第四周
要求:
1、将两个有序的递增链表合并为一个递增的有序链表。要求结果链表仍使用原来两个链表的储存空间,不另外占用其他的储存空间。表中不允许有重复数据。
2、已知两个链表A和B分别表示两个集合,其元素递增排列。设计一个算法用于求出A与B的交集,并存放在A链表中。
思路:首先就是创建链表。一般有前插法和后插法;二 要求递增的话可以用一个排序算法(简单看了一下冒泡排序)。三 链表显示和销毁函数。
四 重点就是合并和交集函数。注意就是对链表操作要释放多余的存储空间,比如:头结点,重复元素结点等
先定义结构
typedef struct LNode//定义结构 { int data; struct LNode *next; }LNode, *Head;
一、创建链表(后插法)
Head Create(void)//创建链表 { LNode *head, *r, *p; head = new LNode; if (head == NULL) cout << "头结点创建失败! "; p = head; int x, cycle = 1; while (cycle) { cout << "输入一个整数. "; cin >> x; if (x != 0) { r = new LNode; r->data = x; p->next = r; p = r; } else { cycle = 0; } } p->next = NULL; cout << "链表创建成功! "; return head; }
二、排序(递增)
Head Order(Head head)//链表节点排序 { LNode *p = head->next, *q = head->next; if (!p) return head; int i = 0, temp = 0, flag = 1; while (q) { q = q->next; ++i;//数据节点个数i } while (flag && i >= 0) {//冒泡排序 flag = 0; while (p->next != NULL) { if (p->data > p->next->data) { temp = p->data; p->data = p->next->data; p->next->data = temp; flag = 1;//标志置为1表示本轮有交换 } p = p->next; } --i; p = head->next;//重新指向首元结点为下轮准备 } return head; }
三、链表显示
Status print(Head head) { int i = 0; LNode *p = head; while (!p) return OK; while (p->next != NULL) { p = p->next; cout << p->data; cout << " "; ++i; } cout << " 共有"<<i<<"个元素 "; return OK; }
四、销毁链表
Status DestroyList(Head head) { LNode *p; while (head->next != NULL) { p = head; head = head->next; delete p; } delete head; return OK; }
五、链表交集
交集AB链表放入A链表中,释放B链表;head1为A链表,head2为B链表。
Head Intersection(Head head1, Head head2)//交集放入A链表 { LNode *head = NULL, *p1 = NULL, *p2 = NULL, *p = NULL; head = head1; //交集为空 while (head1->next==NULL || head2->next==NULL) { while (head2->next != NULL)//A为空链表 直接删除B链表 { p = head2; head2 = head2->next; delete p; } delete head2; return head1; break; } LNode *move = head, *temp = NULL; p1 = head1->next; p2 = head2->next; delete head2; //AB均不为空 while (p1&&p2->next != NULL){ if (p1->data < p2->data) p1 = p1->next; else if (p1->data > p2->data) p2 = p2->next; else if (p1->data == p2->data) { move->next = p1; move = p1; p1 = p1->next; } } if (p2->next == NULL) {//判断B链表最后一个结点 if (p1->data == p2->data) { move->next = p1; move = p1; p1 = p1->next; } } move->next = NULL;//尾部指针为NULL return head; }
六、链表合并
这里AB合并后放入B链表中。
Head Combine(Head head1, Head head2)//合并后放入B链表 { LNode *head=head2, *p1=NULL, *p2=NULL; if (head1->next==NULL) {//A为空链表或者AB都为空 delete head1; return head2; } else if (head2->next == NULL) {//B为空链表 head2->next = head1->next;//A链表赋给B链表 delete head1; return head2; } p1 = head1->next; p2 = head2->next; delete head1; LNode *move = head, *temp = NULL; //按递增顺序依次链接 while (p1&&p2) { if (p1->data < p2->data) { move->next = p1; move = p1; p1 = p1->next; } else if (p1->data > p2->data) { move->next = p2; move = p2; p2 = p2->next; } else if(p1->data == p2->data) {//相同数据只保存一个,p1p2向后移一位 temp = p2; move->next = p1; move = p1; p1 = p1->next; p2 = p2->next; delete temp;//删除p2相同结点 } } if (p1)//p2为NULL,直接连接p1后面的结点 move->next = p1; if (p2)//p1为NULL,直接连接p2后面的结点 move->next = p2; return head; }
测试
int main() { cout << "创建一个链表A. 输入0结束 "; Head head1 = Create(); cout << "创建一个链表B. 输入0结束 "; Head head2 = Create(); char ch; while (1) { cout << "--------------------------------------------------------------------------- "; cout << "+请选择要进行的操作:<a>显示A <b>显示B <c>交集AB <d>合并AB <x>退出+ "; cout << "--------------------------------------------------------------------------- "; ch = _getwch(); if (ch == 'a') { cout << "A链表:"; print(Order(head1)); } else if (ch == 'b') { cout << "B链表:"; print(Order(head2)); } else if (ch == 'c') { cout << "AB交集为:"; print(Order(Intersection(head1, head2))); cout << "输入任意字符结束 "; ch = _getwch(); DestroyList(head1); break; } if (ch == 'd') { cout << "AB合并为:"; print(Order(Combine(head1, head2))); cout << "输入任意字符结束 "; ch = _getwch(); DestroyList(head2); break; } else if (ch == 'x') { break; } } }
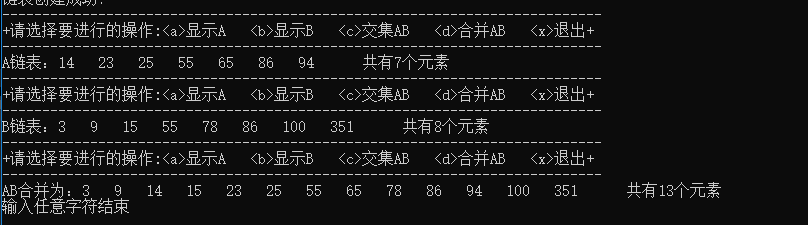
运行结果:
交集:

合并: