概述
- 属于行为型模式
- 对象需要根据自身当前的状态进行不同行为,状态数量多且状态相关的代码频繁变更
- 在一个对象的内部状态变化时改变其行为,使其看上去就像改变了自身所属的类一样
- 组件构建过程中,某些对象的状态经常面临变化,如何对这些变化进行有效的管理?同时又维持高层模块的稳定?“状态变化”模式为这一问题提供了一种解决方案
- 经典模式:State, Memento
- State模式:某些对象的状态如果改变,其行为也会随之变化,如文档处于只读状态,其支持的行为和读写状态支持的行为就可能完全不同
- 如何在运行时根据对象的状态来透明地更改对象的行为?而不会为对象操作和状态转化间引入紧耦合?
- 类似于Strategy模式,解决if-else带来的业务判断问题,未来有新状态怎么办?(多态,运行时改变)
- 先提出抽象基类,将状态有关的操作变成状态对象的虚函数,再设计不同状态对应的类
- 虚函数本质:运行时的 if-else
- 将所有与一个特定状态相关的行为放入一个State的子类对象,在状态切换时切换成相应的对象,但同时维持State接口,实现了具体操作与状态转换间的解耦
- 为不同状态引入不同对象使得状态转换变得更加明确,且可以保证不会出现状态不一致的情况,因为转换是原子性的(彻底转换过来或者不转换)
- 若State对象没有实例变量,那么上下文可以共享一个对象,从而节省对象开销
- 每个状态只关心自己的后继状态
场景
- 对象行为随状态改变而改变
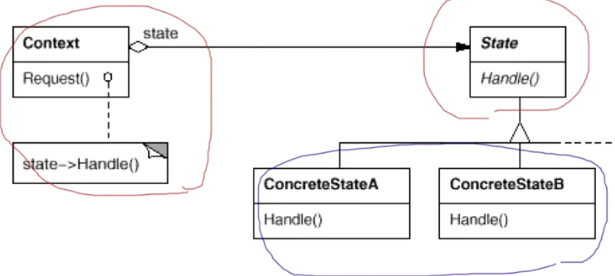
结构
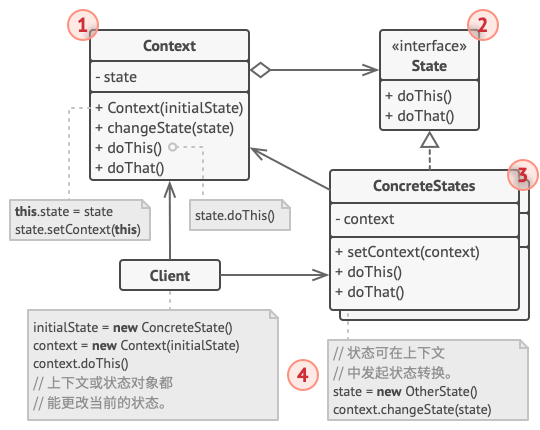
- 上下文类:保存对一个具体状态对象的引用,并将所有与该状态相关的工作委派给它
- 状态接口:声明特定于状态的方法
- 具体状态类:实现特定于状态的方法
示例1
state1.cpp

1 enum NetworkState 2 { 3 Network_Open, 4 Network_Close, 5 Network_Connect, 6 }; 7 8 class NetworkProcessor{ 9 10 NetworkState state; 11 12 public: 13 14 void Operation1(){ 15 if (state == Network_Open){ 16 17 //********** 18 state = Network_Close; 19 } 20 else if (state == Network_Close){ 21 22 //.......... 23 state = Network_Connect; 24 } 25 else if (state == Network_Connect){ 26 27 //$$$$$$$$$$ 28 state = Network_Open; 29 } 30 } 31 32 public void Operation2(){ 33 34 if (state == Network_Open){ 35 36 //********** 37 state = Network_Connect; 38 } 39 else if (state == Network_Close){ 40 41 //..... 42 state = Network_Open; 43 } 44 else if (state == Network_Connect){ 45 46 //$$$$$$$$$$ 47 state = Network_Close; 48 } 49 50 } 51 52 public void Operation3(){ 53 54 } 55 };
state2.cpp

1 class NetworkState{ 2 3 public: 4 NetworkState* pNext; 5 virtual void Operation1()=0; 6 virtual void Operation2()=0; 7 virtual void Operation3()=0; 8 9 virtual ~NetworkState(){} 10 }; 11 12 class OpenState :public NetworkState{ 13 14 static NetworkState* m_instance; 15 public: 16 static NetworkState* getInstance(){ 17 if (m_instance == nullptr) { 18 m_instance = new OpenState(); 19 } 20 return m_instance; 21 } 22 23 void Operation1(){ 24 25 //********** 26 pNext = CloseState::getInstance(); 27 } 28 29 void Operation2(){ 30 31 //.......... 32 pNext = ConnectState::getInstance(); 33 } 34 35 void Operation3(){ 36 37 //$$$$$$$$$$ 38 pNext = OpenState::getInstance(); 39 } 40 41 }; 42 43 class CloseState:public NetworkState{ } 44 //... 45 46 class NetworkProcessor{ 47 48 NetworkState* pState; 49 50 public: 51 52 NetworkProcessor(NetworkState* pState){ 53 54 this->pState = pState; 55 } 56 57 void Operation1(){ 58 //... 59 pState->Operation1(); 60 pState = pState->pNext; 61 //... 62 } 63 64 void Operation2(){ 65 //... 66 pState->Operation2(); 67 pState = pState->pNext; 68 //... 69 } 70 71 void Operation3(){ 72 //... 73 pState->Operation3(); 74 pState = pState->pNext; 75 //... 76 } 77 78 };
示例2

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <typeinfo> 3 /** 4 * The base State class declares methods that all Concrete State should 5 * implement and also provides a backreference to the Context object, associated 6 * with the State. This backreference can be used by States to transition the 7 * Context to another State. 8 */ 9 10 class Context; 11 12 class State { 13 /** 14 * @var Context 15 */ 16 protected: 17 Context *context_; 18 19 public: 20 virtual ~State() { 21 } 22 23 void set_context(Context *context) { 24 this->context_ = context; 25 } 26 27 virtual void Handle1() = 0; 28 virtual void Handle2() = 0; 29 }; 30 31 /** 32 * The Context defines the interface of interest to clients. It also maintains a 33 * reference to an instance of a State subclass, which represents the current 34 * state of the Context. 35 */ 36 class Context { 37 /** 38 * @var State A reference to the current state of the Context. 39 */ 40 private: 41 State *state_; 42 43 public: 44 Context(State *state) : state_(nullptr) { 45 this->TransitionTo(state); 46 } 47 ~Context() { 48 delete state_; 49 } 50 /** 51 * The Context allows changing the State object at runtime. 52 */ 53 void TransitionTo(State *state) { 54 std::cout << "Context: Transition to " << typeid(*state).name() << ". "; 55 if (this->state_ != nullptr) 56 delete this->state_; 57 this->state_ = state; 58 this->state_->set_context(this); 59 } 60 /** 61 * The Context delegates part of its behavior to the current State object. 62 */ 63 void Request1() { 64 this->state_->Handle1(); 65 } 66 void Request2() { 67 this->state_->Handle2(); 68 } 69 }; 70 71 /** 72 * Concrete States implement various behaviors, associated with a state of the 73 * Context. 74 */ 75 76 class ConcreteStateA : public State { 77 public: 78 void Handle1() override; 79 80 void Handle2() override { 81 std::cout << "ConcreteStateA handles request2. "; 82 } 83 }; 84 85 class ConcreteStateB : public State { 86 public: 87 void Handle1() override { 88 std::cout << "ConcreteStateB handles request1. "; 89 } 90 void Handle2() override { 91 std::cout << "ConcreteStateB handles request2. "; 92 std::cout << "ConcreteStateB wants to change the state of the context. "; 93 this->context_->TransitionTo(new ConcreteStateA); 94 } 95 }; 96 97 void ConcreteStateA::Handle1() { 98 { 99 std::cout << "ConcreteStateA handles request1. "; 100 std::cout << "ConcreteStateA wants to change the state of the context. "; 101 102 this->context_->TransitionTo(new ConcreteStateB); 103 } 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * The client code. 108 */ 109 void ClientCode() { 110 Context *context = new Context(new ConcreteStateA); 111 context->Request1(); 112 context->Request2(); 113 delete context; 114 } 115 116 int main() { 117 ClientCode(); 118 return 0; 119 }
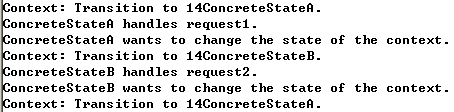
示例3

1 public interface State { 2 public void doAction(Context context); 3 } 4 5 public class StartState implements State { 6 7 public void doAction(Context context) { 8 System.out.println("Player is in start state"); 9 context.setState(this); 10 } 11 12 public String toString(){ 13 return "Start State"; 14 } 15 } 16 17 public class StopState implements State { 18 19 public void doAction(Context context) { 20 System.out.println("Player is in stop state"); 21 context.setState(this); 22 } 23 24 public String toString(){ 25 return "Stop State"; 26 } 27 } 28 29 public class Context { 30 private State state; 31 32 public Context(){ 33 state = null; 34 } 35 36 public void setState(State state){ 37 this.state = state; 38 } 39 40 public State getState(){ 41 return state; 42 } 43 } 44 45 public class StatePatternDemo { 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 Context context = new Context(); 48 49 StartState startState = new StartState(); 50 startState.doAction(context); 51 52 System.out.println(context.getState().toString()); 53 54 StopState stopState = new StopState(); 55 stopState.doAction(context); 56 57 System.out.println(context.getState().toString()); 58 } 59 }
Player is in start state
Start State
Player is in stop state
Stop State
参考
