逻辑回归
解决分类问题里最普遍的baseline model就是逻辑回归,简单同时可解释性好,使得它大受欢迎,我们来用tensorflow完成这个模型的搭建。
1.环境设定
import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2' import numpy as np #import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf tf.disable_v2_behavior() from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import time
2.数据读取
#使用tensorflow自带的工具加载MNIST手写数字集合 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('./data/mnist', one_hot=True)
#查看一下数据维度 mnist.train.images.shape
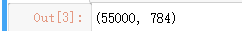
#查看target维度 mnist.train.labels.shape
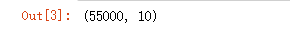
3.准备好placeholder
batch_size = 128 ## 定义参数的数据类型 数据形状(一般为一维)名称 X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 784], name='X_placeholder') Y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, 10], name='Y_placeholder') global X
4.准备好参数/权重
# tf.Variable(initializer,name) 初始化参数 和 自定义的变量名称 #tf.random_normal()函数用于从“服从指定正态分布的序列”中随机取出指定个数的值 w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal(shape=[784, 10], stddev=0.01), name='weights') #tf.zeros() 生成数组 位数 行个数 b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]), name="bias")
5.拿到每个类别的score
#tf.matmul() 两个矩阵中对应元素各自相乘 logits = tf.matmul(X, w) + b
6.计算多分类softmax的loss function
# 求交叉熵损失 entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=Y, name='loss') # 求平均 loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy)
7.准备好optimier
这里的最优化用的是随机梯度下降,我们可以选择AdamOptimizer这样的优化器
learning_rate = 0.01 #自动进行参数的导数计算及优化 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
8.在session里执行graph里定义的运算
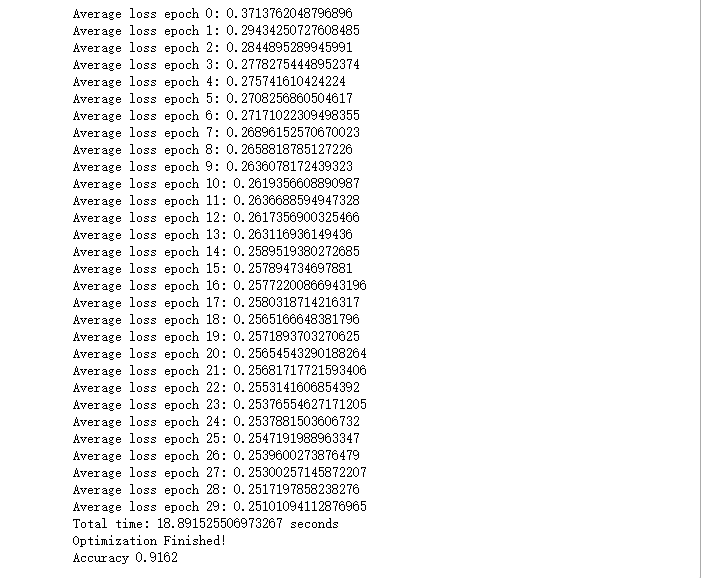
#迭代总轮次 n_epochs = 30 #分配GPU 占用率 gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.333) with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess: # 在Tensorboard里可以看到图的结构 writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./graphs/logistic_reg', sess.graph) start_time = time.time() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) n_batches = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size) for i in range(n_epochs): # 迭代这么多轮 total_loss = 0 for _ in range(n_batches): X_batch, Y_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) _, loss_batch = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={X: X_batch, Y:Y_batch}) total_loss += loss_batch print('Average loss epoch {0}: {1}'.format(i, total_loss/n_batches)) print('Total time: {0} seconds'.format(time.time() - start_time)) print('Optimization Finished!') # 测试模型 preds = tf.nn.softmax(logits) correct_preds = tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds, tf.float32)) n_batches = int(mnist.test.num_examples/batch_size) total_correct_preds = 0 for i in range(n_batches): X_batch, Y_batch = mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size) accuracy_batch = sess.run([accuracy], feed_dict={X: X_batch, Y:Y_batch}) total_correct_preds += accuracy_batch[0] print('Accuracy {0}'.format(total_correct_preds/mnist.test.num_examples)) writer.close()