▶ 使用一个隐藏层的神经网络来为散点作分类
● 代码
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 4 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection 5 from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle 6 7 dataSize = 1000 # 总数据大小 8 trainRatio = 0.3 # 训练集占比 9 ita = 0.4 # 学习率 10 epsilon = 0.01 # 单轮累计误差要求 11 maxTurn = 500 # 最大训练轮数 12 13 def dataSplit(data, part): # 将数据集分割为训练集和测试集 14 return data[0:part,:],data[part:,:] 15 16 def myHash(data): # 将输出的类别向量压成一维索引 17 size = len(data) 18 carry = 2 # 每个输出维度只有(0,1)两个值,使用二进制 19 output = 0 20 for i in range(size): 21 output = output * carry + data[i].astype(int) 22 return output 23 24 def myColor(x): # 颜色函数,用于对散点染色 25 r = np.select([x < 1/2, x < 3/4, x <= 1, True],[0, 4 * x - 2, 1, 0]) 26 g = np.select([x < 1/4, x < 3/4, x <= 1, True],[4 * x, 1, 4 - 4 * x, 0]) 27 b = np.select([x < 1/4, x < 1/2, x <= 1, True],[1, 2 - 4 * x, 0, 0]) 28 return [r,g,b] 29 30 def sigmoid(x): # sigmoid 函数 31 return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) 32 33 def function(x,para): # 回归函数 34 dimIn = np.shape(x)[0] 35 t = sigmoid(np.sum(x * para[0],1) - para[1]) 36 w = sigmoid(np.sum(t * para[2],1) - para[3]) 37 return w 38 39 def judge(x, para): # 分类函数 40 return (function(x, para) > 0.5*np.ones(len(para[3]))).astype(int) 41 42 def createData(dimIn, dimOut, len): # 生成测试数据,输出一个 len 行 dimIn + dimOut 列的矩阵 43 np.random.seed(103) # 该矩阵后 dimOut 列是由前 dimIn 列 乘以一个变换阵 transform 得到的 44 output = np.zeros([len,dimIn+dimOut]) 45 transform = np.random.rand(dimIn, dimOut) 46 output[:,:dimIn] = np.random.rand(len, dimIn) 47 temp = np.matmul(output[:,:dimIn],transform) 48 cut = [ sorted(temp[:,i])[int(len/2)] for i in range(dimOut) ] 49 output[:,dimIn:] = (np.matmul(output[:,:dimIn],transform) > np.array(cut)).astype(int) 50 #print(transform) # 输出变换矩阵 51 #count = np.zeros(2**dimOut,dtype=int) # 输出各类别的频数 52 #for i in range(len): 53 # count[myHash(output[i,dimIn:])]+=1 54 #for i in range(2**dimOut): 55 # print("kind %d-> %4d"%(i,count[i])) 56 return output 57 58 def bp(data,dimIn,dimMid,dimOut): # 单隐层前馈感知机 59 len = np.shape(data)[0] 60 paraIM = np.random.rand(dimMid,dimIn) # 随机初值 61 paraM = np.random.rand(dimMid) 62 paraMO = np.random.rand(dimOut,dimMid) 63 paraO = np.random.rand(dimOut) 64 #for Debug (3,4,1) 65 #paraIM = np.array([[ 2.44978959, 1.03356222, 1.25171316],[ 8.22395895, 3.2859132 , 2.93199359], 66 # [ 9.04487454, 3.58879071, 3.2453638 ],[-0.21185973, 1.01962831, 0.30603421]]) 67 #paraM = np.array([ 2.37018489, 7.43062236, 8.16598833, -2.18858882]) 68 #paraMO = np.array([[ 2.0904244 , 9.27716123, 10.35091348, -3.48496074]]) 69 #paraO = np.array([7.38193999]) 70 # for Debug (3,4,2) 71 #paraIM = np.array([[ 1.17628308, -4.79611491, 7.82715612],[11.86906762, 4.17981756, 15.40884171], 72 # [ 1.78954837, 12.80408325, 7.59701256],[ 3.39085252, 9.78864594, 5.61460097]]) 73 #paraM = np.array([ 0.31998583, 15.6483892 , 11.30653251, 9.63319875]) 74 #paraMO = np.array([[ 4.58270357, 18.69604396, -1.50649708, 5.19598108],[-5.82564925, 2.32813282, 14.310699 , 9.7612375 ]]) 75 #paraO = np.array([13.58839319, 10.01680799]) 76 #for Debug (3,4,3) 77 #paraIM = np.array([[ 7.84220612, 11.00858871, 15.40057016],[ 4.73432349, 11.65162087, 3.72713842], 78 # [ 6.76352431, 18.33213946, 12.05786182],[ 1.10551116, 10.86430962, 13.12483415]]) 79 #paraM = np.array([17.4944 , 9.28877255, 19.01824028, 13.60807014]) 80 #paraMO = np.array([[ 17.1177851 , 4.74404933, 7.25812914, 2.83400745], 81 # [ 8.72608932, -12.893494 , 8.11165234, 18.13834784], 82 # [ 4.01719631, 8.32514887, 15.03075945, 3.91946772]]) 83 #paraO = np.array([17.0558952 , 8.31617509, 15.87453088]) 84 85 count = 0 86 while count < maxTurn: 87 error = 0.0 88 for i in range(len): 89 x = data[i,:dimIn] # 真实输入,1 × dimIn 90 y = data[i,dimIn:] # 真实输出,1 × dimOut 91 t = sigmoid(np.sum(x * paraIM,1) - paraM) # 中间层输出,1 × dimMid 92 w = sigmoid(np.sum(t * paraMO,1) - paraO) # 输出层输出,1 × dimOut 93 g = w * (1 - w) * (y - w) # 1 × dimOut 94 e = t * (1 - t) * np.sum(g * paraMO.T,1) # 1 × dimMid 95 paraMO += ita * np.tile(g,[dimMid,1]).T * np.tile(t,[dimOut,1]) 96 paraO += -ita * g 97 paraIM += ita * np.tile(e,[dimIn,1]).T * np.tile(x,[dimMid,1]) 98 paraM += -ita * e 99 error += np.sum((y - w)**2) 100 error /= len 101 count += 1 102 print("count = ", count, ", error = ", error) 103 if error < epsilon: 104 break 105 return (paraIM, paraM, paraMO, paraO) # 返回两个系数矩阵和两个偏移向量 106 107 def test(dimIn, dimMid, dimOut): # 测试函数,给定输入维度,中间层神经元个数,输出维度 108 allData = createData(dimIn, dimOut, dataSize) 109 trainData, testData = dataSplit(allData, int(dataSize * trainRatio)) 110 111 para = bp(trainData,dimIn,dimMid,dimOut) 112 113 myResult = [ judge(i[0:dimIn], para) for i in testData ] 114 errorRatio = np.sum((np.array(myResult) - testData[:,dimIn:].astype(int))**2) / (dataSize*(1 - trainRatio) * dimOut) 115 print("dimIn = "+ str(dimIn) + ", dimMid = "+ str(dimMid) + ", dimOut = " + str(dimOut) + ", errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4))) 116 117 if dimOut >= 4: # 画图部分,4维以上不画图,只输出测试错误率 118 return 119 errorP = [] 120 classP = [ [] for i in range(2**dimOut) ] 121 for i in range(np.shape(testData)[0]): 122 if (myResult[i] != testData[i,dimIn:]).any(): 123 errorP.append(testData[i,:dimIn]) 124 else: 125 classP[myHash(testData[i,dimIn:])].append(testData[i,:dimIn]) 126 errorP = np.array(errorP) 127 classP = [ np.array(classP[i]) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] 128 129 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 130 131 if dimIn == 1: 132 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 133 plt.ylim(-0.25,1.25) 134 for i in range(2**dimOut): 135 plt.scatter(classP[i][:,0], np.ones(len(classP[i]))*i, color = myColor(i/(2**dimOut)), s = 10, label = "class" + str(i)) 136 if len(errorP) != 0: 137 plt.scatter(errorP[:,0], (errorP[:,0]>0.5).astype(int), color = myColor(1), s = 10, label = "errorData") 138 plt.text(0.75, 0.92, "errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 139 size = 15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 140 R = [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(i / (2**dimOut))) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(1)) ] 141 plt.legend(R, [ "class" + str(i) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + ["errorData"], loc=[0.84, 0.012], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 142 143 if dimIn == 2: 144 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 145 plt.ylim(0.0,1.0) 146 for i in range(2**dimOut): 147 plt.scatter(classP[i][:,0], classP[i][:,1], color = myColor(i/(2**dimOut)), s = 10, label = "class" + str(i)) 148 if len(errorP) != 0: 149 plt.scatter(errorP[:,0], errorP[:,1], color = myColor(1), s = 10, label = "errorData") 150 plt.text(0.75, 0.92, "errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 151 size = 15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 152 R = [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(i / (2**dimOut))) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(1)) ] 153 plt.legend(R, [ "class" + str(i) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + ["errorData"], loc=[0.84, 0.012], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 154 155 if dimIn == 3: 156 ax = Axes3D(fig) 157 ax.set_xlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 158 ax.set_ylim3d(0.0, 1.0) 159 ax.set_zlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 160 ax.set_xlabel('X', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 161 ax.set_ylabel('Y', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 162 ax.set_zlabel('Z', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 163 for i in range(2**dimOut): 164 ax.scatter(classP[i][:,0], classP[i][:,1],classP[i][:,2], color = myColor(i/(2**dimOut)), s = 10, label = "class" + str(i)) 165 if len(errorP) != 0: 166 ax.scatter(errorP[:,0], errorP[:,1],errorP[:,2], color = myColor(1), s = 10, label = "errorData") 167 ax.text3D(0.8, 1, 1.15, "errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 168 size = 12, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1, 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1, 1, 1))) 169 R = [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(i / (2**dimOut))) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + [ Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = myColor(1)) ] 170 plt.legend(R, [ "class" + str(i) for i in range(2**dimOut) ] + ["errorData"], loc=[0.85, 0.02], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 171 172 fig.savefig("R:\dimIn" + str(dimIn) + "dimMid" + str(dimMid) + "dimOut" + str(dimOut) + ".png") 173 plt.close() 174 175 if __name__ == '__main__': 176 test(3,4,1) 177 test(3,4,2) 178 test(3,4,3) 179 test(2,4,1) 180 test(2,4,2) 181 test(2,3,1) 182 test(2,5,1) 183 test(1,3,1)
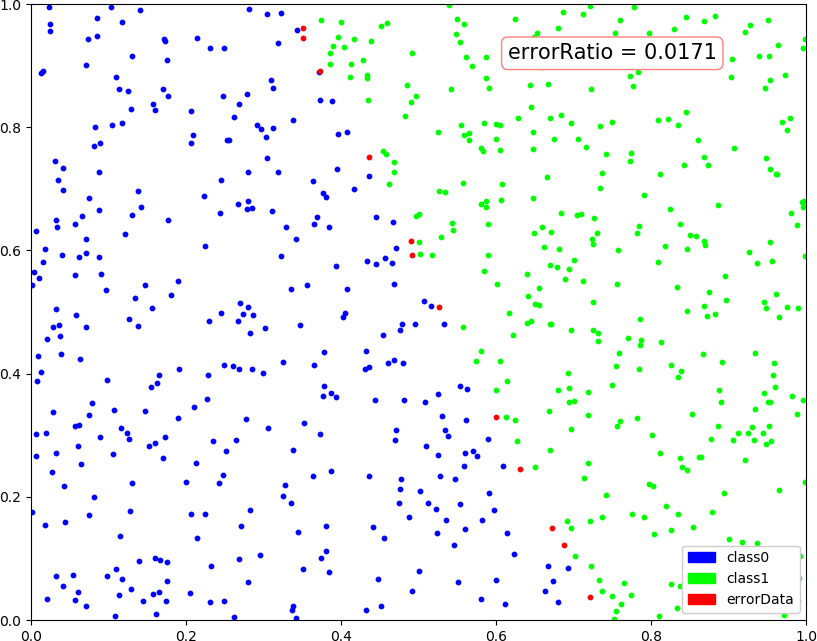
● 输出结果,写明了输入维度,中间层维度,输出维度,前三个的训练论轮较多,偷懒打表了。可见数据维度越高训练时间越长,单纯增加或减少中间层的神经元个数不一定会改善精度或训练速度
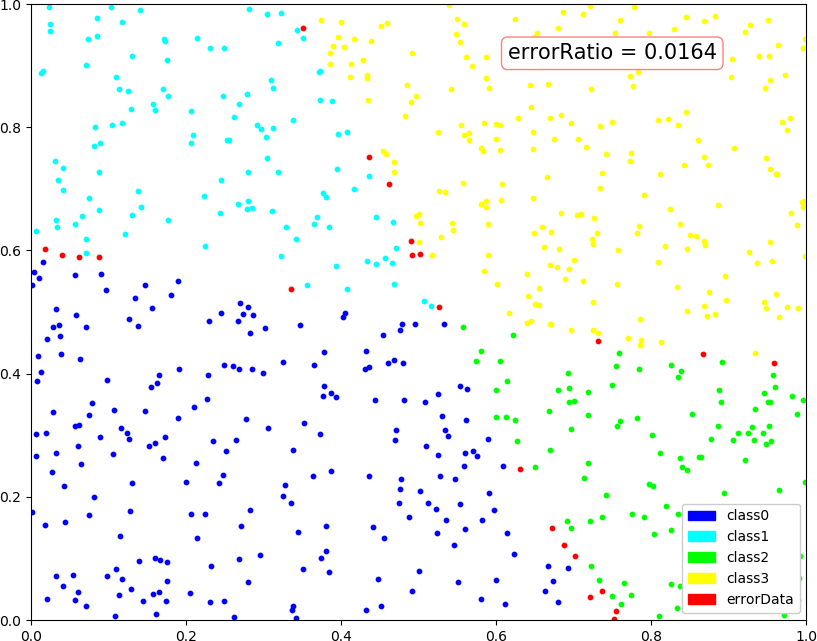
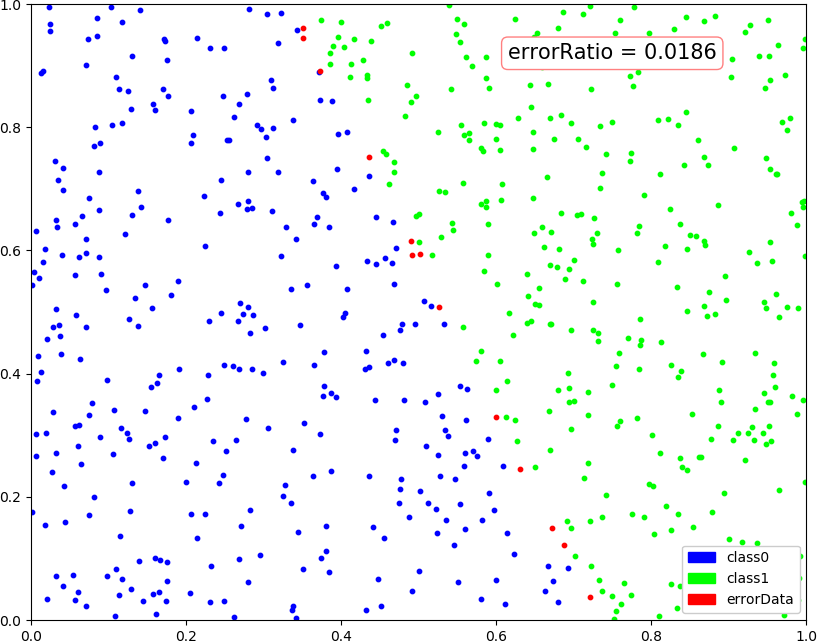
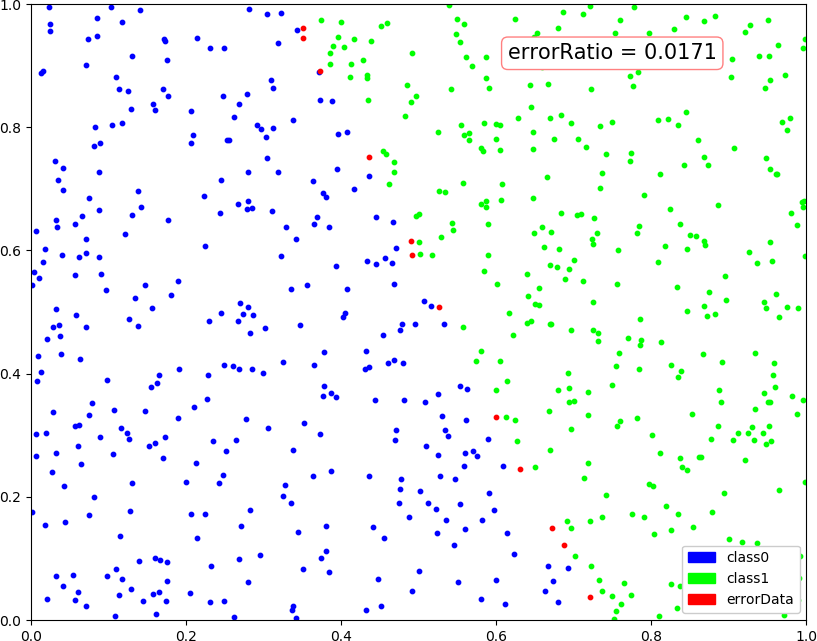
count = 1 , error = 0.009960528091961436 dimIn = 3, dimMid = 4, dimOut = 1, errorRatio = 0.0157 count = 1 , error = 0.009961970578632297 dimIn = 3, dimMid = 4, dimOut = 2, errorRatio = 0.0221 count = 500 , error = 0.01439582086937022 dimIn = 3, dimMid = 4, dimOut = 3, errorRatio = 0.0119 count = 185 , error = 0.01000959424865353 count = 186 , error = 0.009996998960686504 dimIn = 2, dimMid = 4, dimOut = 1, errorRatio = 0.0171 count = 368 , error = 0.010011781526423453 count = 369 , error = 0.009995998845193808 dimIn = 2, dimMid = 4, dimOut = 2, errorRatio = 0.0164 count = 183 , error = 0.01000216394730506 count = 184 , error = 0.009989705432858783 dimIn = 2, dimMid = 3, dimOut = 1, errorRatio = 0.0186 count = 188 , error = 0.010007727220216402 count = 189 , error = 0.009995233860763614 dimIn = 2, dimMid = 5, dimOut = 1, errorRatio = 0.0171
● 画图:(3,4,1),(3,4,2),(3,4,3)
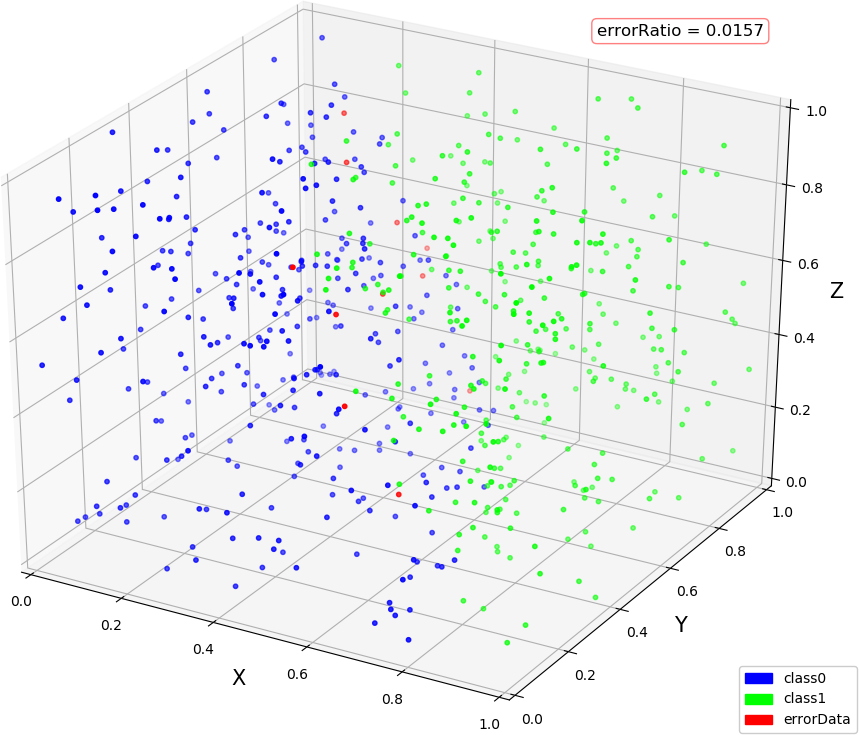
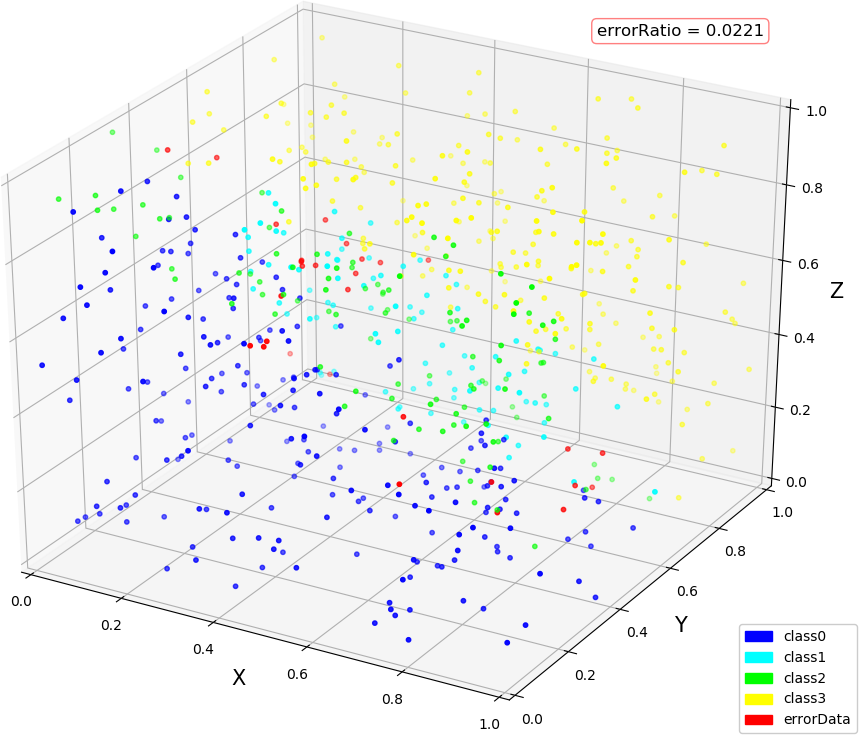
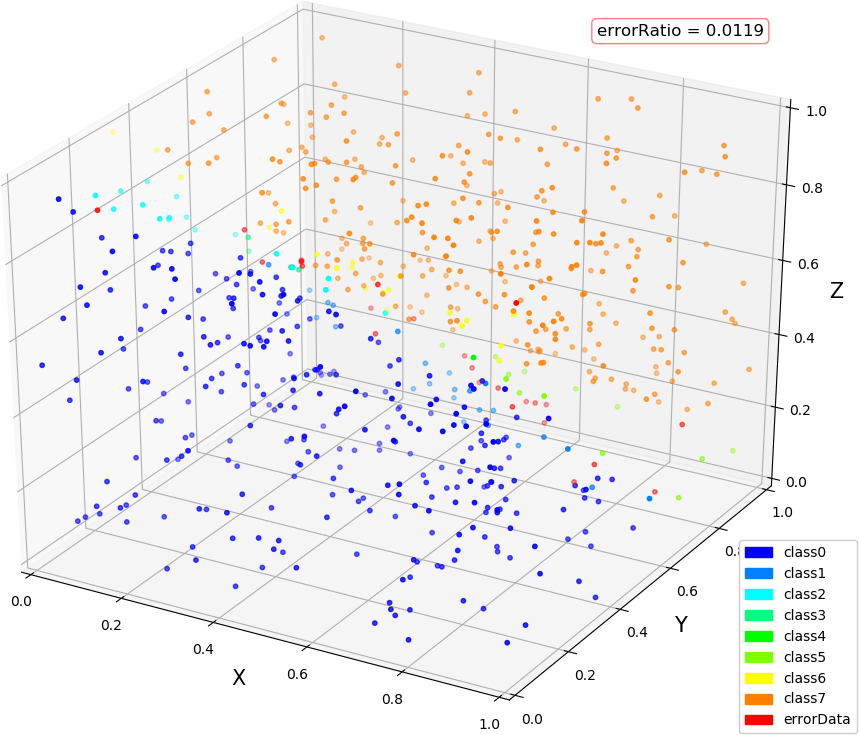
● 画图:(2,4,1),(2,4,2),(2,3,1),(2,5,1)
● 画图:(1,3,1)
