这里列表了我想到的在应用程序中加入AOP支持的所有方法。这里最主要的焦点是拦截,因为一旦有了拦截其它的事情都是细节。
|
Approach 方法 |
Advantages 优点 |
Disadvantages 缺点 |
|
Remoting Proxies 远程代理 |
Easy to implement, because of the .Net framework support 容易实现,因为有.NET框架的支持。 |
Somewhat heavyweight 微显重量级 仅在接口或MarshalByRefObjects 上使用 |
|
Derivingfrom ContextBoundObject 从ContextBoundObject 派生 |
Easiest to implement 很容易实现 原生支持调用拦截 |
Very costly in terms of performance 非常昂贵的性能代价 |
|
Compile-time subclassing 编译时子类化 |
Easiest to understand 很容易理解 |
Interfaces or virtual methods only 仅用于接口或虚方法 |
|
Runtime subclassing 运行时子类化 |
Easiest to understand 很容易理解 非常灵活 |
Complex implementation (but alreadyexists) 复杂的实现(已经实现) 仅用于接口或虚方法 |
|
Hooking into the profiler API 分析 API钩子 |
Extremely powerful 极端强大 |
Performance? 性能未知 复杂实现(COM API,需要单独运行等) |
|
Compile time IL-weaving 编译时 IL织入 |
Very powerful 非常强大 良好的性能 |
Very hard to implement 实现非常困难 |
|
Runtime IL-weaving 运行时 IL织入 |
Very powerful 非常强大 朗好的性能 |
Very hard to implement 实现非常困难 |
英文原文 7 Approaches for AOP in .Net
1.远程代理
使用.Net Remoting/RealProxy
采用TransparentProxy和RealProxy实现对象的代理,实现思路如下:Client -TransparentProxy - RealProxy - Target Object
下面实现自定义的TransparentProxy和RealProxy

using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class User { public string Name; public string PassWord; } //用户注册接口和实现 public interface IUserProcessor { void RegUser(User user); } public class UserProcessor : MarshalByRefObject, IUserProcessor { public void RegUser(User user) { Console.WriteLine("用户已注册。"); } } //客户端调用 class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { try { User user = new User() { Name = "lee", PassWord = "123456" }; UserProcessor userprocessor = TransparentProxy.Create<UserProcessor>(); userprocessor.RegUser(user); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } Console.ReadKey(); } } //RealProxy public class MyRealProxy<T> : RealProxy { private T _target; public MyRealProxy(T target) : base(typeof(T)) { this._target = target; } public override IMessage Invoke(IMessage msg) { PreProceede(msg); IMethodCallMessage callMessage = (IMethodCallMessage)msg; object returnValue = callMessage.MethodBase.Invoke(this._target, callMessage.Args); PostProceede(msg); return new ReturnMessage(returnValue, new object[0], 0, null, callMessage); } public void PreProceede(IMessage msg) { Console.WriteLine("方法执行前"); } public void PostProceede(IMessage msg) { Console.WriteLine("方法执行后"); } } //TransparentProxy public static class TransparentProxy { public static T Create<T>() { T instance = Activator.CreateInstance<T>(); MyRealProxy<T> realProxy = new MyRealProxy<T>(instance); T transparentProxy = (T)realProxy.GetTransparentProxy(); return transparentProxy; } } }

优点:简单实现
缺点:性能差
2. 继承ContextBoundObject方式

using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Activation; namespace ConsoleApplication4 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine(); AopClass ap = new AopClass("XiaoQiang"); Console.WriteLine("Show:" + ap.Hello()); Console.WriteLine(ap.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("Show:" + ap.Say("hello,everybody!")); Console.WriteLine(ap.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(ap.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(); WatchToDo(ToDoA); WatchToDo(ToDoB); Console.ReadKey(); } #region 性能测试 static void ToDoA() { ClsA cl1 = new ClsA(); cl1.ToDo(); } static void ToDoB() { ClsB cl2 = new ClsB(); cl2.ToDo(); } static long WatchToDo(Action act) { System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch stop = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch(); stop.Reset(); stop.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) act(); stop.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("Time: " + stop.ElapsedTicks); return stop.ElapsedTicks; } #endregion } #region AopAttribute [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class, AllowMultiple = false)] public class AopAttribute : ProxyAttribute { private IAopProxyBuilder builder = null; public AopAttribute(Type builderType) { this.builder = (IAopProxyBuilder)Activator.CreateInstance(builderType); } public override MarshalByRefObject CreateInstance(Type serverType) { AopProxy realProxy = new AopProxy(serverType); return realProxy.GetTransparentProxy() as MarshalByRefObject; } } #endregion #region MethodAopAdviceAttribute [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false)] public class MethodAopAdviceAttribute : Attribute { private AdviceType type = AdviceType.None; public MethodAopAdviceAttribute(AdviceType advicetype) { this.type = advicetype; } public AdviceType AdviceType { get { return this.type; } } } public enum AdviceType { None, Before, After, Around } #endregion #region AopProxy partial interface IAopAction { void PreProcess(IMessage requestMsg); void PostProcess(IMessage requestMsg, IMessage Respond); } public class AopProxy : RealProxy, IAopAction { public AopProxy(Type serverType) : base(serverType) { } public virtual void PreProcess(object obj, string method = "", int argCount = 0, object[] args = null) { var o = obj as AopClass; if (o != null) { o.IsLock = false; o.Name = "999999"; } } public virtual void PreProcess(IMessage requestMsg) { var o = GetUnwrappedServer(); IMethodCallMessage call = requestMsg as IMethodCallMessage; if (call != null) { this.PreProcess(o, call.MethodName, call.InArgCount, call.Args); } else { this.PreProcess(o); } } public virtual void PostProcess(object obj, object returnValue = null, string method = "", int argCount = 0, object[] args = null) { var o = obj as AopClass; if (o != null) { o.IsLock = true; o.Name = "10101010"; } } public virtual void PostProcess(IMessage requestMsg, IMessage Respond) { var o = GetUnwrappedServer(); ReturnMessage mm = Respond as ReturnMessage; var ret = mm.ReturnValue; IMethodCallMessage call = requestMsg as IMethodCallMessage; if (call != null) { this.PostProcess(o, ret, call.MethodName, call.InArgCount, call.Args); } else { this.PostProcess(o, ret); } } //public virtual IMessage Proessed(IMessage msg,MarshalByRefObject target) //{ // IMethodCallMessage call = (IMethodCallMessage)msg; // IConstructionCallMessage ctor = call as IConstructionCallMessage; // if (ctor != null) // { // //获取最底层的默认真实代理 // RealProxy default_proxy = System.Runtime.Remoting.RemotingServices.GetRealProxy(target); // default_proxy.InitializeServerObject(ctor); // MarshalByRefObject tp = (MarshalByRefObject)this.GetTransparentProxy(); // //自定义的透明代理 this // return System.Runtime.Remoting.Services.EnterpriseServicesHelper.CreateConstructionReturnMessage(ctor, tp); // } // IMethodReturnMessage result_msg = System.Runtime.Remoting.RemotingServices.ExecuteMessage(target, call); // //将消息转化为堆栈,并执行目标方法,方法完成后,再将堆栈转化为消息 // return result_msg; //} public virtual IMessage Proessed(IMessage msg) { IMessage message; if (msg is IConstructionCallMessage) { message = this.ProcessConstruct(msg); } else { message = this.ProcessInvoke(msg); } return message; } public virtual void ChangeReturnValue(IMessage msg, ref object o) { if (msg is IMethodCallMessage) { var m = msg as IMethodCallMessage; string name = m.MethodName; if (name == "Hello") o = "Hello,Lucy!"; } } public virtual IMessage ProcessInvoke(IMessage msg) { IMethodCallMessage callMsg = msg as IMethodCallMessage; IMessage message; try { object[] args = callMsg.Args; //方法参数 object o = callMsg.MethodBase.Invoke(GetUnwrappedServer(), args); //调用 原型类的 方法 ChangeReturnValue(msg, ref o); message = new ReturnMessage(o, args, args.Length, callMsg.LogicalCallContext, callMsg); // 返回类型 Message } catch (Exception e) { message = new ReturnMessage(e, callMsg); } //Console.WriteLine("Call Method:"+callMsg.MethodName); //Console.WriteLine("Return:"+ message.Properties["__Return"].ToString()); return message; } public virtual IMessage ProcessConstruct(IMessage msg) { IConstructionCallMessage constructCallMsg = msg as IConstructionCallMessage; //构造函数 初始化 IConstructionReturnMessage constructionReturnMessage = this.InitializeServerObject((IConstructionCallMessage)msg); RealProxy.SetStubData(this, constructionReturnMessage.ReturnValue); //Console.WriteLine("Call constructor:"+constructCallMsg.MethodName); //Console.WriteLine("Call constructor arg count:"+constructCallMsg.ArgCount); return constructionReturnMessage; } public override IMessage Invoke(IMessage msg) { #region 获取AdviceType AdviceType type = AdviceType.None; IMethodCallMessage call = (IMethodCallMessage)msg; foreach (Attribute attr in call.MethodBase.GetCustomAttributes(false)) { MethodAopAdviceAttribute mehodAopAttr = attr as MethodAopAdviceAttribute; if (mehodAopAttr != null) { type = mehodAopAttr.AdviceType; break; } } #endregion IMessage message; if (type == AdviceType.Before || type == AdviceType.Around) { this.PreProcess(msg); Console.WriteLine("::Before Or Around"); } message = this.Proessed(msg); if (type == AdviceType.After || type == AdviceType.Around) { this.PostProcess(msg, message); Console.WriteLine("::After Or Around"); } return message; } } #endregion #region AopProxyBuilder public interface IAopProxyBuilder { AopProxy CreateAopProxyInstance(Type type); } public class AopProxyBuilder : IAopProxyBuilder { public AopProxy CreateAopProxyInstance(Type type) { return new AopProxy(type); } } #endregion #region AopClass [AopAttribute(typeof(AopProxyBuilder))] public class AopClass : ContextBoundObject { public string Name { get; set; } public bool IsLock = true; public AopClass(string name) { Name = name; Console.WriteLine("Aop Class Create Name:" + Name); } public AopClass() { Console.WriteLine("Aop Class Create"); } [MethodAopAdvice(AdviceType.Around)] public string Hello() { Console.WriteLine("hello world:"); return "hello world:"; } [MethodAopAdvice(AdviceType.Before)] public string Say(string content) { string c = "IsLock:" + IsLock + " " + Name + " :" + content; Console.WriteLine(c); return c; } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("Name:{0},IsLock:{1}", this.Name, this.IsLock); } } #endregion #region 测试数据 public class ClsA { public void ToDo() { } } public class ClsB : ContextBoundObject { public void ToDo() { } } #endregion }
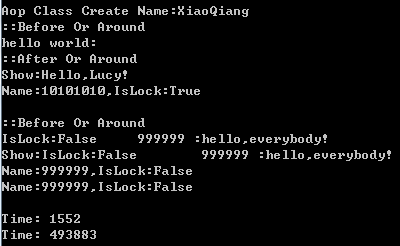
测试结果:性能时间后者是前者的318倍
3.EnterpriseLibary 实现方法

//首先添加EnterpriseLibary的引用 //自定义CallHandler,这里定义两个CallHandler分别用于参数检查和日志记录。 using Microsoft.Practices.Unity.InterceptionExtension; public class UserHandler : ICallHandler { public int Order { get; set; } public IMethodReturn Invoke(IMethodInvocation input, GetNextHandlerDelegate getNext) { User user = input.Inputs[0] as User; if (user.PassWord.Length < 10) { return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new UserException("密码长度不能小于10位")); } Console.WriteLine("参数检测无误"); return getNext()(input, getNext); } } public class LogHandler : ICallHandler { public int Order { get; set; } public IMethodReturn Invoke(IMethodInvocation input, GetNextHandlerDelegate getNext) { User user = input.Inputs[0] as User; Log log = new Log() { Message = string.Format("RegUser:Username:{0},Password:{1}", user.Name, user.PassWord), Ctime = DateTime.Now }; Console.WriteLine("日志已记录,Message:{0},Ctime:{1}", log.Message, log.Ctime); var messagereturn = getNext()(input, getNext); return messagereturn; } } //定义对应的HandlerAttribute using Microsoft.Practices.Unity.InterceptionExtension; using Microsoft.Practices.Unity; public class UserHandlerAttribute : HandlerAttribute { public override ICallHandler CreateHandler(IUnityContainer container) { ICallHandler handler = new UserHandler(){Order=this.Order}; return handler; } } public class LogHandlerAttribute:HandlerAttribute { public int Order { get; set; } public override ICallHandler CreateHandler(IUnityContainer container) { return new LogHandler() { Order = this.Order }; } } //用户注册接口和实现,这里通过为接口添加attribute的方式实现。order值表示执行顺序,值小的先执行。 [LogHandlerAttribute(Order=2)] [UserHandlerAttribute(Order=1)] public interface IUserProcessor { void RegUser(User user); } public class UserProcessor : MarshalByRefObject,IUserProcessor { public void RegUser(User user) { Console.WriteLine("用户已注册。"); } } //测试 using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection; public class Client { public static void Run() { try { User user = new User() { Name = "lee", PassWord = "123123123123" }; UserProcessor userprocessor = PolicyInjection.Create<UserProcessor>(); userprocessor.RegUser(user); } catch(Exception ex) { throw ex; } } }
4.Castle Dynamic Proxy的实现
首先下载Castle.Windsor.dll
自定义Interceptor
public class MyInterceptor : IInterceptor { public void Intercept(IInvocation invocation) { PreProceed(invocation); invocation.Proceed(); PostProceed(invocation); } public void PreProceed(IInvocation invocation) { Console.WriteLine("方法执行前"); } public void PostProceed(IInvocation invocation) { Console.WriteLine("方法执行后"); } }
用户注册接口和实现
public interface IUserProcessor { void RegUser(User user); } public class UserProcessor : IUserProcessor { public virtual void RegUser(User user) { Console.WriteLine("用户已注册。Name:{0},PassWord:{1}", user.Name, user.PassWord); } }
客户端调用
public class Client { public static void Run() { try { ProxyGenerator generator = new ProxyGenerator(); MyInterceptor interceptor = new MyInterceptor(); UserProcessor userprocessor = generator.CreateClassProxy<UserProcessor>(interceptor); User user= new User() { Name = "lee", PassWord = "123123123123" }; userprocessor.RegUser(user); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } }
6.IL织入 PostSharp实现AOP
PostSharp简介
PostSharp是一个用于在.NET平台上实现AOP的框架,是我比较常用的一个AOP框架,官方网站为http://www.sharpcrafters.com。目前最新版本为2.0,但是2.0的license不再免费,因此个人建议下载1.5版,同时下文都是基于PostSharp1.5。
PostSharp使用静态织入方式实现AOP,其连接点非常丰富,使用简单,而且相对其它一些.NET平台上的AOP框架来说,PostSharp较为轻量级,但是功能却一点也不逊色,因此是我比较喜欢的一个AOP框架。更多关于PostSharp的介绍请参看其官方网站。
另外使用PostSharp与其它框架不太一样的是一定要下载安装包安装,只引用类库是不行的,因为上文说过,AOP框架需要为编译器或运行时添加扩展。
使用PostSharp实现AOP示例
这一节将通过一个例子演示如何使用PostSharp在.NET平台上实现AOP。这个例子将通过AOP为核心业务函数增加日志记录功能。
新建项目
首先新建一个C#的WinForm应用程序,如图4所示,这里将工程命名为“PostSharpExample”。
图4、新建项目
编写核心业务函数
首先我们来编写核心业务。当然这里不存在真正的业务,我们只是模拟一个而已。将要模拟的核心业务是预定房间。先构建一个如图5所示的简单UI。
图5、UI界面
下面我们为项目增加一个“CoreBusiness”类,并在其中添加“Subscribe”方法。代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
using System;namespace PostSharpExample{ public class CoreBusiness { public static void Describe(string memberName, string roomNumber) { System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(String.Format("尊敬的会员{0},恭喜您预定房间{1}成功!", memberName, roomNumber), "提示"); } }} |
可以看到,这里Subscribe方法仅仅是输出一个提示框。当然,在真正项目中这种输出型代码不应该写在业务逻辑中,这里这样写主要是为了演示方便。然后,我们在Form1中调用Subscribe业务方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
using System;using System.Windows.Forms;namespace PostSharpExample{ public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void BTN_SUBSCRIBE_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(TXB_NAME.Text.Trim()) && !String.IsNullOrEmpty(TXB_ROOM.Text.Trim())) CoreBusiness.Describe(TXB_NAME.Text.Trim(), TXB_ROOM.Text.Trim()); else MessageBox.Show("信息不完整","提示"); } }} |
运行程序就可以看到相应的效果:
图6、预定房间成功演示效果
使用AOP增加日志记录功能
现在加入我们要为程序添加日志功能,记录业务函数的执行情况。这里我们假定需要将日志记录到纯文本文件中,首先我们完成日志记录工具类,LoggingHelper。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
using System;using System.IO;namespace PostSharpExample{ class LoggingHelper { private const String _errLogFilePath = @"log.txt"; public static void Writelog(String message) { StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(_errLogFilePath, true); String logContent = String.Format("[{0}]{1}", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"), message); sw.WriteLine(logContent); sw.Flush(); sw.Close(); } }} |
如果不使用AOP,则我们要为包括Subscribe在内的每一个方法在核心业务代码的前后插入日志记录代码(Writelog),我们看看使用PostSharp如何将这种横切关注点分离出来。因为要使用PostSharp,所以要先添加对PostSharp库文件的引用,安装过PostSharp后,在系统可引用项中会多出“PostSharp.Laos”、“PostSharp.Public”和“PostSharp.AspNet”,这里我们做的是Winform程序,所以只需添加对“PostSharp.Laos”和“PostSharp.Public”的引用即可。
下面我们就要写Aspect了,PostSharp的Aspect是使用Attribute实现的,下面是我实现的日志记录Aspect代码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
using System;using PostSharp.Laos;namespace PostSharpExample{ [Serializable] [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)] public sealed class LoggingAttribute : OnMethodBoundaryAspect { public string BusinessName { get; set; } public override void OnEntry(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs) { LoggingHelper.Writelog(BusinessName + "开始执行"); } public override void OnExit(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs) { LoggingHelper.Writelog(BusinessName + "成功完成"); } }} |
我们约定每个Aspect类的命名必须为“XXXAttribute”的形式。其中“XXX”就是这个Aspect的名字。PostSharp中提供了丰富的内置“Base Aspect”以便我们继承,其中这里我们继承“OnMethodBoundaryAspect ”,这个Aspect提供了进入、退出函数等连接点方法。另外,Aspect上必须设置“[Serializable] ”,这与PostSharp内部对Aspect的生命周期管理有关,具体为什么请参看这里。
我们的LoggingAttribute非常简单,就是在进入(Entry)和离开(Exit)函数时分别记录日志到log文件。现在我们把这个Aspect应用到业务方法上:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[Logging(BusinessName="预定房间")]public static void Describe(string memberName, string roomNumber){ System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(String.Format("尊敬的会员{0},恭喜您预定房间{1}成功!", memberName, roomNumber), "提示");} |
可以看到,应用Aspect非常简单,就是将相应的Attribute加到业务方法上面。现在我们再运行预定房间程序,结果和上次没什么两样,但是如果我们打开程序目录,会看到多了一个“log.txt”文件,里面记录有类似图7的内容。
图7、日志内容
可以看到,我们已经通过AOP实现了日志记录功能。通过AOP将横切关注点分离出来后,日志记录的代码都放在LoggingAttribute里,需要修改只要修改一处即可。同时,业务方法仅含有业务代码,这样大大提高了程序代码的可读性和可维护性。
对PostSharp运行机制的简要分析
上文已经说到,PostSharp使用的是静态织入技术,下面我们分析一下PostSharp是如何实现的。
首先,当安装PostSharp时,它自动为Visual Studio编译器添加了AOP扩展。如果仔细观察PostSharpExample编译信息,会发现有这么两行:
图8、PostSharp编译信息
很明显,在.NET Complier编译完成后,下面PostSharp又做了一部分工作,这部分工作就是静态织入的过程。如果我们用.NET Reflector查看PostSharpExample.exe中Subscribe方法的反编译代码,会发现多了很多东西:
图9、织入Aspect后的Describe代码(由.NET Reflector反编译)
这些多出来的代码,就是PostSharp静态织入进去的。当然,这些代码在每次编译完成后,PostSharp都会重新织入一次,所以整个过程对程序员是透明的,我们只需维护纯净的业务代码和Aspect代码即可。
使用PostSharp的优点和缺点(即使用AOP的优点和缺点)
总体来说,使用PostSharp,将会带来如下优点:
- 横切关注点单独分离出来,提高了代码的清晰性和可维护性。
- 只要在Aspect中编写辅助性功能代码,在一定程度上减少了工作量和冗余代码。
当然,使用PostSharp也不是没有缺点,主要缺点有如下两方面:
- 增加了调试的难度。
- 相比于不用AOP的代码,运行效率有所降低。
所以,对于是否引入AOP,请根据项目具体情况,权衡而定。
对于PostSharp的进一步学习
本文只是简要介绍了PostSharp以及实现了一个小例子,并不打算详细完整地介绍PostSharp的方方面面,而只想起到一个抛砖引玉的作用。PostSharp还有非常丰富的功能等待各位学习,因此,如果您对PostSharp十分有兴趣,想进一步学习,请参看PostSharp官方参考文档。
相关下载
本文用到的Example请点击这里下载。
PostSharp1.5安装包请点击这里下载。
5. 各种IoC框架下实现AOP
首先介绍几种笔者常见的IOC框架
Castle
AOP框架
Encase 是C#编写开发的为.NET平台提供的AOP框架。Encase 独特的提供了把方面(aspects)部署到运行时代码,而其它AOP框架依赖配置文件的方式。这种部署方面(aspects)的方法帮助缺少经验的开发人员提高开发效率。
NKalore是一款编程语言,它扩展了C#允许在.net平台使用AOP。NKalore的语法简单、直观,它的编译器是基于Mono C#编译器(MCS)。NKalore目前只能在命令行或#Develop内部使用。NKalore兼容公共语言规范CLS(Common Language Specification),它可以在任何.NET开发环境中使用,包括微软的Visual Studio .NET。
PostSharp读取.NET字节模块,转换成对象模型。让插件分析和转换这个模型并写回到MSIL。PostSharp使开发程序分析应用程序容易得像分析代码规则和设计模式,它使程序开发的思想变革为面向方面软件开发(AOSD/AOD)思想。
AspectDNG的目标是为.NET开发人员提供简单而功能强大的AOP-GAOP实现。它效仿java下的开源工具AspectJ 和 Spoon,成熟程度也很接近它们。
RAIL(Runtime Assembly Instrumentation Library) 开源项目可以在C#程序集加载和运行前进行处理控制调整和重新构建。C#在CLR中,我们已经能够动态加载程序集并且获得程序集中的类和方法,RAIL(Runtime Assembly Instrumentation Library)的出现填补了CLR处理过程中的一些空白。
SetPoint是一款.NET框架下的全功能(full-featured)AOP引擎.它着重为称为语义切点(semantic pointcuts)的定义依赖RDF/OWL的使用.它的功能为一个IL-level,highly dynamic weaver&LENDL,一个引人注目的定义语言、、、、、、
DotNetAOP为 CLR language提供AOP 框架基础属性。
NAop是一个DotNet下的AOP框架。
AspectSharp是DotNet下的免费AOP框架,它以Dynamic Proxies和XML作为配置文件。
参考文章
3.NET中的AOP(厉害啊)






