Backup and Recovery: Concepts
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
• Identify the types of failure that can occur in an Oracle database
• Describe instance recovery
• Describe complete and incomplete recovery
目标
完成本课程后,您应该能够:
•确定Oracle数据库中可能发生的故障类型
•描述实例恢复
•描述完全和不完全恢复
DBA Responsibilities
• Protect the database from failure wherever possible
• Increase the mean time between failures (MTBF)
• Protect critical components by using redundancy
• Decrease the mean time to recover (MTTR)
• Minimize the loss of data
DBA职责
•尽可能防止数据库出现故障
•增加平均无故障时间(MTBF)
•使用冗余保护关键组件
•缩短平均恢复时间(MTTR)
•尽量减少数据丢失
Categories of Failure
Failures can generally be divided into the following categories:
• Statement failure
• User process failure
• Network failure
• User error
• Instance failure
• Media failure
故障类别
故障通常可分为以下几类:
•语句失败
•用户过程故障
•网络故障
•用户错误
•实例失败
•媒体故障
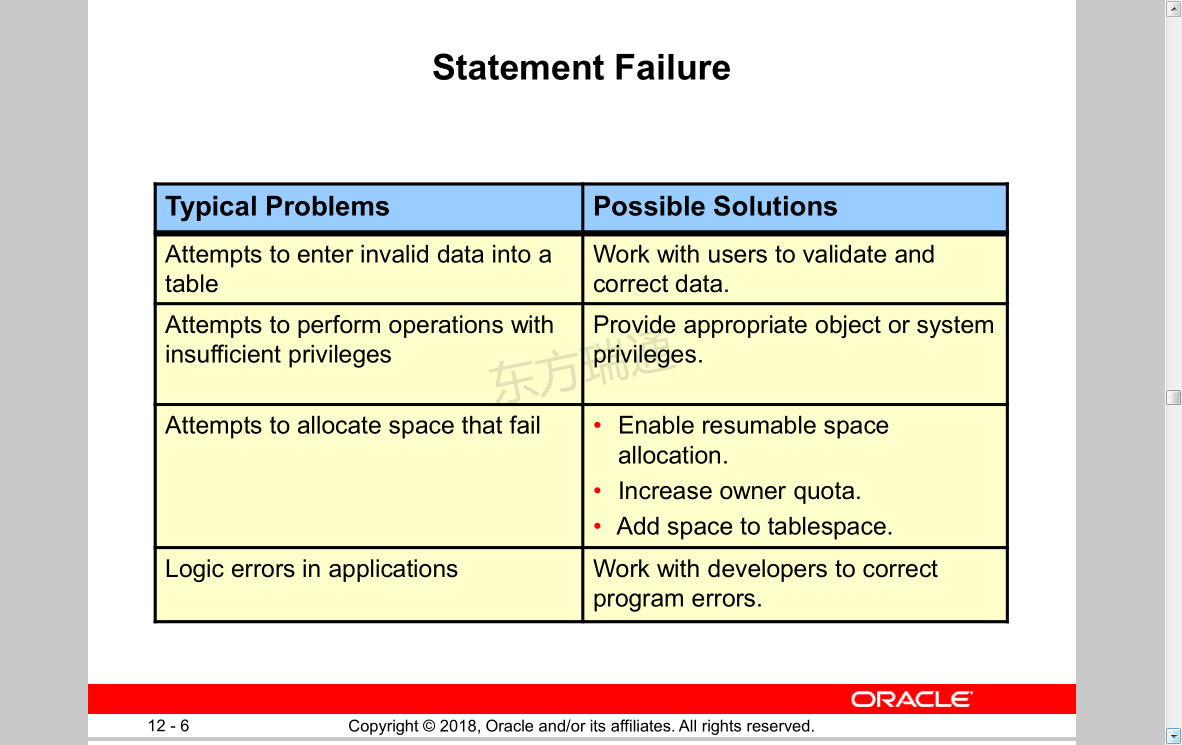
Statement Failure
Typical Problems Possible Solutions
Attempts to enter invalid data into a
table
Work with users to validate and
correct data.
Attempts to perform operations with
insufficient privileges
Provide appropriate object or system
privileges.
Attempts to allocate space that fail • Enable resumable space
allocation.
• Increase owner quota.
• Add space to tablespace.
Logic errors in applications Work with developers to correct
program errors.
Statement Failure
Typical Problems Possible Solutions
Attempts to enter invalid data into a table
Work with users to validate and correct data.
Attempts to perform operations with insufficient privileges
Provide appropriate object or system privileges.
Attempts to allocate space that fail • Enable resumable space allocation.
• Increase owner quota.
• Add space to tablespace.
Logic errors in applications Work with developers to correct program errors.
声明失败
典型问题可能的解决办法
试图将无效数据输入表
与用户一起验证和更正数据。
尝试在权限不足的情况下执行操作
提供适当的对象或系统权限。
尝试分配失败的空间•启用可恢复的空间分配。
•增加业主配额。
•向表空间添加空间。
应用程序中的逻辑错误与开发人员一起纠正程序错误。

User Process Failure
Typical Problems Possible Solutions
A user performs an abnormal disconnect.
A user’s session is abnormally terminated.
A user experiences a program error that terminates the session.
A DBA’s action is not usually needed to resolve user process failures.
Instance background processes roll back uncommitted changes and release locks.
Watch for trends.
用户进程失败
典型问题可能的解决办法
用户执行异常断开连接。
用户的会话异常终止。
用户遇到终止会话的程序错误。
通常不需要DBA的操作来解决用户进程故障。
实例后台进程回滚未提交的更改并释放锁。
注意趋势。
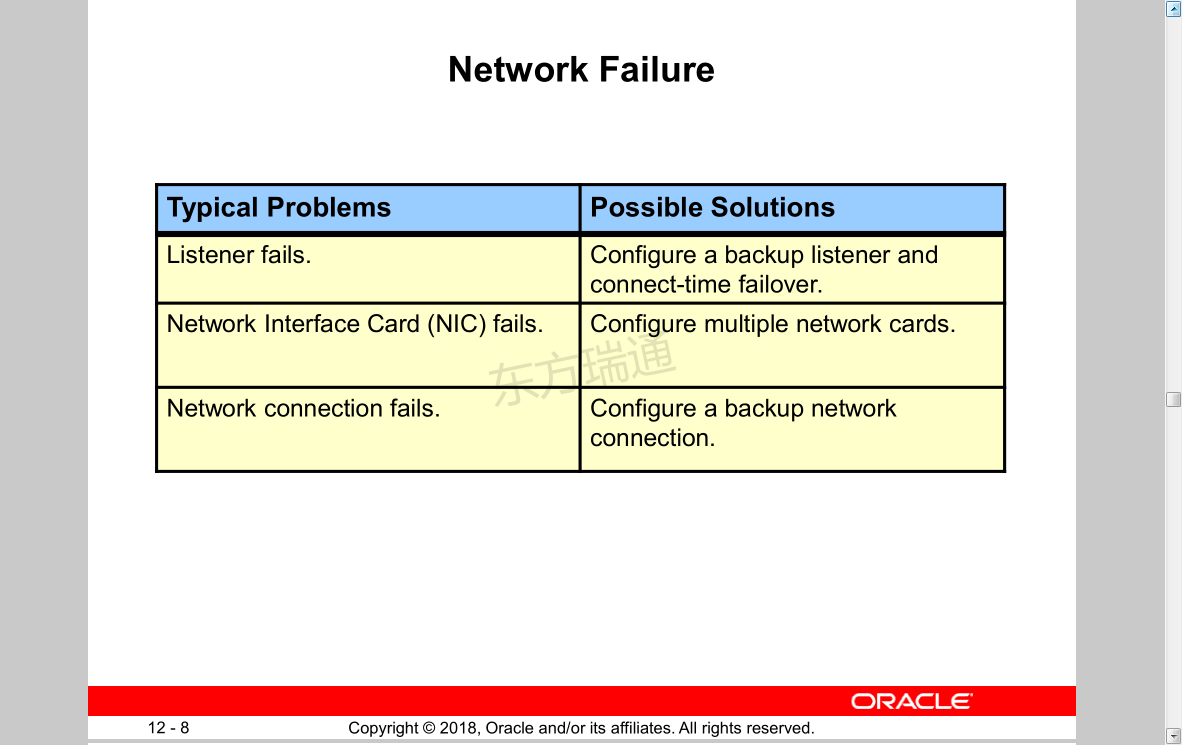
Network Failure
Typical Problems Possible Solutions
Listener fails. Configure a backup listener and connect-time failover.
Network Interface Card (NIC) fails. Configure multiple network cards.
Network connection fails. Configure a backup network connection.
网络故障
典型问题可能的解决办法
侦听器失败。配置备份侦听器和连接时间故障转移。
网络接口卡(NIC)故障。配置多个网卡。
网络连接失败。配置备份网络连接。
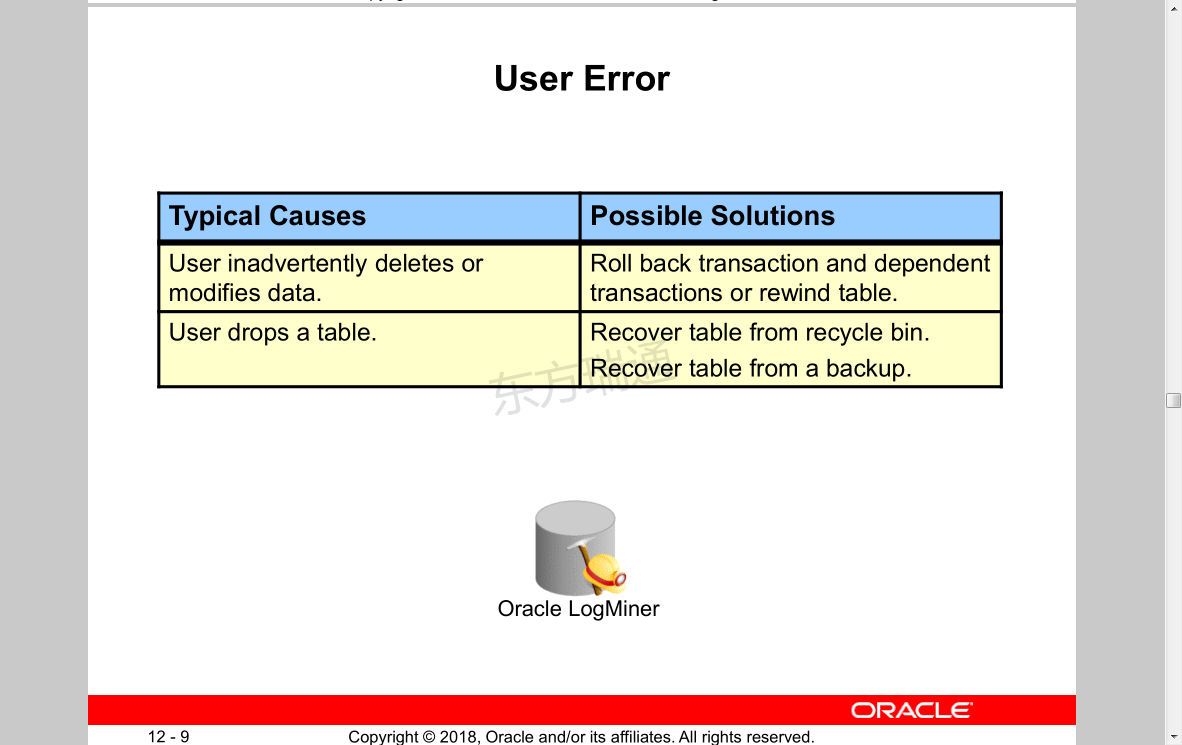
User Error
Typical Causes Possible Solutions
User inadvertently deletes or modifies data.
Roll back transaction and dependent transactions or rewind table.
User drops a table. Recover table from recycle bin.
Recover table from a backup.
Oracle LogMiner
用户错误
典型原因可能的解决办法
用户无意中删除或修改数据。
回滚事务和相关事务或倒带表。
用户删除表。从回收站恢复表。
从备份中恢复表。
Oracle日志挖掘器

Flashback Technology
Use Flashback technology for:
• Viewing past states of data
• Winding data back and forth in time
• Assisting users in error analysis and recovery
For error analysis:
Oracle Flashback Query
Oracle Flashback Versions Query
Oracle Flashback Transaction Query
For error recovery:
Oracle Flashback Transaction Backout
Oracle Flashback Table
Oracle Flashback Drop
Oracle Flashback Database
闪回技术
使用闪回技术:
•查看过去的数据状态
•及时来回缠绕数据
•协助用户进行错误分析和恢复
对于错误分析:
Oracle闪回查询
Oracle Flashback版本查询
Oracle闪回事务查询
对于错误恢复:
Oracle闪回事务回退
Oracle闪回表
Oracle闪回丢弃
闪回数据库
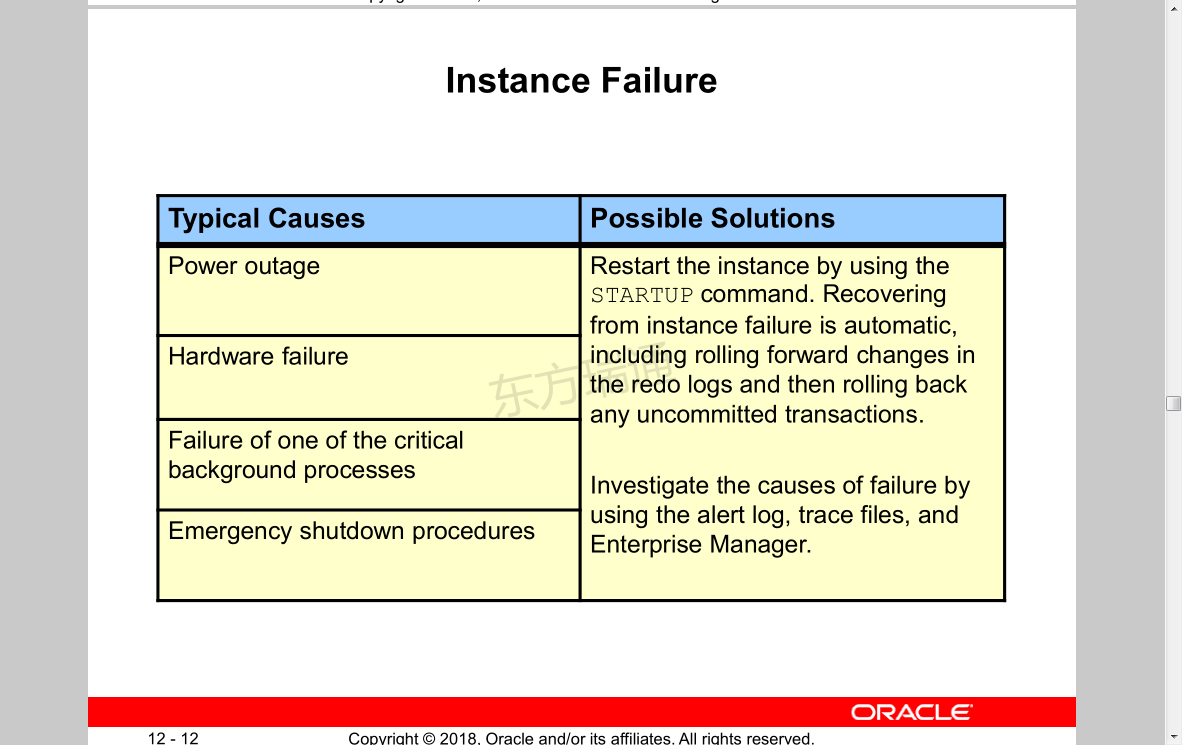
Instance Failure
Typical Causes
Power outage
Hardware failure
Failure of one of the critical background processes
Emergency shutdown procedures
Possible Solutions
Restart the instance by using the STARTUP command.
Recovering from instance failure is automatic, including rolling forward changes in the redo logs and then rolling back any uncommitted transactions.
Investigate the causes of failure by using the alert log, trace files, and Enterprise Manager.
实例失败
典型原因
停电
硬件故障
一个关键后台进程失败
紧急关闭程序
可能的解决方案
使用STARTUP命令重新启动实例。
从实例失败中恢复是自动的,包括在重做日志中前滚更改,然后回滚任何未提交的事务。
使用警报日志、跟踪文件和企业管理器调查失败的原因。
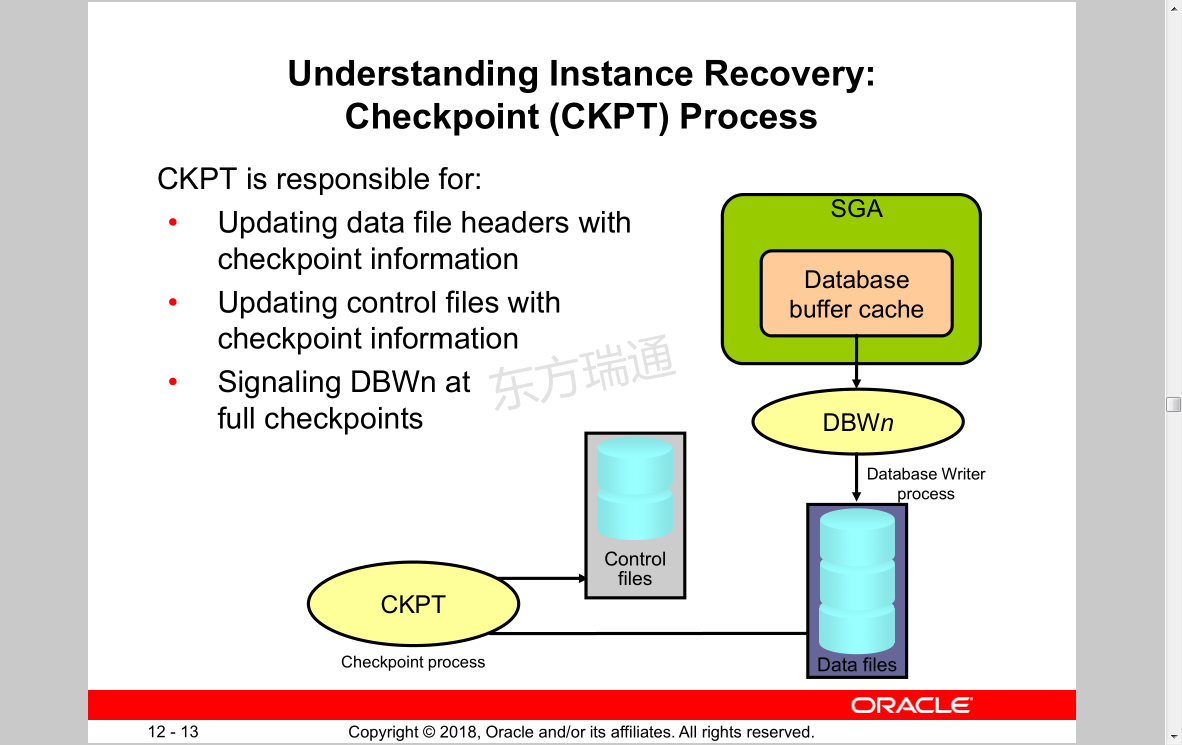
Understanding Instance Recovery:
Checkpoint (CKPT) Process
CKPT is responsible for:
• Updating data file headers with checkpoint information
• Updating control files with checkpoint information
• Signaling DBWn at full checkpoints
SGA
Database
buffer cache
DBWn
Database Writer process
Data files
CKPT 检查点进程,用于维护数据一致性,CKPT被唤醒时会更新 Control files与Data files文件的头部SCN信息
Checkpoint process
Control files
了解实例恢复:
检查点(CKPT)进程
CKPT负责:
•使用检查点信息更新数据文件头
•使用检查点信息更新控制文件
•在完全检查点发送DBWn信号
SGA
数据库
缓冲区缓存
进程
数据库写入程序进程
数据文件
CKPT
检查点进程
控制文件
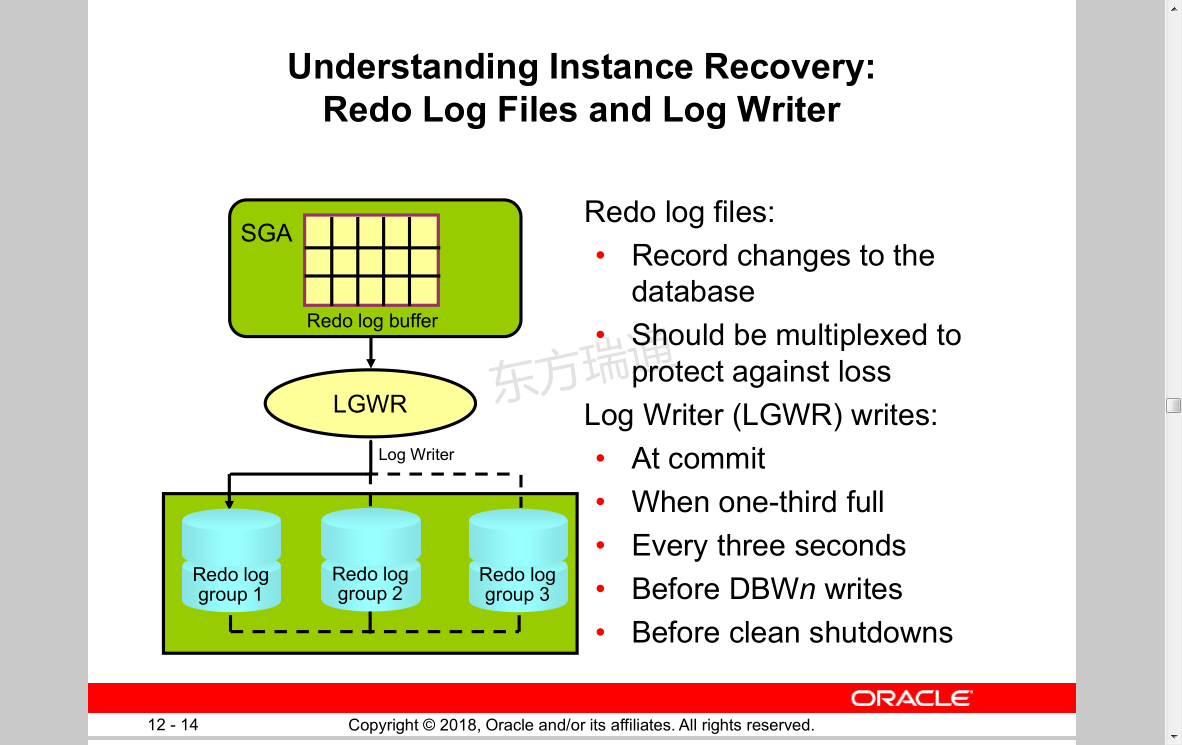
Understanding Instance Recovery:
Redo Log Files and Log Writer Redo log files:
• Record changes to the database
• Should be multiplexed to protect against loss
Log Writer (LGWR) writes:
• At commit
• When one-third full
• Every three seconds
• Before DBWn writes
• Before clean shutdowns
了解实例恢复:
重做日志文件和日志写入程序重做日志文件:
•记录对数据库的更改
•应多路复用以防止丢失
日志写入程序(LGWR)写入:
•承诺时
•满三分之一时
•每三秒
•在DBWn写入之前
•清洁停机前
SGA
Redo log buffer
Log Writer
LGWR 日志写进程
Redo log 可设置不同磁盘,实现多路复制,实现最大可修复性
group 1
Redo log
group 2
Redo log
group 3
SGA
重做日志缓冲区
日志编写器
LGWR
重做日志
第一组
重做日志
第2组
重做日志
第3组
Understanding Instance Recovery
Automatic instance or crash recovery:
• Is caused by attempts to open a database whose files are not synchronized on shutdown
• Uses information stored in redo log groups to synchronize files
• Involves two distinct operations:
– Rolling forward: Redo log changes (both committed and uncommitted) are applied to data files.
– Rolling back: Changes that are made but not committed are returned to their original state.
了解实例恢复
自动实例或崩溃恢复:
•由于试图打开一个数据库而导致,该数据库的文件在关闭时不同步
•使用存储在重做日志组中的信息来同步文件
•涉及两个不同的操作:
–前滚:重做日志更改(已提交和未提交)应用于数据文件。
–回滚:已进行但未提交的更改将返回到其原始状态。
SQL> show user
USER is "HR"
SQL> create table instance_test as select * from employees;
Table created.
SQL> drop table instance_test;
Table dropped.
* drop操作会删除所有的数据以及表结构
* delete操作会删除数据,但会保留表结构,并且在之后需要时可以回滚数据。此外,delete操作还可以加一些其它的where条件,比如删除确定的记录。
SQL> create table instance_test tablespace inventory as select * from employees; 创建一个instance_test表,表中添加数据从employees
Table created.
SQL> insert into instance_test select * from instance_test; 自行复制
107 rows created.
SQL> select count(*) from instance_test; 查看表中有多少行
COUNT(*)
----------
214
SQL> insert into instance_test select * from instance_test; 反复复制自己,就会导致空间占满,从而无法添加
SQL> rollback;
Rollback complete. 未提交之前如果服务器坏了,之前的复制操作会存储在undo表空间中,系统会自动rollback
假设没有手动执行上面的rollback命令
可查看app/diag/rdbms/orcl/orcl/trace下的alert文件 linux命令 tail -f alert_orcl.log 查看表空间错误提示
SQL> shut abort 模拟数据库异常关闭
SQL> start up 此时数据库会执行实例失败修复
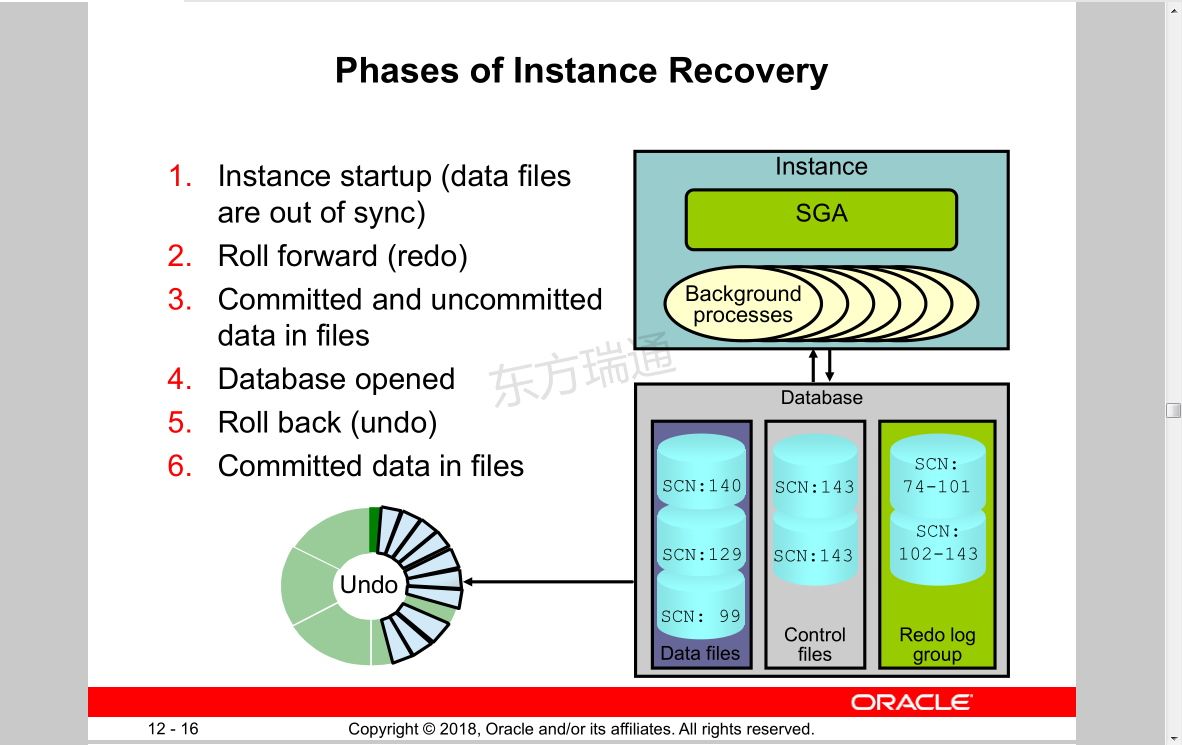
Phases of Instance Recovery
1. Instance startup (data files are out of sync)
2. Roll forward (redo)
3. Committed and uncommitted data in files
4. Database opened
5. Roll back (undo)
6. Committed data in files
实例恢复阶段
1实例启动(数据文件不同步)
2前滚(重做)
3文件中已提交和未提交的数据
4数据库已打开
5回滚(撤消)
6文件中提交的数据
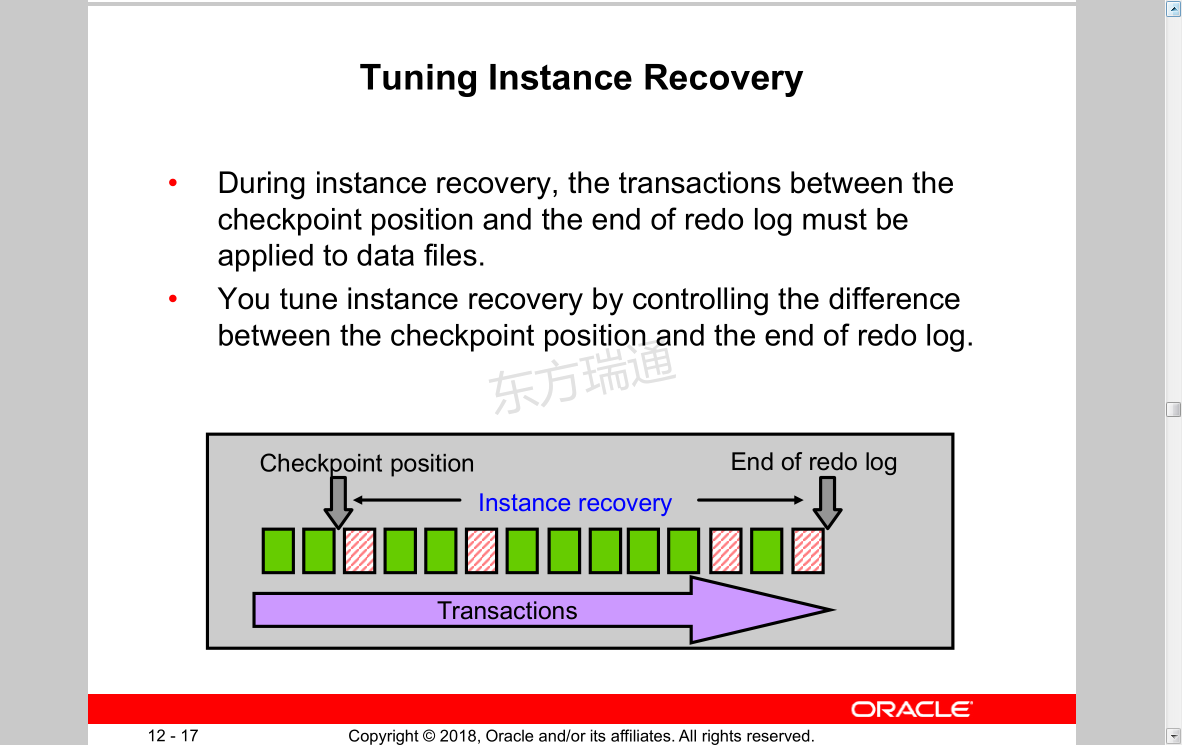
Tuning Instance Recovery
• During instance recovery, the transactions between the checkpoint position and the end of redo log must be applied to data files.
• You tune instance recovery by controlling the difference between the checkpoint position and the end of redo log.
调整实例恢复
•实例恢复时,检查点位置和重做日志结束之间的事务必须应用于数据文件。
•通过控制检查点位置和重做日志结束之间的差异来优化实例恢复

Using the MTTR Advisor
• Specify the desired time in seconds or minutes.
• The default value is 0 (disabled).
• The maximum value is 3,600 seconds (one hour).
使用MTTR顾问
•以秒或分钟为单位指定所需时间。
•默认值为0(禁用)。
•最大值为3600秒(一小时)。
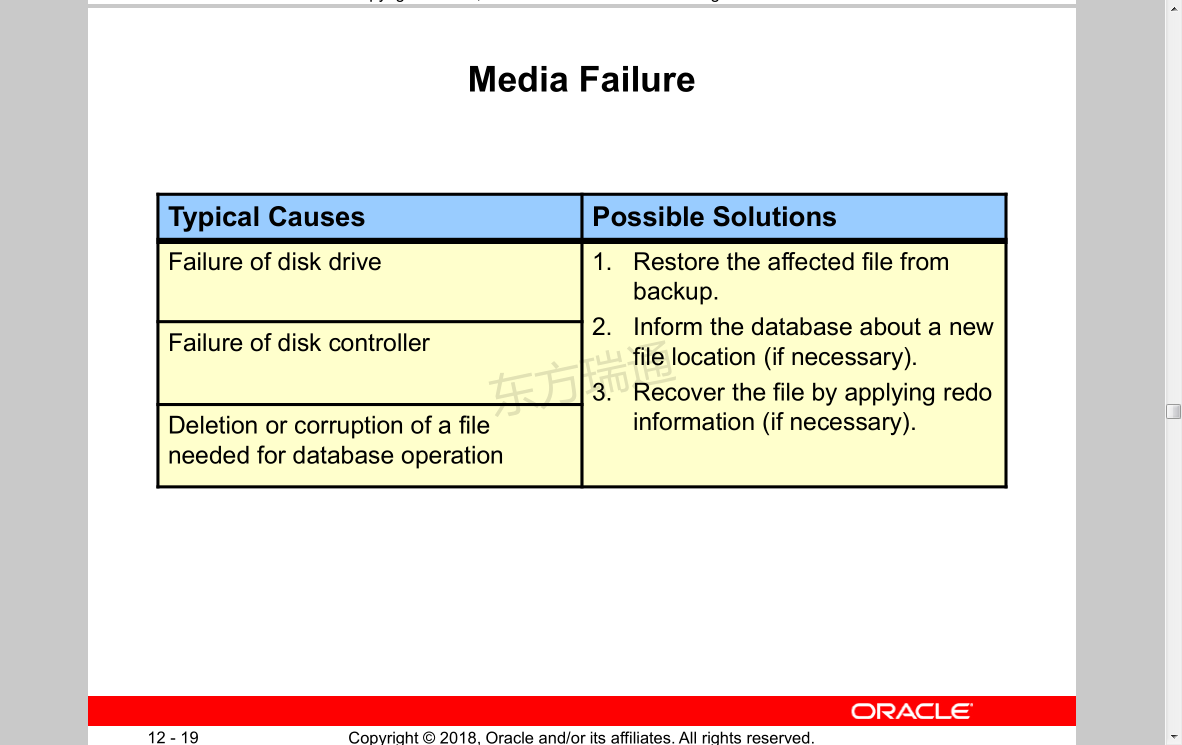
Media Failure
Typical Causes
Failure of disk drive
Failure of disk controller
Deletion or corruption of a file needed for database operation
Possible Solutions
1. Restore the affected file from backup.
2. Inform the database about a new file location (if necessary).
3. Recover the file by applying redo information (if necessary).
媒体故障
典型原因
磁盘驱动器故障
磁盘控制器故障
删除或损坏数据库操作所需的文件
可能的解决方案
1从备份还原受影响的文件。
2通知数据库一个新的文件位置(如果需要)。
3通过应用重做信息(如果需要)恢复文件。
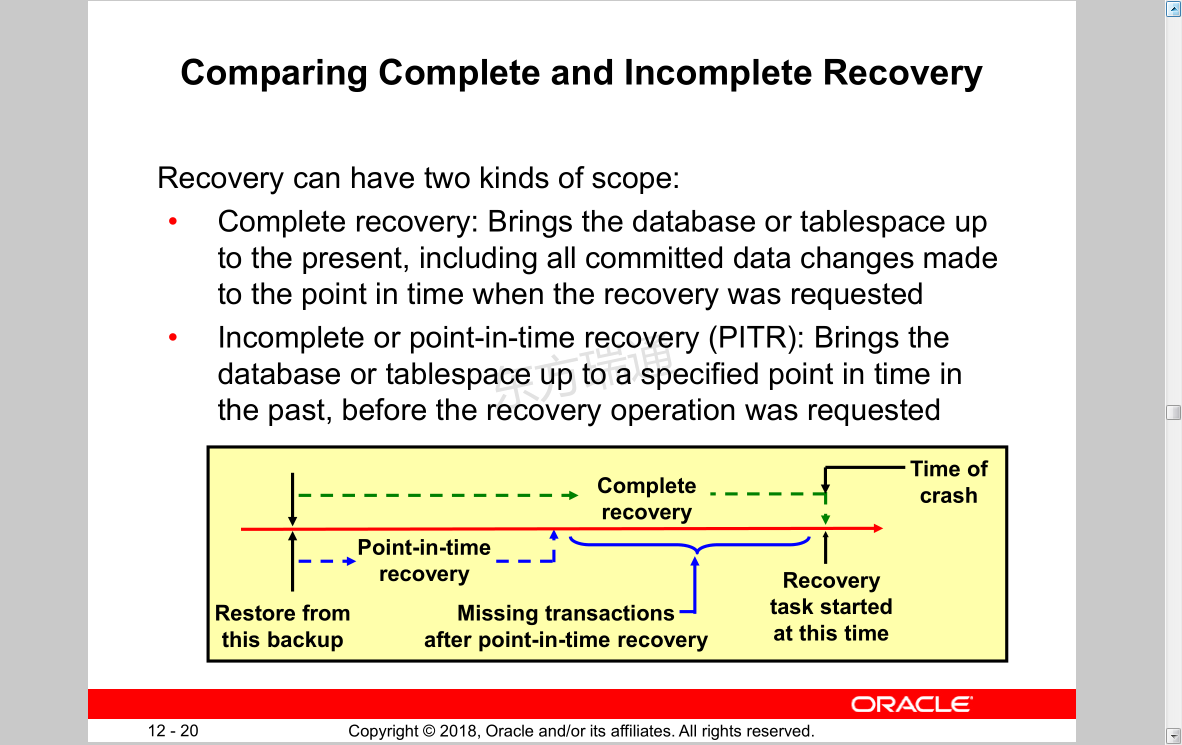
Comparing Complete and Incomplete Recovery
Recovery can have two kinds of scope:
• Complete recovery: Brings the database or tablespace up to the present, including all committed data changes made to the point in time when the recovery was requested
• Incomplete or point-in-time recovery (PITR): Brings the database or tablespace up to a specified point in time in the past, before the recovery operation was requested
比较完全恢复和不完全恢复
恢复可以有两种范围:
•完全恢复:使数据库或表空间保持当前状态,包括在请求恢复时对时间点所做的所有已提交的数据更改
•不完整或时间点恢复(PITR):在请求恢复操作之前,将数据库或表空间提升到指定的时间点
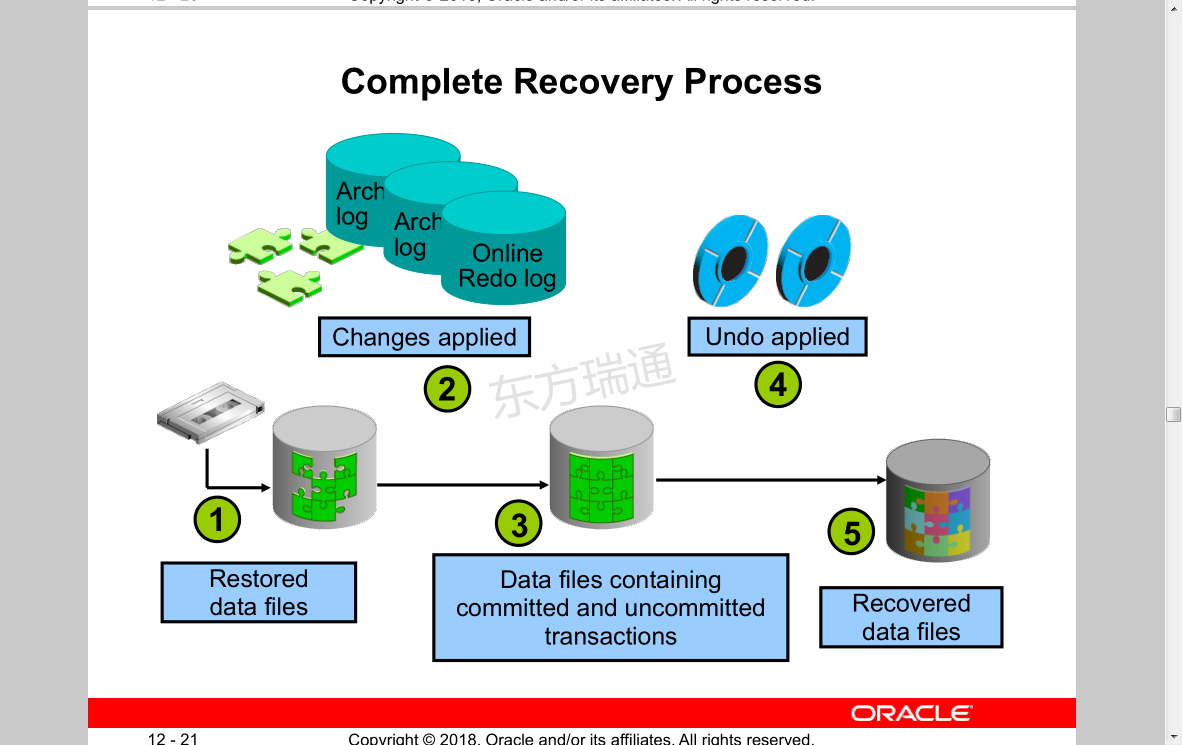
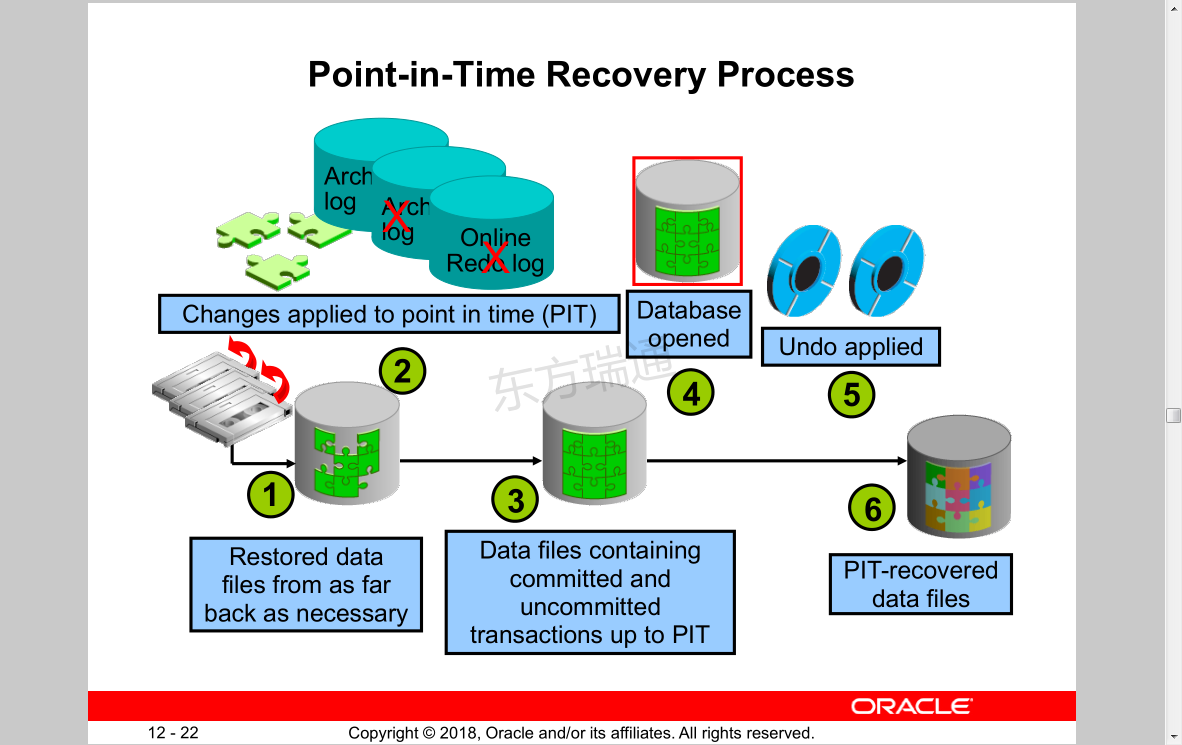

Oracle Data Protection Solutions Oracle数据保护解决方案
Backup and
Recovery Objective
Physical data protection
Logical data protection
Recovery analysis
Recovery Time
Hours/Days
Minutes/Hours
Minimize time for problem identification and recovery planning
Oracle Solution
Recovery Manager ,Oracle Secure Backup 重要数据库恢复工具
Objective (RTO)
Flashback Technologies
Data Recovery Advisor
Disaster Recovery Objective
Physical data protection
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Seconds/Minutes
Oracle Solution
Data Guard,Active Data Guard
备份和
恢复目标
物理数据保护
逻辑数据保护
回收率分析
恢复时间
小时/天
分钟/小时
最小化问题识别和恢复计划的时间
Oracle解决方案
恢复管理器,Oracle安全备份
目标(RTO)
闪回技术
数据恢复顾问
灾难恢复目标
物理数据保护
恢复时间目标(RTO)
秒/分
Oracle解决方案
数据保护,主动数据保护
Statement failure is never by design and always requires the DBA to address the issue.
语句失败从来不是故意的,总是需要DBA来解决这个问题。 错的
Summary
In this lesson, you should have learned how to:
• Identify the types of failure that can occur in an Oracle database
• Describe instance recovery
• Describe complete and incomplete recovery
摘要
在本课中,您应该学习如何:
•确定Oracle数据库中可能发生的故障类型
•描述实例恢复
•描述完全和不完全恢复