5.3.Vuex的核心概念
store: 每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)
state:包含所有应用级别状态的对象
Getter: 在组件内部获取store中状态的函数,可以认为是 store 的计算属性
Mutation: 唯一修改状态的事件回调函数
Action:Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:1、Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。2、Action 可以包含任意异步操
Modules: 将store分割成不同的模块
5.3.1.Mutation
注意; 在Mutation中,是不能提交异步代码的,例如:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 让vuex作为vue的插件来使用
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
console.log(state)
setTimeout(() => {
state.goods_num += num
}, 2000)
}
}
})
// 把这个store实例导出 方便在vue中注入
export default store
5.3.2.Action
在mutation中提交异步代码,状态的改变是没办法追踪的,如果有异步代码,需要放到Action中去,等异步代码执行完成后再提交 store/index.js中的代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 让vuex作为vue的插件来使用
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
}
},
actions: {
changeCarAction (context, num) {
console.log(context)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCar', num)
}, 2000)
}
}
})
// 把这个store实例导出 方便在vue中注入
export default store
触发这个action,在VuexGoodsItem中去修改
export default {
data () {
return {
num: 12
}
},
components: {
},
methods: {
increase () {
this.num++
},
decrease () {
this.num--
},
addCar () {
// this.$store.commit('changeCar', this.num)
this.$store.dispatch('changeCarAction', this.num)
}
}
}
如果上面的都搞定了,再来看执行的流程图就轻松了
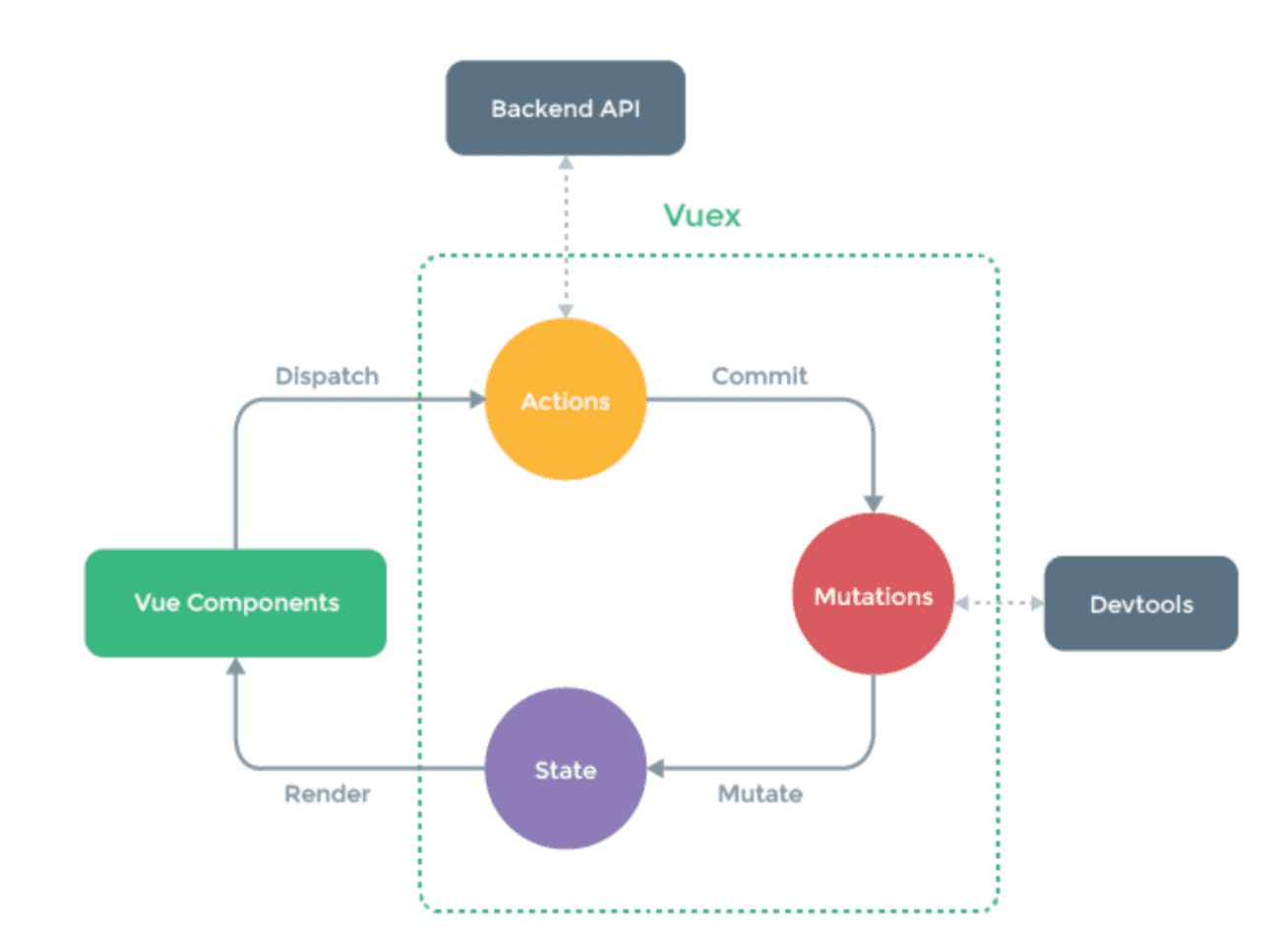
5.3.3.Getter
Getter可以认为是 store 的计算属性,可以对数据进行处理。为了掩饰效果,我们新建一个Count组件来说明
<template>
<div class="page">
<span>{{this.$store.state.count}}</span>
<button @click="increase">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/ecmascript-6">
export default {
data () {
return {
}
},
components: {
},
methods: {
increase () {
this.$store.commit('add')
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.page{
300px;
margin: 100px auto
}
</style>
在store中增加mutation函数和count变量,以下是部分代码
state: {
goods_num: 0,
count: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
},
add (state) {
state.count++
}
}
这样我们就实现了vuex版的加法计数器,如果对count这个变量有一些逻辑判断怎么办呢?我们可以在组件内部使用computed来实现,如果这个逻辑是全局通用的,你可以把它放到Getter里面去,举例:
需求:当计数器加到10的时候就不能继续加了
在store中增加getters选项
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 让vuex作为vue的插件来使用
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0,
count: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
},
add (state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
changeCarAction (context, num) {
console.log(context)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCar', num)
}, 2000)
}
},
getters: {
newCount (state) {
return state.count > 10 ? 10 : state.count
}
}
})
// 把这个store实例导出 方便在vue中注入
export default store
使用到时候,从store.getters对象中去获取
<p><span>{{this.$store.getters.newCount}}</span></p>
注意:如果要给getters里面的函数传参数,需要写成这样
getters: {
newCount (state) {
return state.count > 10 ? 10 : state.count
},
newCount2 (state) {
// 返回一个函数
return (num) => state.count > num ? num : state.count
}
}
调用的时候,这样调用
<p><span>{{this.$store.getters.newCount2(5)}}</span></p>
5.3.4.辅助函数mapState、mapGetters、mapActions
这几个辅助函数可以帮助我们简化一些写法
注意:在使用之前一定要先引入
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
1.mapState,这个函数是和computed的映射,可以把传入mapState的对象或者数组,转化成计算属性
mapState里面可以传入数组和对象,首先来看传入数组的写法
computed: {
...mapState(['num3', 'num4', 'num5'])
}
注意,这里传入的num3、num4、num5需要和state里面定义的状态同名
state: {
goods_num: 0,
count: 0,
num3: 9,
num4: 10,
num5: 11
}
这样写就可以直接去批量拿到state里面的数据,不用再去使用this.$store.state.num3 来获取值了,这就是辅助函数的作用,可以简化一些写法
有些时候,我们需要从state里面取值进行处理,例如这样:
computed: {
num3 () {
return this.$store.state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
}
}
如果使用辅助函数,我们就需要以对象的形式传入了
computed: {
// num3 () {
// return this.$store.state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
// }
...mapState({
num3: state => state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
})
}
使用箭头函数可以简化代码,同时还可以给state里的状态重命名,例如:
computed: {
// num3 () {
// return this.$store.state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
// }
...mapState({
num3: state => state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20,
num100: 'num4' //给num4 取一个别名 num4
})
}
如果你要使用this这个关键字,就不能用箭头函数,因此,可以简写成这样
computed: {
// num3 () {
// return this.$store.state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
// }
...mapState({
num3: state => state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20,
num100: 'num4',
num6 (state) {
//需要取data里面的num99和state里面的num6相加,这个时候需要用到this
return this.num99 + state.num6
}
})
}
以上就是mapState的基本用法,mapMutations、mapGetters、mapActions的用法也一样, 简单举例:
//mapMutations的用法
methods: {
// increase () {
// this.$store.commit('add')
// }
...mapMutations({
increase: 'add'
})
}
//mapActions的用法
methods: {
// increase () {
// this.$store.commit('add')
// }
...mapMutations({
increase: 'add'
}),
// decrease () {
// this.$store.dispatch('decreaseAction')
// },
...mapActions({
decrease: 'decreaseAction'
})
},
//mapGetters的用法
computed: {
// num3 () {
// return this.$store.state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20
// }
...mapState({
num3: state => state.num3 > 10 ? 10 : 20,
num100: 'num4',
num6 (state) {
return this.num99 + state.num6
}
}),
...mapGetters({
num5: 'newCount'
})
}
5.3.5.Module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块, 下面是我们的store/index.js文件,我们可以尝试将其拆分一个子模块出来
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 让vuex作为vue的插件来使用
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0,
//下面状态是count组件里面的状态
count: 0,
num3: 9,
num4: 10,
num5: 11,
num6: 6
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
},
//下面方法是count里面的方法
add (state) {
state.count++
},
decreaseMutation (state) {
state.count--
}
},
actions: {
changeCarAction (context, num) {
console.log(context)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCar', num)
}, 2000)
},
//下面方法是count里面的方法
decreaseAction (context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('decreaseMutation')
}, 1000)
}
},
getters: {
//下面方法是count里面的方法
newCount (state) {
return state.count > 10 ? 10 : state.count
},
newCount2 (state) {
return (num) => state.count > num ? num : state.count
}
}
})
// 把这个store实例导出 方便在vue中注入
export default store
下面开始拆分
1 自定义一个对象
// 直接定义一个子模块
let countModule = {
state: {
count: 0,
num3: 9,
num4: 10,
num5: 11,
num6: 6
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
decreaseMutation (state) {
state.count--
}
},
actions: {
decreaseAction (context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('decreaseMutation')
}, 1000)
}
},
getters: {
newCount (state, getters, rootState) {
return state.count > 10 ? 10 : state.count
},
newCount2 (state) {
return (num) => state.count > num ? num : state.count
}
}
}
2 将这个对象挂在store上
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
}
},
actions: {
changeCarAction (context, num) {
console.log(context)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCar', num)
}, 2000)
}
},
modules: {
countModule //子模块
}
})
完整代码:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 让vuex作为vue的插件来使用
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 直接定义一个子模块
let countModule = {
state: {
count: 0,
num3: 9,
num4: 10,
num5: 11,
num6: 6
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
decreaseMutation (state) {
state.count--
}
},
actions: {
decreaseAction (context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('decreaseMutation')
}, 1000)
}
},
getters: {
newCount (state, getters, rootState) {
return state.count > 10 ? 10 : state.count
},
newCount2 (state) {
return (num) => state.count > num ? num : state.count
}
}
}
// 创建一个容器
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
goods_num: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCar (state, num) {
state.goods_num += num
}
},
actions: {
changeCarAction (context, num) {
console.log(context)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCar', num)
}, 2000)
}
},
modules: {
countModule
}
})
// 把这个store实例导出 方便在vue中注入
export default store
5.5.什么时候使用vuex
虽然 Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,但也附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。确实是如此——如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
螺钉课堂视频课程地址:http://edu.nodeing.com