原文出处:http://my.oschina.net/amince/blog/196426
原 荐 AC(Aho—Corasiek) 多模式匹配算法
摘要 如何在一篇文章中,搜索多个关键字,如何快速查找各关键字.本篇文章会介绍一种在一串字符串中匹配多个子串(不限于字符串)的多模式算法.下面会用到 KMP模式匹配算法 及 有限状态自动机(FSA) 匹配算法原理,建议先去了解下,对于阅读本篇文章有帮助。
目录[-]
简介:
AC多模式匹配算法产生于1975年的贝尔实验室,最早使用于图书馆的书目查询程序中。该算法以有限状态自动机(FSA),以及KMP前缀算法 为基础.(有说法: ac自动机是KMP的多串形式,是一个有限自动机)
AC定义:
AC有限自动机 M 是1个6元组:M =(Q,∑,g,f,qo,F)其中:
1、Q是有限状态集(模式树上的所有节点).
2、∑是有限的输入字符表(模式树所有边上的字符).
3、g是转移函数.
4、f是失效函数,不匹配时自动机的状态转移.
5、qo∈Q是初态(根节点);
6、F量Q是终态集(以模式为标签的节点集).
AC有限状态自动机实现:
首先假设模式集合{he,she his,hers}, 输入字符串"ushers":
AC自动机算法主要建立三个函数,转向函数goto,失效函数failure和输出函数output(output 构造间杂在goto 构造以及failure构造中);
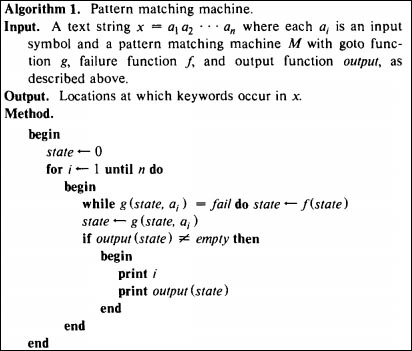
1、AC有限状态自动机M 操作循环框架:
a> 如果g(s,a) = s', 则自动机M 继续调用goto函数,以新状态s',以及新字符x为输入;如果状态s',匹配了某个模式,则输出;
b> 如果f(s,a) = failure, 则自动机M 调用failure状态转移f(s) = s',并以状态s',字符a 调用步骤1;
构造M伪代码:
2、构造goto函数及输出函数output:
goto函数: 是一个状态在接受一个字符后转向另一个状态或者失败的函数(对应于FSA里的转移函数);
定义如下:
g(S,a) 其中S ∈ Q, a ∈ Σ :从当前状态S开始,沿着边上标签为a的路径所到的状态。假如状态节点(U,V)边上的标签为a,那么g(U,a)=V;如果根节点上出来的边上的标签没有a,则g(0,a)=O(失败),即如果没有匹配的字符出现,自动机停留在初态;如果不是根节点,且该节点出来的标签没有字符a,则g(U,a) = failure,称为失败;
下图(a)是用goto函数以{he,she his,hers}模式集构造的字符串模式匹配机:
状态0是初始状态,在状态0和状态1间的有向边标有字符'h',表示g(0,a) = 1;缺失的有向边表示失败,当任意字符σ != e或i,有g(1,σ) = failure;
注意: 所有字符有 g(0,σ) != failure, 状态0的这个属性确保 M 会处理输入的任意字符;任意字符σ不在以状态0开始有向边的字符,有g(0,σ) = 0;同时说明状态0的失效函数(failure) 没有意义,不用计算;
构造goto伪代码:
3、构造失效函数failure及输出函数output;
失效函数: 指的也是状态和状态之间一种转向关系,在goto失败(failure)的情况下使用的转换关系. 基本原理是KMP 算法的前缀函数;
下图(b)是各状态的失效函数值:
下图(c)是各状态i最终的output值:
首先,我们定义状态转移图(a)中状态s的深度为从状态0到状态s的最短路径。例如图(a)起始状态的深度是0,状态1和3的深度是1,状态2,4,和6的深度是2,等等。
计算思路:先计算所有深度是1的状态的失效函数值,然后计算所有深度为2的状态,以此类推,直到所有状态(除了状态0,因为它的失效函数没有定义)的失效函数值都被计算出。
计算方法:用于计算某个状态失效函数值的算法在概念上是非常简单的。首先,令所有深度为1的状态s的函数值为f(s) = 0。假设所有深度小于d的状态的f值都已经被算出了,那么深度为d的状态的失效函数值将根据深度小于d的状态的失效函数值来计算。
具体步骤:
为了计算深度为d 状态的失效函数值,假设深度为d-1的状态r,执行以下步骤:
Step1: 如果对所有字符a,有g(r, a) = fail,那么什么都不做;(好像是废话,这如果成立,说明状态r节点下面没有节点了,根本不需要计算)
Step2: 否则,对每个使g(r, a) = s成立的字符a,执行以下操作:
a) 记state = f(r);
b) 执行零次或者多次令state = f(state),直到出现一个state使得g(state, a) != fail; (注意到,因为对任意字符a,g(0, a) != fail,所以这种状态一定能够找到);
c) 记f(s) = g(state, a);
注意: 这里有点拗口,不好理解,一句话来说: 就是看当前状态节点前一个状态节点(父节点)的failure节点是否有当前字符的外向边,如果有,则当前状态failure状态就是对应外向边对应的节点;如果没有,则根据对应failure状态的failure状态;
举个例子:求图(a)中状态4 的failure 状态, 已知其前一个(父节点)的f(3)= 0,且状态0(根节点)有字符'h'的外向边,该外向边对应状态1,则有f(4) = 1;类似前缀规则:求已经匹配字串"sh" 最大后缀,同时是某个模式串的前缀(类似于kmp中单个模式串的前缀和后缀的相同的计算next数组的方式);
failure 函数伪代码:
4、最后是遍历搜索:
状态机搜索过程中会有一种特殊情况:如果模式集中某个模式是另一个模式的子串,为了防止这种情况下漏掉子串模式,需要在这种子串的终态添加到长模式中;代码实现中就是某个状态的failure状态是某个终态,则当前状态也是终态,需要输出failure状态匹配的模式;
具体实现代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
|
#include<iostream>#include<string.h>#include<malloc.h>#include <queue>using namespace std;/* reallocation step for AC_NODE_t.outgoing array */#define REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING 2struct ac_edge;typedef struct node{ unsigned int id; /* Node ID : just for debugging purpose */ unsigned short depth; /* depth: distance between this node and the root */ struct node *parent; /*parent node, for compute failure function*/ struct node *failure_node; /* The failure node of this node */ short int final; /* 0: no ; 1: yes, it is a final node */ int patternNo; /*Accept pattern index: just for debugging purpose */ /* Outgoing Edges */ struct ac_edge* outgoing_edge;/* Array of outgoing character edges */ unsigned short outgoing_num; /* Number of outgoing character edges */ unsigned short outgoing_max; /* Max capacity of allocated memory for outgoing character edges */}AC_NODE_t;/* The Ougoing Edge of the Node */struct ac_edge{ char alpha; /* Edge alpha */ AC_NODE_t * next; /* Target of the edge */};static void node_assign_id (AC_NODE_t * thiz);static AC_NODE_t * node_find_next(AC_NODE_t * pAc_node, char ch);/****************************************************************************** * Create node******************************************************************************/AC_NODE_t *node_create(){ AC_NODE_t* pNode = (AC_NODE_t*)malloc(sizeof(AC_NODE_t)); memset(pNode, 0, sizeof(AC_NODE_t)); pNode->failure_node = NULL; pNode->parent = NULL; pNode->final = 0; /*init outgoing character edges*/ pNode->outgoing_max = REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING; pNode->outgoing_edge = (struct ac_edge *) malloc (pNode->outgoing_max*sizeof(struct ac_edge)); node_assign_id(pNode); return pNode;}/****************************************************************************** * assign a unique ID to the node (used for debugging purpose).******************************************************************************/static void node_assign_id (AC_NODE_t * thiz){ static int unique_id = 0; thiz->id = unique_id ++;}/****************************************************************************** * Establish an new edge between two nodes******************************************************************************/void node_add_outgoing (AC_NODE_t * thiz, AC_NODE_t * next, char alpha){ if(thiz->outgoing_num >= thiz->outgoing_max) { thiz->outgoing_max += REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING; thiz->outgoing_edge = (struct ac_edge *)realloc(thiz->outgoing_edge, thiz->outgoing_max*sizeof(struct ac_edge)); } thiz->outgoing_edge[thiz->outgoing_num].alpha = alpha; thiz->outgoing_edge[thiz->outgoing_num++].next = next;}/****************************************************************************** * Create a next node with the given alpha.******************************************************************************/AC_NODE_t * node_create_next (AC_NODE_t * pCur_node, char alpha){ AC_NODE_t * pNext_node = NULL; pNext_node = node_find_next (pCur_node, alpha); if (pNext_node) { /* The (labeled alpha) edge already exists */ return NULL; } /* Otherwise add new edge (node) */ pNext_node = node_create (); node_add_outgoing(pCur_node, pNext_node, alpha); return pNext_node;}/****************************************************************************** * Find out the next node for a given Alpha to move. this function is used in * the pre-processing stage in which edge array is not sorted. so it uses linear search.******************************************************************************/static AC_NODE_t * node_find_next(AC_NODE_t * pAc_node, char ch){ int i = 0; if(NULL == pAc_node) { return NULL; } for (i=0; i < pAc_node->outgoing_num; i++) { if(pAc_node->outgoing_edge[i].alpha == ch) return (pAc_node->outgoing_edge[i].next); } return NULL;}/******************************************************************************* add parent node's all leaf node(outgoing node) into queue******************************************************************************/int queue_add_leaf_node(AC_NODE_t *parent, queue<AC_NODE_t*> &myqueue){ int i; for (i = 0; i < parent->outgoing_num; i++) { myqueue.push (parent->outgoing_edge[i].next); } return 0;}/****************************************************************************** * Initialize automata; allocate memories and add patterns into automata******************************************************************************/AC_NODE_t * ac_automata_create(char pattern[][255], int patterns_num){ int iPattern_index, iChar_index; AC_NODE_t *root = node_create(); AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL, *pNext_node = NULL; char alpha; for(iPattern_index=0; iPattern_index<patterns_num; iPattern_index++) { pCur_node = root; for(iChar_index=0; iChar_index<strlen(pattern[iPattern_index]); iChar_index++) ///对每个模式进行处理 { alpha = pattern[iPattern_index][iChar_index]; pNext_node = node_find_next(pCur_node, alpha); if(NULL != pNext_node) { pCur_node = pNext_node; } else { pNext_node = node_create_next(pCur_node, alpha); if(NULL != pNext_node) { pNext_node->parent = pCur_node; pNext_node->depth = pCur_node->depth + 1; pCur_node = pNext_node; } } } pCur_node->final = 1; pCur_node->patternNo = iPattern_index; } return root;}/****************************************************************************** * find failure node for all node, actually failure function maps a state into a new state. * the failure function is consulted whenever the goto function reports fail; * specificialy compute the failue node, we use it's parent node's failure node******************************************************************************/int ac_automata_setfailure(AC_NODE_t * root){ int i =0; queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue; char edge_ch = '�'; AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL, *parent = NULL, *pNext_Node = NULL; for(i= 0; i< root->outgoing_num; i++) //f(s) = 0 for all states s of depth 1 { root->outgoing_edge[i].next->failure_node = root; } queue_add_leaf_node(root, myqueue); while(!myqueue.empty()) { parent = myqueue.front(); myqueue.pop(); queue_add_leaf_node(parent, myqueue); for(i = 0; i < parent->outgoing_num; i++) { edge_ch = parent->outgoing_edge[i].alpha; pCur_node = parent->outgoing_edge[i].next; pNext_Node = node_find_next(parent->failure_node, edge_ch); if(NULL == pNext_Node) { if(parent->failure_node == root) { pCur_node->failure_node = root; } else { parent = parent->failure_node->parent; } } else { pCur_node->failure_node = pNext_Node; } } } return 0;}/****************************************************************************** * Search in the input text using the given automata.******************************************************************************/int ac_automata_search(AC_NODE_t * root, char* text, int txt_len, char pattern[][255]){ AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = root; AC_NODE_t *pNext_node = NULL; int position = 0; while(position < txt_len) { pNext_node = node_find_next(pCur_node, text[position]); if (NULL == pNext_node) { if(pCur_node == root) { position++; } else { pCur_node = pCur_node->failure_node; } } else { pCur_node = pNext_node; position++; } if(pCur_node->final == 1) ///some pattern matched { cout<<position-strlen(pattern[pCur_node->patternNo])<< ' ' << ' ' <<pCur_node->patternNo<< ' ' << ' ' <<pattern[pCur_node->patternNo]<<endl; } } return 0;}/****************************************************************************** * Prints the automata to output in human readable form.******************************************************************************/void ac_automata_display (AC_NODE_t * root){ unsigned int i; AC_NODE_t * pCur_node = root; struct ac_edge * pEdge = NULL; if(root == NULL) { return; } printf("---------------------------------
"); queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue; myqueue.push( pCur_node ); while(!myqueue.empty()) { pCur_node = myqueue.front(); myqueue.pop(); printf("NODE(%3d)/----fail----> NODE(%3d)
", pCur_node->id, (pCur_node->failure_node)?pCur_node->failure_node->id:0); for (i = 0; i < pCur_node->outgoing_num; i++) { myqueue.push (pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i].next); pEdge = &pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i]; printf(" |----("); if(isgraph(pEdge->alpha)) printf("%c)---", pEdge->alpha); else printf("0x%x)", pEdge->alpha); printf("--> NODE(%3d)
", pEdge->next->id); } printf("---------------------------------
"); }}/****************************************************************************** * Release all allocated memories to the automata******************************************************************************/int ac_automata_release(AC_NODE_t * root){ if(root == NULL) { return 0; } queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue; AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL; myqueue.push( root ); root = NULL; while(!myqueue.empty()) { pCur_node = myqueue.front(); myqueue.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < pCur_node->outgoing_num; i++) { myqueue.push (pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i].next); } free(pCur_node); } return 0;}int main(){ unsigned int i = 0; char haystack[] = "ushers"; char needle[4][255]={"he","she", "his","hers"}; /* 1. create ac finite state automata match machine, compute goto and output func*/ AC_NODE_t *root = ac_automata_create(needle, sizeof(needle)/sizeof(needle[0])); /* 2. compute failure function*/ ac_automata_setfailure( root ); /* 3. Display automata (if you are interested)*/ ac_automata_display( root ); cout << endl << "haystack : " << haystack << endl; cout << "needles : "; for(i = 0; i<sizeof(needle)/sizeof(needle[0]); i++) { cout << needle[i] << " "; } cout << endl << endl; cout << "match result : " << endl << "position " << "node_id " << "pattern" << endl; /* 3. seaching multi patterns use automata*/ ac_automata_search(root, haystack, strlen(haystack), needle); /* 4. Release the automata */ ac_automata_release ( root ); return 0;} |
这里是杭电OJ problem list 2222 的字符串匹配的题解,利用AC自动机,代码如下:
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2222
题目大意:
给你很多个单词,然后给你一篇文章,问给出的单词在文章中出现的次数。
解题思路:
AC自动机入门题。需要注意的就是可能有重复单词,坑死人不偿命!~~~~
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define N 500010
char str[1000010], keyword[51];
int head, tail;
struct node
{
node *fail;
node *next[26];
int count;
node() //init
{
fail = NULL;
count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
next[i] = NULL;
}
}*q[N];
node *root;
void insert(char *str) //建立Trie
{
int temp, len;
node *p = root;
len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
temp = str[i] - 'a';
if(p->next[temp] == NULL)
p->next[temp] = new node();
p = p->next[temp];
}
p->count++;
}
void build_ac() //初始化fail指针,BFS
{ //利用队列q以广度优先遍历的方式进行计算每个节点的失效指针
q[tail++] = root;
while(head != tail)
{
node *p = q[head++]; //弹出队头
node *temp = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
{
if(p->next[i] != NULL)
{
if(p == root) //第一个元素fail必指向根
p->next[i]->fail = root;
else
{
temp = p->fail; //失败指针
while(temp != NULL) //2种情况结束:匹配为空or找到匹配
{
if(temp->next[i] != NULL) //找到匹配
{
p->next[i]->fail = temp->next[i]; //(找到父节点的当前字符对应的外向边作为当前节点的实效指针,对应上文中描述实效函数的计算方法)
break;
}
temp = temp->fail;
}
if(temp == NULL) //为空则从头匹配
p->next[i]->fail = root;
}
q[tail++] = p->next[i]; //入队
}
}
}
}
int query() //扫描
{
int index, len, result;
node *p = root; //Tire入口
result = 0;
len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
index = str[i] - 'a';
while(p->next[index] == NULL && p != root) //跳转失败指针
p = p->fail;
p = p->next[index];
if(p == NULL)
p = root;
node *temp = p; //p不动,temp计算后缀串
while(temp != root && temp->count != -1)
{
result += temp->count;
temp->count = -1;
temp = temp->fail; //解决如果模式串中某个模式是另一个模式的子串的问题
}
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int ncase, num;
scanf("%d", &ncase);
while(ncase--)
{
head= tail = 0;
root = new node();
scanf("%d", &num);
getchar();
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
gets(keyword);
insert(keyword);
}
build_ac();
scanf("%s", str);
printf("%d
", query());
}
return 0;
}
下图为我自己对代码的理解。

后记:
根据不同的AC_NODE结构设计,实现会有些不同,但原理一样;
可以改进的地方:
1、可以把同深度节点排序,后面查找某状态的指定字符外向边状态,可以使用二分查找,加快速度;
2、这里的AC_NODE 里面每个节点只对应一个匹配模式(patternNo),理论上是有多个的匹配模式的,有待完善;
3、已知g(4,e) = 5; 假设M 当前状态为4, 且下一个字符不是'e',这时候M 会调用f(4)=1,其实这时候我们已经不需要去查找状态1以'e'为外向边的状态了,因为下一个字符确定不是'e';如果没有"his"模式,我们可以直接从状态1跳到状态0;而现在代码是会去做这个多余查找动作的。这个可以用确定有限自动机来避免,下篇文章我会详细和大家讨论下.
有任何问题,还请不吝赐教~
references:
<1>、Efficient String Matching: An Aid to Bibliographic Search.pdf(june 1975)
<2>、http://blog.csdn.net/sunnianzhong/article/details/8832496
<3>、http://blog.csdn.net/sealyao/article/details/4560427
<4>、http://www.it165.net/pro/html/201311/7860.html
<5>、http://sourceforge.net/projects/multifast/
<6>、多模式匹配算法的研究.pdf
<7>、模式匹配算法在网络入侵系统中的应用研究.pdf