Key Task
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1809 Accepted Submission(s): 770
Problem Description
The Czech Technical University is rather old — you already know that it celebrates 300 years of its existence in 2007. Some of the university buildings are old as well. And the navigation in old buildings can sometimes be a little bit tricky, because of strange
long corridors that fork and join at absolutely unexpected places.
The result is that some first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes. Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves this game.
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and green. Each key can open only doors of the same color.
You can move between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on a square with an appropriate key before.
The result is that some first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes. Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves this game.
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and green. Each key can open only doors of the same color.
You can move between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on a square with an appropriate key before.
Input
The input consists of several maps. Each map begins with a line containing two integer numbers R and C (1 ≤ R, C ≤ 100) specifying the map size. Then there are R lines each containing C characters. Each character is one of the following:
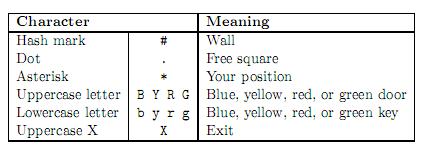
Note that it is allowed to have
- more than one exit,
- no exit at all,
- more doors and/or keys of the same color, and
- keys without corresponding doors and vice versa.
You may assume that the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.
There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two zeros in place of the map size.

Note that it is allowed to have
You may assume that the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.
There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two zeros in place of the map size.
Output
For each map, print one line containing the sentence “Escape possible in S steps.”, where S is the smallest possible number of step to reach any of the exits. If no exit can be reached, output the string “The poor student is trapped!” instead.
One step is defined as a movement between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as a step.
One step is defined as a movement between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as a step.
Sample Input
1 10 *........X 1 3 *#X 3 20 #################### #XY.gBr.*.Rb.G.GG.y# #################### 0 0
Sample Output
Escape possible in 9 steps. The poor student is trapped! Escape possible in 45 steps.BFS:#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; int n,m1; char a[105][105]; int vis[105][105][20]; int dir[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; struct Node { int x,y; int state; int step; Node(){}; Node(int x,int y,int state,int step) { this->x=x; this->y=y; this->state=state; this->step=step; } }; int judge(char a) { if(a=='B'||a=='Y'||a=='R'||a=='G') return 1; if(a=='b'||a=='y'||a=='r'||a=='g') return 0; } int bfs(int x,int y) { map<char,int>m; m['B']=0;m['Y']=1;m['R']=2;m['G']=3; m['b']=0;m['y']=1;m['r']=2;m['g']=3; queue<Node> q; q.push(Node(x,y,0,0)); vis[x][y][0]=1; while(!q.empty()) { Node term=q.front(); q.pop(); if(a[term.x][term.y]=='X') return term.step; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { int xx=term.x+dir[i][0]; int yy=term.y+dir[i][1]; if(xx<0||yy<0||xx>=n||yy>=m1||a[xx][yy]=='#') continue; if(a[xx][yy]=='.'||a[xx][yy]=='X'||a[xx][yy]=='*') { if(!vis[xx][yy][term.state]) { q.push(Node(xx,yy,term.state,term.step+1)); vis[xx][yy][term.state]=1; continue; } } if(!(term.state&(1<<m[a[xx][yy]]))&&judge(a[xx][yy])) continue; if((term.state&(1<<m[a[xx][yy]]))&&judge(a[xx][yy])) { if(!vis[xx][yy][term.state]) { q.push(Node(xx,yy,term.state,term.step+1)); vis[xx][yy][term.state]=1; continue; } } if(!judge(a[xx][yy])) { if(!vis[xx][yy][term.state|(1<<m[a[xx][yy]])]) { q.push(Node(xx,yy,term.state|(1<<m[a[xx][yy]]),term.step+1)); vis[xx][yy][term.state|(1<<m[a[xx][yy]])]=1; continue; } } } } return -1; } int main() { int x,y; while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m1)!=EOF) { if(n==0&&m1==0) break; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",a[i]); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m1;j++) { if(a[i][j]=='*') x=i,y=j; } memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); int ans=bfs(x,y); if(ans==-1) printf("The poor student is trapped! "); else printf("Escape possible in %d steps. ",ans); } return 0; }