mybatis的两大重要组件:配置和映射文件,都是可以通过xml配置的(新版本新增了注解的方式配置Mapper),下面来解析下mybatis是怎么做的
其中,关于配置文件解析的主要是在这个类XMLConfigBuilder里面的parseConfiguration方法,XMLConfigBuilder在初始化的时候会新建一个XPathParser对象用于XML配置文件的解析
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) { this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props); }
public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); loadCustomVfs(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
这面有个重要的类XPathParser和重要的方法evalNode,所以我们引出了这两个类:
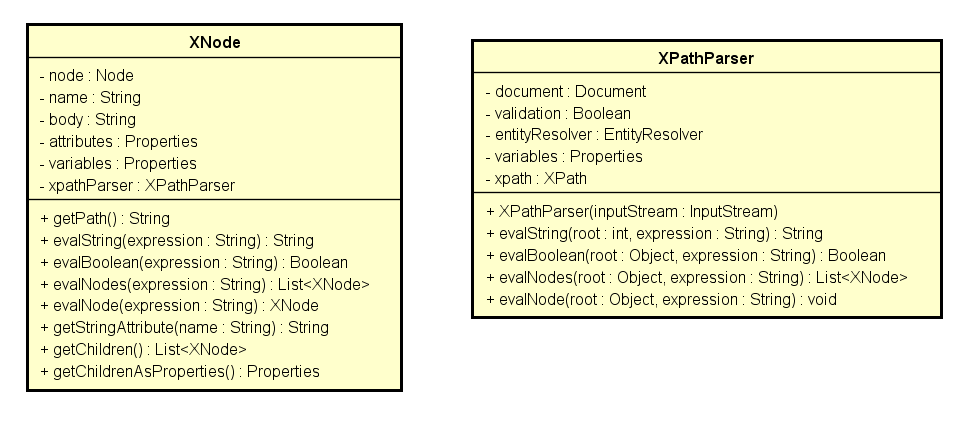
Mybatis在xml解析这一块用的是java dom API
XNode类是对Node的简单封装,用于表示一个xml 节点,是配置的模型类。其中variables中存放的是变量配置的键值对,用于解析${xx}的字符串(见下文的PropertyParser)xpathParser是一个用于解析节点的解析器,XNode中的大部分方法都是委托给xpathParser对象来进行的。
XPathParser是整个配置的上下文类,document对象表示这个xml的整个文档,variables和XNode一样。
document建立过程:
初始化xpath
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance(); this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
创建document
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) { // important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor try { DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); factory.setValidating(validation); factory.setNamespaceAware(false); factory.setIgnoringComments(true); factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false); factory.setCoalescing(false); factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true); DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() { @Override public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { throw exception; } @Override public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { throw exception; } @Override public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { } }); return builder.parse(inputSource); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }
XPathParser中实现了大量的解析节点的方法和重载:
private Object evaluate(String expression, Object root, QName returnType) { try { return xpath.evaluate(expression, root, returnType); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error evaluating XPath. Cause: " + e, e); } }
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) { Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE); if (node == null) { return null; } return new XNode(this, node, variables); }
PropertyParser类
在XNode和XPathParser中我们都见过对PropertyParser的使用,主要是根据variables解析字符串中的变量用的,
private String getBodyData(Node child) { if (child.getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) { String data = ((CharacterData) child).getData(); data = PropertyParser.parse(data, variables); return data; } return null; }
public String evalString(Object root, String expression) { String result = (String) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.STRING); result = PropertyParser.parse(result, variables); return result; }
下面是这个方法的实现,它借助于GenericTokenParser来进行解析,
public static String parse(String string, Properties variables) { VariableTokenHandler handler = new VariableTokenHandler(variables); GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler); return parser.parse(string); }
这里引入了一个新的东西:TokenHandler和GenericTokenParser
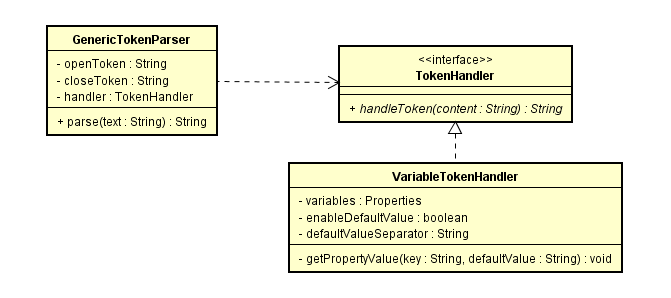
GenericTokenParser的parse方法用来解析文本(替换参数),openToken是开始标记,这里是"${",closeToken是结束标记,这里是"}"
public String parse(String text) { final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); final StringBuilder expression = new StringBuilder(); if (text != null && text.length() > 0) { char[] src = text.toCharArray(); int offset = 0; // search open token int start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset); while (start > -1) { if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\') { // this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue. builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken); offset = start + openToken.length(); } else { // found open token. let's search close token. expression.setLength(0); builder.append(src, offset, start - offset); offset = start + openToken.length(); int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset); while (end > -1) { if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\') { // this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue. expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken); offset = end + closeToken.length(); end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset); } else { expression.append(src, offset, end - offset); offset = end + closeToken.length(); break; } } if (end == -1) { // close token was not found. builder.append(src, start, src.length - start); offset = src.length; } else { builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString())); offset = end + closeToken.length(); } } start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset); } if (offset < src.length) { builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset); } } return builder.toString(); }
上面标红的代码比较重要,其他的代码只是清除噪声,根据openToken和closeToken定位到这个位置,解析出expression,也就是${xxx}的那段字符串,之后交给TokenHandler处理,这里是VariableTokenHandler
@Override public String handleToken(String content) { if (variables != null) { String key = content; if (enableDefaultValue) { final int separatorIndex = content.indexOf(defaultValueSeparator); String defaultValue = null; if (separatorIndex >= 0) { key = content.substring(0, separatorIndex); defaultValue = content.substring(separatorIndex + defaultValueSeparator.length()); } if (defaultValue != null) { return variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue); } } if (variables.containsKey(key)) { return variables.getProperty(key); } } return "${" + content + "}"; }
然后就会得到了解析后的字符串。
最后,我们来看看创建XPathParser时候指定的XMLMapperEntityResolver类,这个是用于验证xml是否符合dtd的(根据doctype)
/** * Offline entity resolver for the MyBatis DTDs * * @author Clinton Begin * @author Eduardo Macarron */ public class XMLMapperEntityResolver implements EntityResolver { private static final String IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"; /* * Converts a public DTD into a local one * * @param publicId The public id that is what comes after "PUBLIC" * @param systemId The system id that is what comes after the public id. * @return The InputSource for the DTD * * @throws org.xml.sax.SAXException If anything goes wrong */ @Override public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException { try { if (systemId != null) { String lowerCaseSystemId = systemId.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH); if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM)) { return getInputSource(MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD, publicId, systemId); } else if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM)) { return getInputSource(MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD, publicId, systemId); } } return null; } catch (Exception e) { throw new SAXException(e.toString()); } } private InputSource getInputSource(String path, String publicId, String systemId) { InputSource source = null; if (path != null) { try { InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path); source = new InputSource(in); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); } catch (IOException e) { // ignore, null is ok } } return source; } }