Java提供了三种字符串对象,分别为String,StringBulider,StringBuffer
String在操作时不修改原对象,而是会生成一个新的String对象来作为返回结果。 //适用于较少修改字符串的情况。
StringBulider是为了解决对String频繁修改的效率底下问题产生的,对StringBulider的操作会修改原对象。 // 适用于单线程频繁修改字符串的情况。
StringBuffer效果与StringBuilder类似,但它加入了线程安全。 //适用于多线程频繁修改字符串的情况。
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ String s1 = "hello",s3; StringBuilder s2 = new StringBuilder("hello"); StringBuilder s4; s3 = s1.toUpperCase(); s4 = s2.append("world"); System.out.printf("String:" + s1 + " " + "StringBuilder:" + s2); //String:hello s1无变化 //StringBuilder:helloworld s2发生变化 } }
对于效率问题需要注意,即便有时候编译器会进行优化(隐式地创建StringBulider来防止频繁创建String对象),在部分情况下它仍比不上完全使用StringBuilder。显式地创建StringBuilder并给定最大长度能极大地提升对字符串频繁操作的效率。
toString()
集合类都继承自Object,故都有toString()方法并覆盖了它,以便容器能表达自身。希望toString()方法打印对象内存地址
import java.util.*; public class Test{ public String toString(){ return "TestAddress:" + super.toString() + " "; //return "TestAddress:" + this + " "; } public static void main(String[] args){ List<Test> t = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0;i < 5;i++){ t.add(new Test()); } System.out.println(t); } }
编译器看见TestAddress后,发现一个+号,会试着将后面对象转换为String类型,即调用对象的toString方法。如果写成注释样子,则会发生toString方法的递归调用,从而导致栈溢出。
String基本方法
格式化
Java提供了printf(),该方法类似于c语言的输出格式,可以进行格式化输出;又提供了同样效果的format(),但它可用于PrintWriter和PrintStream。
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x = 10; double y = 10.333; System.out.println("[" + x + " "+ y + "]"); System.out.printf("[%d %.3f] ", x, y); System.out.format("[%d %.3f]", x, y); //结果 //[10 10.333] //[10 10.333] //[10 10.333] } }
Java中,所有新格式化功能都由java.util.Formatter处理,可以将它看作一个翻译器,将格式化字符串与数据翻译成想要的结果,创建Formatter对象时,还需要向其构造器传入参数,以便告诉它需要向哪里输出结果。
import java.util.Formatter; public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x = 10; double y = 10.333; Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out); f.format("[%d %.3f] ", x, y); Formatter g = new Formatter(System.err); g.format("[%d %.3f] ", x, y); //输出到标准流 //输出到错误流 } }
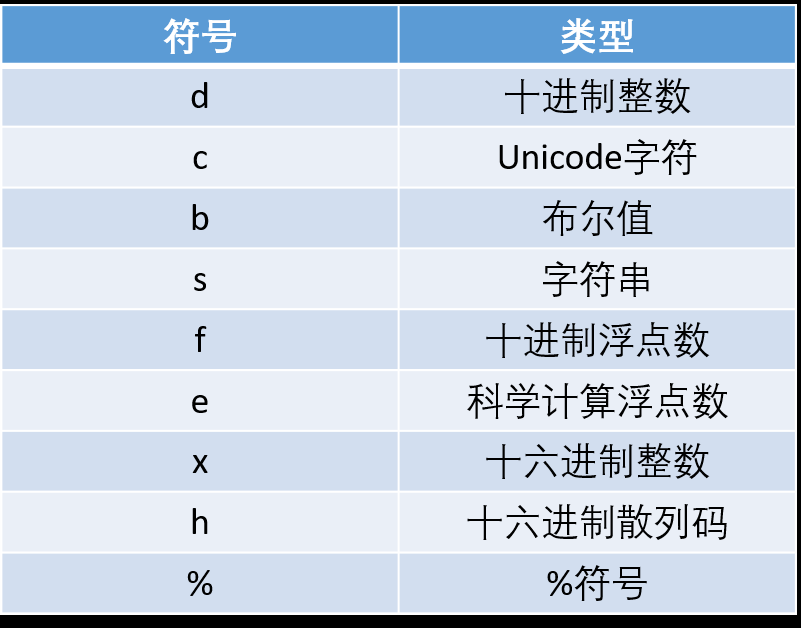
更精细的格式话说明符需要可以达到更加美观的输出效果,抽象语法为:
%[argument_index$][flags][width][.precision]conversion
argument_index就是格式化字符串;flags表示左对齐或右对齐,有-符号即左对齐,默认为右对齐;width为一个域的最小宽度;.precision用于字符串表示字符串输出的最大长度,用于小数则表示要保留的小数位数。
import java.util.Formatter; public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out); f.format("%-8s %-8s %-8s %-10s ","name","id","salary","address"); f.format("%-8s %-8.8s %-8.3f %-10.12s ","sakura","2015100320",8000.64651,"wuhan of Chinese"); //f.format("%-8s %-8.8d %-8.3f %-10.12s ","sakura",2015100320,8000.64651,"wuhan of Chinese");
//结果如下 //name id salary address //sakura 20151003 8000.647 wuhan of Chi //注:第三条语句将.precision用于整数,抛出异常 } }
Formatter常用类型转换