Paraview是一个开源的可视化软件。
用到matlab子程序从这里下载
或者到博客末尾复制粘贴
子程序名为 vtkwrite
示例1:
1 load mri 2 D = squeeze(D); 3 vtkwrite('mri.vtk', 'structured_points', 'mri', D)
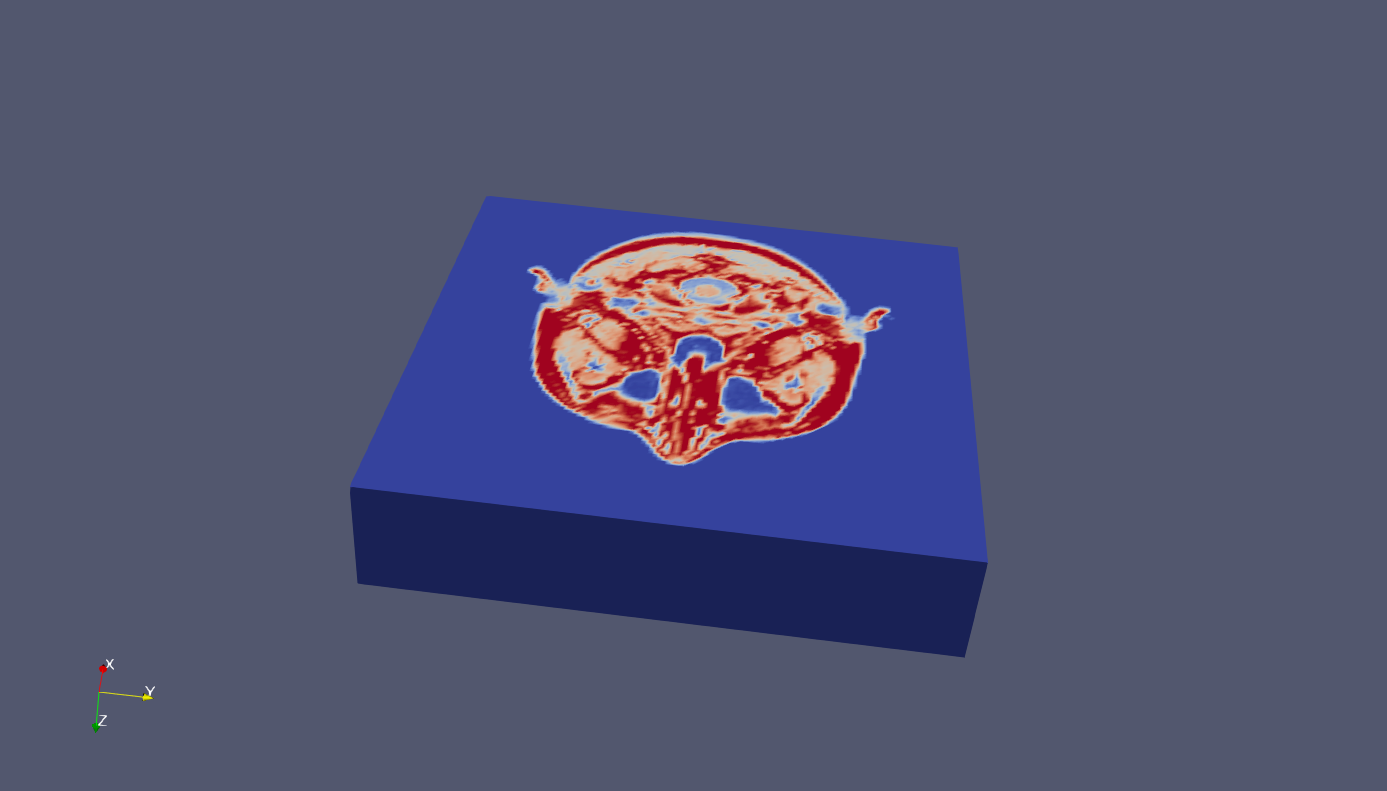
示例2:云图
1 load wind 2 [cu,cv,cw] = curl(x, y, z, u, v, w); 3 div = divergence(x, y, z, u, v, w); 4 vtkwrite('wind.vtk', 'structured_grid', x, y, z, ... 5 'vectors', 'vector_field', u, v, w, 'vectors', 'vorticity', cu, cv, cw, 'scalars', 'divergence', div);
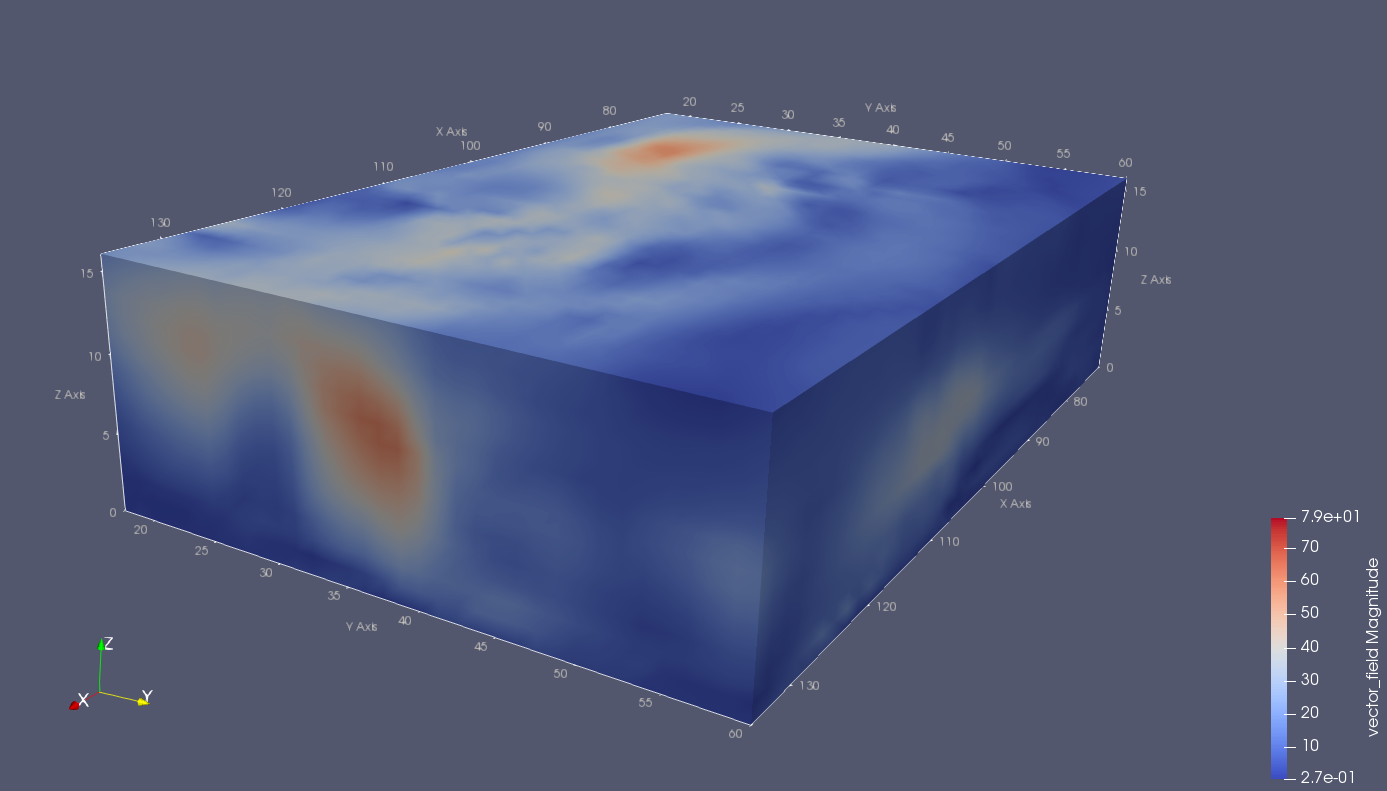
示例3:二维曲线
1 x = 1:100; 2 y = sin(x); 3 z = sqrt(x); 4 vtkwrite('execute','polydata','lines',x,y,z);
示例4:三角形
1 [x,y,z] = peaks(100); 2 z = .4*z; 3 tri = delaunay(x,y); 4 vtkwrite('peaks.vtk','polydata','triangle',x,y,z,tri);
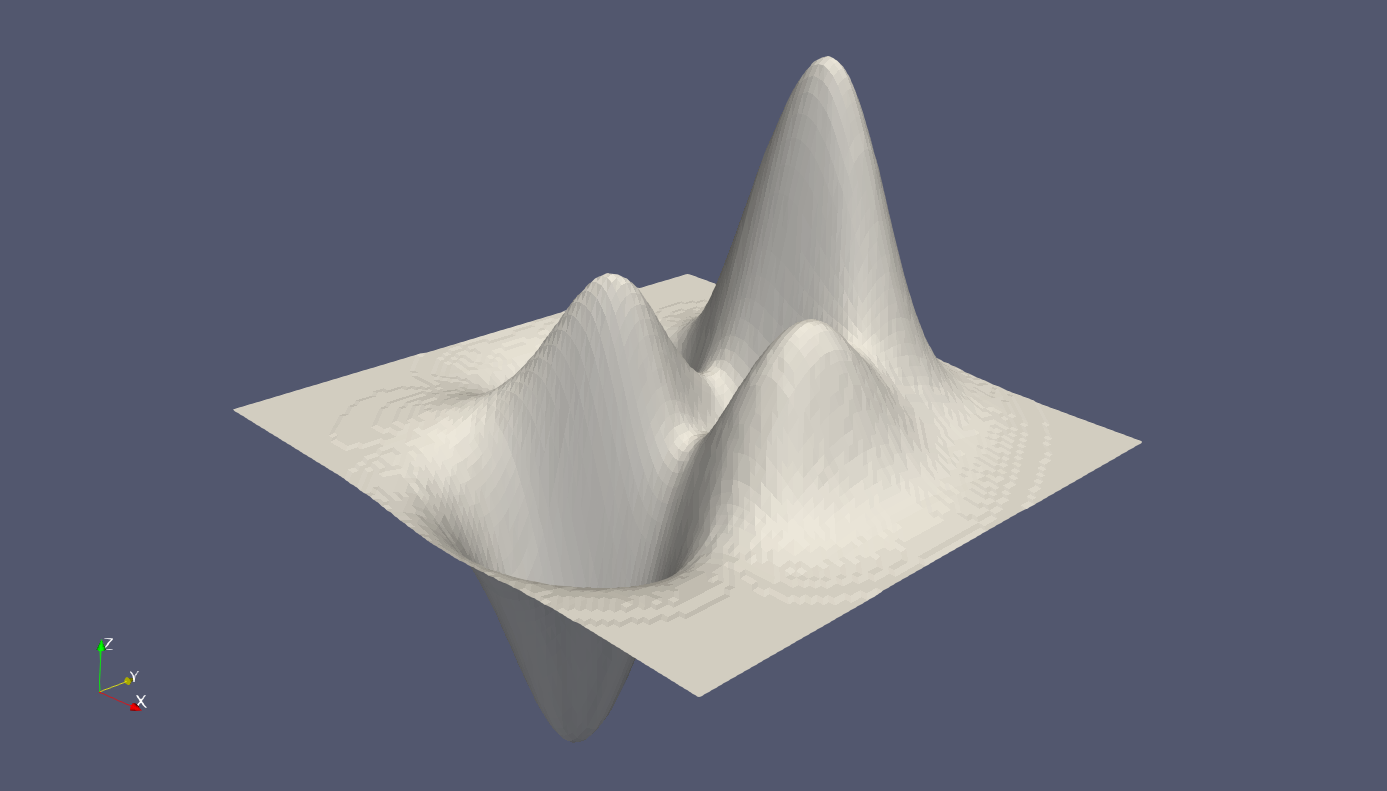
示例5:四面体
1 d = [-1 1]; 2 [x, y, z] = meshgrid(d, d, d); 3 DT = delaunayTriangulation(x(:), y(:), z(:)); 4 vtkwrite('execute', 'polydata','tetrahedron', x, y, z, DT.ConnectivityList);
vtkwrite
1 function vtkwrite( filename,dataType,varargin ) 2 % VTKWRITE Writes 3D Matlab array into VTK file format. 3 % vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w) writes 4 % a structured 3D vector data into VTK file, with name specified by the string 5 % filename. (u,v,w) are the vector components at the points (x,y,z). x,y,z 6 % should be 3-D matrices like those generated by meshgrid, where 7 % point(ijk) is specified by x(i,j,k), y(i,j,k) and z(i,j,k). 8 % The matrices x,y,z,u,v,w must all be the same size and contain 9 % corrresponding position and vector component. The string title specifies 10 % the name of the vector field to be saved. 11 % 12 % vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'scalars',title,r) writes a 3D 13 % scalar data into VTK file whose name is specified by the string 14 % filename. r is the scalar value at the points (x,y,z). The matrices 15 % x,y,z,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding position 16 % and scalar values. 17 % 18 % vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w,'scalars', 19 % title2,r) writes a 3D structured grid that contains both vector and scalar values. 20 % x,y,z,u,v,w,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding 21 % positon, vector and scalar values. 22 % 23 % vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m) saves matrix m (could 24 % be 1D, 2D or 3D array) into vtk as structured points. 25 % 26 % vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m, 'spacing', sx, sy, sz) 27 % allows user to specify spacing. (default: 1, 1, 1). This is the aspect 28 % ratio of a single voxel. 29 % 30 % vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m, 'origin', ox, oy, oz) 31 % allows user to speicify origin of dataset. (default: 0, 0, 0). 32 % 33 % vtkwrite(filename,'unstructured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w,'scalars', 34 % title2,r) writes a 3D unstructured grid that contains both vector and scalar values. 35 % x,y,z,u,v,w,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding 36 % positon, vector and scalar values. 37 % 38 % vtkwrite(filename, 'polydata', 'lines', x, y, z) exports a 3D line where 39 % x,y,z are coordinates of the points that make the line. x, y, z are 40 % vectors containing the coordinates of points of the line, where point(n) 41 % is specified by x(n), y(n) and z(n). 42 % 43 % vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','lines',x,y,z,'Precision',n) allows you to 44 % specify precision of the exported number up to n digits after decimal 45 % point. Default precision is 3 digits. 46 % 47 % vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','triangle',x,y,z,tri) exports a list of 48 % triangles where x,y,z are the coordinates of the points and tri is an 49 % m*3 matrix whose rows denote the points of the individual triangles. 50 % 51 % vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','tetrahedron',x,y,z,tetra) exports a list 52 % of tetrahedrons where x,y,z are the coordinates of the points 53 % and tetra is an m*4 matrix whose rows denote the points of individual 54 % tetrahedrons. 55 % 56 % vtkwrite('execute','polydata','lines',x,y,z) will save data with default 57 % filename ''matlab_export.vtk' and automatically loads data into 58 % ParaView. 59 % 60 % Version 2.3 61 % Copyright, Chaoyuan Yeh, 2016 62 % Codes are modified from William Thielicke and David Gingras's submission. 63 64 if strcmpi(filename,'execute'), filename = 'matlab_export.vtk'; end 65 fid = fopen(filename, 'w'); 66 % VTK files contain five major parts 67 % 1. VTK DataFile Version 68 fprintf(fid, '# vtk DataFile Version 2.0 '); 69 % 2. Title 70 fprintf(fid, 'VTK from Matlab '); 71 72 73 binaryflag = any(strcmpi(varargin, 'BINARY')); 74 if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'PRECISION')) 75 precision = num2str(varargin{find(strcmpi(vin, 'PRECISION'))+1}); 76 else 77 precision = '2'; 78 end 79 80 switch upper(dataType) 81 case 'STRUCTURED_POINTS' 82 title = varargin{1}; 83 m = varargin{2}; 84 if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing')) 85 sx = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+1}; 86 sy = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+2}; 87 sz = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+3}; 88 else 89 sx = 1; 90 sy = 1; 91 sz = 1; 92 end 93 if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin')) 94 ox = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+1}; 95 oy = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+2}; 96 oz = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+3}; 97 else 98 ox = 0; 99 oy = 0; 100 oz = 0; 101 end 102 [nx, ny, nz] = size(m); 103 setdataformat(fid, binaryflag); 104 105 fprintf(fid, 'DATASET STRUCTURED_POINTS '); 106 fprintf(fid, 'DIMENSIONS %d %d %d ', nx, ny, nz); 107 fprintf(fid, ['SPACING ', num2str(sx), ' ', num2str(sy), ' ',... 108 num2str(sz), ' ']); 109 fprintf(fid, ['ORIGIN ', num2str(ox), ' ', num2str(oy), ' ',... 110 num2str(oz), ' ']); 111 fprintf(fid, 'POINT_DATA %d ', nx*ny*nz); 112 fprintf(fid, ['SCALARS ', title, ' float 1 ']); 113 fprintf(fid,'LOOKUP_TABLE default '); 114 if ~binaryflag 115 spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f ']; 116 fprintf(fid, spec, m(:)'); 117 else 118 fwrite(fid, m(:)', 'float', 'b'); 119 end 120 121 case {'STRUCTURED_GRID','UNSTRUCTURED_GRID'} 122 % 3. The format data proper is saved in (ASCII or Binary). Use 123 % fprintf to write data in the case of ASCII and fwrite for binary. 124 if numel(varargin)<6, error('Not enough input arguments'); end 125 setdataformat(fid, binaryflag); 126 % fprintf(fid, 'BINARY '); 127 x = varargin{1}; 128 y = varargin{2}; 129 z = varargin{3}; 130 if sum(size(x)==size(y) & size(y)==size(z))~=length(size(x)) 131 error('Input dimesions do not match') 132 end 133 n_elements = numel(x); 134 % 4. Type of Dataset ( can be STRUCTURED_POINTS, STRUCTURED_GRID, 135 % UNSTRUCTURED_GRID, POLYDATA, RECTILINEAR_GRID or FIELD ) 136 % This part, dataset structure, begins with a line containing the 137 % keyword 'DATASET' followed by a keyword describing the type of dataset. 138 % Then the geomettry part describes geometry and topology of the dataset. 139 if strcmpi(dataType,'STRUCTURED_GRID') 140 fprintf(fid, 'DATASET STRUCTURED_GRID '); 141 fprintf(fid, 'DIMENSIONS %d %d %d ', size(x,1), size(x,2), size(x,3)); 142 else 143 fprintf(fid, 'DATASET UNSTRUCTURED_GRID '); 144 end 145 fprintf(fid, ['POINTS ' num2str(n_elements) ' float ']); 146 output = [x(:)'; y(:)'; z(:)']; 147 148 if ~binaryflag 149 spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f ']; 150 fprintf(fid, spec, output); 151 else 152 fwrite(fid, output, 'float', 'b'); 153 end 154 % 5.This final part describe the dataset attributes and begins with the 155 % keywords 'POINT_DATA' or 'CELL_DATA', followed by an integer number 156 % specifying the number of points of cells. Other keyword/data combination 157 % then define the actual dataset attribute values. 158 fprintf(fid, [' POINT_DATA ' num2str(n_elements)]); 159 % Parse remaining argument. 160 vidx = find(strcmpi(varargin,'VECTORS')); 161 sidx = find(strcmpi(varargin,'SCALARS')); 162 if vidx~=0 163 for ii = 1:length(vidx) 164 title = varargin{vidx(ii)+1}; 165 % Data enteries begin with a keyword specifying data type 166 % and numeric format. 167 fprintf(fid, [' VECTORS ', title,' float ']); 168 output = [varargin{ vidx(ii) + 2 }(:)';... 169 varargin{ vidx(ii) + 3 }(:)';... 170 varargin{ vidx(ii) + 4 }(:)']; 171 172 if ~binaryflag 173 spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f ']; 174 fprintf(fid, spec, output); 175 else 176 fwrite(fid, output, 'float', 'b'); 177 end 178 % fwrite(fid, [reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+2},1,n_elements);... 179 % reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+3},1,n_elements);... 180 % reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+4},1,n_elements)],'float','b'); 181 end 182 end 183 if sidx~=0 184 for ii = 1:length(sidx) 185 title = varargin{sidx(ii)+1}; 186 fprintf(fid, [' SCALARS ', title,' float ']); 187 fprintf(fid, 'LOOKUP_TABLE default '); 188 if ~binaryflag 189 spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f ']; 190 fprintf(fid, spec, varargin{ sidx(ii) + 2}); 191 else 192 fwrite(fid, varargin{ sidx(ii) + 2}, 'float', 'b'); 193 end 194 % fwrite(fid, reshape(varargin{sidx(ii)+2},1,n_elements),'float','b'); 195 end 196 end 197 198 case 'POLYDATA' 199 200 fprintf(fid, 'ASCII '); 201 if numel(varargin)<4, error('Not enough input arguments'); end 202 x = varargin{2}(:); 203 y = varargin{3}(:); 204 z = varargin{4}(:); 205 if numel(varargin)<4, error('Not enough input arguments'); end 206 if sum(size(x)==size(y) & size(y)==size(z))~= length(size(x)) 207 error('Input dimesions do not match') 208 end 209 n_elements = numel(x); 210 fprintf(fid, 'DATASET POLYDATA '); 211 if mod(n_elements,3)==1 212 x(n_elements+1:n_elements+2,1)=[0;0]; 213 y(n_elements+1:n_elements+2,1)=[0;0]; 214 z(n_elements+1:n_elements+2,1)=[0;0]; 215 elseif mod(n_elements,3)==2 216 x(n_elements+1,1)=0; 217 y(n_elements+1,1)=0; 218 z(n_elements+1,1)=0; 219 end 220 nbpoint = numel(x); 221 fprintf(fid, ['POINTS ' num2str(nbpoint) ' float ']); 222 223 spec = [repmat(['%0.', precision, 'f '], 1, 9), ' ']; 224 225 output = [x(1:3:end-2), y(1:3:end-2), z(1:3:end-2),... 226 x(2:3:end-1), y(2:3:end-1), z(2:3:end-1),... 227 x(3:3:end), y(3:3:end), z(3:3:end)]'; 228 229 fprintf(fid, spec, output); 230 231 switch upper(varargin{1}) 232 case 'LINES' 233 if mod(n_elements,2)==0 234 nbLine = 2*n_elements-2; 235 else 236 nbLine = 2*(n_elements-1); 237 end 238 conn1 = zeros(nbLine,1); 239 conn2 = zeros(nbLine,1); 240 conn2(1:nbLine/2) = 1:nbLine/2; 241 conn1(1:nbLine/2) = conn2(1:nbLine/2)-1; 242 conn1(nbLine/2+1:end) = 1:nbLine/2; 243 conn2(nbLine/2+1:end) = conn1(nbLine/2+1:end)-1; 244 fprintf(fid,' LINES %d %d ',nbLine,3*nbLine); 245 fprintf(fid,'2 %d %d ',[conn1';conn2']); 246 case 'TRIANGLE' 247 ntri = length(varargin{5}); 248 fprintf(fid,' POLYGONS %d %d ',ntri,4*ntri); 249 fprintf(fid,'3 %d %d %d ',(varargin{5}-1)'); 250 case 'TETRAHEDRON' 251 ntetra = length(varargin{5}); 252 fprintf(fid,' POLYGONS %d %d ',ntetra,5*ntetra); 253 fprintf(fid,'4 %d %d %d %d ',(varargin{5}-1)'); 254 end 255 end 256 fclose(fid); 257 if strcmpi(filename,'matlab_export.vtk') 258 switch computer 259 case {'PCWIN','PCWIN64'} 260 !paraview.exe --data='matlab_export.vtk' & 261 % Exclamation point character is a shell escape, the rest of the 262 % input line will be sent to operating system. It can not take 263 % variables, though. The & at the end of line will return control to 264 % Matlab even when the outside process is still running. 265 case {'GLNXA64','MACI64'} 266 !paraview --data='matlab_export.vtk' & 267 end 268 end 269 end 270 271 function setdataformat(fid, binaryflag) 272 273 if ~binaryflag 274 fprintf(fid, 'ASCII '); 275 else 276 fprintf(fid, 'BINARY '); 277 end 278 end