零.引言
PropertyGrid用来显示某一对象的属性,但是并不是所有的属性都能编辑,基本数据类型(int, double等)和.Net一些封装的类型(Size,Color等)可以编辑,但是对于自己定义的类型属性,是不能编辑的,本文主要讲述如何为自定义类型作为属性时,在PropertyGrid中进行编辑,以及进行设计时序列化,本文主要参考MSDN,错误和不足之处还望指正。
一.自定义类属性
在PropertyGrid中能够编辑的都是.Net中自己封装的类,如果在一个类中有一个属性是我们自己定义的类型,在PropertyGrid中会是怎样的呢?看下面这个例子:
假如现在有一个类Line:
public class Line { Point P1; Point P2; public Point Point1 { get{return P1;} set{P1 = value;} } public Point Point2 { get{return P2;} set{P2 = value;} } public Line(Point point1, Point point2) { P1 = point1; P2 = point2; } }
有一个控件类包含一个Line类型的属性:
public class MyControl : System.Windows.Forms.UserControl { Line _line; public MyControl() { _line = new Line(new Point(0, 0),new Point(100, 100)); } public Line MyLine { get{return _line;} set{_line = value;} } protected override void OnPaint(System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs e) { e.Graphics.DrawLine(Pens.Red, this._line.Point1, this._line.Point2); base.OnPaint(e); } }
重新生成,从工具箱中将该控件拖入Form中,查看他的属性,在PropertyGrid中显示如下:
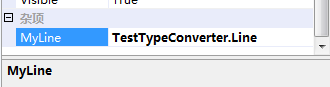
可见MyLine属性的值不显示,且是不能编辑的。这是因为PropertyGrid根本不知道Line是个什么类型,不知道要怎么显示,如果要其能在PropertyGrid中显示,必须给他提供转换器。
二.转换器概念
PropertyGrid中属性的值都是以字符串的形式呈现给我们看的,显示一个对象的属性时,要将对象的属性值转换为字符串显示出来,而设置属性时,要将字符串转换为对象的属性值。这就需要一个转换器。在.Net中定义了一个TypeConverter 类,用来作为这些转换器的基类。.Net为一些类设计了专门的转换类,如:System.Drawing.ColorConverter ,System.Drawing.FontConverter等等,(具体参见MSDN中TypeConverter的继承关系)因此在PropertyGrid中能直接编辑这些属性。我们自己定义的类没有这样的类型转换器,因此在PropertyGrid中无法编辑,需要设计自己的转换器。
先来看一下MSDN中对TypeConverter的描述:TypeConverter类提供一种将值的类型转换为其他类型以及访问标准值和子属性的统一方法。
继承者说明:
从 TypeConverter 继承,以实现您自己的转换要求。当从类继承时,可以重写以下方法:
- 若要支持自定义类型转换,请重写 CanConvertFrom、CanConvertTo、ConvertFrom 和 ConvertTo 方法。
- 若要转换必须重新创建对象才能更改其值的类型,请重写 CreateInstance 和 GetCreateInstanceSupported 方法。
- 若要转换支持属性 (Property) 的类型,请重写 GetProperties 和 GetPropertiesSupported 方法。如果转换的类没有属性 (Property),而您需要实现属性 (Property),则可以将 TypeConverter.SimplePropertyDescriptor 类用作实现属性 (Property) 说明符的基。当从 TypeConverter.SimplePropertyDescriptor 继承时,必须重写 GetValue 和 SetValue 方法。
- 若要转换支持标准值的类型,请重写 GetStandardValues、GetStandardValuesExclusive、GetStandardValuesSupported 和 IsValid 方法。
三.添加转换器
好了,了解了基本原理后,我们来为Line添加转换器。这里新建一个LineConverter类,并继承于TypeConverter。

public class LineConverter : TypeConverter { //该方法判断此类型可以转换为哪些类型 public override bool CanConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type destinationType) { if (destinationType == typeof(string)) { return true; } if (destinationType == typeof(InstanceDescriptor)) { return true; } //调用基类方法处理其他情况 return base.CanConvertTo(context, destinationType); } //该方法判断哪些类型可以转换为此类型 public override bool CanConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type sourceType) { if (sourceType == typeof(string)) { return true; } return base.CanConvertFrom(context, sourceType); } // 将该类型转换为字符串和InstanceDescriptor public override object ConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value, Type destinationType) { if (destinationType == typeof(string) && value != null) { Line t = (Line)value; string str = t.Point1.X + "," + t.Point1.Y + "," + t.Point2.X + "," + t.Point2.Y; return str; } if (destinationType == typeof(InstanceDescriptor) && value != null) { ConstructorInfo ci = typeof(TestTypeConverter.Line).GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(Point), typeof(Point) }); Line t = (Line)value; return new InstanceDescriptor(ci, new object[] { t.Point1, t.Point2 }); } return base.ConvertTo(context, culture, value, destinationType); } //字符串和InstanceDescriptor转换为该类 public override object ConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value) { if (value is string) { string str = (string)value; str = str.Trim(); string[] v = str.Split(','); if (v.Length != 4) { throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); } int x1 = 0; int y1 = 0; int x2 = 0; int y2 = 0; bool res = int.TryParse(v[0], out x1); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[1], out y1); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[2], out x2); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[3], out y2); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); Line line = new Line(new Point(x1, y1), new Point(x2, y2)); return line; } return base.ConvertFrom(context, culture, value); } }
在转换器类中,我们重写了四个函数,也就是在继承者说明中第一条的四个函数:
① CanConvertTo:用来说明此类可以转换为哪些类型,能转换就返回true,这里我们让他能转换为string和InstanceDescriptor,InstanceDescriptor是存储描述对象实例的信息,这些信息可用于创建对象的实例。一般转换都要实现这个转换,后面进行说明。
② CanConvertFrom:说明该类能有什么类型转换过来,能转换返回true,这里只对string类型进行转换。
③ ConvertTo:具体的转换实现,也就是提供方法将该类转换为在CanConvertTo中确定可以转换的类型。这里实现string和InstanceDescriptor的转换。
④ ConvertFrom:具体的转换实现,也就是提供方法将该类转换为在CanConvertFrom中确定可以转换的类型。这里实现string的转换。
注意,每个方法处理完自己的转换后,依然要调用基类的函数来处理其他的情况。
重写这四个方法后,给Line类型加上TypeConverter特性,在Line类定义的上面加上[TypeConverter(typeof(LineConverter))]。这样在需要转换的地方,就会调用我们所写的方法进行转换,Line属性在PropertyGrid中显示时,会调用ConvertTo,转换为字符串输出;设置属性时,会调用ConvertFrom将字符串转换为属性值,当然,字符串必须要有一定的格式,这就需要在转换的过程中进行判断,见ConvertFrom方法。
重新生成,现在看MyControl中MyLine属性在PropertyGrid中的显示:

可以看到MyLine属性显示出来了(以x1,y1,x2,y2的格式,我们在ConverTo方法中指定的),并可以编辑了,但必须是x1,y1,x2,y2的格式,否则会出现如下错误提示:
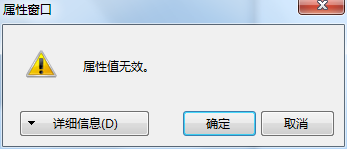
这是我们在ConvertFrom方法中进行判断的。
四.编辑复杂属性的子属性
现在可以编辑属性了,但是必须使用x1,y1,x2,y2固定的格式,不方便,而且容易出错,可不可以分别设置Line的两个点呢,可以,这里就需要编辑子属性了。Line中有Point1和Point2两个属性,我们让他们也显示出来。
这里就是继承者说明中的第三条了。重写 GetProperties 和 GetPropertiesSupported 方法。在LineConverter中重写这两个方法:
public override bool GetPropertiesSupported(ITypeDescriptorContext context) { return true; //return base.GetPropertiesSupported(context); } public override PropertyDescriptorCollection GetProperties(ITypeDescriptorContext context, object value, Attribute[] attributes) { return TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(value, attributes); //return base.GetProperties(context, value, attributes); }
重新生成,现在看MyControl中MyLine属性在PropertyGrid中的显示:
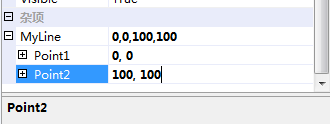
可以看到现在我们可以编辑MyLine的子属性了。
五.属性的设计时串行化
最后说一说ConvertTo方法中为什么要实现InstanceDescriptor的转换。Visual Studio在我们编辑控件时,会在Form1.Designer.cs文件中自动的生成代码,设置控件的属性,这叫属性对设计时序列化,如下:

我们定义的MyLine属性,在这里并没有,如何使它出现在这里呢,只需给MyLine属性加上DesignerSerializationVisibility特性。如下
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public Line MyLine { get { return _line; } set { _line = value; } }
这里DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible表明代码生成器生成对象的代码。DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content说明该属性在编辑时要代码生成器产生对象内容的代码,而不是对象本身的代码。DesignerSerializationVisibility.Hide代码生成器不生成对象的代码。
重新生成,并改变控件的位置,打开Form1.Designer.cs,会发现自动生成了MyLine属性的设置值。

这是如何生成的呢,关键就在ConvertTo方法中实现InstanceDescriptor的转换,该方法告诉代码生成器,如何去构造一个Line类型,生成时,调用Line的构造函数构造新对象初始化MyLine属性值。
六.总体的代码
下面是完整的代码:

using System; using System.ComponentModel; using System.ComponentModel.Design.Serialization; using System.Drawing; using System.Globalization; using System.Reflection; namespace TestTypeConverter { //线条类 [TypeConverter(typeof(LineConverter))] public class Line { // Line members. Point P1; Point P2; public Point Point1 { get { return P1; } set { P1 = value; } } public Point Point2 { get { return P2; } set { P2 = value; } } public Line(Point point1, Point point2) { P1 = point1; P2 = point2; } } //转换器类 public class LineConverter : TypeConverter { public override bool CanConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type destinationType) { if (destinationType == typeof(string)) { return true; } if (destinationType == typeof(InstanceDescriptor)) { return true; } return base.CanConvertTo(context, destinationType); } public override bool CanConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type sourceType) { if (sourceType == typeof(string)) { return true; } return base.CanConvertFrom(context, sourceType); } public override object ConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value, Type destinationType) { if (destinationType == typeof(string) && value != null) { Line t = (Line)value; string str = t.Point1.X + "," + t.Point1.Y + "," + t.Point2.X + "," + t.Point2.Y; return str; } if (destinationType == typeof(InstanceDescriptor)) { ConstructorInfo ci = typeof(TestTypeConverter.Line).GetConstructor(new Type[] { typeof(Point), typeof(Point) }); Line t = (Line)value; return new InstanceDescriptor(ci, new object[] { t.Point1, t.Point2 }); } return base.ConvertTo(context, culture, value, destinationType); } public override object ConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value) { if (value is string) { string str = (string)value; str = str.Trim(); string[] v = str.Split(','); if (v.Length != 4) { throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); } int x1 = 0; int y1 = 0; int x2 = 0; int y2 = 0; bool res = int.TryParse(v[0], out x1); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[1], out y1); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[2], out x2); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); res = int.TryParse(v[3], out y2); if (res == false) throw new NotSupportedException("Invalid parameter format"); Line line = new Line(new Point(x1, y1), new Point(x2, y2)); return line; } return base.ConvertFrom(context, culture, value); } public override bool GetPropertiesSupported(ITypeDescriptorContext context) { return true; //return base.GetPropertiesSupported(context); } public override PropertyDescriptorCollection GetProperties(ITypeDescriptorContext context, object value, Attribute[] attributes) { return TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(value, attributes); //return base.GetProperties(context, value, attributes); } } //控件类 public class MyControl : System.Windows.Forms.UserControl { Line _line; public MyControl() { _line = new TestTypeConverter.Line( new Point(0, 0), new Point(100, 100) ); } [DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] public Line MyLine { get { return _line; } set { _line = value; } } protected override void OnPaint(System.Windows.Forms.PaintEventArgs e) { e.Graphics.DrawLine(Pens.Red, this._line.Point1, this._line.Point2); base.OnPaint(e); } } }
新建一个Windows工程,添加该文件,在工具箱中找到我们的MyControl控件,拖入Form中,在属性框中查看控件的属性。
(原文)
