1. 线程池
Java语言内置多线程支持:
- 创建线程需要操作系统资源(线程资源,栈空间)
- 频繁创建和销毁线程需要消耗大量时间
假设我们有大量的小任务,可以让它排队执行,然后在一个线程池里有少量的线程来执行大量的任务。
使用线程池来复用线程,可以非常高效的执行大量小任务。
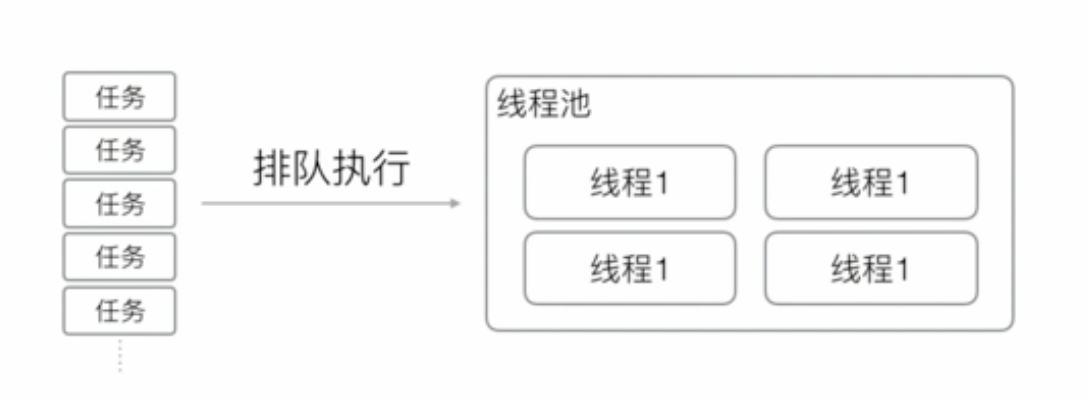
线程池:
- 线程池维护若干个线程,处于等待状态
- 如果有新任务,就分配一个空闲线程执行
- 如果所有线程都处于忙碌状态,新任务放入队列等待
2. ExecutorService
JDK提供了ExecutorService接口表示线程池:
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); //固定大小的线程池
executor.submit(task1); //提交任务到线程池
executor.submit(task2);
executor.submit(task3)
常用的ExecutorService:
- FixedThreadPool:线程数固定
- CachedThreadPool:线程数根据任务动态调整
- SingleThreadExecutor:仅单线程执行
2.1 FixedThreadPool示例
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
class PrintTask implements Runnable{
String name;
public PrintTask(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println(i+" Hello,"+name+"!");
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
}
}
}
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //指定线程池大小为3,提供了4个任务,会有1个任务等待有空闲线程后执行。
executor.submit(new PrintTask("Bob"));
executor.submit(new PrintTask("Alice"));
executor.submit(new PrintTask("Tim"));
executor.submit(new PrintTask("Robot"));
Thread.sleep(10000);
executor.shutdown(); //结束线程池
}
}
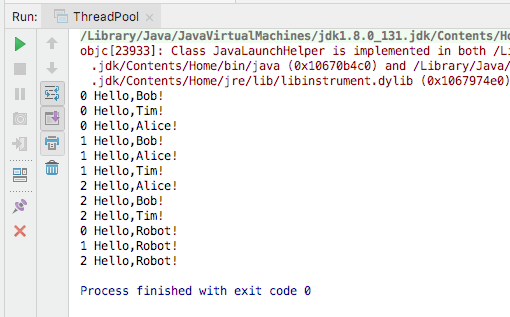 ### 2.2 SingleThreadExecutor示例
```#java
//单个线程,所有的任务将串行执行
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
```
### 2.2 SingleThreadExecutor示例
```#java
//单个线程,所有的任务将串行执行
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
```
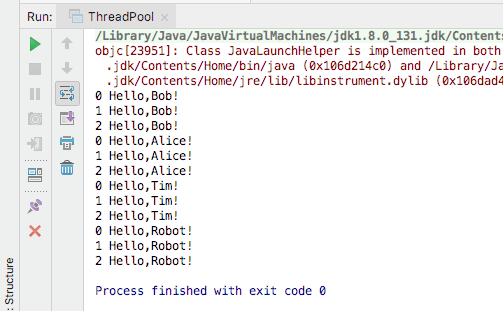 ### 2.3 CachedThreadPool示例
```#java
//动态调整的线程池。由于CachedThreadPool会根据我们的任务,动态的调整线程的数量,所以这个任务提交后,线程池会立刻创建4个线程来执行它。
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
```
### 2.3 CachedThreadPool示例
```#java
//动态调整的线程池。由于CachedThreadPool会根据我们的任务,动态的调整线程的数量,所以这个任务提交后,线程池会立刻创建4个线程来执行它。
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
```
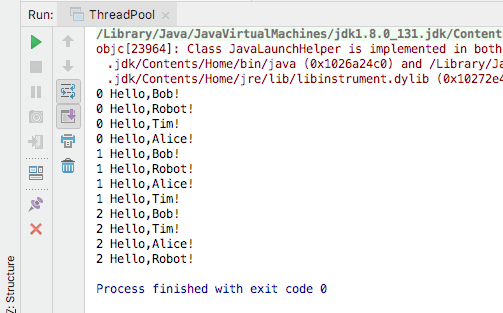 ### 2.4 动态线程池指定最大线程数量
如果我们想要限制动态线程池中线程的上限,例如最多10个线程,这个时候,CachedThreadPool就不能够满足这个要求。
查看newCachedThreadPool源码,发现其实现的是ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法,
```#java
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
0, //初始化线程池的大小
Integer.MAX_VALUE, //线程池的最大值
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue
### 2.4 动态线程池指定最大线程数量
如果我们想要限制动态线程池中线程的上限,例如最多10个线程,这个时候,CachedThreadPool就不能够满足这个要求。
查看newCachedThreadPool源码,发现其实现的是ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法,
```#java
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
0, //初始化线程池的大小
Integer.MAX_VALUE, //线程池的最大值
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue3. ScheduledThreadPool
JDK还提供了ScheduledThreadPool,使一个任务可以定期反复执行。
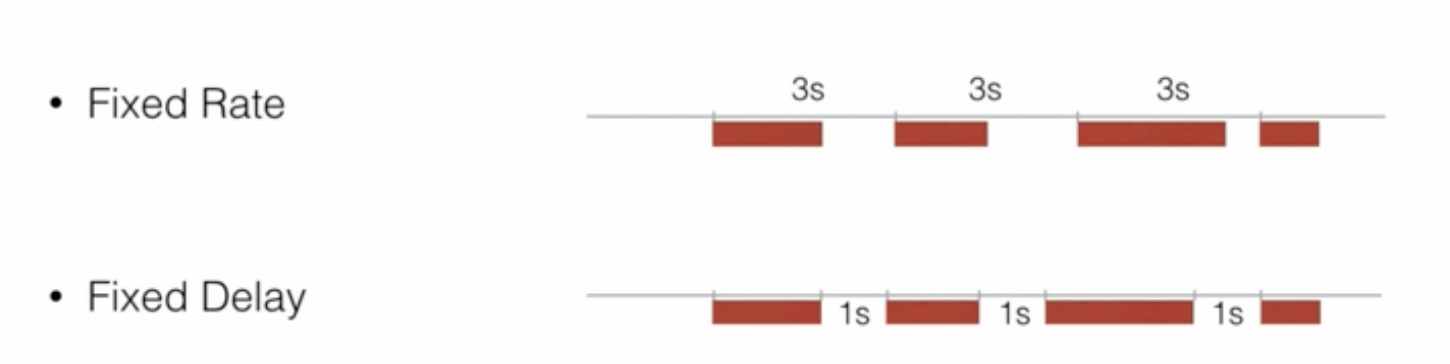
执行模式:
- Fixed Rate:在固定的间隔,任务就会执行。例如每隔3秒任务就会启动,而不管这个任务已执行了多长时间、是否结束
- Fixed Delay:当任务执行完毕以后,等待1秒钟再继续执行。无论任务执行多久,只有在任务结束以后,等待1秒钟才会开始执行下一次的任务。
注意:ScheduledThreadPool不会自动停止,需要手动强制结束。
3.1示例
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class HelloTask implements Runnable{
String name;
public HelloTask(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("Hello,"+name+" ! It is "+LocalTime.now());
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println("Goodbye, "+name+"! It is "+LocalTime.now());
}
}
public class SchedulePool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new HelloTask("Bob"),2,5,TimeUnit.SECONDS); //2秒以后开始执行,每5秒就执行这个任务
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new HelloTask("Alice"),2,5,TimeUnit.SECONDS); //2秒以后开始执行,执行结束等待5秒再执行
}
}
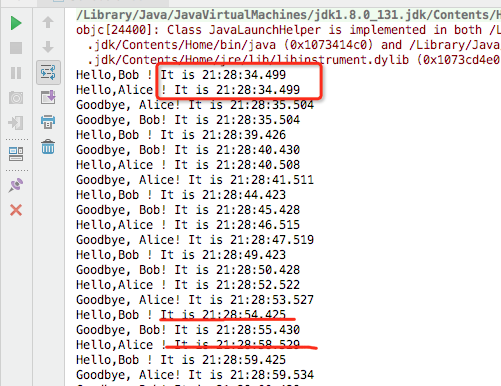 Bob的执行频率比Alice高的多,任务开始的时间差也越来越大
问题:
1.FixedRate模式下,如果任务执行时间过长,后续任务会不会并发执行?
Bob的执行频率比Alice高的多,任务开始的时间差也越来越大
问题:
1.FixedRate模式下,如果任务执行时间过长,后续任务会不会并发执行?
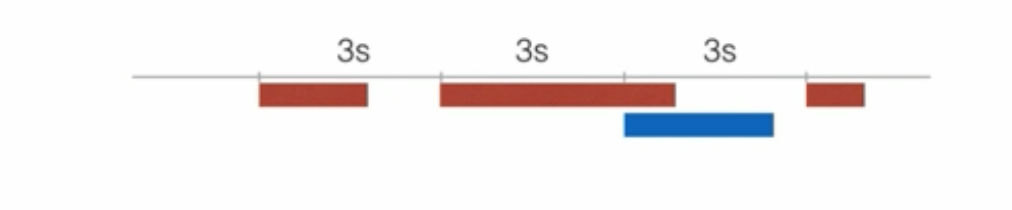 不会
```#java
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
不会
```#java
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class HelloTask implements Runnable{
String name;
public HelloTask(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("Hello,"+name+" ! It is "+LocalTime.now());
try{
Thread.sleep(10000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println("Goodbye, "+name+"! It is "+LocalTime.now());
}
}
public class SchedulePool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
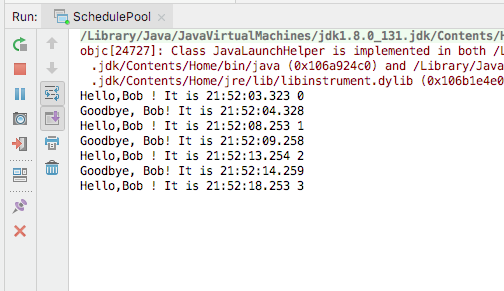
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new HelloTask("Bob"),2,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
<img src="https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1418970/201906/1418970-20190613214419984-1491212580.png" width="500" />
<font color=#FF0000><strong>2.如果任务抛出了异常,后续任务是否继续执行?</strong></font>
<font color=#458B00>不会</font>
```#java
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class HelloTask implements Runnable{
String name;
int count;
public HelloTask(String name,int count){
this.name = name;
this.count = count;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("Hello,"+name+" ! It is "+LocalTime.now()+" "+count);
try{
if(count == 3){
throw new RuntimeException("我是故意的");
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println("Goodbye, "+name+"! It is "+LocalTime.now());
count++;
}
}
public class SchedulePool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new HelloTask("Bob",0),2,5,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
4. java.util.Timer
jdk还提供了java.util.Timer类,这个类也可以定期执行一个任务:
- 一个Timer对应一个Thread,只能定期执行一个任务。如果要执行多个定时任务,就必须要启动多个Timer。
- 必须在主线程结束时跳用Timer.cancel()
而一个ScheduledPool就可以调度多个任务,所以完全可以用新的Scheduled取代Timer类。
5. 总结:
- JDK提供了ExecutorService实现了线程池功能
- 线程池内部维护一组线程,可以搞笑执行大量小任务
- Executors提供了静态方法创建不同类型的ExecutorService
- 必须调用shutdown()关闭ExecutorService
- ScheduledThreadPool可以定期调度多个任务