简要解释:
序列化就是一种用来处理对象流的机制,所谓对象流也就是将对象的内容进行流化。可以对流化后的对象进行读写操作,也可将流化后的对象传输于网络之间。
序列化是为了解决在对对象流进行读写操作时所引发的问题。序列化的实现:将需要被序列化的类实现Serializable接口,该接口没有需要实现的方法,implements Serializable只是为了标注该对象是可被序列化的,
然后使用一个输出流(如:FileOutputStream)来构造一个ObjectOutputStream(对象流)对象,接着,使用ObjectOutputStream对象的writeObject(Object obj)方法就可以将参数为obj的对象写出(即保存其状态),要恢复的话则用输入流。
详细解释:
当两个进程在进行远程通信时,彼此可以发送各种类型的数据。无论是何种类型的数据,都会以二进制序列的形式在网络上传送。发送方需要把这个Java对象转换为字节序列,才能在网络上传送;接收方则需要把字节序列再恢复为Java对象。
只能将支持 java.io.Serializable 接口的对象写入流中。每个 serializable 对象的类都被编码,编码内容包括类名和类签名、对象的字段值和数组值,以及从初始对象中引用的其他所有对象的闭包。
1.概念
序列化:把Java对象转换为字节序列的过程。
反序列化:把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程。
2.用途
对象的序列化主要有两种用途:
1) 把对象的字节序列永久地保存到硬盘上,通常存放在一个文件中;
2) 在网络上传送对象的字节序列。
3.对象序列化
序列化API
java.io.ObjectOutputStream代表对象输出流,它的writeObject(Object obj)方法可对参数指定的obj对象进行序列化,把得到的字节序列写到一个目标输出流中。只有实现了Serializable和Externalizable接口的类的对象才能被序列化。
java.io.ObjectInputStream代表对象输入流,它的readObject()方法从一个源输入流中读取字节序列,再把它们反序列化为一个对象,并将其返回。
代码示例
1 import java.io.*;
2 import java.util.Date;
3
4 public class ObjectSaver {
5 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
6 /*其中的 D:\objectFile.obj 表示存放序列化对象的文件*/
7
8
9 //序列化对象
10 ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\objectFile.obj"));
11 Customer customer = new Customer("王麻子", 24);
12 out.writeObject("你好!"); //写入字面值常量
13 out.writeObject(new Date()); //写入匿名Date对象
14 out.writeObject(customer); //写入customer对象
15 out.close();
16
17
18 //反序列化对象
19 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\objectFile.obj"));
20 System.out.println("obj1 " + (String) in.readObject()); //读取字面值常量
21 System.out.println("obj2 " + (Date) in.readObject()); //读取匿名Date对象
22 Customer obj3 = (Customer) in.readObject(); //读取customer对象
23 System.out.println("obj3 " + obj3);
24 in.close();
25 }
26 }
27
28 class Customer implements Serializable {
29 private String name;
30 private int age;
31 public Customer(String name, int age) {
32 this.name = name;
33 this.age = age;
34 }
35
36 public String toString() {
37 return "name=" + name + ", age=" + age;
38 }
39 }
执行结果

4.说明
读取对象的顺序与写入时的顺序要一致。
对象的默认序列化机制写入的内容是:对象的类,类签名,以及非瞬态和非静态字段的值。
=========================================================================================================
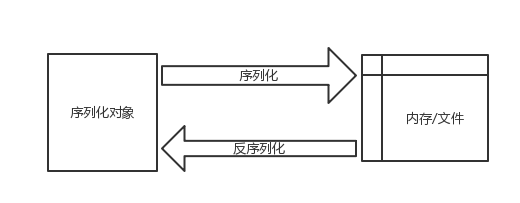
一、Java序列化和反序列化是什么?
通俗的来讲,序列化过程就是将对象转成二进制流存入内存或者文件,反序列化从内存或文件中读取二进制流转换成对象。
二、为什么需要序列化与反序列化?
其实这个问题也就是它们的应用场景有哪些?这样就容易回答多了。比如文件(文本、图片等)进行传输,这些文件都是通过二进制序列的形式进行传输的(序列化过程),而接收方则要读取这些二进制数据进行相对应的转换(反序列化过程)。除了这个它主要用于网络传输(进程之间的通信等)。
三、怎么实现Java序列化和反序列化?
要想实现序列化有个必要条件就是要实现Serializable接口或Externalizable接口。大部分可能只知道有Serializable接口没有关注Externalizable接口,那么你看了本文之后就应该知道了,后面再介绍它们的区别。
有了上面个必要条件后还需要借助jdk中有两个类:java.io.ObjectOutputStream和java.io.ObjectInputStream,它们分别负责序列化和反序列化。我们可以看下这两个类的说明就知道是这两个类负责相对应的功能。
/**
* An ObjectOutputStream writes primitive data types and graphs of Java objects
* to an OutputStream. The objects can be read (reconstituted) using an
* ObjectInputStream. Persistent storage of objects can be accomplished by
* using a file for the stream. If the stream is a network socket stream, the
* objects can be reconstituted on another host or in another process.
*
* <p>Only objects that support the java.io.Serializable interface can be
* written to streams. The class of each serializable object is encoded
* including the class name and signature of the class, the values of the
* object's fields and arrays, and the closure of any other objects referenced
* from the initial objects.
* ...
*/
public class ObjectOutputStream
extends OutputStream implements ObjectOutput, ObjectStreamConstants{}
/**
* An ObjectInputStream deserializes primitive data and objects previously
* written using an ObjectOutputStream.
*
* <p>ObjectOutputStream and ObjectInputStream can provide an application with
* persistent storage for graphs of objects when used with a FileOutputStream
* and FileInputStream respectively. ObjectInputStream is used to recover
* those objects previously serialized. Other uses include passing objects
* between hosts using a socket stream or for marshaling and unmarshaling
* arguments and parameters in a remote communication system.
* ...
*/
public class ObjectInputStream
extends InputStream implements ObjectInput, ObjectStreamConstants{
}
下面我们以学生对象为例,将对象序列化保存至文件中,再从文件中反序列化转换成对象。
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Description: 学生类 已实现序列化接口
* @author yuanfy
* @date 2018年1月11日 上午11:36:37
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Student implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6415983562512521049L;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + "]";
}
}
上面已经定义Java对象, 下面进行序列化测试。
@Test
public void testSerializable() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{
Student s = new Student("james", 31, "man");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\Student.txt")));
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
如果电脑E盘存在的话运行肯定通过(windows系统),单元测试通过后(说明序列化过程已完成)查看Student.txt文件中的内容,如下:
上面是正常的情况, 如果Student类没有实现Serializable接口呢?那么序列化时会存在什么样的问题。我们把Student类去掉Serializable接口的实现,然后再进行序列化测试。这时你会发现单元测试后不通过,先看看报错原因:下面截图中的错误信息提示Student类没有被序列化。

那么为什么java.io.ObjectOutputStream类会抛出这样的异常呢,它是怎么识别有没有实现Serializable接口的。接下来,我们来看看他的源码:writeObject方法中调用了writeObject()方法,所以主要逻辑在它里面。
/**
* Underlying writeObject/writeUnshared implementation.
*/
private void writeObject0(Object obj, boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
boolean oldMode = bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
depth++;
try {
//前面部分代码省略
// remaining cases
if (obj instanceof String) {
writeString((String) obj, unshared);
} else if (cl.isArray()) {
writeArray(obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Enum) {
writeEnum((Enum<?>) obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Serializable) {//判断是否是Serializable的子类。
writeOrdinaryObject(obj, desc, unshared);
} else {
//除了String类型、数组类型和枚举类型,其他对象如果没有实现Serializable接口,都会抛出NotSerializableException异常
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
throw new NotSerializableException(
cl.getName() + "
" + debugInfoStack.toString());
} else {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName());
}
}
} finally {
depth--;
bout.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
从中可以看出,除了String类型、数组类型和枚举类型,其他对象如果没有实现Serializable接口,都会抛出NotSerializableException异常。
接下来进行反序列化测试:
@Test
public void testDeserialize() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("E:\Student.txt")));
Student s = (Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s);
ois.close();
}
在进行正常的序列化测试后接着测试反序列化测试,正常来说是不会报错的。看看测试结果就明了了。

同样上面是正常的情况。接下来异常的情况就能体现出Student类中serialVersionUID变量的作用了:它就是验证序列化与反序列化的唯一性。在序列化后修改Student类中的serialVersionUID= 61234L,然后再测试反序列化,测试结果如下:
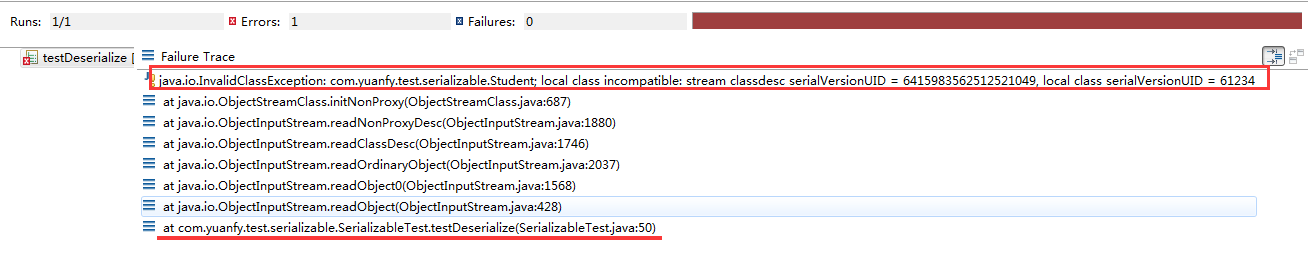
从错误提示中可以看出,会从解析出来的serialVersionUID和要转换的class中serialVersionUID做对比,判断是否相等。java.io.ObjectStreamClass关键源码如下:
/**
* Initializes class descriptor representing a non-proxy class.
*/
void initNonProxy(ObjectStreamClass model,
Class<?> cl,
ClassNotFoundException resolveEx,
ObjectStreamClass superDesc)
throws InvalidClassException
{
long suid = Long.valueOf(model.getSerialVersionUID());
ObjectStreamClass osc = null;
if (cl != null) {
osc = lookup(cl, true);
if (osc.isProxy) {
throw new InvalidClassException(
"cannot bind non-proxy descriptor to a proxy class");
}
if (model.isEnum != osc.isEnum) {
throw new InvalidClassException(model.isEnum ?
"cannot bind enum descriptor to a non-enum class" :
"cannot bind non-enum descriptor to an enum class");
}
//这里会判断serialVersionUID是否一致
if (model.serializable == osc.serializable &&
!cl.isArray() &&
suid != osc.getSerialVersionUID()) {
throw new InvalidClassException(osc.name,
"local class incompatible: " +
"stream classdesc serialVersionUID = " + suid +
", local class serialVersionUID = " +
osc.getSerialVersionUID());
}
//后面代码略
}
}
四、几个序列化注意事项
1、对继承父类的子类序列化
public class Person {
public int age;
public int weight;
public Person(int age, int weight) {
this.age = age;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
}
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Women extends Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1259423203325949704L;
private String name;
public Women(String name, int age, int weight) {
super(age, weight);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
单元测试代码如下,先猜错下会不会运行通过,结果又是啥?
@Test
public void test2() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
Women w = new Women("Scarlett Johansson", 34, 50);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\Women.txt")));
oos.writeObject(w);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("E:\Women.txt")));
Women s = (Women)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s);
ois.close();
}
测试结果如下,居然报错。该错误提示需要提供无参构造函数(During deserialization, the fields of non-serializable classes will be initialized using the public or protected no-arg constructor of the class. A no-arg constructor must be accessible to the subclass that is serializable. The fields of serializable subclasses will be restored from the stream.),具体详情解释见这here.
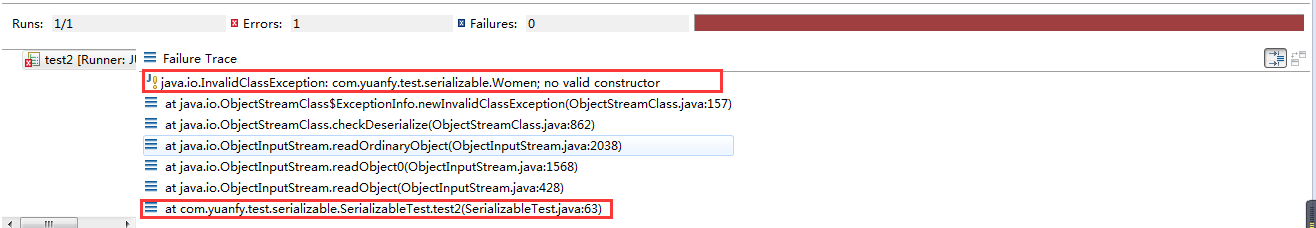
当我们提供无参构造函数后再进行单元测试得到结果:Student [name=Scarlett Johansson, age=0, weight=0]。所以可以得出结论:父类中的字段不参与序列化,只是将其初始化而已。
2、transient 关键字
使用transient关键字来修饰变量,然后进行序列化(在实现serializable接口情况下)效果其实和父类的序列化一样,它所修饰的变量不参与序列化。这里就不举例说明了,自己可以写个案例测试下。
另外transient关键字只能修饰变量, 不能修饰类和方法。
3、static关键字
使用static关键字来修饰变量,不管有没有transient修饰,同样不参与序列化(在实现serializable接口情况下)。
4、Externalizable接口
Externalizable接口extends Serializable接口,而且在其基础上增加了两个方法:writeExternal()和readExternal()。这两个方法会在序列化和反序列化还原的过程中被自动调用,以便执行一些特殊的操作。
下面看案例:
import java.io.Externalizable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInput;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
/**
* @Description: 学生类 已实现序列化接口
* @author yuanfy
* @date 2018年1月11日 上午11:36:37
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Student implements Externalizable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 61234L;
private String name;
private transient int age;
private static String sex;
//如果覆盖了无参构造函数就一定要显示声明无参构造函数,跟父类序列化的案例一样。
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + "]";
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeInt(age);
out.writeObject(sex);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.name = in.readUTF();
this.age = in.readInt();
this.sex = (String)in.readObject();
}
}
@Test
public void test3() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
Student s1 = new Student("james", 31, "man");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\Student.txt")));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("E:\Student.txt")));
Student s2 = (Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s2);
ois.close();
}
上面是正常完整案例,其中要注意的是,要序列化的类要提供无参构造函数,否则反序列化会报错(When an Externalizable object is reconstructed, an instance is created using the public no-arg constructor, then the readExternal method called. Serializable objects are restored by reading them from an ObjectInputStream.)详解here。得出结论如下:
与Serizable对象不同,使用Externalizabled,就意味着没有任何东西可以自动序列化, 为了正常的运行,我们需要在writeExtenal()方法中将自对象的重要信息写入,从而手动的完成序列化。对于一个Externalizabled对象,对象的默认构造函数都会被调用(包括哪些在定义时已经初始化的字段),然后调用readExternal(),在此方法中必须手动的恢复数据。这就说明在Externalizable接口下不管是transient或static修饰的变量,如果没有指定写入,就不会序列化。
