一、 二叉树
1. 什么是二叉树?
在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。
通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。
二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。
2. 二叉树是一个递归的定义
(1)根结点为空则定义该二叉树为空
(2)一个根结点,可以导出一棵完整的二叉树,而它的左孩子或者右孩子,同样可以是代表一棵完整二叉树的根结点,不论它是否为空。即左子树和右子树同样为二叉树。
3. 二叉堆
(1)二叉堆一般由数组实现,分为大根堆和小根堆,可以实现O(1)的时间查找最大值(最小值)。
(2)插入一个元素O(logN),先插到末尾,然后通过swim操作上浮调整,保持堆结构
(3)删除一个元素O(logN),先把头尾元素交换,删去尾,对头进行sink操作下沉调整,保持堆结构。
(4)详情可见另外一篇博客排序系列及其拓展优化 中的基于堆的优先队列实现
二、 基于数组的二叉查找树
1. 保证数组有序
2. 通过【二分】的方法实现对数时间内查找
3. 由于是数组,要保持元素个数变化后数组依然有序,则插入和删除必然导致有一段元素需要整体移动,因此代价是O(N)
4. 基于数组的二叉查找树和堆的区别?为什么堆能保持对数级别的插入和删除?
(1)二叉查找树和堆虽然都基于数组,但是前者的数组有序,而后者只是保持堆结构(堆结构只是顶头元素是最值但是不是整体有序)
(2)二叉查找树可以查找任意关键字的元素,而堆是为了保持顶头元素的最值特性并不具备优秀的查找功能。
5. 代码实现

package search; import java.util.Random; /* * 基于有序数组的二叉搜索树 * */ public class BinarySearchST<Key extends Comparable<Key> , Value> { private Key[] keys; //键 private Value[] vals; //值 private int N;// 当前使用容量 public BinarySearchST(int capacity) { keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity]; vals = (Value[]) new Object[capacity]; } public int size() { return N; } //根据键来查找对应值 public Value get(Key key) { //找出该键在数组中的下标 int pos = rank(key); //如果找到的下标在范围内并且确实是这个键,说明找到了 if(pos < N && keys[pos].compareTo(key) == 0) { return vals[pos]; } else return null;//否则没有找到,返回空 } //二分法查找键的位置 public int rank(Key key) { int lo = 0, hi = N - 1; //二分查找 while(lo <= hi) { int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; if(keys[mid].compareTo(key) > 0) { hi = mid - 1; } else if(keys[mid].compareTo(key) < 0 ) { lo = mid + 1; } else { return mid; } } //如果找不到 之前一步lo必定等于hi, 看这个数字是大于还是小于,不论怎样,lo的位置都代表如果这个数存在 //它应该处于的位置 return lo; } public void put(Key key, Value val) { int pos = rank(key);//先看这个键有木有 //如果有只需要修改一下值就行了 if(pos < N && keys[pos].compareTo(key) == 0) { vals[pos] = val; } //如果没有就新建一个键值对 插入 //插入的位置正好是pos 那么pos之后的数都要后移一位 //如果容量已满需要扩容 for(int i=N-1; i>=pos; i--) { keys[i + 1] = keys[i]; vals[i + 1] = vals[i]; } //空出来的位置插入新键值对 keys[pos] = key; vals[pos] = val; N++; } public void delete(Key key) { int pos = rank(key);//先看这个键有木有 //如果有就删除 并且后移一位 if(pos < N && keys[pos].compareTo(key) == 0) { for(int i=pos; i<N-1; i++) { keys[i] = keys[i+1]; vals[i] = vals[i+1]; } N--; } //如果没有就返回 return; } public void show() { for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { System.out.println(keys[i].toString() + " : " + vals[i].toString()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub BinarySearchST<Integer, Integer> bs = new BinarySearchST<Integer , Integer>(20); Random r = new Random(); for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { Integer t1 = new Integer(r.nextInt(1000)); Integer t2 = new Integer(r.nextInt(1000)); bs.put(t1, t2); } bs.show(); System.out.println("size = " + bs.size()); System.out.println("*********************"); bs.put(999, 999); bs.put(555, 555); bs.show(); System.out.println("size = " + bs.size()); System.out.println("*********************"); bs.delete(555); bs.delete(1024); bs.show(); System.out.println("size = " + bs.size()); } }
三、 基于链表的二叉查找树BST
1. 结点结构
private class Node{ private Key key;//键 private Value val;//值 private Node left , right;//左孩子和右孩子 private int N ; //该子树的总结点个数 public Node() {} public Node(Key key, Value val, int N) { this.key = key; this.val = val; this.N = N; } }
2. BST类结构
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key> , Value> { private Node root; private class Node{...}//结点内部类声明 //一系列方法 }
3. 核心方法:增删改查
(1)查找
a. 基于二分
b. 利用树天生的递归特性,递归查找
//根据键找值 public Value get(Key key) { return get(root , key); } private Value get(Node x, Key key) { if(x == null) return null; int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp == 0) return x.val; else if(cmp > 0) return get(x.left , key); else return get(x.right , key); }
(2)插入
a. 插入从某种意义上包括了修改,因为改某一个键所对应的值只需要插入同键不同值即可。
b. 插入总是被插入到了某一个结点的空的左右子结点中
public void put(Key key, Value val) { root = put(root , key, val); } private Node put(Node x , Key key, Value val) { //如果没有这个键就新增一个 if(x == null) { return x = new Node(key , val, 1); } //沿途二分找键,遇到的根节点键大,则在其左子树递归查找,键小,在右子树递归查找, //直到找到相等或者发现根节点为空为止 int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp > 0) { x.left = put(x.left , key, val); } else if(cmp < 0) { x.right = put(x.right , key , val); } else { x.val = val; } //沿途回溯更新结点的size 自底向上 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; }
(3)删除
删除是BST的最复杂的操作,先考虑一下几种情况 ,假设被删除的结点记为z:
(a)z左右孩子均为空。这种情况十分简单,直接删除这个结点即可,正棵BST仍然有序

(b)z有一个孩子不空。不妨假设右孩子不空,那么只需要把z.right 作为z的父节点x的新的孩子结点即可。
比如结点x.right = z, 则只需要把x.right = z.right 即可,(x.left = z同理)BST有序性不变

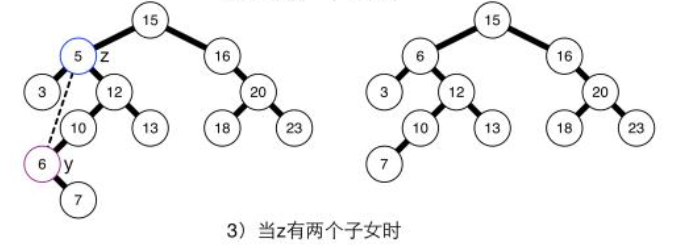
(c)z的左右孩子均不空。
-
- 假设z的父节点为x,且x.left = z (x.right = z同理可得)
- 首先把 z 暂存,存为结点 t
- 找z的右子树的最小结点(该操作为deleteMin(Node x)),不妨设为y,则y.left必为空,并且满足t.left < y < t.right。也就是说,如果把y结点放到要删除的z结点的位置,树还是有序的
- 把z结点指针指向y (z和y是同一结点), 把按照(b)情况删除结点z并返回z结点,注意经过b操作后,此时z的父节点与z的右孩子结点已经连接
- 把z的左右孩子设置为t的左右孩子
- x.left = z即可。
- 若看不明白只需要记住加黑字体是该算法的主要思想,详情见代码。
【代码实现】
//删除一棵树的最小结点 public void deleteMin() { root = deleteMin(root); } private Node deleteMin(Node x) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(x.left != null) { x.left = deleteMin(x.left); x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; } return x.right; } public void delete(Key key) { root = delete(root , key); } public Node delete(Node x, Key key) { if(x == null) return null; int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp > 0) { x.left = delete(x.left , key); } else if(cmp < 0) { x.right = delete(x.right , key); } else { //找到要删除的结点了 if(x.left == null) return x.right; if(x.right == null) return x.left; Node t = x; x = minK(t.right); x.right = deleteMin(t.right); x.left = t.left; } x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; }
4. 其他操作
- public Key ceiling(Key key) //返回大于等于key的最大值所在结点
-
public Keyfloor(Key key) //返回小于等于key的最大值所在结点
- public Key select(int k) //查找排名为K的键(树中恰好有K个小于他的键)
- public ...... //其他操作
四、 BST数据结构源码

package search; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Random; public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key> , Value> { private Node root; //结点内部类声明 private class Node{ private Key key;//键 private Value val;//值 private Node left , right;//左孩子和右孩子 private int N ; //该子树的总结点个数 public Node() {} public Node(Key key, Value val, int N) { this.key = key; this.val = val; this.N = N; } } public int size(){ return size(root); } private int size(Node x) { if(x == null) return 0; return x.N; } //根据键找值 public Value get(Key key) { return get(root , key); } private Value get(Node x, Key key) { if(x == null) return null; int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp == 0) return x.val; else if(cmp > 0) return get(x.left , key); else return get(x.right , key); } public void put(Key key, Value val) { root = put(root , key, val); } private Node put(Node x , Key key, Value val) { //如果没有这个键就新增一个 if(x == null) { return x = new Node(key , val, 1); } //沿途二分找键,遇到的根节点键大,则在其左子树递归查找,键小,在右子树递归查找, //直到找到相等或者发现根节点为空为止 int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp > 0) { x.left = put(x.left , key, val); } else if(cmp < 0) { x.right = put(x.right , key , val); } else { x.val = val; } //沿途回溯更新结点的size 自底向上 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; } //返回键的最小值 public Key minK() { return minK(root).key; } private Node minK(Node x) { if(x.left != null) { return minK(x.left); } return x; } //返回键的最小值 public Key maxK() { return maxK(root).key; } private Node maxK(Node x) { if(x.right != null) { return maxK(x.right); } return x; } //返回小于等于key的最大值 public Key floor(Key key) { Node x = floor(root , key); if(x != null) return x.key; return null; } //返回小于等于key的最大值所在结点 private Node floor(Node x , Key key) { if(x == null) return null; //比较当前根节点的键值是否大于key int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp == 0) return x; //如果根结点的键值小于key,那么小于等于key的键值有可能在根节点的右子树中,如果没有则就是根节点 else if(cmp < 0) { Node t = floor(x.right , key); if(t == null) return x; else { return t; } } //如果根节点的键值大于key,则小于等于key的键值必定在根节点的左子树中 else { return floor(x.left , key); } } public Key ceiling(Key key) { Node x = ceiling(root , key); if(x != null) return x.key; return null; } //返回大于等于key的最小值所在结点 private Node ceiling(Node x , Key key) { if(x == null) return null; //比较当前根节点的键值是否大于key int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp == 0) return x; //如果根节点的键值大于key,则大于等于key的键值有可能在根节点的左子树中,如果没有就是根节点 else if(cmp > 0) { Node t = ceiling(x.left , key); if(t == null) return x; else { return t; } } //如果根结点的键值小于key,那么大于等于key的键值一定在根节点的右子树中 else { return ceiling(x.right , key); } } //查找排名为K的键(树中恰好有K个小于他的键) public Key select(int k) { Node x = select(root , k); if(x == null) return null; return x.key; } private Node select(Node x , int k) { if(x == null) return null; int t = size(x.left); if( t > k) { return select(x.left , k); } else if(t == k) { return x; } else { return select(x.right , k - t - 1); } } //给定一个键求其排名(即求有多少个键小于它) public int rank(Key key) { return rank(root , key); } private int rank(Node x , Key key) { if(x == null) return 0; int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp == 0) { return size(x.left); } else if(cmp > 0) { return rank(x.left , key); } else { return size(x.left) + rank(x.right , key) + 1; } } //删除一棵树的最小结点 public void deleteMin() { root = deleteMin(root); } private Node deleteMin(Node x) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(x.left != null) { x.left = deleteMin(x.left); x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; } return x.right; } public void delete(Key key) { root = delete(root , key); } public Node delete(Node x, Key key) { if(x == null) return null; int cmp = x.key.compareTo(key); if(cmp > 0) { x.left = delete(x.left , key); } else if(cmp < 0) { x.right = delete(x.right , key); } else { //找到要删除的结点了 if(x.left == null) return x.right; if(x.right == null) return x.left; Node t = x; x = minK(t.right); x.right = deleteMin(t.right); x.left = t.left; } x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; return x; } //返回整棵树的迭代对象 public Iterable<Key> keys(){ return keys(minK() , maxK()); } //返回范围[lo , hi]内所有key的迭代对象 public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Queue<Key> queue = new LinkedList<Key>(); keys(root , queue, lo, hi); return queue; } //把[lo , hi]范围内的所有元素加入指定迭代对象中 private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(x == null) return ; int cmplo = x.key.compareTo(lo); int cmphi = x.key.compareTo(hi); //如果根节点大于lo说明根节点的左子树可能还有元素在此范围内 if(cmplo > 0) { keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi); } //如果根节点小于hi说明根节点的右子树可能还有元素在此范围内 if(cmphi < 0) { keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi); } //遇到一个结点在此范围内就将其加入集合 if(cmplo >= 0 && cmphi <= 0) { queue.add(x.key); } } //前序遍历 左中右遍历 顺序遍历 public void show(Node x) { if(x != null) { show(x.left); System.out.println(x.key.toString() + " : " + x.val.toString()); show(x.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub BST bst = new BST<Integer , Integer>(); Random r = new Random(); for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { Integer key = new Integer(r.nextInt(1000)); Integer value = new Integer(r.nextInt(1000)); System.out.println("key = " + key + " value = " + value); bst.put(key, value); } System.out.println("put 操作完毕"); // 186 244 336 481 507 514 663 729 743 759 761 891 bst.show(bst.root); System.out.println("show 操作完毕"); //bst.put(759, 19999); //bst.put(761, 19999); System.out.println(bst.get(9999)); System.out.println(bst.get(8888)); System.out.println(bst.floor(760)); System.out.println(bst.ceiling(760)); System.out.println(bst.maxK()); System.out.println(bst.select(0)); System.out.println(bst.rank(0)); bst.deleteMin(); bst.put(1000, 9999); bst.show(bst.root); bst.delete(1000); bst.show(bst.root); System.out.println("################"); Iterable<Integer> it = bst.keys(200,600); for(Integer i : it) { System.out.print(i.toString() + " "); } } }
