背景说明
公司的电脑一般都是windows系统的。但是windows系统如果配置开发环境,在安装一些依赖的时候经常会抓狂。
Vagrant是一个基于Ruby的工具,用于创建和部署虚拟机。
通过vagrant工具在windows系统上拉起一台linux系统的虚拟机,在上面安装emacs,然后通过 mobaxterm 工具的X server 功能,在windows上远程打开虚拟机中的emacs GUI界面。
vagrant
vagrant下载地址:https://www.vagrantup.com/
从官网上下载vagrant的最新版后直接安装在机器上。
vagrant box
在拉起虚拟机前我们需要有一个基础的虚拟机镜像包,镜像包一般是xxxx.box文件。
假设我们从同事手中或者从网上获取到了一个ubuntu18.04的box。
我们可以将这个box添加到我们的box list中
vagrant box add box的名字 box的绝对路径
添加完后查看系统中存在的box
vagrant box list
配置
在D盘下创建一个目录,然后进入到目录里。在目录中按住shift+右键,选择在此处打开命令行。
在打开的cmd窗口中执行命令。
vagrant init python_emacs_VM
python_emacs_VM 名字根据个人需要修改。
这个时候,在当前目录下就会生成一个Vagrantfile文件。
使用编辑器打开这个文件。
# -*- mode: ruby -*- # vi: set ft=ruby : Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| config.vm.box = "ubuntu18.04" config.vm.hostname = "myVM" config.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.1.120" config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb| # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine vb.gui = false # Customize the amount of memory on the VM: # vb.memory = "1024" # vb.name = "mywork" vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "python_emacs", "--memory", "512"] end end
config.vm.box 指定基础镜像文件的名称,如果box名称在本地的box list不存在,那么vagrant会尝试去vagrant cloud中在线寻找,如果找到就会自动下载。
你也可以到https://app.vagrantup.com/boxes/search 里搜寻你想要的镜像包,然后把名字填到这里就可以了。不过这个下载速度会比较慢。
config.vm.network "public_network" 指定使用公共网络,需要指定一个ip。在cmd命令行中执行ipconfig可以查看本机的IP,然后配置一个同网段中没人使用的配置上去就好。
当然也有其他网络配置。你可以自己搜索解决。
vb.customize 指定了虚拟机在vm box中显示的名称,和使用的内存大小。
文件配置好了后,执行 vagrant up 就可以启动虚拟机了。
然后执行vagrant ssh 就可以通过默认的用户vagrant连上虚拟机。
新增个人用户
ubuntu新增用户命令自行查找。
建议新增一个有sudo权限的用户。
一般新建的虚拟机会碰到在windows上使用xshell等工具连不上的问题。
可以通过修改/etc/ssh/sshd_confg文件解决。
sshd_config文件参考:

1 # Package generated configuration file 2 # See the sshd_config(5) manpage for details 3 4 # What ports, IPs and protocols we listen for 5 Port 22 6 # Use these options to restrict which interfaces/protocols sshd will bind to 7 #ListenAddress :: 8 ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 9 Protocol 2 10 # HostKeys for protocol version 2 11 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key 12 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key 13 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key 14 HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key 15 #Privilege Separation is turned on for security 16 UsePrivilegeSeparation yes 17 18 # Lifetime and size of ephemeral version 1 server key 19 KeyRegenerationInterval 3600 20 ServerKeyBits 1024 21 22 # Logging 23 SyslogFacility AUTH 24 LogLevel INFO 25 26 # Authentication: 27 LoginGraceTime 120 28 PermitRootLogin prohibit-password 29 StrictModes yes 30 31 RSAAuthentication yes 32 PubkeyAuthentication yes 33 #AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys 34 35 # Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files 36 IgnoreRhosts yes 37 # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh_known_hosts 38 RhostsRSAAuthentication no 39 # similar for protocol version 2 40 HostbasedAuthentication no 41 # Uncomment if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for RhostsRSAAuthentication 42 #IgnoreUserKnownHosts yes 43 44 # To enable empty passwords, change to yes (NOT RECOMMENDED) 45 PermitEmptyPasswords no 46 47 # Change to yes to enable challenge-response passwords (beware issues with 48 # some PAM modules and threads) 49 ChallengeResponseAuthentication no 50 51 # Change to no to disable tunnelled clear text passwords 52 PasswordAuthentication yes 53 54 # Kerberos options 55 #KerberosAuthentication no 56 #KerberosGetAFSToken no 57 #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes 58 #KerberosTicketCleanup yes 59 60 # GSSAPI options 61 #GSSAPIAuthentication no 62 #GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes 63 64 X11Forwarding yes 65 X11DisplayOffset 10 66 PrintMotd no 67 PrintLastLog yes 68 TCPKeepAlive yes 69 #UseLogin no 70 71 #MaxStartups 10:30:60 72 #Banner /etc/issue.net 73 74 # Allow client to pass locale environment variables 75 AcceptEnv LANG LC_* 76 77 Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server 78 79 # Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing, 80 # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will 81 # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and 82 # PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration, 83 # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass 84 # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". 85 # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without 86 # PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication 87 # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'. 88 UsePAM yes
修改配置文件后,需要重启ssh服务
sudo service ssh restart
这个时候我们可以配置vagrantfile,指定vagrantg 的默认登陆用户为我们新增的用户。
参考:
# -*- mode: ruby -*- # vi: set ft=ruby : # All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure # configures the configuration version (we support older styles for # backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what # you're doing. Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| # The most common configuration options are documented and commented below. # For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at # https://docs.vagrantup.com. # Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for # boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search. config.vm.box = "ubuntu18.04" config.vm.hostname = "emacs" config.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.1.120" config.ssh.username = 'ubuntu' config.ssh.password = 'ubuntu' config.ssh.insert_key = false config.ssh.private_key_path = ["~/.ssh/id_rsa"] config.vm.provision "file", source: "~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub", destination: "~/.ssh/authorized_keys" config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", disabled: true # config.vm.network "public_network", bridge: "en0: Wi-Fi (AirPort)" config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb| # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine vb.gui = false # Customize the amount of memory on the VM: # vb.memory = "1024" # vb.name = "mywork" vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--name", "emacs", "--memory", "512"] end end
修改文件后,执行
vagrant provision
将ssh的公钥放到虚拟机上,免去连接虚拟机时需要输入密码的麻烦。ssh公钥私钥怎么配置,请百度windows配置ssh。
emacs
个人使用emacs作为平时的编辑器。如果你使用pycharm等IDE工具,这些工具有很好的vagrant插件,可以根据相关攻略配置。
安装配置
安装, 最好使用ubuntu的官方源。不知是什么原因,我换为阿里云的源是找不到emacs25的。
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install git sudo apt-get install emacs25
下载完成后就可以将自己的配置文件下载到虚拟机上了。
emacs远程编辑
爽歪歪的时候到了。
打开mobaxterm 工具,ssh连接上虚拟机。
emacs&
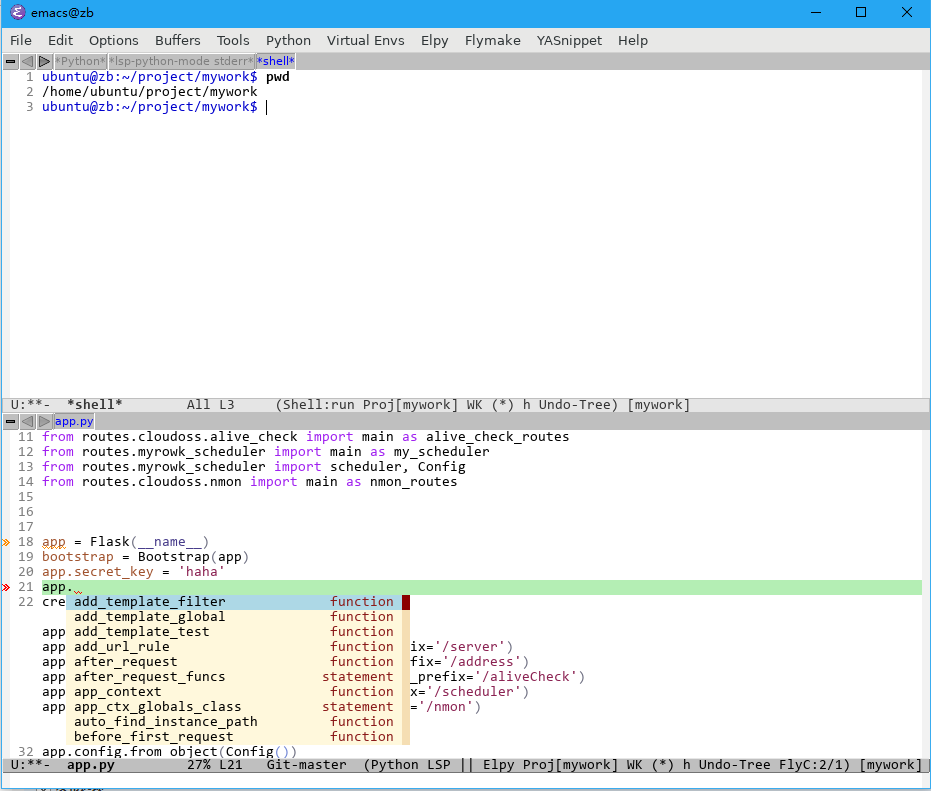
开始写代码吧!
打包
我们这个安装了emacs的镜像可以打个包,作为基础镜像。
在cmd中输入打包命令
vagrant package ubuntu18.04_emacs.box
