XML是一种数据表示形式。
- 可以描述非常复杂的数据数据结构
- 用于传输和传输数据
DOM:Document Object Model
DOM模型就是把XML文档作为一个树形结构,从根结点开始,每个节点都可以包含任意个字节点。
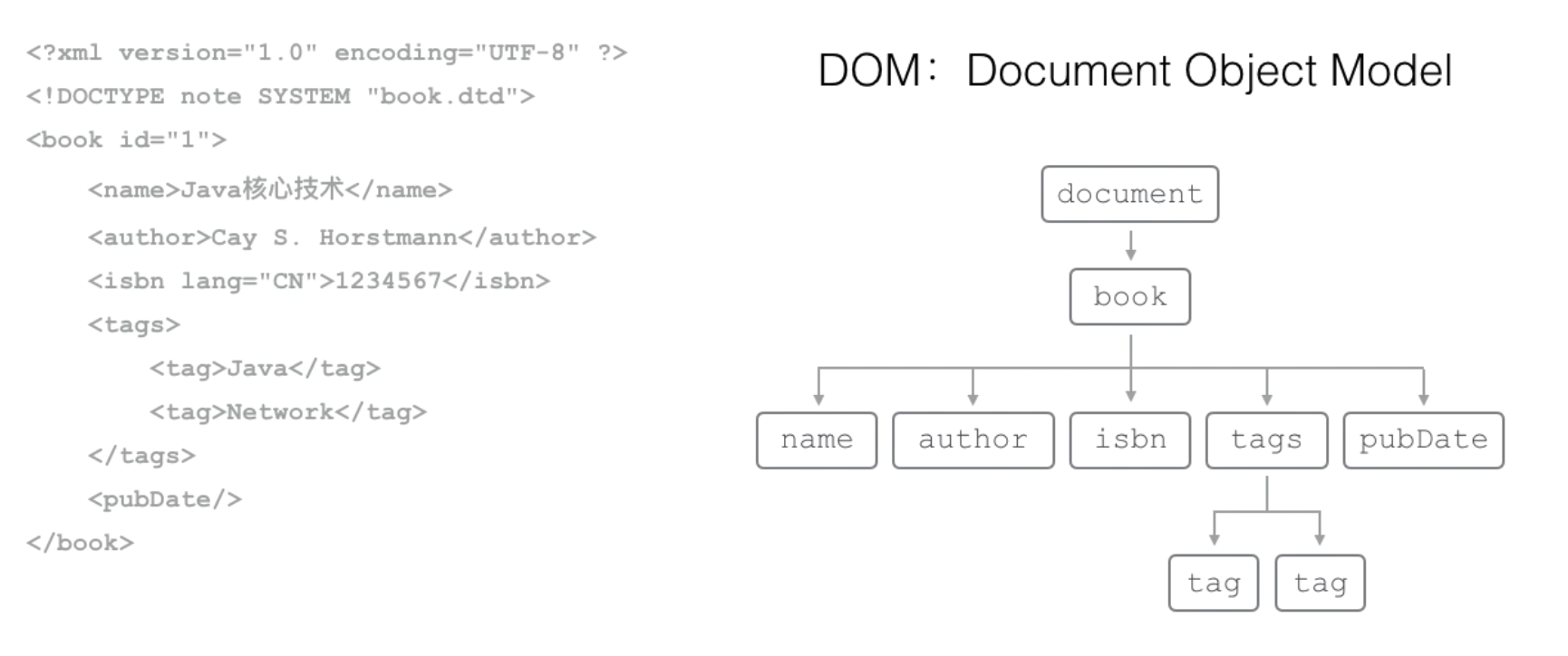
用Java解析XML时,
- Document代表整个XML文档
- Element表示元素
- Attribute:属性
- Comment表示注释
Java DOM核心API:
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse(XML_URL);
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); //获取根结点的元素
//从根结点document出发,可以便利所有的子节点,获取所有元素、属性、文本、数据、注释。每个Node都有自己的type,根据type来区分一个Node到底是元素,还是属性,还是文本。
遍历XML文件
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
public class DomSample {
static final String XML_URL = "http://rss.sina.com.cn/tech/internet/home28.xml";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse(XML_URL);
printNode(doc,0);
}
static void printNode(Node n, int indent){
for(int i=0;i<indent;i++){
System.out.print(' ');
}
switch (n.getNodeType()){
case Node.DOCUMENT_NODE://根节点
System.out.println("Document:"+n.getNodeName());
break;
case Node.ELEMENT_NODE: //元素
System.out.println("Element:"+n.getNodeName());
break;
case Node.TEXT_NODE: //字符
System.out.println("Text:"+n.getNodeName()+"="+n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE: //属性
System.out.println("Attr:"+n.getNodeName()+"="+n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE: //CDATA
System.out.println("CDATA:"+n.getNodeName()+"="+n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.COMMENT_NODE: //注释
System.out.println("Commment:"+n.getNodeName()+"="+n.getNodeValue());
break;
default:
System.out.println("NodeType:"+n.getNodeType()+",NodeName:"+n.getNodeName());
}
for(Node child=n.getFirstChild();child != null;child=child.getNextSibling()){
printNode(child, indent+1);
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<bookstore>
<book id="1" date="08/08/2008">
<name>冰与火之歌</name>
<author>乔治马丁</author>
<year>2014</year>
<price>89</price>
</book>
<book id="2">
<name>安徒生童话</name>
<year>2004</year>
<price>77</price>
<language>English</language>
</book>
</bookstore>
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse("./src/main/resources/test.xml");
//通过元素名称解析得到所有子节点的集合
NodeList books = doc.getElementsByTagName("book");
for(int i=0;i<books.getLength();i++){
Node book = books.item(i);
NamedNodeMap mapOfAttr = book.getAttributes();
//打印节点book的属性值
for(int j=0;j<mapOfAttr.getLength();j++){
Node nodeOfAttr = mapOfAttr.item(j);
System.out.println(nodeOfAttr.getNodeName()+" "+nodeOfAttr.getNodeValue());
}
//获取节点book的子节点,并打印子节点名称和节点值
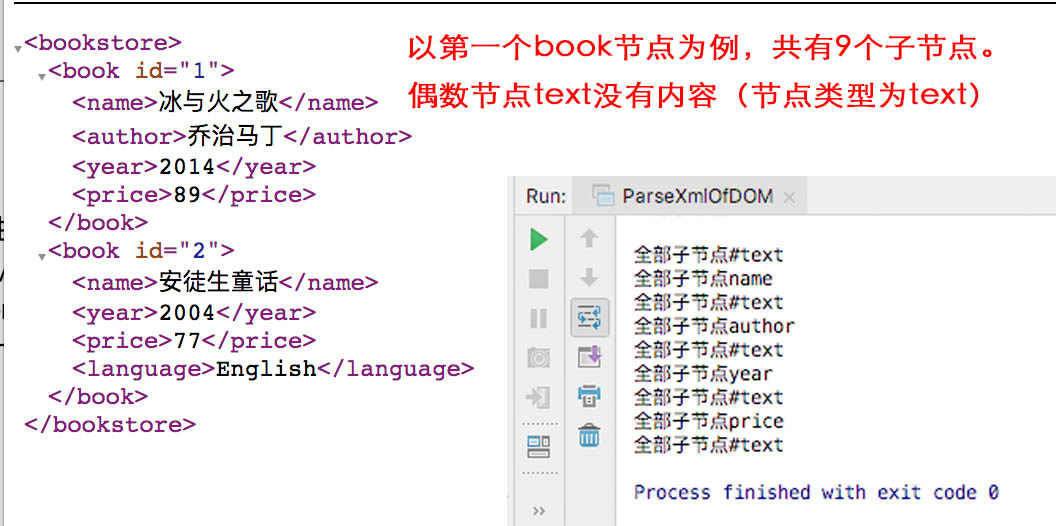
NodeList childsOfBook = book.getChildNodes();
for(int l=0;l<childsOfBook.getLength();l++){
if(l%2 != 0){//节点共有9个,偶数节点没有内容
Node childOfbook = childsOfBook.item(l);
System.out.print(childOfbook.getNodeName()+" = ");
//闭合标签内部被认为是子节点
Node grandchildNodeBook = childOfbook.getFirstChild();
System.out.println(grandchildNodeBook.getNodeValue());
}
}
}
}
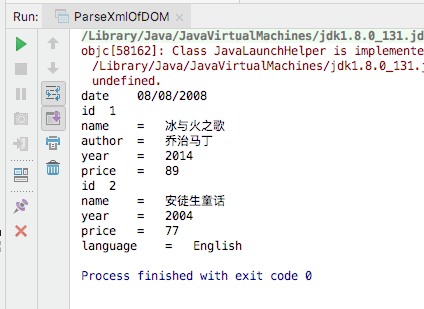
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse("./src/main/resources/test.xml");
NodeList books2 = doc.getElementsByTagName("book");
Node book = books.item(0);
NodeList childsOfBook = book.getChildNodes();
for(int l=0;l<childsOfBook.getLength();l++){
System.out.println("全部子节点"+ childsOfBook.item(l).getNodeName());
}
}
总结:
Java DOM API:
- 将XML解析为DOM
- 可在内存中完整表示XML数据结构
- 解析速度慢,内存占用大
学习链接https://blog.csdn.net/root_dream/article/details/61195793