returns(TypeName.VOID)
.addAnnotation(Override.class)
.addParameter(className, "target", Modifier.FINAL);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
FieldViewBinding fieldViewBinding = list.get(i);
String pacckageNameString = fieldViewBinding.getTypeMirror().toString();
ClassName viewClass = ClassName.bestGuess(pacckageNameString);
methodBuilder.addStatement("target.$L=($T)target.findViewById($L)",
fieldViewBinding.getName(), viewClass, fieldViewBinding.getResId());
}
result.addMethod(methodBuilder.build());
try {
JavaFile.builder(packageName, result.build())
.addFileComment("auto create make")
.build().writeTo(filer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
private String getClassName(TypeElement enclosingElement, String packageName) {
int packageLength = packageName.length() + 1;
return enclosingElement.getQualifiedName().toString()
.substring(packageLength).replace(".", "$");
}
private String getPackageName(TypeElement enclosingElement) {
return elementUtils.getPackageOf(enclosingElement).getQualifiedName().toString();
}
}
由于编译库内不能存在中文,故将代码注释单独解释
@AutoService
这是一个其他注解处理器中引入的注解。AutoService注解处理器是Google开发的,用来生成META-INF/services/javax.annotation.processing.Processor文件的。我们可以在注解处理器中使用注解。非常方便Elements
一个用来处理Element的工具类:在注解处理过程中,我们扫描所有的Java源文件。源代码的每一个部分都是一个特定类型的Element。换句话说:Element代表程序的元素,例如包、类或者方法。每个Element代表一个静态的、语言级别的构件
PackageElement:包元素,可以获取包名
TypeElement:类型元素,某个字段属于某种类型
ExcutableElement:可执行元素
VariabeElement:变量元素
TypeParameterElement:类型参数元素Types
一个用来处理TypeMirror的工具类Filer
使用Filer你可以创建Java文件process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment env)
相当于每个处理器的主函数main()。你在这里写你的扫描、评估和处理注解的代码,以及生成Java文件。输入参数RoundEnviroment,可以让你查询出包含特定注解的被注解元素getSupportedAnnotationTypes
这个注解处理器是注册给哪个注解的。注意,它的返回值是一个字符串的集合,包含本处理器想要处理的注解类型的合法全称。换句话说,你在这里定义你的注解处理器注册到哪些注解上getSupportedSourceVersion
用来指定你使用的Java版本。通常这里返回SourceVersion.latestSupported()。如果你有足够的理由只支持Java 6的话,你也可以返回SourceVersion.RELEASE_6