- 最小生成树(Minimum Span Tree):对于带权无向连通图。所有节点都连通且总权值最小。应用:电缆布线、网络、电路设计
- 找V-1条边,连接V个顶点,总权值最小
- 切分定理(Cut Property):给定任意切分,横切边中权值最小的边必属于最小生成树
- 切分:把图中节点分为两部分
- 横切边:边的两个端点属于切分的不同两边
- 证明:反证法,假设横切边中一条权值不是最小的边属于最小生成树,给生成树添加横切边中权值最小的边形成环,删掉权值不是最小的边打破环得到新的权值更小的生成树,与假设矛盾
- 实现:从一个点开始,不断扩散,求出最小生成树
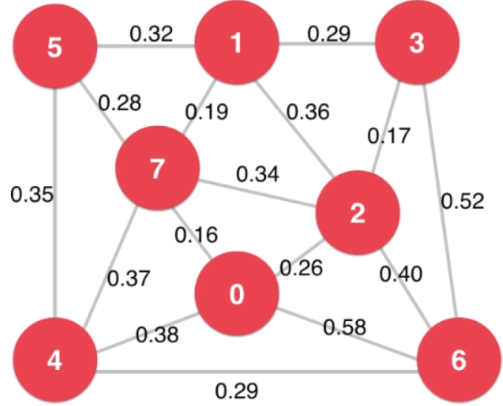
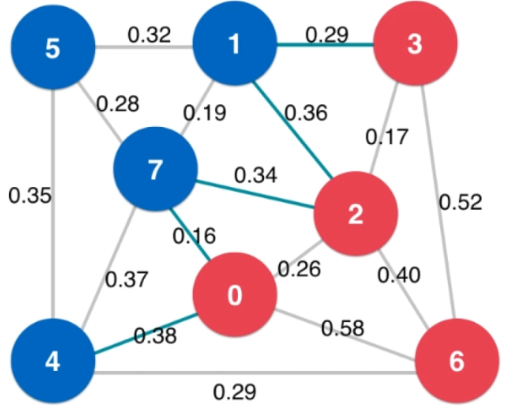
main.cpp(测试有权图)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include "SparseGraph.h" 4 #include "DenseGraph.h" 5 #include "ReadGraph.h" 6 #include "Component.h" 7 #include "Path.h" 8 #include "ShortestPath.h" 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 int main(){ 13 14 string filename = "testG1.txt"; 15 int V = 8; 16 cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2); 17 18 // Test Weighted Dense Graph 19 DenseGraph<double> g1 = DenseGraph<double>(V,false); 20 ReadGraph<DenseGraph<double>,double> readGraph(g1, filename); 21 g1.show(); 22 cout<<endl; 23 24 // Test Weighted Dense Graph 25 SparseGraph<double> g2 = SparseGraph<double>(V,false); 26 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> SparseGraph(g2, filename); 27 g2.show(); 28 cout<<endl; 29 30 return 0; 31 }
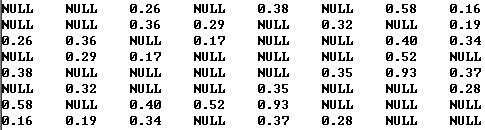
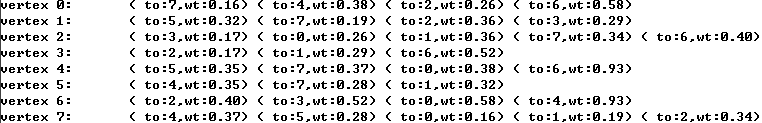
Edge.h

1 #ifndef INC_01_WEIGHTED_GRAPH_EDGE_H 2 #define INC_01_WEIGHTED_GRAPH_EDGE_H 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 // 边 9 template<typename Weight> 10 class Edge{ 11 private: 12 int a,b; // 边的两边 13 Weight weight; // 边的权值 14 public: 15 // 构造函数 16 Edge(int a, int b, Weight weight){ 17 this->a = a; 18 this->b = b; 19 this->weight = weight; 20 } 21 // 空的构造函数,所有成员变量取默认值 22 Edge(){} 23 ~Edge(){} 24 int v(){ return a; } // 返回第一个顶点 25 int w(){ return b; } // 返回第二个顶点 26 Weight wt(){ return weight;} // 返回权值 27 28 // 给定一个顶点,返回另一个顶点 29 int other(int x){ 30 assert( x == a || x == b ); 31 return x == a ? b : a; 32 } 33 34 // 输出边的信息 35 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, const Edge &e){ 36 os<<e.a<<"-"<<e.b<<": "<<e.weight; 37 return os; 38 } 39 40 // 边的大小比较,比较边的权值 41 bool operator<(Edge<Weight>& e){ 42 return weight < e.wt(); 43 } 44 bool operator<=(Edge<Weight>& e){ 45 return weight <= e.wt(); 46 } 47 bool operator>(Edge<Weight>& e){ 48 return weight > e.wt(); 49 } 50 bool operator>=(Edge<Weight>& e){ 51 return weight >= e.wt(); 52 } 53 bool operator==(Edge<Weight>& e){ 54 return weight == e.wt(); 55 } 56 }; 57 58 #endif //INC_01_WEIGHTED_GRAPH_EDGE_H
ReadGraph.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <fstream> 4 #include <sstream> 5 #include <cassert> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template <typename Graph, typename Weight> 10 class ReadGraph{ 11 public: 12 // 从文件filename中读取图的信息,存进graph中 13 ReadGraph(Graph &graph, const string &filename){ 14 ifstream file(filename); 15 string line; 16 int V,E; 17 18 assert(file.is_open()); 19 20 // 读取图中第一行节点数和边数 21 assert(getline(file,line)); 22 stringstream ss(line); 23 ss>>V>>E; 24 25 assert( V == graph.V() ); 26 27 // 读取每一条边的信息 28 for( int i = 0 ; i < E ; i ++ ){ 29 30 assert( getline(file, line) ); 31 stringstream ss(line); 32 33 int a,b; 34 Weight w; 35 ss>>a>>b>>w; 36 assert( a >= 0 && a < V ); 37 assert( b >= 0 && b < V ); 38 graph.addEdge( a , b, w ); 39 } 40 } 41 };
- Lazy Prim:MinHeap实现,复杂度O(ElogE),E为边数
main.cpp(测试Lazy Prim)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include "SparseGraph.h" 4 #include "DenseGraph.h" 5 #include "ReadGraph.h" 6 #include "Component.h" 7 #include "Path.h" 8 #include "ShortestPath.h" 9 #include "LazyPrimMST.h" 10 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int main(){ 14 15 string filename = "testG1.txt"; 16 int V = 8; 17 SparseGraph<double> g = SparseGraph<double>(V, false); 18 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> readGraph(g, filename); 19 20 // Test Weighted Dense Graph 21 cout << "Test Lazy Prim MST:"<< endl; 22 LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST(g); 23 vector<Edge<double>> mst = lazyPrimMST.mstEdge(); 24 for( int i = 0 ; i < mst.size() ; i ++ ) 25 cout << mst[i] << endl; 26 cout << "The MST weight is: "<<lazyPrimMST.result()<<endl; 27 28 cout<<endl; 29 30 return 0; 31 }
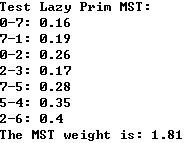
LazyPrimMST.h

1 #include "MinHeap.h" 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template<typename Graph, typename Weight> 6 class LazyPrimMST{ 7 private: 8 Graph &G; // 图的引用 9 MinHeap<Edge<Weight>> pq; // 用最小堆作为优先队列 10 vector<Edge<Weight>> mst; // 最小生成树包含的所有边 11 bool *marked; // 标记数组,标记节点i在运行过程中是否被访问 12 Weight mstWeight; // 最小生成树的权 13 14 void visit(int v){ 15 assert( !marked[v] ); 16 // 将节点v标记为访问过 17 marked[v] = true; 18 19 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G,v); 20 for( Edge<Weight>* e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ) 21 if( !marked[e->other(v)] ) 22 pq.insert(*e); 23 } 24 25 public: 26 // 初始化,最差情况下所有边都要进入最小堆 27 LazyPrimMST(Graph &graph):G(graph), pq(MinHeap<Edge<Weight>>(graph.E())){ 28 marked = new bool[G.V()]; // 顶点个数 29 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ) 30 marked[i] = false; 31 mst.clear(); 32 33 // Lazy Prim 34 // 时间复杂度O(ElogE),E为边数 35 visit(0); 36 while( !pq.isEmpty() ){ 37 Edge<Weight> e = pq.extractMin(); 38 // e不是横切边 39 if( marked[e.v()] == marked[e.w()] ) 40 continue; 41 mst.push_back( e ); 42 if( !marked[e.v()] ) 43 visit( e.v() ); 44 else 45 visit( e.w() ); 46 } 47 mstWeight = mst[0].wt(); 48 for( int i = 1 ; i < mst.size() ; i ++ ) 49 mstWeight += mst[i].wt(); 50 } 51 52 ~LazyPrimMST(){ 53 delete[] marked; 54 } 55 56 vector<Edge<Weight>> mstEdge(){ 57 return mst; 58 } 59 60 Weight result(){ 61 return mstWeight; 62 } 63 };
PrimMST.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cassert> 4 #include "Edge.h" 5 #include "IndexMinHeap.h" 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template<typename Graph, typename Weight> 10 class PrimMST{ 11 private: 12 Graph &G; // 图的引用 13 IndexMinHeap<Weight> ipq; // 最小索引堆(辅助) 14 vector<Edge<Weight>*> edgeTo; // 访问的点所对应的边(辅助) 15 bool *marked; // 标记数组,运行过程中节点i是否被访问 16 vector<Edge<Weight>> mst; // 最小生成树包含的所有边(为什么不加*) 17 Weight mstWeight; // 最小生成树的权值 18 void visit(int v){ 19 assert( !marked[v] ); 20 marked[v] = true; 21 22 // 遍历 23 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G,v); 24 for( Edge<Weight>* e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ){ 25 // 相邻顶点 26 int w = e->other(v); 27 // 若边的另一端未被访问 28 if( !marked[w] ){ 29 // 如果未考虑过这个端点,将端点和与之相连的边加入索引堆 30 if( !edgeTo[w] ){ 31 ipq.insert(w, e->wt()); 32 edgeTo[w] = e; 33 } 34 // 如果考虑过这个端点,但现在的边比之前考虑的更短,则替换 35 else if( e->wt() < edgeTo[w]->wt() ){ 36 edgeTo[w] = e; 37 ipq.change(w, e->wt()); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 public: 44 PrimMST(Graph &graph):G(graph),ipq(IndexMinHeap<double>(graph.V())){ 45 marked = new bool[G.V()]; 46 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 47 marked[i] = false; 48 edgeTo.push_back(NULL); 49 } 50 mst.clear(); 51 // Prim 52 visit(0); 53 while( !ipq.isEmpty() ){ 54 int v = ipq.extractMinIndex(); 55 assert( edgeTo[v] ); 56 mst.push_back( *edgeTo[v] ); 57 visit(v); 58 } 59 60 mstWeight = mst[0].wt(); 61 for( int i = 1 ; i < mst.size() ; i ++ ) 62 mstWeight += mst[i].wt(); 63 } 64 65 ~PrimMST(){ 66 delete[] marked; 67 } 68 69 vector<Edge<Weight>> mstEdge(){ 70 return mst; 71 } 72 73 Weight result(){ 74 return mstWeight; 75 } 76 };
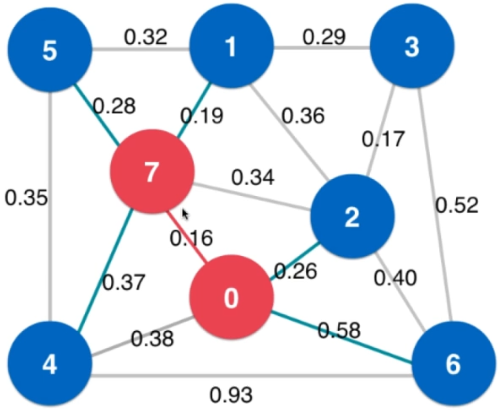
- Prim:IndexMinHeap实现,复杂度O(ElogV),V为节点数
- 索引堆存放当前在最小生成树中的节点与其他节点相连的边
- 从起点开始,遍历相邻节点,更新索引堆中的权值
- visit(7)操作后索引堆状态(0.19加入最小生成树)
![]()
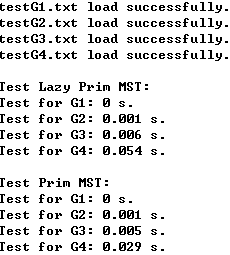
main_performance.cpp(测试算法性能)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include "SparseGraph.h" 4 #include "DenseGraph.h" 5 #include "ReadGraph.h" 6 #include "Component.h" 7 #include "Path.h" 8 #include "ShortestPath.h" 9 #include "LazyPrimMST.h" 10 #include "PrimMST.h" 11 #include <ctime> 12 13 using namespace std; 14 15 int main(){ 16 17 string filename1 = "testG1.txt"; 18 int V1 = 8; 19 20 string filename2 = "testG2.txt"; 21 int V2 = 250; 22 23 string filename3 = "testG3.txt"; 24 int V3 = 1000; 25 26 string filename4 = "testG4.txt"; 27 int V4 = 10000; 28 29 SparseGraph<double> g1 = SparseGraph<double>(V1, false); 30 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> readGraph1(g1, filename1); 31 cout<<filename1<<" load successfully."<<endl; 32 33 SparseGraph<double> g2 = SparseGraph<double>(V2, false); 34 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> readGraph2(g2, filename2); 35 cout<<filename2<<" load successfully."<<endl; 36 37 SparseGraph<double> g3 = SparseGraph<double>(V3, false); 38 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> readGraph3(g3, filename3); 39 cout<<filename3<<" load successfully."<<endl; 40 41 SparseGraph<double> g4 = SparseGraph<double>(V4, false); 42 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<double>,double> readGraph4(g4, filename4); 43 cout<<filename4<<" load successfully."<<endl; 44 45 cout<<endl; 46 47 clock_t startTime, endTime; 48 49 // Test Lazy Prim MST 50 cout<<"Test Lazy Prim MST:"<<endl; 51 52 startTime = clock(); 53 LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST1(g1); 54 endTime = clock(); 55 cout<<"Test for G1: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 56 57 startTime = clock(); 58 LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST2(g2); 59 endTime = clock(); 60 cout<<"Test for G2: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 61 62 startTime = clock(); 63 LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST3(g3); 64 endTime = clock(); 65 cout<<"Test for G3: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 66 67 startTime = clock(); 68 LazyPrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> lazyPrimMST4(g4); 69 endTime = clock(); 70 cout<<"Test for G4: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 71 72 cout<<endl; 73 74 // Test Prim MST 75 cout<<"Test Prim MST:"<<endl; 76 77 startTime = clock(); 78 PrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> PrimMST1(g1); 79 endTime = clock(); 80 cout<<"Test for G1: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 81 82 startTime = clock(); 83 PrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> PrimMST2(g2); 84 endTime = clock(); 85 cout<<"Test for G2: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 86 87 startTime = clock(); 88 PrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> PrimMST3(g3); 89 endTime = clock(); 90 cout<<"Test for G3: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 91 92 startTime = clock(); 93 PrimMST<SparseGraph<double>, double> PrimMST4(g4); 94 endTime = clock(); 95 cout<<"Test for G4: "<<(double)(endTime-startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<" s."<<endl; 96 97 cout<<endl; 98 99 return 0; 100 }
- Kruskal:MinHeap+Union Find实现,复杂度O(ElogE)
- 先把边按权值排序,把权最小的边加入最小生成树,并判断是否生成环,直到得到V-1条边构成的生成树
- 如果横切边有相等的边:算法依然成立,任选一个边,图存在多个最小生成树
- Vyssotsky's Algorithm:将边逐渐地添加到生成树中,一旦形成环,删除环中权值最大的边(没有好的数据结构支撑)
KruskalMST.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include "MinHeap.h" 4 #include "UF.h" 5 #include "Edge.h" 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template <typename Graph, typename Weight> 10 class KruskalMST{ 11 12 private: 13 vector<Edge<Weight>> mst; // MST的所有边 14 Weight mstWeight; // MST的权值 15 public: 16 KruskalMST(Graph &graph){ 17 MinHeap<Edge<Weight>> pq( graph.E() ); 18 // 将所有边放进最小堆中,完成排序 19 for( int i = 0 ; i < graph.V() ; i ++ ){ 20 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(graph,i); 21 for( Edge<Weight> *e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ){ 22 // 1-2 2-1 放一个 23 if( e->v() < e->w() ) 24 pq.insert(*e); 25 } 26 } 27 // 创建并查集查看已访问节点的连通情况 28 UnionFind uf(graph.V()); 29 while( !pq.isEmpty() && mst.size() < graph.V() - 1 ){ 30 Edge<Weight> e = pq.extractMin(); 31 // 是否成环 32 if( uf.isConnected( e.v() , e.w() )) 33 continue; 34 mst.push_back( e ); 35 uf.unionElements( e.v() , e.w() ); 36 } 37 38 mstWeight = mst[0].wt(); 39 for( int i = 1 ; i < mst.size() ; i ++ ) 40 mstWeight += mst[i].wt(); 41 } 42 ~KruskalMST(){ 43 44 } 45 // 返回MST的所有边 46 vector<Edge<Weight>> mstEdge(){ 47 return mst; 48 } 49 // 返回MST的权值 50 Weight result(){ 51 return mstWeight; 52 } 53 };
- 单源最短路径:最短路径树(所有顶点距离起始顶点权值最小)
- 广度优先遍历求出了无向图中的单源最短路径
- 松弛操作(Relaxation):找到一条经过更多顶点但总权值更小的路径。是最短路径求解的核心操作

- dijkstra:IndexMinHeap实现,复杂度O(ElogV)。可解决有/无向图的单源最短路径问题(无向图相当于每条边保存方向相反的两条边),要求图中不能有负权边
- 访问距上个点最短的点,遍历邻边,Relaxation,更新IndexMinHeap
main.cpp(测试dijkstra算法)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SparseGraph.h" 3 #include "DenseGraph.h" 4 #include "ReadGraph.h" 5 #include "Dijkstra.h" 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int main(){ 10 11 string filename = "testG1.txt"; 12 int V = 5; 13 SparseGraph<int> g = SparseGraph<int>(V, true); 14 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<int>,int> readGraph(g, filename); 15 16 cout<<"Test Dijkstra:"<<endl<<endl ; 17 Dijkstra<SparseGraph<int>, int> dij(g,0); 18 for( int i = 0 ; i < V ; i ++ ){ 19 if(dij.hasPathTo(i)){ 20 cout<<"Shortest Path to "<<i<<" : "<<dij.shortestPathTo(i)<<endl; 21 dij.showPath(i); 22 } 23 else 24 cout<<"No Path to "<<i<<endl; 25 cout<<"-----------"<<endl; 26 } 27 return 0; 28 }
dijkstra.h

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include "Edge.h" 5 #include "IndexMinHeap.h" 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 template<typename Graph, typename Weight> 10 class Dijkstra{ 11 private: 12 Graph &G; 13 int s; // 起始点 14 Weight *distTo; // distTo[i]记录从s到i的最短路径长度 15 bool *marked; // marked[i]记录节点i是否被访问 16 vector<Edge<Weight>*> from; // from[i]记录到达i的边是哪条 17 // 用于恢复最短路径 18 // 使用*便于初始化赋空值 19 20 public: 21 Dijkstra(Graph &graph, int s):G(graph){ 22 assert( s >= 0 && s < G.V() ); 23 this->s = s; 24 distTo = new Weight[G.V()]; 25 marked = new bool[G.V()]; 26 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 27 // 初始化为默认值 28 distTo[i] = Weight(); 29 marked[i] = false; 30 from.push_back(NULL); 31 } 32 // 索引堆记录当前找到的到达每个顶点的最短距离 33 IndexMinHeap<Weight> ipq(G.V()); 34 // Dijkstra 35 // 初始化起始点s 36 distTo[s] = Weight(); 37 from[s] = new Edge<Weight>(s, s, Weight()); 38 ipq.insert(s, distTo[s] ); 39 marked[s] = true; 40 ipq.insert( s , distTo[s] ); 41 while( !ipq.isEmpty() ){ 42 int v = ipq.extractMinIndex(); 43 // distTo[v]是s到v的最短距离 44 marked[v] = true; 45 // 松弛操作 46 // 访问v的所有邻边 47 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G, v); 48 for( Edge<Weight>* e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ){ 49 int w = e->other(v); 50 // 若s到w的最短路径还未找到 51 if( !marked[w] ){ 52 // 若w以前未访问过 53 // 或访问过,但通过当前v点到w点距离更短,则更新 54 if( from[w] == NULL || distTo[v] + e->wt() < distTo[w] ){ 55 distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e->wt(); 56 from[w] = e; 57 if( ipq.contain(w) ) 58 ipq.change(w, distTo[w]); 59 else 60 ipq.insert(w, distTo[w]); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 ~Dijkstra(){ 68 delete[] distTo; 69 delete[] marked; 70 delete from[0]; 71 } 72 73 // 返回从s到w的最短路径长度 74 Weight shortestPathTo( int w ){ 75 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 76 assert( hasPathTo(w) ); 77 return distTo[w]; 78 } 79 // 判断从s到w是否连通 80 bool hasPathTo( int w ){ 81 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 82 return marked[w]; 83 } 84 // 寻找从s到w的最短路径,将整个路径经过的边放入vec 85 void shortestPath( int w, vector<Edge<Weight>> &vec){ 86 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 87 assert( hasPathTo(w) ); 88 // 通过from数组逆向查找从s到w的路径,存入栈中 89 stack<Edge<Weight>*> s; 90 Edge<Weight> *e = from[w]; 91 while( e->v() != e->w() ){ 92 s.push(e); 93 e = from[e->v()]; 94 } 95 // 从栈取出元素,获得顺序的从s到w的路径 96 while( !s.empty() ){ 97 e = s.top(); 98 vec.push_back( *e ); 99 s.pop(); 100 } 101 } 102 // 打印从s到w的路径 103 void showPath( int w ){ 104 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 105 vector<Edge<Weight>> vec; 106 shortestPath(w, vec); 107 for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){ 108 cout << vec[i].v() << " -> "; 109 if( i == vec.size()-1 ) 110 cout << vec[i].w() << endl; 111 } 112 } 113 };



- 负权边问题:本质上仍是松弛操作
- 如果一个图有负权环,则不存在最短路径,如下图的1-2
- Bellman-Ford单源最短路径算法:可判断图中是否有负权环,运行前不需检测。复杂度O(EV)
- 若一个图没有负权环,则从一个点到另一点的最短路径,最多经过所有的V个顶点,有V-1条边,否则存在顶点经过了两次,既存在负权环
- 对一个点的一次松弛操作,就是找到经过这个点的另外一条路径,多一条边,权值更小;若图没有负权环,从一个点到另外一点的最短路径,最多经过所有的V个顶点,有V-1条边;对所有点进行V-1次松弛操作,即可找到从原点到其他所有点的最短路径;如果还可以继续松弛,则原图中有负权环
- 适用于有向图,若是无向图,负边自身构成负权环


main.cpp(测试Bellman-Ford)

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "SparseGraph.h" 3 #include "DenseGraph.h" 4 #include "ReadGraph.h" 5 #include "BellmanFord1.h" 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 // 测试Bellman-Ford算法 10 int main() { 11 string filename = "testG2.txt"; 12 //string filename = "testG_negative_circle.txt"; 13 int V = 5; 14 SparseGraph<int> g = SparseGraph<int>(V, true); 15 ReadGraph<SparseGraph<int>, int> readGraph(g, filename); 16 cout<<"Test Bellman-Ford:"<<endl<<endl; 17 int s = 0; 18 BellmanFord<SparseGraph<int>, int> bellmanFord(g, s); 19 if( bellmanFord.negativeCycle() ) 20 cout<<"The graph contain negative cycle!"<<endl; 21 else 22 for( int i = 0 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { 23 if(i == s) 24 continue; 25 if (bellmanFord.hasPathTo(i)) { 26 cout << "Shortest Path to " << i << " : " << bellmanFord.shortestPathTo(i) << endl; 27 bellmanFord.showPath(i); 28 } 29 else 30 cout << "No Path to " << i << endl; 31 cout << "----------" << endl; 32 } 33 return 0; 34 }
BellmanFord.h

1 #include <stack> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include "Edge.h" 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 template <typename Graph, typename Weight> 8 class BellmanFord{ 9 private: 10 Graph &G; 11 int s; // 起始点 12 Weight* distTo; // distTo[i]为从起始点s到i的最短路径长度 13 vector<Edge<Weight>*> from; // from[i]为最短路径中,到达i的是哪条边 14 bool hasNegativeCycle; // 是否有负权环 15 // 判断是否有负权环 16 bool detectNegativeCycle(){ 17 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 18 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G,i); 19 for( Edge<Weight>* e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ) 20 if( from[e->v()] && distTo[e->v()] + e->wt() < distTo[e->w()] ) 21 return true; 22 } 23 return false; 24 } 25 26 public: 27 BellmanFord(Graph &graph, int s):G(graph){ 28 this->s = s; 29 distTo = new Weight[G.V()]; 30 // 初始化,所有节点s都不可达 31 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ) 32 from.push_back(NULL); 33 // 设置distTo[s] = 0,from[s]不为NULL,表示初始点s可达且距离为0 34 distTo[s] = Weight(); 35 from[s] = new Edge<Weight>(s, s, Weight()); 36 // Bellman-Ford 37 // 进行V-1轮松弛操作,每次求出从起点到其余所有点,最多用pass步可到达的最短距离 38 for( int pass = 1 ; pass < G.V() ; pass ++ ){ 39 // 每次循环中对所有边进行一遍松弛操作 40 // 先遍历所有顶点,然后遍历和所有顶点相邻的所有边 41 for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){ 42 typename Graph::adjIterator adj(G,i); 43 for( Edge<Weight>* e = adj.begin() ; !adj.end() ; e = adj.next() ) 44 // e为i的邻边 45 // 对每个边首先判断e->v()是否到过 46 // 如果e->w()以前没有到达过,则更新distTo[e->w()] 47 // 或虽然e->w()以前到达过,但通过这个e可获得一个更短的距离 48 // 即进行一次松弛操作,更新distTo[e->w()] 49 if( from[e->v()] && (!from[e->w()] || distTo[e->v()] + e->wt() < distTo[e->w()])){ 50 distTo[e->w()] = distTo[e->v()] + e->wt(); 51 // 通过e到达e->w() 52 from[e->w()] = e; 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 hasNegativeCycle = detectNegativeCycle(); 57 } 58 ~BellmanFord(){ 59 delete[] distTo; 60 delete from[s]; 61 } 62 // 返回图中是否有负环 63 bool negativeCycle(){ 64 return hasNegativeCycle; 65 } 66 // 返回s到w的最短路径长度 67 Weight shortestPathTo( int w ){ 68 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 69 assert( !hasNegativeCycle ); 70 assert( hasPathTo(w) ); 71 return distTo[w]; 72 } 73 // 判断从s到w是否连通 74 bool hasPathTo( int w ){ 75 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 76 return from[w] != NULL; 77 } 78 // 从s到w的最短路径,将经过的边放在vec中 79 void shortestPath( int w, vector<Edge<Weight>> &vec ){ 80 // w不越界 81 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 82 // 无负权环 83 assert( !hasNegativeCycle ); 84 assert( hasPathTo(w) ); 85 // 通过from逆向查找从s到w的路径,存在栈中 86 stack<Edge<Weight>*> s; 87 Edge<Weight> *e = from[w]; 88 while( e->v() != this->s ){ 89 s.push(e); 90 e = from[e->v()]; 91 } 92 s.push(e); 93 // 从栈中依次取出元素,获得顺序的从s到w的路径 94 while( !s.empty() ){ 95 e = s.top(); 96 vec.push_back( *e ); 97 s.pop(); 98 } 99 } 100 // 打印从s到w的路径 101 void showPath(int w){ 102 assert( w >= 0 && w < G.V() ); 103 assert( !hasNegativeCycle); 104 assert( hasPathTo(w) ); 105 106 vector<Edge<Weight>> vec; 107 shortestPath(w,vec); 108 for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){ 109 cout << vec[i].v()<<" -> "; 110 if( i == vec.size()-1 ) 111 cout << vec[i].w() << endl; 112 } 113 } 114 };

- 单源最短路径算法对比(指定起点s)
dijkstra 无负权边 有向无向图均可 O(ElogV)
Bellman-Ford 无负权环 有向图 O(VE)
利用拓扑排序 有向无环图 有向图 O(V+E)
- 所有对最短路径算法(任意两点a、b)
- Floyed算法,处理无负权环的图,复杂度O(V^3)
- 最长路径算法
- 不能有正权环
- 无权图的最长路径问题是指数级难度
- 有权图,不能使用Dijkstra求最长路径
- 可使用Bellman-Ford
