装饰者模式
Decorator模式或者Wrapper模式允许修饰或者封装(在字面意义中,即修改行为)一个对象,即使你没有该对象的源代码或者该对象标识为final。
Decorator模式适用于无法继承该类(例如,对象的实现类使用final标识)或者无法创建该类的实例,但可以从另外的系统中可以取得该类的实现时。例如,Servlet容器方法。只有一种方法可以修改ServletRequest或者ServletResponse行为,即在另外的对象中封装该实例。唯一的限制是,修饰对象必须继承一个接口,然后实现接口以封装这些方法。
UML类图
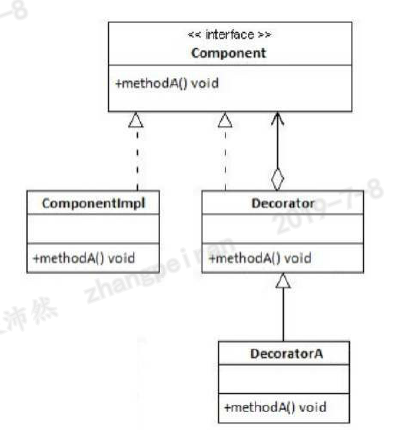
上面类图说明了一个Component接口以及它的实现类ComponentImpl。Component接口定义了A的方法。为了修饰ComponentImpl的实例,需要创建一个Decorator类,并实现Component的接口,然后在子类中扩展Decorator的新行为。在类图中DecoratorA就是Decorator的一个子类。每个Decorator实例需要包含Component的一个实例。Decorator类代码如下(注意在构建函数中获取了Component的实例,这意味着创建Decorator对象只能传入Component的实例)
在Decorator类中,有修饰的方法就是可能在子类中需要修改行为的方法,在子类中不需要修饰的方法可以不需要实现。所有的方法,无论是否需要修饰,都叫作Component中的配对方法。Decorator是一个非常简单的类,便于提供每个方法的默认实现。修改行为在它的子类中。需要牢记一点,Decorator类及被修饰对象的类需要实现相同的接口。为了实现Decorator,可以在Decorator中封装修饰对象,并把Decorator作为Component的一个实现。任何Component的实现都可以在Decorator中注入。事实上,你可以把一个修饰的对象传入另一个修饰的对象,以实现双重的修饰。
Servlet API中的装饰者模式应用
Servlet API源自于4个实现类,它很少被使用,但是十分强大:ServletRequestWrapper、ServletResponseWrapper以及HttpServletRequestWrapper、HttpServletResponseWrapper。ServletRequestWrapper(或者其他3个Wrapper类)非常便于使用,因为它提供了每个方法的默认实现:即ServletRequest封闭的配置方法。通过继承ServletRequestWrapper,只需要实现你需要变更的方法就可以了。如果不用ServletRequestWrapper,则需要继承ServletRequest并实现ServletRequest中所有的方法。
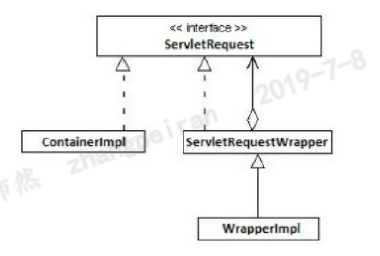
下图所示为Decorator模式中ServletRequestWrapper的类图。Servlet容器在每次Servlet服务调用时创建ServletRequest、ContainerImpl。直接扩展ServletRequestWrapper就可以修饰ServletRequest了。
ServletRequestWrapper源码
public class ServletRequestWrapper implements ServletRequest {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings";
private static final ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings");
private ServletRequest request;
public ServletRequestWrapper(ServletRequest request) {
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(lStrings.getString("wrapper.nullRequest"));
} else {
this.request = request;
}
}
public ServletRequest getRequest() {
return this.request;
}
public void setRequest(ServletRequest request) {
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(lStrings.getString("wrapper.nullRequest"));
} else {
this.request = request;
}
}
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
return this.request.getAttribute(name);
}
public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames() {
return this.request.getAttributeNames();
}
public String getCharacterEncoding() {
return this.request.getCharacterEncoding();
}
public void setCharacterEncoding(String enc) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this.request.setCharacterEncoding(enc);
}
public int getContentLength() {
return this.request.getContentLength();
}
public long getContentLengthLong() {
return this.request.getContentLengthLong();
}
public String getContentType() {
return this.request.getContentType();
}
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return this.request.getInputStream();
}
public String getParameter(String name) {
return this.request.getParameter(name);
}
public Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap() {
return this.request.getParameterMap();
}
public Enumeration<String> getParameterNames() {
return this.request.getParameterNames();
}
public String[] getParameterValues(String name) {
return this.request.getParameterValues(name);
}
public String getProtocol() {
return this.request.getProtocol();
}
public String getScheme() {
return this.request.getScheme();
}
public String getServerName() {
return this.request.getServerName();
}
public int getServerPort() {
return this.request.getServerPort();
}
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return this.request.getReader();
}
public String getRemoteAddr() {
return this.request.getRemoteAddr();
}
public String getRemoteHost() {
return this.request.getRemoteHost();
}
public void setAttribute(String name, Object o) {
this.request.setAttribute(name, o);
}
public void removeAttribute(String name) {
this.request.removeAttribute(name);
}
public Locale getLocale() {
return this.request.getLocale();
}
public Enumeration<Locale> getLocales() {
return this.request.getLocales();
}
public boolean isSecure() {
return this.request.isSecure();
}
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path) {
return this.request.getRequestDispatcher(path);
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public String getRealPath(String path) {
return this.request.getRealPath(path);
}
public int getRemotePort() {
return this.request.getRemotePort();
}
public String getLocalName() {
return this.request.getLocalName();
}
public String getLocalAddr() {
return this.request.getLocalAddr();
}
public int getLocalPort() {
return this.request.getLocalPort();
}
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.request.getServletContext();
}
public AsyncContext startAsync() throws IllegalStateException {
return this.request.startAsync();
}
public AsyncContext startAsync(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.request.startAsync(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
public boolean isAsyncStarted() {
return this.request.isAsyncStarted();
}
public boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return this.request.isAsyncSupported();
}
public AsyncContext getAsyncContext() {
return this.request.getAsyncContext();
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(ServletRequest wrapped) {
if (this.request == wrapped) {
return true;
} else {
return this.request instanceof ServletRequestWrapper ? ((ServletRequestWrapper)this.request).isWrapperFor(wrapped) : false;
}
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> wrappedType) {
if (wrappedType.isAssignableFrom(this.request.getClass())) {
return true;
} else {
return this.request instanceof ServletRequestWrapper ? ((ServletRequestWrapper)this.request).isWrapperFor(wrappedType) : false;
}
}
public DispatcherType getDispatcherType() {
return this.request.getDispatcherType();
}
}
只需继承ServletRequestWrapper类,覆盖需要修改的方法,即可自定实现类。
内容源自《Servlet、JSP和Srping MVC学习指南》