1. Django ORM
通过代码来描述数据库中的表
类名 - 表名
类属性 - 表字段
表中的每一个记录在代码的层面都是由类实例化的对象, 表中的字段是其属性
2. 配置ORM
2.1 安装django 和 pg 模块
pip install psycopg2
pip install django==2.2.15
2.2 准备django项目
创建库 ormtest
django-admin startproject salary .
- 创建应用
python manage.py startapp employee
-
配置
打开salary/settings.py主配置文件
# 应用注册
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'employee'
]
# 数据库配置
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql_psycopg2',
'NAME': 'ormtest',
'USER': 'postgres',
'PASSWORD': 'postgres',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': '5432',
}
}
# 时区配置
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
2.3 Django日志配置
打开salary/settings.py主配置文件
LOGGING = {
'version': 1,
'disable_existing_loggers': False,
'handlers': {
'console': {
'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
},
},
'loggers': {
'django.db.backends': {
'handlers': ['console'],
'level': 'DEBUG',
},
},
}
2.4 模型Model下编写ORM类
打开employee/models.py
- 基类 django.db.models.Model
- 表名不指定默认使用 _ 。使用Meta类db_table修改表名
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Employee(models.Model):
class Meta:
db_table = 'employees'
emp_no = models.IntegerField(primary_key=True) # Django中如果model类中定义了主键, 自增整数字段主键不会自动创建了
birth_date = models.DateField(null=False)
first_name = models.CharField(null=False, max_length=14)
last_name = models.CharField(null=False, max_length=16)
gender = models.SmallIntegerField(null=False, default=1) # M=1 F=2
hire_date = models.DateField(null=False)
def __repr__(self):
return "<Employee: {} {} {}>".format(self.emp_no, self.first_name,self.last_name)
__str__ = __repr__
# ORM 查询返回n条员工记录, 每一个记录都是一个实例(employee())
- 创建表
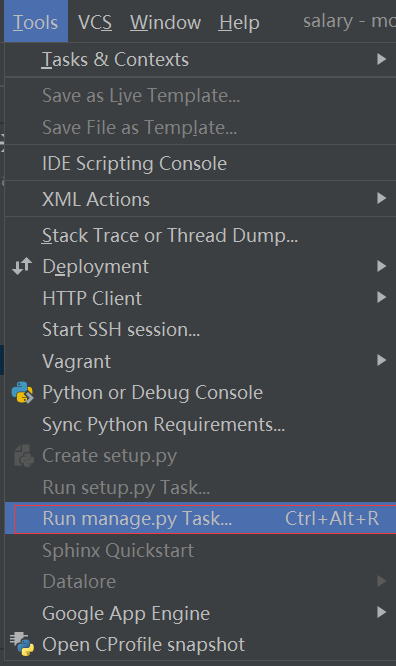
makemigrations
migrate
2.5 插入数据
在项目根目录编写一个test.py,内容如下
# 参考wsgi.py
from datetime import datetime
import os
import django
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'salary.settings')
django.setup(set_prefix=False)
# 其他测试代码都放到这4行下面
from employee.models import Employee
def birth_date(year, month, day):
dt = datetime(year=year, month=month, day=day)
return dt.strftime('{}-{}-{}'.format(dt.year, dt.month, dt.day))
# Employee.objects 管理类对象
emp_mgr = Employee.objects # employee.Employee.objects
birth_date_list = [birth_date(1953, 9, 2), birth_date(1964, 6, 2), birth_date(1959, 12, 3), birth_date(1954, 5, 1),
birth_date(1955, 1, 21),
birth_date(1953, 4, 20), birth_date(1957, 5, 23), birth_date(1958, 2, 19), birth_date(1952, 4, 19),
birth_date(1963, 6, 1),
birth_date(1953, 11, 7), birth_date(1960, 10, 4), birth_date(1963, 6, 7), birth_date(1956, 2, 12),
birth_date(1959, 8, 19),
birth_date(1961, 5, 12), birth_date(1958, 7, 6), birth_date(1954, 6, 19), birth_date(1953, 1, 23),
birth_date(1952, 12, 24)
]
first_name_list = ['Georgi', 'Bezalel', 'Parto', 'Christian', 'Kyoichi',
'Anneke', 'Tzvetan', 'Saniya', 'Sumant', 'Duangkaew',
'Mary', 'Patricio', 'Eberhardt', 'Berni', 'Guoxiang',
'Kazuhito', 'Cristinel', 'Kazuhide', 'Lillian', 'Mayuko'
]
last_name_list = ['Facello', 'Simmel', 'Bamford', 'Koblick', 'Maliniak',
'Preusig', 'Zielinski', 'Kalloufi', 'Peac', 'Piveteau',
'Sluis', 'Bridgland', 'Terkki', 'Genin', 'Nooteboom',
'Cappelletti', 'Bouloucos', 'Peha', 'Haddadi', 'Warwick'
]
gender_list = [1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1]
hire_date_list = [birth_date(1986, 6, 26), birth_date(1985, 11, 21), birth_date(1986, 8, 28), birth_date(1986, 12, 1),
birth_date(1989, 9, 12),
birth_date(1989, 6, 12), birth_date(1989, 2, 10), birth_date(1994, 9, 15), birth_date(1985, 2, 18),
birth_date(1989, 8, 24),
birth_date(1990, 1, 22), birth_date(1992, 12, 18), birth_date(1985, 10, 20), birth_date(1987, 3, 11),
birth_date(1987, 7, 12),
birth_date(1995, 11, 27), birth_date(1993, 8, 3), birth_date(1987, 4, 3), birth_date(1999, 4, 30),
birth_date(1991, 1, 26)
]
data = []
for i in range(20):
data.append(Employee(emp_no=i+10001, birth_date=birth_date_list[i], first_name=first_name_list[i], last_name=last_name_list[i],
gender=gender_list[i], hire_date=hire_date_list[i]))
Employee.objects.bulk_create(data)
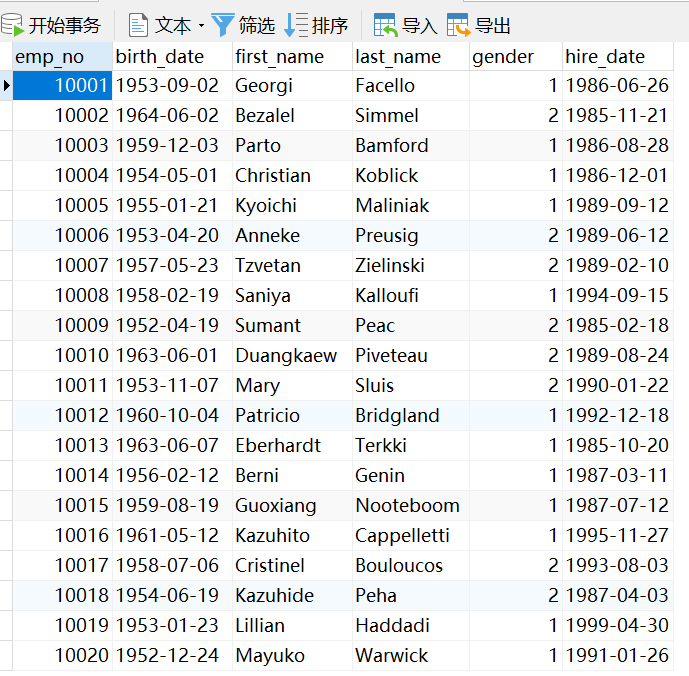
3. ORM查询
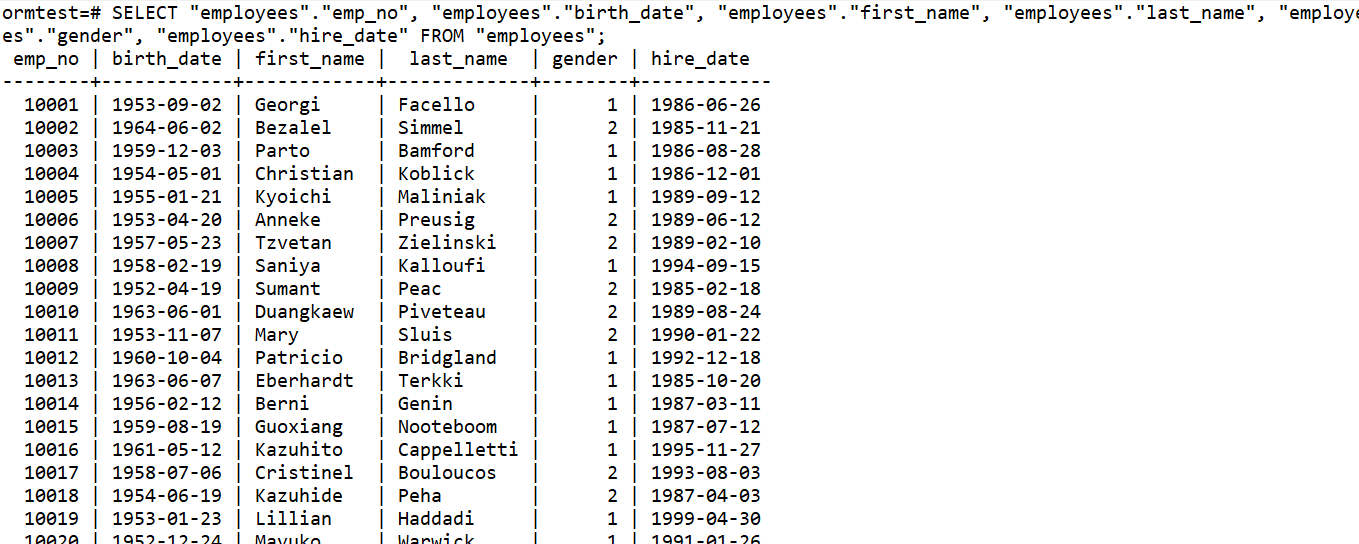
3.1 查询所有
SELECT "employees"."emp_no", "employees"."birth_date", "employees"."first_name", "employees"."last_name", "employees"."gender", "employees"."hire_date" FROM "employees";
# Employee.objects 管理类对象
emp_mgr = Employee.objects # employee.Employee.objects
x = emp_mgr.all() # 操作这个对象就意味着select * from employees; (比如for循环, 比如print)
for i in x:
print(i.pk, i.birth_date, i.first_name, i.last_name, i.gender, i.hire_date)
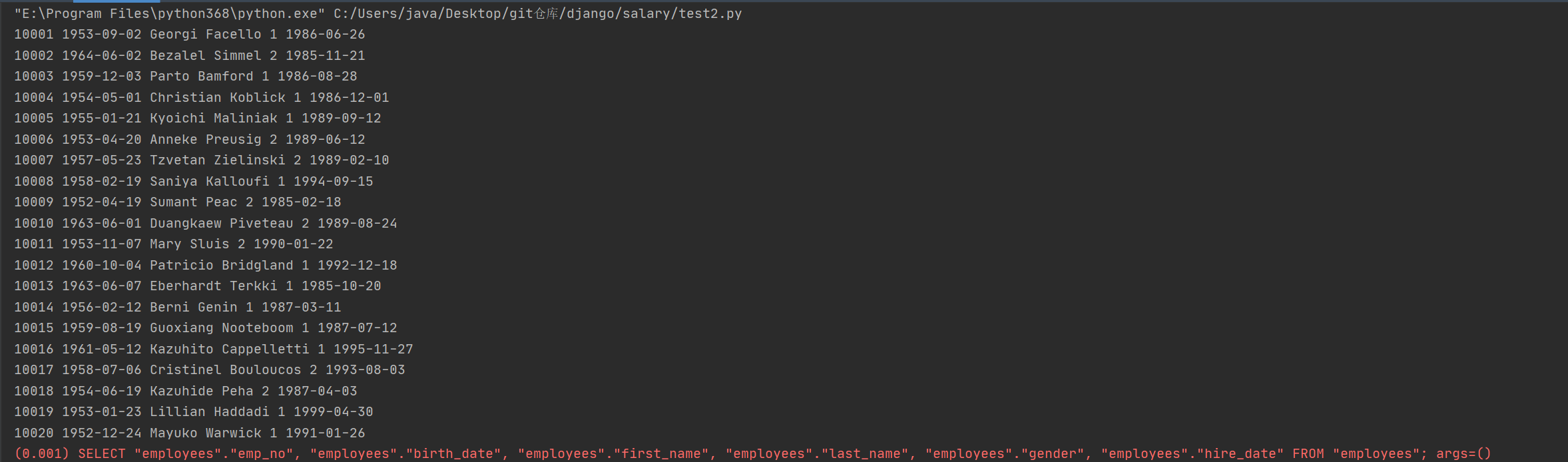
3.2 高效率查询所有
将 查询集 emp_mgr.all() 封装成列表
x = list(emp_mgr.all()) # 如果这个对象需要用到多次, 使用列表封装对象, 这样触发这个对象的查询只会执行一次
print(x)
print(x)

说明:
1、惰性求值:
创建查询集不会带来任何数据库的访问,直到调用方法使用数据时,才会访问数据库。在迭代、序列
化、if语句中都会立即求值。
2、缓存:
每一个查询集都包含一个缓存,来最小化对数据库的访问。
新建查询集,缓存为空。首次对查询集求值时,会发生数据库查询,Django会把查询的结果存在这个缓
存中,并返回请求的结果,接下来对查询集求值将使用缓存的结果。
观察下面的2个例子是要看真正生成的语句了
3.3 条件查询 (filter / exclude)
- filter
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE "employees"."emp_no" = 10001 LIMIT 21;
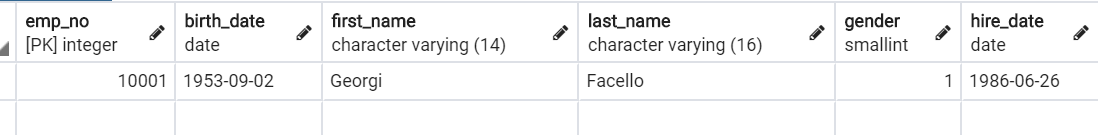
print(emp_mgr.filter(pk=10001))
- exclude
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE NOT ("employees"."emp_no" = 10001) LIMIT 21;
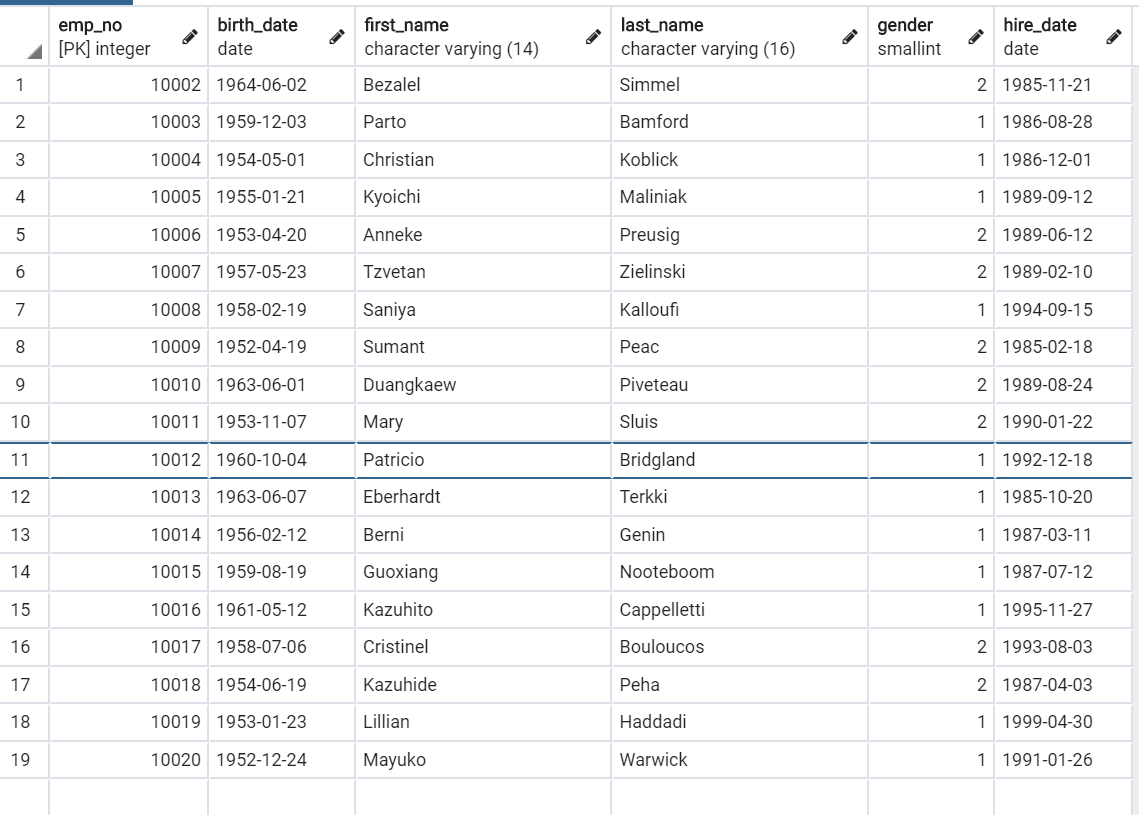
print(emp_mgr.exclude(pk=10001))
3.4 与查询
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE (UPPER("employees"."first_name"::text) LIKE UPPER('p%') AND "employees"."emp_no" > 10009) LIMIT 21;

from django.db.models import Q
print(emp_mgr.filter(pk__gt=10009, first_name__istartswith='p'))
print(emp_mgr.filter(pk__gt=10009) & emp_mgr.filter(first_name__istartswith='p'))
print(emp_mgr.filter(Q(pk__gt=10009) & Q(first_name__istartswith='p')))
3.5 或查询
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE "employees"."emp_no" IN (10005, 10006, 10007) LIMIT 21;
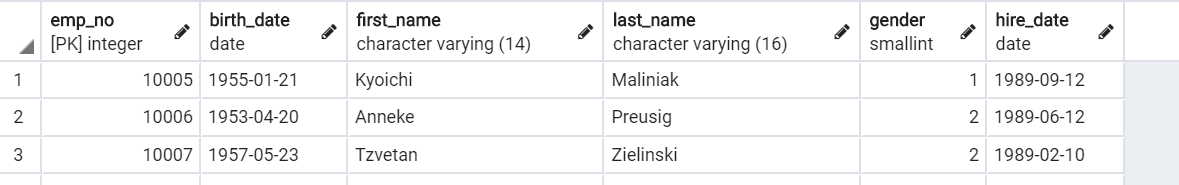
print(emp_mgr.filter(pk__in=[10005, 10006, 10007]))
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE ("employees"."emp_no" = 10005 OR "employees"."emp_no" = 10006 OR "employees"."emp_no" = 10007) LIMIT 21;

print(emp_mgr.filter(pk__exact=10005) | emp_mgr.filter(pk__exact=10006) | emp_mgr.filter(pk__exact=10007))
print(emp_mgr.filter(Q(pk__exact=10005) | Q(pk__exact=10006) | Q(pk__exact=10007)))
3.6 非查询
SELECT * FROM "employees" WHERE not ("employees"."emp_no" < 10017) LIMIT 21;
print(emp_mgr.filter(~(Q(pk__lte=10017))))
3.7 排序(order_by)
- 升序 (默认)
SELECT * FROM "employees" ORDER BY "employees"."gender" ASC;
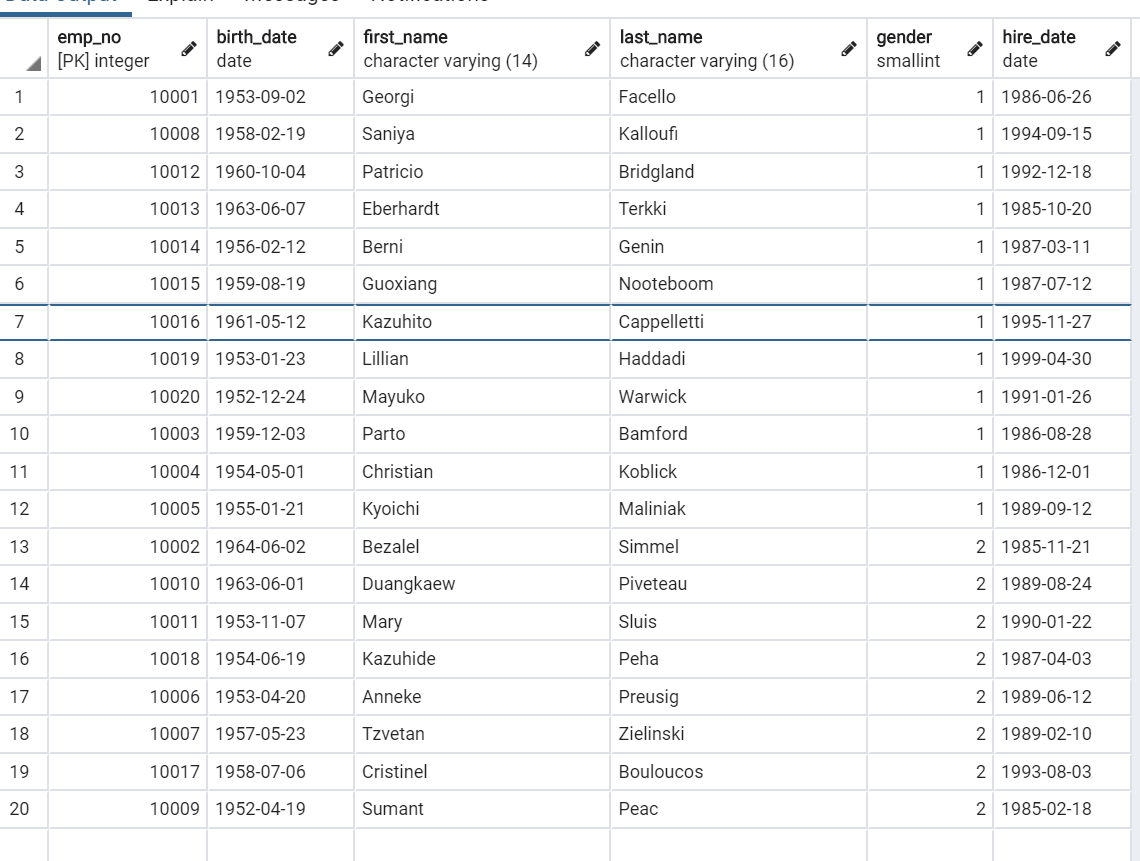
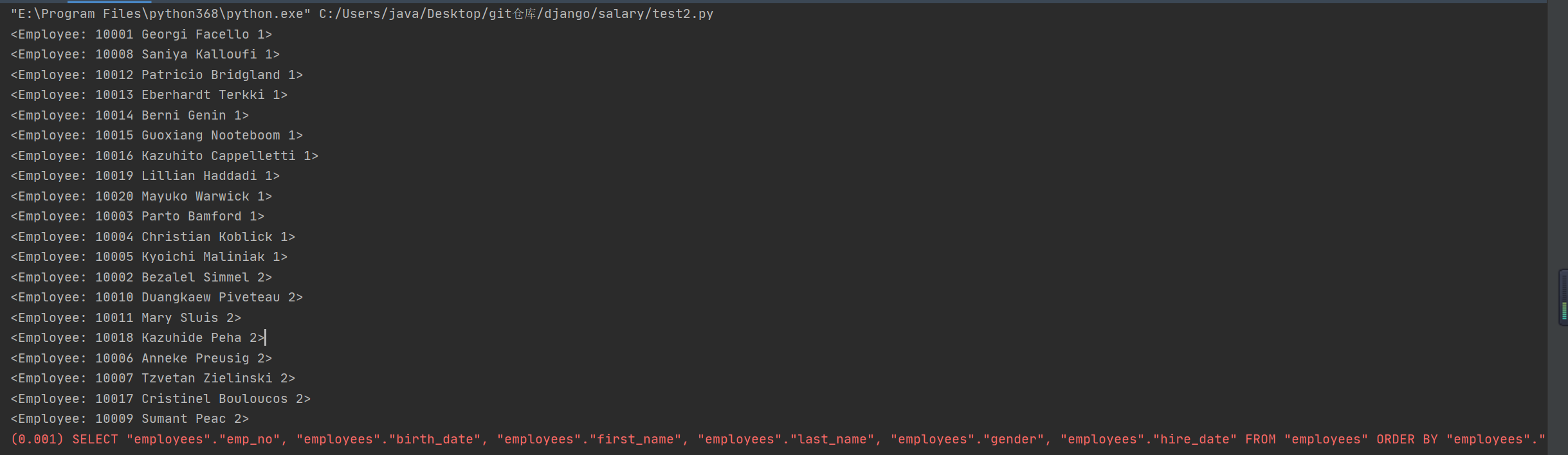
print(*emp_mgr.all().order_by('gender'), sep='
')
- 降序
SELECT * FROM "employees" ORDER BY "employees"."gender" DESC;
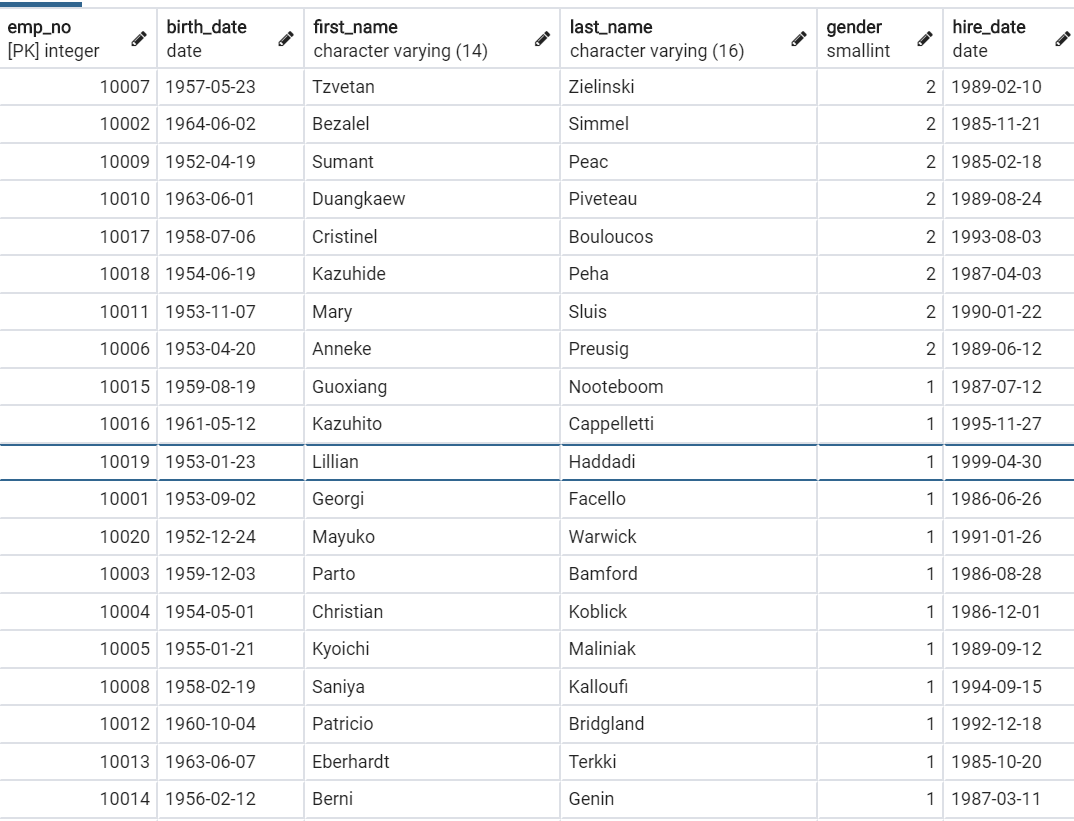
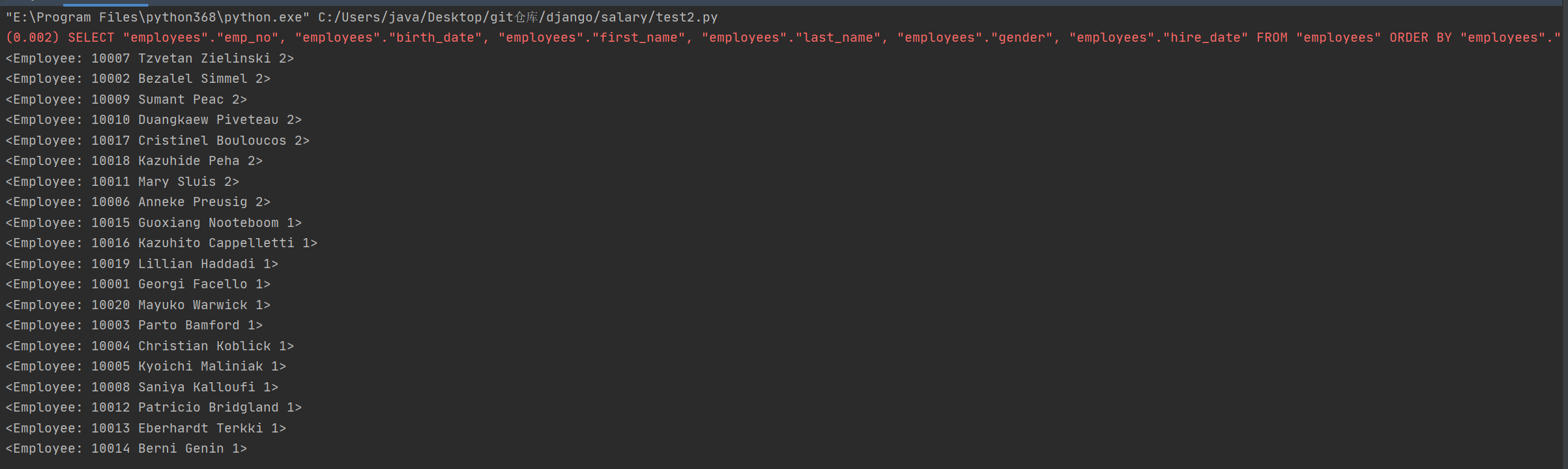
print(*emp_mgr.all().order_by('-gender'), sep='
')
3.8 字典 / 列表 查询集
- 字典查询集
SELECT * FROM "employees" LIMIT 1 OFFSET 5;
print(emp_mgr.values()[5:6]) # 字典的查询集

- 列表查询集
SELECT * FROM "employees" LIMIT 1 OFFSET 5;
print(emp_mgr.values_list()[5:6]) # 列表的查询集

3.9 返回单个值的方法
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| get() | 仅返回单个满足条件的对象 如果未能返回对象则抛出DoesNotExist异常; 如果能返回多条,抛出MultipleObjectsReturned异常 |
| count() | 返回当前查询的总条数 |
| first() | 返回第一个对象 |
| last() | 返回最后一个对象 |
| exist() | 判断查询集中是否有数据,如果有则返回True |
mgr = Employee.objects
print(mgr.filter(pk=10010).get()) # <Employee: 10010 Duangkaew Piveteau 2>
print(mgr.get(pk=10009)) # <Employee: 10009 Sumant Peac 2>
print(mgr.get(pk=10029)) # pk=10029的数据不存在, 抛异常, employee.models.DoesNotExist: Employee matching query does not exist.
print(mgr.first()) # <Employee: 10001 Georgi Facello 1>
print(mgr.filter(pk=10010, gender=1).first()) # None
print(mgr.exclude(pk=10020).last()) # <Employee: 10019 Lillian Haddadi 1>
print(mgr.count()) # 20
print(mgr.exclude(pk=10010).count()) # 19
3.10 聚合查询
SELECT COUNT("employees"."emp_no") AS "数量" FROM "employees" WHERE "employees"."emp_no" <= 10010;
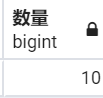
from django.db.models import Count
print(emp_mgr.values().filter(pk__lte=10010).aggregate(数量=Count('pk')))
3.11 分组查询
SELECT "employees"."gender", COUNT("employees"."gender") AS "数量" FROM "employees" WHERE "employees"."emp_no" <= 10010 GROUP BY "employees"."gender" LIMIT 21;
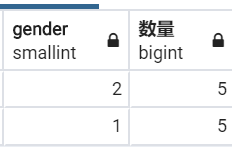
print(emp_mgr.filter(pk__lte=10010).values('gender').annotate(数量=Count('gender')).values('gender', '数量'))