转载请注明出处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/12152119.html
论文:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.12004
官方pytorch代码:
https://github.com/Daniil-Osokin/lightweight-human-pose-estimation.pytorch
1 简介
light weight openpose是openpose的简化版本,使用了openpose的大体流程。
Light weight openpose和openpose的区别是:
a 前者使用的是Mobilenet V1(到conv5_5),后者使用的是Vgg19(前10层)。
b 前者部分层使用了空洞卷积(dilated convolution)来提升感受视野,后者使用一般的卷积。
c 前者卷积核大小为3*3,后者为7*7。
d 前者只有一个refine stage,后者有5个stage。
e 前者的initial stage和refine stage里面的两个分支(hotmaps和pafs)使用权值共享,后者则是并行的两个分支。
2 改进
2.1 骨干网络
论文中分析了openpose各阶段的mAP及GFLOPs
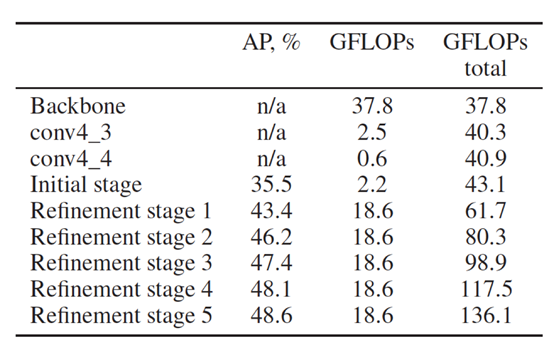
发现从refine stage1之后,性能的提升不是非常明显,但是GFLOPs增加的相当明显,因而只保留了refine stage1,后面的都删除了。
2.2 权值共享
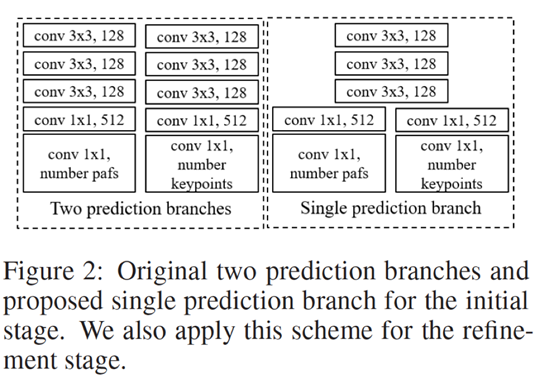
openpose的每个stage使用下图中左侧的两个并行的分支,分别预测hotmaps和pafs,为了进一步降低计算量,light weight openpose中将前几层进行权值共享,如下图右侧所示。
2.3 空洞卷积
进一步的,light weight openpose使用含有空洞卷积的mobilenet v1替换掉了vgg10,GFLOPs进一步降低了很多,如下图所示(下图中2-stage network中的那个n/a,是指使用所有的refine stage进行训练,但是使用的时候,只到refine stage 1,这样测试时的计算量不变,后几个阶段无计算量,因而为n/a,同时最后一栏GFLOPs还是9)。
2.4 3*3 卷积
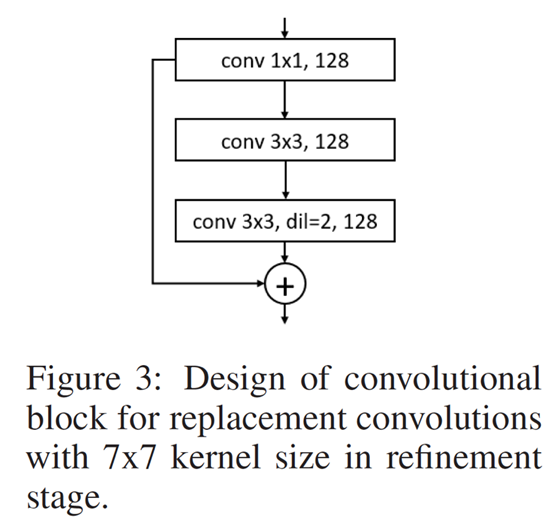
为了和vgg19有相同的感受视野,light weight openpose中使用下面的卷积块来替代vgg19中的7*7卷积(具体的感受视野怎么计算的,不太清楚了。。。)。该图对应代码中的RefinementStageBlock。
3 训练过程
分三个阶段(不要和initial stage、refine stage弄混了)
a 使用MobileNet V1预训练的模型训练1个stage(initial stage + stage 1)的light weight openpose。此阶段mAP大约在38%。
b 使用a的结果继续训练light weight openpose。此阶段mAP大约在39%。
c 使用b的结果,将stage设置为3(initial stage + stage 1+ stage 2+ stage 3),继续训练light weight openpose;但是测试时,只使用stage=1时的结果估计姿态。此阶段mAP大约在40%。
注意:
a每次训练时,直接使用上次训练得到的最后一个模型重新训练,同时没有改学习率等参数。
b每个阶段验证时,为了节约时间,可以只在在验证集的子集上验证(和在整个验证集上性能差距很小)。
4 代码
4.1 整体网络结构
主要网络代码如下:

1 class PoseEstimationWithMobileNet(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, num_refinement_stages=1, num_channels=128, num_heatmaps=19, num_pafs=38): 3 super().__init__() 4 self.model = nn.Sequential( # mobilenet V1的骨干网络 5 conv( 3, 32, stride=2, bias=False), # conv+BN+ReLU 6 conv_dw( 32, 64), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 7 conv_dw( 64, 128, stride=2), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 8 conv_dw(128, 128), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 9 conv_dw(128, 256, stride=2), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 10 conv_dw(256, 256), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 11 conv_dw(256, 512), # conv4_2 # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 12 conv_dw(512, 512, dilation=2, padding=2), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 13 conv_dw(512, 512), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 14 conv_dw(512, 512), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 15 conv_dw(512, 512), # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 16 conv_dw(512, 512) # conv5_5 # dw_conv(in,in, stride)+BN+ReLU + conv(in,out)+BN+ReLU 17 ) 18 self.cpm = Cpm(512, num_channels) # 降维模块 19 20 self.initial_stage = InitialStage(num_channels, num_heatmaps, num_pafs) # 初始阶段 21 self.refinement_stages = nn.ModuleList() 22 for idx in range(num_refinement_stages): 23 self.refinement_stages.append(RefinementStage(num_channels + num_heatmaps + num_pafs, num_channels, num_heatmaps, num_pafs)) # refine阶段 24 25 def forward(self, x): 26 backbone_features = self.model(x) 27 backbone_features = self.cpm(backbone_features) 28 29 stages_output = self.initial_stage(backbone_features) 30 for refinement_stage in self.refinement_stages: 31 stages_output.extend(refinement_stage(torch.cat([backbone_features, stages_output[-2], stages_output[-1]], dim=1))) 32 33 return stages_output 34 35 由于mobilenet V1输出为512维,有一个cpm的降维层,降维到128维,如下: 36 class Cpm(nn.Module): 37 def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): 38 super().__init__() 39 self.align = conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False) # conv+ReLU 40 self.trunk = nn.Sequential( 41 conv_dw_no_bn(out_channels, out_channels), # dw_conv(in,in)+ELU + conv(in,out)+ELU 42 conv_dw_no_bn(out_channels, out_channels), # dw_conv(in,in)+ELU + conv(in,out)+ELU 43 conv_dw_no_bn(out_channels, out_channels) # dw_conv(in,in)+ELU + conv(in,out)+ELU 44 ) 45 self.conv = conv(out_channels, out_channels, bn=False) # conv+ReLU 46 47 def forward(self, x): 48 x = self.align(x) 49 x = self.conv(x + self.trunk(x)) 50 return x
4.2 initial stage

1 class InitialStage(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, num_channels, num_heatmaps, num_pafs): 3 super().__init__() 4 self.trunk = nn.Sequential( # 权值共享 5 conv(num_channels, num_channels, bn=False), # conv+ReLU 6 conv(num_channels, num_channels, bn=False), # conv+ReLU 7 conv(num_channels, num_channels, bn=False) # conv+ReLU 8 ) 9 self.heatmaps = nn.Sequential( # heatmaps 10 conv(num_channels, 512, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False), # 1*1conv+ReLU 11 conv(512, num_heatmaps, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False, relu=False) # 1*1conv 12 ) 13 self.pafs = nn.Sequential( # pafs 14 conv(num_channels, 512, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False), # 1*1conv+ReLU 15 conv(512, num_pafs, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False, relu=False) # 1*1conv 16 ) 17 18 def forward(self, x): 19 trunk_features = self.trunk(x) 20 heatmaps = self.heatmaps(trunk_features) 21 pafs = self.pafs(trunk_features) 22 return [heatmaps, pafs]
4.3 refine stage
refine stage包括5个相同的RefinementStageBlock,用于权值共享。每个RefinementStageBlock如2.4所示。

1 class RefinementStageBlock(nn.Module): 2 def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): 3 super().__init__() 4 self.initial = conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False) # 1*1conv+ReLU 5 self.trunk = nn.Sequential( 6 conv(out_channels, out_channels), # conv+BN+ReLU 7 conv(out_channels, out_channels, dilation=2, padding=2) # conv+BN+ReLU 8 ) 9 10 def forward(self, x): 11 initial_features = self.initial(x) 12 trunk_features = self.trunk(initial_features) 13 return initial_features + trunk_features # 论文中2个3*3conv代替7*7conv 14 15 16 class RefinementStage(nn.Module): 17 def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_heatmaps, num_pafs): 18 super().__init__() 19 self.trunk = nn.Sequential( # 权值共享 20 RefinementStageBlock(in_channels, out_channels), 21 RefinementStageBlock(out_channels, out_channels), 22 RefinementStageBlock(out_channels, out_channels), 23 RefinementStageBlock(out_channels, out_channels), 24 RefinementStageBlock(out_channels, out_channels) 25 ) 26 self.heatmaps = nn.Sequential( # heatmaps 27 conv(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False), # 1*1conv+ReLU 28 conv(out_channels, num_heatmaps, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False, relu=False) # 1*1conv 29 ) 30 self.pafs = nn.Sequential( # pafs 31 conv(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False), # 1*1conv+ReLU 32 conv(out_channels, num_pafs, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bn=False, relu=False) # 1*1conv 33 ) 34 35 def forward(self, x): 36 trunk_features = self.trunk(x) 37 heatmaps = self.heatmaps(trunk_features) 38 pafs = self.pafs(trunk_features) 39 return [heatmaps, pafs]
4.4 各种自定义的conv
上面网络中使用的conv结构如下:

1 def conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bn=True, dilation=1, stride=1, relu=True, bias=True): 2 modules = [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, bias=bias)] 3 if bn: 4 modules.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)) 5 if relu: 6 modules.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True)) 7 return nn.Sequential(*modules) 8 9 10 def conv_dw(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, dilation=1): 11 return nn.Sequential( 12 nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation=dilation, groups=in_channels, bias=False), 13 nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels), 14 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 15 16 nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), 17 nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), 18 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), 19 ) 20 21 22 def conv_dw_no_bn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, dilation=1): 23 return nn.Sequential( 24 nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation=dilation, groups=in_channels, bias=False), 25 nn.ELU(inplace=True), 26 27 nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), 28 nn.ELU(inplace=True), 29 )
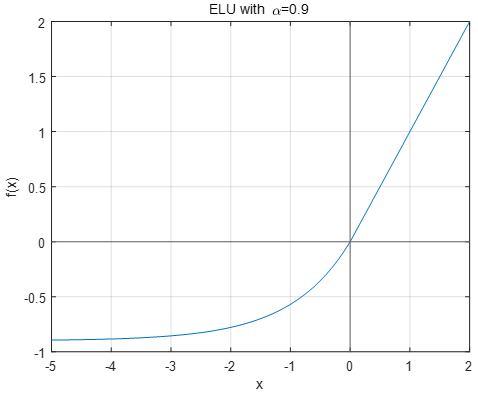
ELU激活函数如下:
4.5 损失函数
网络的损失函数如下,由于COCO数据库对某些很小的人没有标注,将这些地方的mask设置为0,防止这些人对训练造成干扰。

1 def l2_loss(input, target, mask, batch_size): 2 loss = (input - target) * mask 3 loss = (loss * loss) / 2 / batch_size 4 5 return loss.sum()
如下图a为图像,b为mask_miss。COCO中把远处的人标注了,但是没有标注关节点信息,为了防止这些人干扰训练,因而才有了mask_miss。所有人的mask减去mask_miss,就是上面的mask了。

(a)

(b)
4.6 train
train用到了ConvertKeypoints,Scale Rotate,CropPad,Flip等变换,见4.7.

1 def train(prepared_train_labels, train_images_folder, num_refinement_stages, base_lr, batch_size, batches_per_iter, 2 num_workers, checkpoint_path, weights_only, from_mobilenet, checkpoints_folder, log_after, 3 val_labels, val_images_folder, val_output_name, checkpoint_after, val_after): 4 net = PoseEstimationWithMobileNet(num_refinement_stages) 5 6 stride = 8 # 输入图像是特征图的倍数 7 sigma = 7 # 生成关节点heatmaps时,高斯核的标准差 8 path_thickness = 1 # 生成paf时躯干的宽度 9 dataset = CocoTrainDataset(prepared_train_labels, train_images_folder, 10 stride, sigma, path_thickness, 11 transform=transforms.Compose([ 12 ConvertKeypoints(), 13 Scale(), 14 Rotate(pad=(128, 128, 128)), 15 CropPad(pad=(128, 128, 128)), 16 Flip()])) 17 train_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers) 18 19 optimizer = optim.Adam([ 20 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.model, 'weight')}, 21 {'params': get_parameters_conv_depthwise(net.model, 'weight'), 'weight_decay': 0}, 22 {'params': get_parameters_bn(net.model, 'weight'), 'weight_decay': 0}, 23 {'params': get_parameters_bn(net.model, 'bias'), 'lr': base_lr * 2, 'weight_decay': 0}, 24 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.cpm, 'weight'), 'lr': base_lr}, 25 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.cpm, 'bias'), 'lr': base_lr * 2, 'weight_decay': 0}, 26 {'params': get_parameters_conv_depthwise(net.cpm, 'weight'), 'weight_decay': 0}, 27 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.initial_stage, 'weight'), 'lr': base_lr}, 28 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.initial_stage, 'bias'), 'lr': base_lr * 2, 'weight_decay': 0}, 29 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.refinement_stages, 'weight'), 'lr': base_lr * 4}, 30 {'params': get_parameters_conv(net.refinement_stages, 'bias'), 'lr': base_lr * 8, 'weight_decay': 0}, 31 {'params': get_parameters_bn(net.refinement_stages, 'weight'), 'weight_decay': 0}, 32 {'params': get_parameters_bn(net.refinement_stages, 'bias'), 'lr': base_lr * 2, 'weight_decay': 0}, 33 ], lr=base_lr, weight_decay=5e-4) 34 35 num_iter = 0 36 current_epoch = 0 37 drop_after_epoch = [100, 200, 260] 38 scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=drop_after_epoch, gamma=0.333) 39 if checkpoint_path: 40 checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path) 41 if from_mobilenet: 42 load_from_mobilenet(net, checkpoint) 43 else: 44 load_state(net, checkpoint) 45 if not weights_only: 46 optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer']) 47 scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['scheduler']) 48 num_iter = checkpoint['iter'] 49 current_epoch = checkpoint['current_epoch'] 50 51 net = DataParallel(net).cuda() 52 net.train() 53 for epochId in range(current_epoch, 280): 54 scheduler.step() 55 total_losses = [0, 0] * (num_refinement_stages + 1) # heatmaps loss, paf loss per stage(initial stage + refine stage) 56 batch_per_iter_idx = 0 57 for batch_data in train_loader: 58 if batch_per_iter_idx == 0: 59 optimizer.zero_grad() 60 61 images = batch_data['image'].cuda() 62 keypoint_masks = batch_data['keypoint_mask'].cuda() 63 paf_masks = batch_data['paf_mask'].cuda() 64 keypoint_maps = batch_data['keypoint_maps'].cuda() 65 paf_maps = batch_data['paf_maps'].cuda() 66 67 stages_output = net(images) 68 69 losses = [] 70 for loss_idx in range(len(total_losses) // 2): 71 losses.append(l2_loss(stages_output[loss_idx * 2], keypoint_maps, keypoint_masks, images.shape[0])) # 2i维为热图 72 losses.append(l2_loss(stages_output[loss_idx * 2 + 1], paf_maps, paf_masks, images.shape[0])) # 2i+1维为paf 73 total_losses[loss_idx * 2] += losses[-2].item() / batches_per_iter # 累积loss 74 total_losses[loss_idx * 2 + 1] += losses[-1].item() / batches_per_iter # 累积loss 75 76 loss = losses[0] 77 for loss_idx in range(1, len(losses)): 78 loss += losses[loss_idx] # 计算所有stage的loss 79 loss /= batches_per_iter # loss平均 80 loss.backward() 81 batch_per_iter_idx += 1 82 if batch_per_iter_idx == batches_per_iter: 83 optimizer.step() 84 batch_per_iter_idx = 0 85 num_iter += 1 86 else: 87 continue 88 89 if num_iter % log_after == 0: 90 print('Iter: {}'.format(num_iter)) 91 for loss_idx in range(len(total_losses) // 2): 92 print(' '.join(['stage{}_pafs_loss: {}', 'stage{}_heatmaps_loss: {}']).format( 93 loss_idx + 1, total_losses[loss_idx * 2 + 1] / log_after, loss_idx + 1, total_losses[loss_idx * 2] / log_after)) 94 for loss_idx in range(len(total_losses)): 95 total_losses[loss_idx] = 0 96 if num_iter % checkpoint_after == 0: 97 snapshot_name = '{}/checkpoint_iter_{}.pth'.format(checkpoints_folder, num_iter) 98 torch.save({'state_dict': net.module.state_dict(), 99 'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(), 100 'scheduler': scheduler.state_dict(), 101 'iter': num_iter, 102 'current_epoch': epochId}, 103 snapshot_name) 104 # if num_iter % val_after == 0: 105 #print('Validation...') 106 #evaluate(val_labels, val_output_name, val_images_folder, net) 107 #net.train()
4.7 transformations
transformations主要包括ConvertKeypoints,Scale Rotate,CropPad,Flip等变换。
4.7.1 ConvertKeypoints
ConvertKeypoints用于将coco的关键点顺序变换到代码中的关键点顺序。

1 class ConvertKeypoints(object): 2 def __call__(self, sample): 3 label = sample['label'] 4 h, w, _ = sample['image'].shape 5 keypoints = label['keypoints'] # keypoint[2]=0: 遮挡 1:可见 2:不在图像内 6 for keypoint in keypoints: # keypoint[2] == 0: occluded, == 1: visible, == 2: not in image 7 if keypoint[0] == keypoint[1] == 0: 8 keypoint[2] = 2 9 if (keypoint[0] < 0 or keypoint[0] >= w or keypoint[1] < 0 or keypoint[1] >= h): 10 keypoint[2] = 2 11 for other_label in label['processed_other_annotations']: 12 keypoints = other_label['keypoints'] 13 for keypoint in keypoints: 14 if keypoint[0] == keypoint[1] == 0: 15 keypoint[2] = 2 16 if (keypoint[0] < 0 or keypoint[0] >= w or keypoint[1] < 0 or keypoint[1] >= h): 17 keypoint[2] = 2 18 label['keypoints'] = self._convert(label['keypoints'], w, h) # 变成文中关节点的顺序,同时增加脖子 19 20 for other_label in label['processed_other_annotations']: 21 other_label['keypoints'] = self._convert(other_label['keypoints'], w, h) # 变成文中关节点的顺序,同时增加脖子 22 return sample 23 24 def _convert(self, keypoints, w, h): 25 # Nose, Neck, R hand, L hand, R leg, L leg, Eyes, Ears 26 reorder_map = [1, 7, 9, 11, 6, 8, 10, 13, 15, 17, 12, 14, 16, 3, 2, 5, 4] # COCO关节点到文中关节点的映射 27 converted_keypoints = list(keypoints[i - 1] for i in reorder_map) # 映射到文中的关节点顺序 28 # Add neck as a mean of shoulders 29 converted_keypoints.insert(1, [(keypoints[5][0] + keypoints[6][0]) / 2, (keypoints[5][1] + keypoints[6][1]) / 2, 0]) # 增加脖子 30 if keypoints[5][2] == 2 and keypoints[6][2] == 2: 31 converted_keypoints[1][2] = 2 32 elif keypoints[5][2] == 3 and keypoints[6][2] == 3: 33 converted_keypoints[1][2] = 3 34 elif keypoints[5][2] == 1 and keypoints[6][2] == 1: 35 converted_keypoints[1][2] = 1 36 if (converted_keypoints[1][0] < 0 or converted_keypoints[1][0] >= w or converted_keypoints[1][1] < 0 or converted_keypoints[1][1] >= h): 37 converted_keypoints[1][2] = 2 38 return converted_keypoints
其中coco和代码中的关键点顺序分别如下图所示,通过reorder_map中的值-1变换,并插入neck。
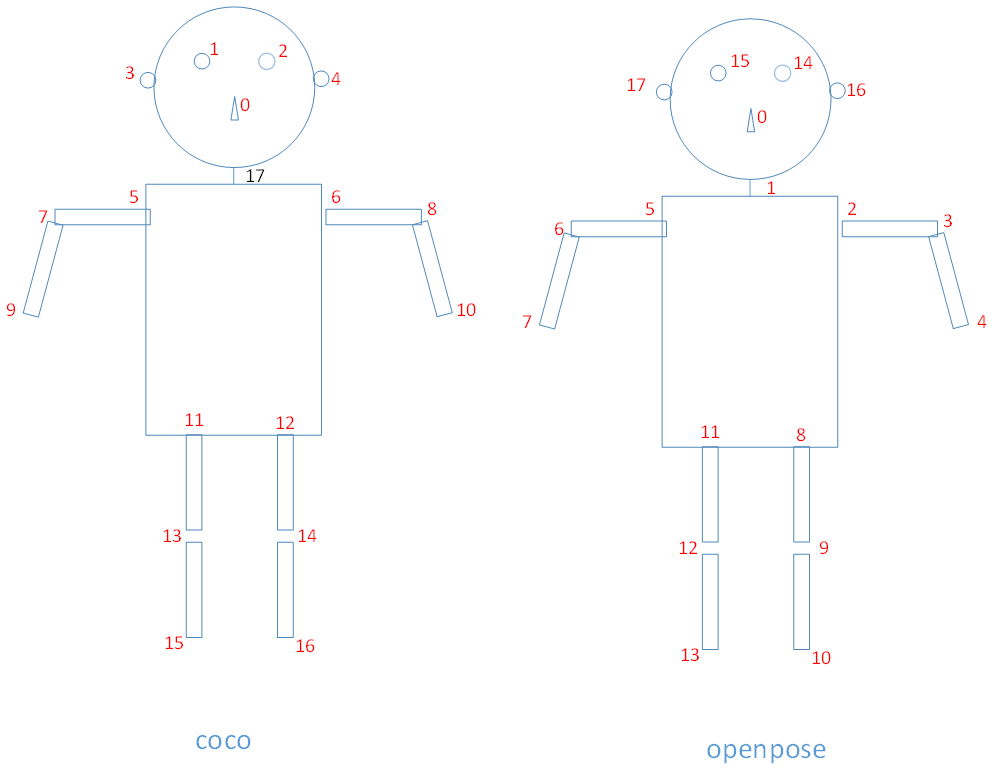
4.7.2 Scale
Scale用于缩放图像及关键点信息。

1 class Scale(object): 2 def __init__(self, prob=1, min_scale=0.5, max_scale=1.1, target_dist=0.6): 3 self._prob = prob 4 self._min_scale = min_scale 5 self._max_scale = max_scale 6 self._target_dist = target_dist 7 8 def __call__(self, sample): 9 prob = random.random() 10 scale_multiplier = 1 11 if prob <= self._prob: 12 prob = random.random() 13 scale_multiplier = (self._max_scale - self._min_scale) * prob + self._min_scale 14 label = sample['label'] 15 scale_abs = self._target_dist / label['scale_provided'] 16 scale = scale_abs * scale_multiplier 17 sample['image'] = cv2.resize(sample['image'], dsize=(0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale) 18 label['img_height'], label['img_width'], _ = sample['image'].shape 19 sample['mask'] = cv2.resize(sample['mask'], dsize=(0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale) 20 21 label['objpos'][0] *= scale 22 label['objpos'][1] *= scale 23 for keypoint in sample['label']['keypoints']: 24 keypoint[0] *= scale 25 keypoint[1] *= scale 26 for other_annotation in sample['label']['processed_other_annotations']: 27 other_annotation['objpos'][0] *= scale 28 other_annotation['objpos'][1] *= scale 29 for keypoint in other_annotation['keypoints']: 30 keypoint[0] *= scale 31 keypoint[1] *= scale 32 return sample
4.7.3 Rotate
Rotate用于旋转图像及关键点信息。

1 class Rotate(object): 2 def __init__(self, pad, max_rotate_degree=40): 3 self._pad = pad 4 self._max_rotate_degree = max_rotate_degree 5 6 def __call__(self, sample): 7 prob = random.random() 8 degree = (prob - 0.5) * 2 * self._max_rotate_degree 9 h, w, _ = sample['image'].shape 10 img_center = (w / 2, h / 2) 11 R = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(img_center, degree, 1) 12 13 abs_cos = abs(R[0, 0]) 14 abs_sin = abs(R[0, 1]) 15 16 bound_w = int(h * abs_sin + w * abs_cos) 17 bound_h = int(h * abs_cos + w * abs_sin) 18 dsize = (bound_w, bound_h) 19 20 R[0, 2] += dsize[0] / 2 - img_center[0] 21 R[1, 2] += dsize[1] / 2 - img_center[1] 22 sample['image'] = cv2.warpAffine(sample['image'], R, dsize=dsize, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, borderValue=self._pad) 23 sample['label']['img_height'], sample['label']['img_width'], _ = sample['image'].shape 24 sample['mask'] = cv2.warpAffine(sample['mask'], R, dsize=dsize, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, borderValue=(1, 1, 1)) # border is ok 25 label = sample['label'] 26 label['objpos'] = self._rotate(label['objpos'], R) # 旋转位置坐标 27 for keypoint in label['keypoints']: 28 point = [keypoint[0], keypoint[1]] 29 point = self._rotate(point, R) # 旋转位置坐标 30 keypoint[0], keypoint[1] = point[0], point[1] 31 for other_annotation in label['processed_other_annotations']: 32 for keypoint in other_annotation['keypoints']: 33 point = [keypoint[0], keypoint[1]] 34 point = self._rotate(point, R) # 旋转位置坐标 35 keypoint[0], keypoint[1] = point[0], point[1] 36 return sample 37 38 def _rotate(self, point, R): 39 return [R[0, 0] * point[0] + R[0, 1] * point[1] + R[0, 2], R[1, 0] * point[0] + R[1, 1] * point[1] + R[1, 2]]
4.7.4 CropPad
CropPad用于随机裁剪

1 class CropPad(object): 2 def __init__(self, pad, center_perterb_max=40, crop_x=368, crop_y=368): 3 self._pad = pad 4 self._center_perterb_max = center_perterb_max 5 self._crop_x = crop_x 6 self._crop_y = crop_y 7 8 def __call__(self, sample): 9 prob_x = random.random() 10 prob_y = random.random() 11 12 offset_x = int((prob_x - 0.5) * 2 * self._center_perterb_max) 13 offset_y = int((prob_y - 0.5) * 2 * self._center_perterb_max) 14 label = sample['label'] 15 shifted_center = (label['objpos'][0] + offset_x, label['objpos'][1] + offset_y) 16 offset_left = -int(shifted_center[0] - self._crop_x / 2) 17 offset_up = -int(shifted_center[1] - self._crop_y / 2) 18 19 cropped_image = np.empty(shape=(self._crop_y, self._crop_x, 3), dtype=np.uint8) 20 for i in range(3): 21 cropped_image[:, :, i].fill(self._pad[i]) 22 cropped_mask = np.empty(shape=(self._crop_y, self._crop_x), dtype=np.uint8) 23 cropped_mask.fill(1) 24 25 image_x_start = int(shifted_center[0] - self._crop_x / 2) 26 image_y_start = int(shifted_center[1] - self._crop_y / 2) 27 image_x_finish = image_x_start + self._crop_x 28 image_y_finish = image_y_start + self._crop_y 29 crop_x_start = 0 30 crop_y_start = 0 31 crop_x_finish = self._crop_x 32 crop_y_finish = self._crop_y 33 34 w, h = label['img_width'], label['img_height'] 35 should_crop = True 36 if image_x_start < 0: # Adjust crop area 37 crop_x_start -= image_x_start 38 image_x_start = 0 39 if image_x_start >= w: 40 should_crop = False 41 42 if image_y_start < 0: 43 crop_y_start -= image_y_start 44 image_y_start = 0 45 if image_y_start >= w: 46 should_crop = False 47 48 if image_x_finish > w: 49 diff = image_x_finish - w 50 image_x_finish -= diff 51 crop_x_finish -= diff 52 if image_x_finish < 0: 53 should_crop = False 54 55 if image_y_finish > h: 56 diff = image_y_finish - h 57 image_y_finish -= diff 58 crop_y_finish -= diff 59 if image_y_finish < 0: 60 should_crop = False 61 62 if should_crop: 63 cropped_image[crop_y_start:crop_y_finish, crop_x_start:crop_x_finish, :] = 64 sample['image'][image_y_start:image_y_finish, image_x_start:image_x_finish, :] 65 cropped_mask[crop_y_start:crop_y_finish, crop_x_start:crop_x_finish] = 66 sample['mask'][image_y_start:image_y_finish, image_x_start:image_x_finish] 67 68 sample['image'] = cropped_image 69 sample['mask'] = cropped_mask 70 label['img_width'] = self._crop_x 71 label['img_height'] = self._crop_y 72 73 label['objpos'][0] += offset_left 74 label['objpos'][1] += offset_up 75 for keypoint in label['keypoints']: 76 keypoint[0] += offset_left 77 keypoint[1] += offset_up 78 for other_annotation in label['processed_other_annotations']: 79 for keypoint in other_annotation['keypoints']: 80 keypoint[0] += offset_left 81 keypoint[1] += offset_up 82 83 return sample 84 85 def _inside(self, point, width, height): 86 if point[0] < 0 or point[1] < 0: 87 return False 88 if point[0] >= width or point[1] >= height: 89 return False 90 return True
4.7.5 Flip
此处的Flip,用于在训练阶段左右镜像图像。此时只需要将关键点对应位置左右互换(如_swap_left_right中的right和left),由于还未得到paf,因而不需要对paf进行任何处理。

1 class Flip(object): 2 def __init__(self, prob=0.5): 3 self._prob = prob 4 5 def __call__(self, sample): 6 prob = random.random() 7 do_flip = prob <= self._prob 8 if not do_flip: 9 return sample 10 11 sample['image'] = cv2.flip(sample['image'], 1) 12 sample['mask'] = cv2.flip(sample['mask'], 1) 13 14 label = sample['label'] 15 w, h = label['img_width'], label['img_height'] 16 label['objpos'][0] = w - 1 - label['objpos'][0] 17 for keypoint in label['keypoints']: 18 keypoint[0] = w - 1 - keypoint[0] 19 label['keypoints'] = self._swap_left_right(label['keypoints']) # 交换左右关节点 20 21 for other_annotation in label['processed_other_annotations']: 22 other_annotation['objpos'][0] = w - 1 - other_annotation['objpos'][0] # 水平镜像,只宽度需要重新计算 23 for keypoint in other_annotation['keypoints']: 24 keypoint[0] = w - 1 - keypoint[0] 25 other_annotation['keypoints'] = self._swap_left_right(other_annotation['keypoints']) # 交换左右关节点 26 27 return sample 28 29 def _swap_left_right(self, keypoints): 30 right = [2, 3, 4, 8, 9, 10, 14, 16] # 左右关节点索引 31 left = [5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 15, 17] 32 for r, l in zip(right, left): 33 keypoints[r], keypoints[l] = keypoints[l], keypoints[r] 34 return keypoints
4.8 val
val的代码没啥好说的,也就是convert_to_coco_format

1 def convert_to_coco_format(pose_entries, all_keypoints): 2 coco_keypoints = [] 3 scores = [] 4 for n in range(len(pose_entries)): 5 if len(pose_entries[n]) == 0: 6 continue 7 keypoints = [0] * 17 * 3 8 to_coco_map = [0, -1, 6, 8, 10, 5, 7, 9, 12, 14, 16, 11, 13, 15, 2, 1, 4, 3] 9 person_score = pose_entries[n][-2] 10 position_id = -1 11 for keypoint_id in pose_entries[n][:-2]: # 最后一个为分配给当前人的关节点的数量,倒数第二个为得分。因而去掉这两个。 12 position_id += 1 13 if position_id == 1: # no 'neck' in COCO。COCO中没有neck,而本代码中neck的idx为1,因而idx为1时,continue 14 continue 15 16 cx, cy, score, visibility = 0, 0, 0, 0 # keypoint not found 17 if keypoint_id != -1: 18 cx, cy, score = all_keypoints[int(keypoint_id), 0:3] 19 cx = cx + 0.5 20 cy = cy + 0.5 21 visibility = 1 22 keypoints[to_coco_map[position_id] * 3 + 0] = cx 23 keypoints[to_coco_map[position_id] * 3 + 1] = cy 24 keypoints[to_coco_map[position_id] * 3 + 2] = visibility 25 coco_keypoints.append(keypoints) 26 scores.append(person_score * max(0, (pose_entries[n][-1] - 1))) # -1 for 'neck' 27 return coco_keypoints, scores
4.9 gt label的生成
gt label通过coco.py生成,如下。其中BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS将4.7中openpose的关键点映射到下面的躯干。
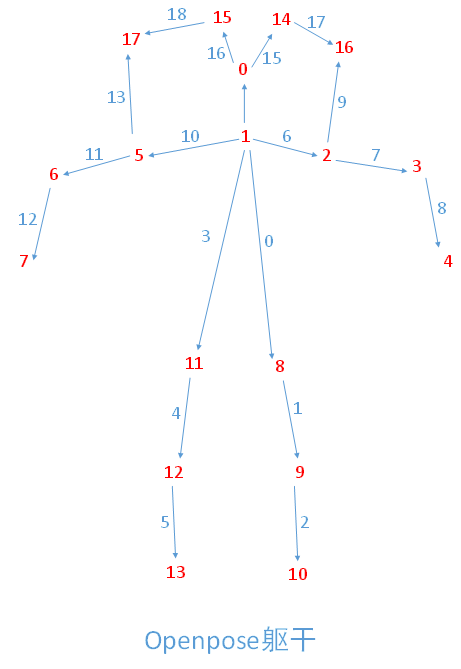

1 BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS = [[1, 8], [8, 9], [9, 10], [1, 11], [11, 12], [12, 13], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [2, 16], 2 [1, 5], [5, 6], [6, 7], [5, 17], [1, 0], [0, 14], [0, 15], [14, 16], [15, 17]] 3 4 5 def get_mask(segmentations, mask): 6 for segmentation in segmentations: 7 rle = pycocotools.mask.frPyObjects(segmentation, mask.shape[0], mask.shape[1]) 8 mask[pycocotools.mask.decode(rle) > 0.5] = 0 9 return mask 10 11 12 class CocoTrainDataset(Dataset): 13 def __init__(self, labels, images_folder, stride, sigma, paf_thickness, transform=None): 14 super().__init__() 15 self._images_folder = images_folder 16 self._stride = stride 17 self._sigma = sigma 18 self._paf_thickness = paf_thickness 19 self._transform = transform 20 with open(labels, 'rb') as f: 21 self._labels = pickle.load(f) 22 23 def __getitem__(self, idx): 24 label = copy.deepcopy(self._labels[idx]) # label modified in transform 25 image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self._images_folder, label['img_paths']), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) 26 mask = np.ones(shape=(label['img_height'], label['img_width']), dtype=np.float32) 27 mask = get_mask(label['segmentations'], mask) 28 sample = {'label': label, 'image': image, 'mask': mask} 29 if self._transform: 30 sample = self._transform(sample) 31 32 mask = cv2.resize(sample['mask'], dsize=None, fx=1/self._stride, fy=1/self._stride, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) 33 keypoint_maps = self._generate_keypoint_maps(sample) # 生成高斯分布的热图 34 sample['keypoint_maps'] = keypoint_maps 35 keypoint_mask = np.zeros(shape=keypoint_maps.shape, dtype=np.float32) # 热图的mask 36 for idx in range(keypoint_mask.shape[0]): 37 keypoint_mask[idx] = mask # 将实际mask复制到热图mask的每一层上面 38 sample['keypoint_mask'] = keypoint_mask 39 40 paf_maps = self._generate_paf_maps(sample) # 增加paf 41 sample['paf_maps'] = paf_maps 42 paf_mask = np.zeros(shape=paf_maps.shape, dtype=np.float32) 43 for idx in range(paf_mask.shape[0]): 44 paf_mask[idx] = mask # 将实际mask复制到paf mask的每一层上面 45 sample['paf_mask'] = paf_mask 46 47 image = sample['image'].astype(np.float32) 48 image = (image - 128) / 256 # 归一化 49 sample['image'] = image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # bgr to rgb 50 return sample 51 52 def __len__(self): 53 return len(self._labels) 54 55 def _generate_keypoint_maps(self, sample): 56 n_keypoints = 18 # 关节点总数量 57 n_rows, n_cols, _ = sample['image'].shape 58 keypoint_maps = np.zeros(shape=(n_keypoints + 1, n_rows // self._stride, n_cols // self._stride), dtype=np.float32) # +1 for bg,增加背景 59 60 label = sample['label'] 61 for keypoint_idx in range(n_keypoints): 62 keypoint = label['keypoints'][keypoint_idx] 63 if keypoint[2] <= 1: 64 self._add_gaussian(keypoint_maps[keypoint_idx], keypoint[0], keypoint[1], self._stride, self._sigma) # 热图每一层增加高斯分布的热图 65 for another_annotation in label['processed_other_annotations']: 66 keypoint = another_annotation['keypoints'][keypoint_idx] 67 if keypoint[2] <= 1: 68 self._add_gaussian(keypoint_maps[keypoint_idx], keypoint[0], keypoint[1], self._stride, self._sigma) # 热图每一层增加高斯分布的热图 69 keypoint_maps[-1] = 1 - keypoint_maps.max(axis=0) # 背景 70 return keypoint_maps 71 72 def _add_gaussian(self, keypoint_map, x, y, stride, sigma): 73 n_sigma = 4 74 tl = [int(x - n_sigma * sigma), int(y - n_sigma * sigma)] # 根据当前坐标,算出在4sigma内的起点和终点,此处为起点 75 tl[0] = max(tl[0], 0) 76 tl[1] = max(tl[1], 0) 77 78 br = [int(x + n_sigma * sigma), int(y + n_sigma * sigma)] # 根据当前坐标,算出在4sigma内的起点和终点,此处为终点 79 map_h, map_w = keypoint_map.shape # 特征图大小 80 br[0] = min(br[0], map_w * stride) # 放大回原始图像大小 81 br[1] = min(br[1], map_h * stride) # 放大回原始图像大小 82 83 shift = stride / 2 - 0.5 84 for map_y in range(tl[1] // stride, br[1] // stride): # y在特征图上的范围 85 for map_x in range(tl[0] // stride, br[0] // stride): # x在特征图上的范围 86 d2 = (map_x * stride + shift - x) * (map_x * stride + shift - x) + (map_y * stride + shift - y) * (map_y * stride + shift - y) # 距离的平方 87 exponent = d2 / 2 / sigma / sigma 88 if exponent > 4.6052: # threshold, ln(100), ~0.01 89 continue 90 keypoint_map[map_y, map_x] += math.exp(-exponent) # 不同关节点热图求和,而非像论文中那样使用max 91 if keypoint_map[map_y, map_x] > 1: 92 keypoint_map[map_y, map_x] = 1 93 94 def _generate_paf_maps(self, sample): 95 n_pafs = len(BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS) 96 n_rows, n_cols, _ = sample['image'].shape 97 paf_maps = np.zeros(shape=(n_pafs * 2, n_rows // self._stride, n_cols // self._stride), dtype=np.float32) 98 99 label = sample['label'] 100 for paf_idx in range(n_pafs): 101 keypoint_a = label['keypoints'][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[paf_idx][0]] # 当前躯干起点 102 keypoint_b = label['keypoints'][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[paf_idx][1]] # 当前躯干终点 103 if keypoint_a[2] <= 1 and keypoint_b[2] <= 1: # 起点和终点均在图像内,则增加paf 104 self._set_paf(paf_maps[paf_idx * 2:paf_idx * 2 + 2], keypoint_a[0], keypoint_a[1], keypoint_b[0], keypoint_b[1], self._stride, self._paf_thickness) 105 for another_annotation in label['processed_other_annotations']: 106 keypoint_a = another_annotation['keypoints'][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[paf_idx][0]] # 当前躯干起点 107 keypoint_b = another_annotation['keypoints'][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[paf_idx][1]] # 当前躯干终点 108 if keypoint_a[2] <= 1 and keypoint_b[2] <= 1: # 起点和终点均在图像内,则增加paf 109 self._set_paf(paf_maps[paf_idx * 2:paf_idx * 2 + 2], keypoint_a[0], keypoint_a[1], keypoint_b[0], keypoint_b[1], self._stride, self._paf_thickness) 110 return paf_maps 111 112 def _set_paf(self, paf_map, x_a, y_a, x_b, y_b, stride, thickness): 113 x_a /= stride # 原始坐标映射到特征图上坐标 114 y_a /= stride 115 x_b /= stride 116 y_b /= stride 117 x_ba = x_b - x_a # x方向长度 118 y_ba = y_b - y_a # y方向长度 119 _, h_map, w_map = paf_map.shape 120 x_min = int(max(min(x_a, x_b) - thickness, 0)) # 起点到终点的方框四周增加thickness个像素 121 x_max = int(min(max(x_a, x_b) + thickness, w_map)) 122 y_min = int(max(min(y_a, y_b) - thickness, 0)) 123 y_max = int(min(max(y_a, y_b) + thickness, h_map)) 124 norm_ba = (x_ba * x_ba + y_ba * y_ba) ** 0.5 # 起点指向终点的向量的模长 125 if norm_ba < 1e-7: # Same points, no paf 126 return 127 x_ba /= norm_ba # 起点指向终点的单位向量的x长度 128 y_ba /= norm_ba # 起点指向终点的单位向量的y长度 129 130 for y in range(y_min, y_max): # 依次遍历该方框中每一个点 131 for x in range(x_min, x_max): 132 x_ca = x - x_a # 起点指向当前点的向量 133 y_ca = y - y_a 134 d = math.fabs(x_ca * y_ba - y_ca * x_ba) # 起点指向当前点的向量在起点指向终点的单位向量垂直的单位向量上的投影 135 if d <= thickness: # 投影小于阈值,则增加该单位向量到paf对应躯干中 136 paf_map[0, y, x] = x_ba 137 paf_map[1, y, x] = y_ba 138 139 140 class CocoValDataset(Dataset): 141 def __init__(self, labels, images_folder): 142 super().__init__() 143 with open(labels, 'r') as f: 144 self._labels = json.load(f) 145 self._images_folder = images_folder 146 147 def __getitem__(self, idx): 148 file_name = self._labels['images'][idx]['file_name'] 149 img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self._images_folder, file_name), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) 150 return {'img': img, 'file_name': file_name} 151 152 def __len__(self): 153 return len(self._labels['images'])
注意:_add_gaussian的最后两行,合并多个高斯confidence maps时,没有使用论文中的max,而是使用min(sum(peaks), 1)。此处和官方openpose代码一致,该文件位于caffe_train-master/src/caffe/cpm_data_transformer.cpp,具体代码如下:

另一方面,_set_paf函数最后两行,直将当前的单位向量增加到pafs中。若一个人某躯干将另一个人相同的躯干遮挡(或出现交叉的情况),则只会计算某一个躯干(依遍历顺序而定),但是实际上这种情况发生的概率应该相当低。
4.10 extract_keypoints和group_keypoints
在提取关节点extract_keypoints的函数中,给每个提取到的关节点分配了一个索引,这样所有的关节点索引均不相同。在group_keypoints 中,将这个索引放到pose_entries对应的位置,这样不会有关节点被分配给2个人。如下面(a)、(b)两个图所示。

(a)

(b)
keypoints.py如下:

1 # 本文件中新的paf顺序,不确定为何不用coco.py中原始的顺序??? 2 BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS = [[1, 2], [1, 5], [2, 3], [3, 4], [5, 6], [6, 7], [1, 8], [8, 9], [9, 10], [1, 11], 3 [11, 12], [12, 13], [1, 0], [0, 14], [14, 16], [0, 15], [15, 17], [2, 16], [5, 17]] 4 # 本文件中新的paf顺序在原始paf(coco.py)中的x和y坐标的索引 5 BODY_PARTS_PAF_IDS = ([12, 13], [20, 21], [14, 15], [16, 17], [22, 23], [24, 25], [0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5], [6, 7], 6 [8, 9], [10, 11], [28, 29], [30, 31], [34, 35], [32, 33], [36, 37], [18, 19], [26, 27]) 7 8 9 def linspace2d(start, stop, n=10): 10 points = 1 / (n - 1) * (stop - start) # 起点和终点之间插值点,包括终点共n个 11 return points[:, None] * np.arange(n) + start[:, None] 12 13 14 def extract_keypoints(heatmap, all_keypoints, total_keypoint_num): 15 heatmap[heatmap < 0.1] = 0 # 热图中小于阈值的置0 16 heatmap_with_borders = np.pad(heatmap, [(2, 2), (2, 2)], mode='constant') # 边界各填充2个像素 17 heatmap_center = heatmap_with_borders[1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[0]-1, 1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[1]-1] # heatmap_center中心,比热图四边各多1个像素 18 heatmap_left = heatmap_with_borders[1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[0]-1, 2:heatmap_with_borders.shape[1]] # 实际上为热图右边的图 19 heatmap_right = heatmap_with_borders[1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[0]-1, 0:heatmap_with_borders.shape[1]-2] # 实际上为热图左边的图 20 heatmap_up = heatmap_with_borders[2:heatmap_with_borders.shape[0], 1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[1]-1] # 实际上为热图下边的图 21 heatmap_down = heatmap_with_borders[0:heatmap_with_borders.shape[0]-2, 1:heatmap_with_borders.shape[1]-1] # 实际上为热图上边的图 22 23 heatmap_peaks = (heatmap_center > heatmap_left) & (heatmap_center > heatmap_right) & 24 (heatmap_center > heatmap_up) & (heatmap_center > heatmap_down) # 热图当前像素比上下左右的热图的像素都大的,为峰值 25 heatmap_peaks = heatmap_peaks[1:heatmap_center.shape[0]-1, 1:heatmap_center.shape[1]-1] # 得到和原始的热图一样大的热图 26 keypoints = list(zip(np.nonzero(heatmap_peaks)[1], np.nonzero(heatmap_peaks)[0])) # (w, h) 得到峰值(关节点)的xy坐标 np.nonzero得到2*N向量,0为x,1为y 27 keypoints = sorted(keypoints, key=itemgetter(0)) # 按照x坐标从小到大排序 28 29 suppressed = np.zeros(len(keypoints), np.uint8) # 第i个坐标(关节点)应该被抑制的flag 30 keypoints_with_score_and_id = [] 31 keypoint_num = 0 32 for i in range(len(keypoints)): 33 if suppressed[i]: 34 continue 35 for j in range(i+1, len(keypoints)): # 依次比较第i点和后面所有j点距离的平方的和,小于阈值,则抑制后面第j个点 36 if math.sqrt((keypoints[i][0] - keypoints[j][0]) ** 2 + (keypoints[i][1] - keypoints[j][1]) ** 2) < 6: 37 suppressed[j] = 1 38 keypoint_with_score_and_id = (keypoints[i][0], keypoints[i][1], heatmap[keypoints[i][1], keypoints[i][0]], total_keypoint_num + keypoint_num) 39 keypoints_with_score_and_id.append(keypoint_with_score_and_id) # 当前点的x、y坐标,当前点热图值,当前点在所有特征点中的index 40 keypoint_num += 1 # 特征点数量+1 41 all_keypoints.append(keypoints_with_score_and_id) # 将当前热图上检测到的所有关节点添加到所有关节点中 42 return keypoint_num # 返回总共特征点的数量 43 44 45 def group_keypoints(all_keypoints_by_type, pafs, pose_entry_size=20, min_paf_score=0.05, demo=False): 46 pose_entries = [] 47 all_keypoints = np.array([item for sublist in all_keypoints_by_type for item in sublist]) # 将所有关节点展开成N*4的array 48 for part_id in range(len(BODY_PARTS_PAF_IDS)): # 将躯干某个连接的单位向量映射到paf对应的通道 49 part_pafs = pafs[:, :, BODY_PARTS_PAF_IDS[part_id]] # 得到当前躯干的2维单位向量(xy) 50 kpts_a = all_keypoints_by_type[BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][0]] # 当前躯干所有起点 BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS为将关节点连接成躯干的映射 51 kpts_b = all_keypoints_by_type[BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][1]] # 当前躯干所有终点 kpts_a和kpts_b为[],里面可能有几个4维向量,也可能为空 52 num_kpts_a = len(kpts_a) # 起点个数 53 num_kpts_b = len(kpts_b) # 终点个数 54 kpt_a_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][0] # 当前躯干起点的id 55 kpt_b_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][1] # 当前躯干终点的id 56 57 if num_kpts_a == 0 and num_kpts_b == 0: # no keypoints for such body part # 当前躯干无关节点 58 continue 59 elif num_kpts_a == 0: # body part has just 'b' keypoints 当前躯干只有终点的关节点 60 for i in range(num_kpts_b): # 依次遍历所有终点 61 num = 0 62 for j in range(len(pose_entries)): # check if already in some pose, was added by another body part 和已经分配的所有人依次比较 63 if pose_entries[j][kpt_b_id] == kpts_b[i][3]: # 如果当前终点已经分配给了某个人 64 num += 1 # 数量+1 65 continue # 退出此处for j的循环 66 if num == 0: # 当前终点未分配给任何人,则新建一个人 67 pose_entry = np.ones(pose_entry_size) * -1 68 pose_entry[kpt_b_id] = kpts_b[i][3] # keypoint idx 69 pose_entry[-1] = 1 # num keypoints in pose 70 pose_entry[-2] = kpts_b[i][2] # pose score 71 pose_entries.append(pose_entry) 72 continue 73 elif num_kpts_b == 0: # body part has just 'a' keypoints 当前躯干只有起点的关节点 74 for i in range(num_kpts_a): # 依次遍历所有起点 75 num = 0 76 for j in range(len(pose_entries)): # 和分配的所有人依次比较 77 if pose_entries[j][kpt_a_id] == kpts_a[i][3]: # 如果当前起点已经分配给了某个人 78 num += 1 # 数量+1 79 continue # 退出此处for j的循环 80 if num == 0: # 当前起点未分配给任何人,则新建一个人 81 pose_entry = np.ones(pose_entry_size) * -1 82 pose_entry[kpt_a_id] = kpts_a[i][3] 83 pose_entry[-1] = 1 84 pose_entry[-2] = kpts_a[i][2] 85 pose_entries.append(pose_entry) 86 continue 87 88 connections = [] # 躯干的连接 # 当前躯干起点和终点都有关节点 89 for i in range(num_kpts_a): # 依次遍历起点的每个关节点 90 kpt_a = np.array(kpts_a[i][0:2]) # 起点当前关节点的坐标 91 for j in range(num_kpts_b): # 依次遍历终点的每个关节点 92 kpt_b = np.array(kpts_b[j][0:2]) # 终点当前关节点的坐标 93 mid_point = [(), ()] 94 mid_point[0] = (int(round((kpt_a[0] + kpt_b[0]) * 0.5)), int(round((kpt_a[1] + kpt_b[1]) * 0.5))) 95 mid_point[1] = mid_point[0] # 起点和终点的中点 96 97 vec = [kpt_b[0] - kpt_a[0], kpt_b[1] - kpt_a[1]] # 起点指向终点的单位向量 98 vec_norm = math.sqrt(vec[0] ** 2 + vec[1] ** 2) 99 if vec_norm == 0: 100 continue 101 vec[0] /= vec_norm 102 vec[1] /= vec_norm 103 cur_point_score = (vec[0] * part_pafs[mid_point[0][1], mid_point[0][0], 0] + # part_pafs第0维为y索引,第1维为x索引,第2维为paf单位 104 vec[1] * part_pafs[mid_point[1][1], mid_point[1][0], 1]) # 向量的x或者y索引,此处为nx*x+ny*y,即paf在单位向量上的投影长度 105 106 height_n = pafs.shape[0] // 2 107 success_ratio = 0 108 point_num = 10 # number of points to integration over paf # paf上两点之间抽10个点,累计paf 109 if cur_point_score > -100: 110 passed_point_score = 0 111 passed_point_num = 0 112 x, y = linspace2d(kpt_a, kpt_b) # 起点和终点之间插值,得到point_num个点 113 for point_idx in range(point_num): 114 if not demo: 115 px = int(round(x[point_idx])) # 四舍五入坐标 116 py = int(round(y[point_idx])) 117 else: 118 px = int(x[point_idx]) # 截断坐标 119 py = int(y[point_idx]) 120 paf = part_pafs[py, px, 0:2] # 得到起点和终点中间抽点处paf的xy向量 121 cur_point_score = vec[0] * paf[0] + vec[1] * paf[1] # 该向量在起点指向终点单位向量上的投影 122 if cur_point_score > min_paf_score: # 投影大于阈值 123 passed_point_score += cur_point_score # 累计插值点score 124 passed_point_num += 1 # 累计插值点数量 125 success_ratio = passed_point_num / point_num # 插值点中大于阈值的点的数量占总插值点数量的比例 126 ratio = 0 127 if passed_point_num > 0: 128 ratio = passed_point_score / passed_point_num # 累计paf的平均值 129 ratio += min(height_n / vec_norm - 1, 0) # 两特征点距离较远,则惩罚paf平均值(较远左侧小于0) 130 if ratio > 0 and success_ratio > 0.8: # 累计paf平均值大于0,且两关节点之间插值的点大于阈值的点的比例大于阈值 131 score_all = ratio + kpts_a[i][2] + kpts_b[j][2] # paf+起点热图+终点热图,作为当前起点和终点是一个躯干的score 132 connections.append([i, j, ratio, score_all]) # 当前起点和终点是一个躯干时起点在该关节点所有起点中的索引,终点在该关节点中所有终点的索引,paf均值,是一个躯干的得分 133 if len(connections) > 0: 134 connections = sorted(connections, key=itemgetter(2), reverse=True) # 按照paf均值排序 135 136 num_connections = min(num_kpts_a, num_kpts_b) # 当前图像上该躯干最多的数量(起点和终点较少值) 137 has_kpt_a = np.zeros(num_kpts_a, dtype=np.int32) # 起点被占用的flag 138 has_kpt_b = np.zeros(num_kpts_b, dtype=np.int32) # 终点被占用的flag 139 filtered_connections = [] # 清理之后的connections:当前躯干起点在所有关节点中的索引,终点在所有关节点中的索引,paf均值 140 for row in range(len(connections)): 141 if len(filtered_connections) == num_connections: # 已经达到最多关节点数量了,不用继续比较了 142 break 143 i, j, cur_point_score = connections[row][0:3] # 当前起点和终点是一个躯干时起点在该关节点所有起点中的索引,终点在该关节点中所有终点的索引,paf均值 144 if not has_kpt_a[i] and not has_kpt_b[j]: # 起点和终点均未被占用(如果i某个起点或者某个终点被分配给了不同的躯干,因paf从大到小排序,故paf较小的忽略) 145 filtered_connections.append([kpts_a[i][3], kpts_b[j][3], cur_point_score]) # 当前躯干起点在所有关节点中的索引,终点在所有关节点中的索引,paf均值 146 has_kpt_a[i] = 1 # 对应起点被占用 147 has_kpt_b[j] = 1 # 对应终点被占用 148 connections = filtered_connections # 使用清理之后的connections,实际上score_all未使用 149 if len(connections) == 0: # 当前无躯干,计算下一个躯干 150 continue 151 152 if part_id == 0: # 第一次计算躯干 153 pose_entries = [np.ones(pose_entry_size) * -1 for _ in range(len(connections))] # 前18个为每个人各个关节点在所有关节点中的索引,最后两个分别为总分值和分配给这个人关节点的数量 154 for i in range(len(connections)): # 依次遍历当前找到的所有该躯干 155 pose_entries[i][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[0][0]] = connections[i][0] # 起点在所有关节点中的索引 156 pose_entries[i][BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[0][1]] = connections[i][1] # 终点在所有关节点中的索引 157 pose_entries[i][-1] = 2 # 当前人所有关节点的数量 158 pose_entries[i][-2] = np.sum(all_keypoints[connections[i][0:2], 2]) + connections[i][2] # 两个关节点热图值+平均paf值 159 elif part_id == 17 or part_id == 18: # 最后两个躯干 160 kpt_a_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][0] # 起点的id 161 kpt_b_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][1] # 终点的id 162 for i in range(len(connections)): # 将当前躯干和part_id=0时分配的所有人依次比较。此处为当前躯干 163 for j in range(len(pose_entries)): # 此处为分配的所有人 164 if pose_entries[j][kpt_a_id] == connections[i][0] and pose_entries[j][kpt_b_id] == -1: # 当前躯干的起点和分配到的某个人的起点一致,且当前躯干的终点未分配 165 pose_entries[j][kpt_b_id] = connections[i][1] # 将当前躯干的终点分配到这个人对应终点上 166 elif pose_entries[j][kpt_b_id] == connections[i][1] and pose_entries[j][kpt_a_id] == -1: # 当前躯干的终点和分配到的某个人的终点一致,且当前躯干的起点未分配 167 pose_entries[j][kpt_a_id] = connections[i][0] # 将当前躯干的起点分配到这个人对应起点上 168 continue 169 else: 170 kpt_a_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][0] # 起点的id 171 kpt_b_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][1] # 终点的id 172 for i in range(len(connections)): # 将当前躯干和part_id=0时分配的所有人依次比较。此处为当前躯干 173 num = 0 174 for j in range(len(pose_entries)): # 此处为分配的所有人 175 if pose_entries[j][kpt_a_id] == connections[i][0]: # 当前躯干的起点和分配到的某个人的起点一致 176 pose_entries[j][kpt_b_id] = connections[i][1] # 将当前躯干的终点分配到这个人对应终点上 177 num += 1 # 分配的人+1 178 pose_entries[j][-1] += 1 # 当前人所有关节点的数量+1 179 pose_entries[j][-2] += all_keypoints[connections[i][1], 2] + connections[i][2] # 当前人socre增加 180 if num == 0: # 如果没有分配到的人,则新建一个人 181 pose_entry = np.ones(pose_entry_size) * -1 182 pose_entry[kpt_a_id] = connections[i][0] 183 pose_entry[kpt_b_id] = connections[i][1] 184 pose_entry[-1] = 2 185 pose_entry[-2] = np.sum(all_keypoints[connections[i][0:2], 2]) + connections[i][2] 186 pose_entries.append(pose_entry) 187 188 filtered_entries = [] 189 for i in range(len(pose_entries)): # 依次遍历所有分配的人 190 if pose_entries[i][-1] < 3 or (pose_entries[i][-2] / pose_entries[i][-1] < 0.2): # 如果当前人关节点数量少于3,或者当前人平均得分小于0.2,则删除该人 191 continue 192 filtered_entries.append(pose_entries[i]) 193 pose_entries = np.asarray(filtered_entries) 194 return pose_entries, all_keypoints # 返回所有分配的人(前18维为每个人各个关节点在所有关节点中的索引,后两唯为每个人得分及每个人关节点数量),及所有关节点信息
4.11 demo
demo中两个函数代码如下:

1 def infer_fast(net, img, net_input_height_size, stride, upsample_ratio, cpu, 2 pad_value=(0, 0, 0), img_mean=(128, 128, 128), img_scale=1/256): 3 height, width, _ = img.shape # 实际高宽 4 scale = net_input_height_size / height # 将实际高所放到期望高的缩放倍数 5 6 scaled_img = cv2.resize(img, (0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) # 缩放后的图像 7 scaled_img = normalize(scaled_img, img_mean, img_scale) # 归一化图像 8 min_dims = [net_input_height_size, max(scaled_img.shape[1], net_input_height_size)] 9 padded_img, pad = pad_width(scaled_img, stride, pad_value, min_dims) # 填充到高宽为stride整数倍的值 10 11 tensor_img = torch.from_numpy(padded_img).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0).float() # 由HWC转成CHW(BGR格式) 12 if not cpu: 13 tensor_img = tensor_img.cuda() 14 15 stages_output = net(tensor_img) # 得到网络的输出 16 17 stage2_heatmaps = stages_output[-2] # 最后一个stage的热图 18 heatmaps = np.transpose(stage2_heatmaps.squeeze().cpu().data.numpy(), (1, 2, 0)) # 最后一个stage的热图作为最终的热图 19 heatmaps = cv2.resize(heatmaps, (0, 0), fx=upsample_ratio, fy=upsample_ratio, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) # 热图放大upsample_ratio倍 20 21 stage2_pafs = stages_output[-1] # 最后一个stage的paf 22 pafs = np.transpose(stage2_pafs.squeeze().cpu().data.numpy(), (1, 2, 0)) # 最后一个stage的paf作为最终的paf 23 pafs = cv2.resize(pafs, (0, 0), fx=upsample_ratio, fy=upsample_ratio, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC) # paf放大upsample_ratio倍 24 25 return heatmaps, pafs, scale, pad # 返回热图,paf,输入模型图像相比原始图像缩放倍数,输入模型图像padding尺寸 26 27 28 def run_demo(net, image_provider, height_size, cpu): 29 net = net.eval() 30 if not cpu: 31 net = net.cuda() 32 33 stride = 8 34 upsample_ratio = 4 35 color = [0, 224, 255] 36 for img in image_provider: 37 orig_img = img.copy() 38 heatmaps, pafs, scale, pad = infer_fast(net, img, height_size, stride, upsample_ratio, cpu) # 热图,paf,输入模型图像相比原始图像缩放倍数,输入模型图像padding尺寸 39 40 total_keypoints_num = 0 41 all_keypoints_by_type = [] # all_keypoints_by_type为18个list,每个list包含Ni个当前点的x、y坐标,当前点热图值,当前点在所有特征点中的index 42 for kpt_idx in range(18): # 19th for bg 第19个为背景,之考虑前18个关节点 43 total_keypoints_num += extract_keypoints(heatmaps[:, :, kpt_idx], all_keypoints_by_type, total_keypoints_num) 44 45 pose_entries, all_keypoints = group_keypoints(all_keypoints_by_type, pafs, demo=True) # 得到所有分配的人(前18维为每个人各个关节点在所有关节点中的索引,后两唯为每个人得分及每个人关节点数量),及所有关节点信息 46 for kpt_id in range(all_keypoints.shape[0]): # 依次将每个关节点信息缩放回原始图像上 47 all_keypoints[kpt_id, 0] = (all_keypoints[kpt_id, 0] * stride / upsample_ratio - pad[1]) / scale 48 all_keypoints[kpt_id, 1] = (all_keypoints[kpt_id, 1] * stride / upsample_ratio - pad[0]) / scale 49 for n in range(len(pose_entries)): # 依次遍历找到的每个人 50 if len(pose_entries[n]) == 0: 51 continue 52 for part_id in range(len(BODY_PARTS_PAF_IDS) - 2): # 将躯干某个连接的单位向量映射到paf对应的通道 53 kpt_a_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][0] # 当前躯干起点的id 54 global_kpt_a_id = pose_entries[n][kpt_a_id] # 当前关节点在所有关节点中的索引 55 if global_kpt_a_id != -1: # 分配了当前关节点 56 x_a, y_a = all_keypoints[int(global_kpt_a_id), 0:2] # 当前关节点在原图像上的坐标 57 cv2.circle(img, (int(x_a), int(y_a)), 3, color, -1) # 原图画圆 58 kpt_b_id = BODY_PARTS_KPT_IDS[part_id][1] # 当前躯干终点的id 59 global_kpt_b_id = pose_entries[n][kpt_b_id] # 当前关节点在所有关节点中的索引 60 if global_kpt_b_id != -1: # 分配了当前关节点 61 x_b, y_b = all_keypoints[int(global_kpt_b_id), 0:2] # 当前关节点在原图像上的坐标 62 cv2.circle(img, (int(x_b), int(y_b)), 3, color, -1) # 原图画圆 63 if global_kpt_a_id != -1 and global_kpt_b_id != -1: # 起点和终点均分配 64 cv2.line(img, (int(x_a), int(y_a)), (int(x_b), int(y_b)), color, 2) # 画连接起点和终点的直线 65 66 img = cv2.addWeighted(orig_img, 0.6, img, 0.4, 0) # 0.6 * orig_img + 0.4 * img 67 cv2.imwrite('res.jpg', img)
4.12 左右镜像
此处的左右镜像,指测试阶段的左右镜像。不要和4.7.5中训练阶段的Flip弄混。由于在测试阶段,已经得到了关键点和paf,因而若左右镜像图像,需要将heatmaps及pafs进行重新映射,如下表所示。另一方面,需要将paf的x坐标取负,因为paf是从起点指向终点的向量。左右镜像后,起点指向终点的向量的y分量不变,但是x分量则相反。

