FP-Growth是一种常被用来进行关联分析,挖掘频繁项的算法。与Aprior算法相比,FP-Growth算法采用前缀树的形式来表征数据,减少了扫描事务数据库的次数,通过递归地生成条件FP-tree来挖掘频繁项。参考资料[1]详细分析了这一过程。事实上,面对大数据量时,FP-Growth算法生成的FP-tree非常大,无法放入内存,挖掘到的频繁项也可能有指数多个。本文将分析如何并行化FP-Growth算法以及Mahout中并行化FP-Growth算法的源码。
1. 并行化FP-Growth
并行化FP-Growth的方法有很多,最早提出使用MapReduce并行化FP-Growth算法的应该是来自Google Beijing Research的Haoyuan Li等(见参考资料[2])。他们提出使用三次MapReduce来并行化FP-Growth,整个过程大致可以分为五个步骤:
Step 1:Sharding
为了均衡整个集群的读写性能,将事务数据库分成若干个数据片段(shard),存储到P个节点中。
Step 2:Parallel Counting
与WordCount类似,通过一次MapReduce来计算每一个项(item)的支持度。具体来说,每一个mapper将从hdfs中取得事务数据库的若干个数据片段(shards),所以mapper的输入是<key, value=Ti>,Ti表示数据片段中的一条数据。对于Ti中的每一个项aj,mapper输出<key=aj, value=1>。当集群中的所有mapper处理完数据之后,所有key=aj的键值对将被分配到同一个reducer,所以reducer的输入是<key=aj, value={1, 1, ... , 1}>。reducer只需要进行一次求和,然后输出<key=aj, value=sum{1, 1, ... , 1}>。最终将得到一张按照支持度递减排序的列表,称之为F-List:

图1
Step 3:Grouping Items
将F-List中的项(item)分为Q个组(group),每一个组都有一个唯一的group-id,我们将所有项以及其所对应的group-id记为G-List。
Step 4:Parallel FP-Growth
这一步骤是并行化FP-Growth的关键,也是整个算法中相对难以理解的部分。这一步骤中将用到一次MapReduce。每一个mapper的输入来自第一步生成的数据片段,所以mapper的输入是<key, value=Ti>。在处理这些数据片段之前,mapper将读取第三步生成的G-List。G-List其实是一张Hashmap,键是项,值是项所对应的group-id,所占空间一般并不会很大,可以放入内存中。从Ti的最后一项开始向前扫描,或者说从右向左扫描,如果aL在G-List中对应的group-id是第一次被扫描,则输出{a0,a1,…,aL},否则不输出任何数据。以图1中所示的数据为例,假如支持度阈值为1,Q为3,那么将得到G-List:
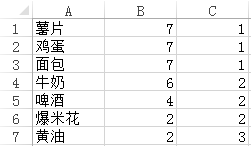
图2
其中,第三列是group-id。假如mapper的输入是{牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,薯片},从最后一项开始扫描,输出<key=1,value={牛奶,鸡蛋,面包,薯片}>。之后的两项是面包和鸡蛋,其所对应的group-id和薯片相同,所以不输出任何数据。第一项是牛奶,其所对应的group-id未曾出现过,所以输出<key=2,value={牛奶}>。
所有group-id相同的数据将被推送到同一个reducer,所以reducer的输入是<key=group-id,value={{ValueList1},{ValueList2},…,{ValueListN}}>。reducer在本地构建FP-tree,然后像传统的FP-Growth算法那样递归地构建条件FP-tree,并挖掘频繁模式。与传统的FP-Growth算法不一样的是,reducer并不直接输出所挖掘到的频繁模式,而是将其放入一个大小为K,根据支持度排序建立的大根堆,然后输出K个支持度较高的频繁模式:<key=item,reduce={包含该item的Top K Frequent Patterns}>。
Step 5:Aggregating
上一步挖掘到的频繁模式Top K Frequent Patterns已经包含了所有频繁模式,然而上一步的MapReduce是按照groupID来划分数据,因此key=item对应的频繁模式会存在于若干个不同groupID的reduce节点上。为了合并所有key=item的键值对,优化结果展现形式,可利用MapReduce默认对key排序的特点,对挖掘到的频繁模式进行一下处理:依次将Top K Frequent Patterns的每一个item作为key,然后输出包含该key的这一条Top K Frequent Patterns。所以,每一个mapper的输出是<key=item, value={该节点上的包含该item的频繁模式}>,reducer汇总所有mapper的输出结果,并输出最终的结果<key=item, value={包含该item的所有频繁模式}>。
2. Parallel FP-Growth源码分析
Mahout提供了一些机器学习领域经典算法的实现。Mahout0.9之后的版本已经移除了Parallel FP-Growth算法。本文将分析Mahout0.8中Parallel FP-Growth的源码。

图3
FPGrowthDriver.java
FPGrowthDriver是FPGrowth算法的驱动类,继承自AbstractJob类。运行Hadoop任务一般都是通过命令行中执行bin/hadoop脚本,同时传入一些参数。ToolRunner类中的GenericOptionsParser可获取这些命令行参数。AbstractJob类封装了addInputOption,addOutputOption,addOption,parseArguments等方法,为解析命令行参数提供了帮助。params对象存储了整个算法所需要的参数。FPGrowthDriver根据命令行参数,若顺序执行,则调用该文件内的runFPGrowth方法,若并行化执行,则调用PFPGrowth.java文件中的runPFPGrowth方法。
1 public final class FPGrowthDriver extends AbstractJob { 2 3 private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FPGrowthDriver.class); 4 5 private FPGrowthDriver() { 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 9 //ToolRunner的静态方法run()内有GenericOptionsParser。通过GenericOptionsParser.getRemainingArgs()可获取传入的命令行参数。之后,ToolRunner.run()将调用FPGrowthDriver.run()。 10 ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new FPGrowthDriver(), args); 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * Run TopK FPGrowth given the input file, 15 */ 16 @Override 17 public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { 18 addInputOption(); //添加默认的输入目录路径 19 addOutputOption(); //添加默认的输出目录路径 20 21 addOption("minSupport", "s", "(Optional) The minimum number of times a co-occurrence must be present." 22 + " Default Value: 3", "3"); //添加支持度阈值 23 addOption("maxHeapSize", "k", "(Optional) Maximum Heap Size k, to denote the requirement to mine top K items." 24 + " Default value: 50", "50"); //添加大根堆的大小 25 addOption("numGroups", "g", "(Optional) Number of groups the features should be divided in the map-reduce version." 26 + " Doesn't work in sequential version Default Value:" + PFPGrowth.NUM_GROUPS_DEFAULT, 27 Integer.toString(PFPGrowth.NUM_GROUPS_DEFAULT)); //添加组数g 28 addOption("splitterPattern", "regex", "Regular Expression pattern used to split given string transaction into" 29 + " itemsets. Default value splits comma separated itemsets. Default Value:" 30 + " "[ ,\t]*[,|\t][ ,\t]*" ", "[ , ]*[,| ][ , ]*"); //添加分隔符 31 addOption("numTreeCacheEntries", "tc", "(Optional) Number of entries in the tree cache to prevent duplicate" 32 + " tree building. (Warning) a first level conditional FP-Tree might consume a lot of memory, " 33 + "so keep this value small, but big enough to prevent duplicate tree building. " 34 + "Default Value:5 Recommended Values: [5-10]", "5"); 35 addOption("method", "method", "Method of processing: sequential|mapreduce", "sequential"); //添加训练方法,顺序执行或并行执行 36 addOption("encoding", "e", "(Optional) The file encoding. Default value: UTF-8", "UTF-8"); //添加编码方式 37 addFlag("useFPG2", "2", "Use an alternate FPG implementation"); 38 39 //如果解析命令行参数失败,则退出 40 if (parseArguments(args) == null) { 41 return -1; 42 } 43 44 Parameters params = new Parameters(); 45 46 if (hasOption("minSupport")) { 47 String minSupportString = getOption("minSupport"); 48 params.set("minSupport", minSupportString); 49 } 50 if (hasOption("maxHeapSize")) { 51 String maxHeapSizeString = getOption("maxHeapSize"); 52 params.set("maxHeapSize", maxHeapSizeString); 53 } 54 if (hasOption("numGroups")) { 55 String numGroupsString = getOption("numGroups"); 56 params.set("numGroups", numGroupsString); 57 } 58 59 if (hasOption("numTreeCacheEntries")) { 60 String numTreeCacheString = getOption("numTreeCacheEntries"); 61 params.set("treeCacheSize", numTreeCacheString); 62 } 63 64 if (hasOption("splitterPattern")) { 65 String patternString = getOption("splitterPattern"); 66 params.set("splitPattern", patternString); 67 } 68 69 String encoding = "UTF-8"; 70 if (hasOption("encoding")) { 71 encoding = getOption("encoding"); 72 } 73 params.set("encoding", encoding); 74 75 if (hasOption("useFPG2")) { 76 params.set(PFPGrowth.USE_FPG2, "true"); 77 } 78 79 Path inputDir = getInputPath(); 80 Path outputDir = getOutputPath(); 81 82 params.set("input", inputDir.toString()); 83 params.set("output", outputDir.toString()); 84 85 String classificationMethod = getOption("method"); 86 if ("sequential".equalsIgnoreCase(classificationMethod)) { 87 runFPGrowth(params); 88 } else if ("mapreduce".equalsIgnoreCase(classificationMethod)) { 89 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 90 HadoopUtil.delete(conf, outputDir); 91 PFPGrowth.runPFPGrowth(params); 92 } 93 94 return 0; 95 }
PFPGrowth.java
PFPGrowth是并行化FP-Growth算法的驱动类。runPFPGrowth(params)方法内初始化了一个Configuration对象,之后调用runPFPGrowth(params, conf)方法。runPFPGrowth(params, conf)方法包括了并行化FP-Growth算法的五个关键步骤。其中,startParallelCounting(params, conf)对应Step1和Step2,通过类似WordCount的方法统计每一项的支持度,其输出结果将被readFList()和saveList()用于生成FList。之后,将按照用户输入的命令行参数NUM_GROUPS来计算每一个group所含项的个数,并将其存储到params。startParallelFPGrowth(params, conf)对应Step3和Step4。startAggregating(params, conf)对应Step5。
1 public static void runPFPGrowth(Parameters params, Configuration conf) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { 2 conf.set("io.serializations", "org.apache.hadoop.io.serializer.JavaSerialization," + "org.apache.hadoop.io.serializer.WritableSerialization"); 3 4 startParallelCounting(params, conf); //对应Step1和Step2 5 6 // save feature list to dcache 7 List<Pair<String,Long>> fList = readFList(params); 8 saveFList(fList, params, conf); 9 10 // set param to control group size in MR jobs 11 int numGroups = params.getInt(NUM_GROUPS, NUM_GROUPS_DEFAULT); 12 int maxPerGroup = fList.size() / numGroups; 13 if (fList.size() % numGroups != 0) { 14 maxPerGroup++; 15 } 16 params.set(MAX_PER_GROUP, Integer.toString(maxPerGroup)); 17 18 startParallelFPGrowth(params, conf); //对应Step3和Step4 19 20 startAggregating(params, conf); //对应Step5 21 }
startParallelCounting方法初始化了一个Job对象。该Job对象将调用ParallelCountingMapper和ParallelCountingReducer来完成支持度的统计。
1 /** 2 * Count the frequencies of various features in parallel using Map/Reduce 3 */ 4 public static void startParallelCounting(Parameters params, Configuration conf) 5 throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { 6 conf.set(PFP_PARAMETERS, params.toString()); 7 8 conf.set("mapred.compress.map.output", "true"); 9 conf.set("mapred.output.compression.type", "BLOCK"); 10 11 String input = params.get(INPUT); 12 Job job = new Job(conf, "Parallel Counting Driver running over input: " + input); 13 job.setJarByClass(PFPGrowth.class); 14 15 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 16 job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); 17 18 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(input)); 19 Path outPath = new Path(params.get(OUTPUT), PARALLEL_COUNTING); 20 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outPath); 21 22 HadoopUtil.delete(conf, outPath); 23 24 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); 25 job.setMapperClass(ParallelCountingMapper.class); 26 job.setCombinerClass(ParallelCountingReducer.class); 27 job.setReducerClass(ParallelCountingReducer.class); 28 job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class); 29 30 boolean succeeded = job.waitForCompletion(true); 31 if (!succeeded) { 32 throw new IllegalStateException("Job failed!"); 33 } 34 35 }
ParallelCountingMapper.java
ParallelCountingMapper中map方法的输入分别是字节偏移量offset和事务数据库中的某一行数据input。所有input数据中多次出现的项都被视为出现一次,所以将input数据split之后存储到HashSet中。map方法的输出是<key=item, value=one>。
1 public class ParallelCountingMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,LongWritable> { 2 3 private static final LongWritable ONE = new LongWritable(1); 4 5 private Pattern splitter; 6 7 @Override 8 protected void map(LongWritable offset, Text input, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 9 10 String[] items = splitter.split(input.toString()); 11 Set<String> uniqueItems = Sets.newHashSet(Arrays.asList(items)); 12 for (String item : uniqueItems) { 13 if (item.trim().isEmpty()) { 14 continue; 15 } 16 context.setStatus("Parallel Counting Mapper: " + item); 17 context.write(new Text(item), ONE); 18 } 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 23 super.setup(context); 24 Parameters params = new Parameters(context.getConfiguration().get(PFPGrowth.PFP_PARAMETERS, "")); 25 splitter = Pattern.compile(params.get(PFPGrowth.SPLIT_PATTERN, PFPGrowth.SPLITTER.toString())); 26 } 27 }
ParallelCountingReducer.java
ParallelCountingReducer中reduce方法的输入是<key=item, value={one, one, ... , one}>。所有key=item的键值对将被分配到一台机器上,所以只需要对values进行遍历求和就可以求出该item的支持度。
1 public class ParallelCountingReducer extends Reducer<Text,LongWritable,Text,LongWritable> { 2 3 @Override 4 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, 5 InterruptedException { 6 long sum = 0; 7 for (LongWritable value : values) { 8 context.setStatus("Parallel Counting Reducer :" + key); 9 sum += value.get(); 10 } 11 context.setStatus("Parallel Counting Reducer: " + key + " => " + sum); 12 context.write(key, new LongWritable(sum)); 13 14 } 15 }
PFPGrowth.java
通过params中的OUTPUT参数可以获取ParallelCountingReducer的输出路径。在readFList这个方法中用到了几个数据结构。Pair实现了Comparable接口和Serializable接口,其数据成员first和second分别用来表示item和item所对应的支持度。PriorityQueue是一个用平衡二叉树实现的小顶堆,如果指定了Comparator,将按照Comparator对PriorityQueue中的元素进行排序,如果未指定Comparator,则将按照元素实现的Comparable接口进行排序。在并行化FP-Growth算法中,初始化PriorityQueue时指定了Comparator,其按照Pair的第一个元素进行排序,如果第一个元素相等,则按照第二个元素进行排序。通过初始化SequenceFileDirIterable来遍历上一次MapReduce输出的结果,每次将Pair添加到PriorityQueue的同时完成排序。最后,逐一将PriorityQueue中的元素取出放入fList。因此,fList是一个按照支持度递减的列表。
1 /** 2 * read the feature frequency List which is built at the end of the Parallel counting job 3 * 4 * @return Feature Frequency List 5 */ 6 public static List<Pair<String,Long>> readFList(Parameters params) { 7 int minSupport = Integer.valueOf(params.get(MIN_SUPPORT, "3")); 8 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 9 10 Path parallelCountingPath = new Path(params.get(OUTPUT), PARALLEL_COUNTING); 11 12 PriorityQueue<Pair<String,Long>> queue = new PriorityQueue<Pair<String,Long>>(11, 13 new Comparator<Pair<String,Long>>() { 14 @Override 15 public int compare(Pair<String,Long> o1, Pair<String,Long> o2) { 16 int ret = o2.getSecond().compareTo(o1.getSecond()); 17 if (ret != 0) { 18 return ret; 19 } 20 return o1.getFirst().compareTo(o2.getFirst()); 21 } 22 }); 23 24 for (Pair<Text,LongWritable> record 25 : new SequenceFileDirIterable<Text,LongWritable>(new Path(parallelCountingPath, FILE_PATTERN), 26 PathType.GLOB, null, null, true, conf)) { 27 long value = record.getSecond().get(); 28 if (value >= minSupport) { 29 queue.add(new Pair<String,Long>(record.getFirst().toString(), value)); 30 } 31 } 32 List<Pair<String,Long>> fList = Lists.newArrayList(); 33 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 34 fList.add(queue.poll()); 35 } 36 return fList; 37 }
由于已经生成了fList,上一次MapReduce的输出结果已经没有用了,因此,saveFList方法首先删除了这些文件。之后,saveFList方法将flist写入到hdfs上。对于存储在hdfs上的文件,DistributedCache提供了缓存文件的功能,在Slave Node进行计算之前可将hdfs上的文件复制到这些节点上。
1 /** 2 * Serializes the fList and returns the string representation of the List 3 */ 4 public static void saveFList(Iterable<Pair<String,Long>> flist, Parameters params, Configuration conf) 5 throws IOException { 6 Path flistPath = new Path(params.get(OUTPUT), F_LIST); 7 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(flistPath.toUri(), conf); 8 flistPath = fs.makeQualified(flistPath); 9 HadoopUtil.delete(conf, flistPath); 10 SequenceFile.Writer writer = new SequenceFile.Writer(fs, conf, flistPath, Text.class, LongWritable.class); 11 try { 12 for (Pair<String,Long> pair : flist) { 13 writer.append(new Text(pair.getFirst()), new LongWritable(pair.getSecond())); 14 } 15 } finally { 16 writer.close(); 17 } 18 DistributedCache.addCacheFile(flistPath.toUri(), conf); 19 }
startParallelFPGrowth方法初始化了一个Job对象。该Job对象将调用ParallelFPGrowthMapper和ParallelFPGrowthReducer来实现Step3和Step4。
1 /** 2 * Run the Parallel FPGrowth Map/Reduce Job to calculate the Top K features of group dependent shards 3 */ 4 public static void startParallelFPGrowth(Parameters params, Configuration conf) 5 throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { 6 conf.set(PFP_PARAMETERS, params.toString()); 7 conf.set("mapred.compress.map.output", "true"); 8 conf.set("mapred.output.compression.type", "BLOCK"); 9 Path input = new Path(params.get(INPUT)); 10 Job job = new Job(conf, "PFP Growth Driver running over input" + input); 11 job.setJarByClass(PFPGrowth.class); 12 13 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); 14 job.setMapOutputValueClass(TransactionTree.class); 15 16 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 17 job.setOutputValueClass(TopKStringPatterns.class); 18 19 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, input); 20 Path outPath = new Path(params.get(OUTPUT), FPGROWTH); 21 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outPath); 22 23 HadoopUtil.delete(conf, outPath); 24 25 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); 26 job.setMapperClass(ParallelFPGrowthMapper.class); 27 job.setCombinerClass(ParallelFPGrowthCombiner.class); 28 job.setReducerClass(ParallelFPGrowthReducer.class); 29 job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class); 30 31 boolean succeeded = job.waitForCompletion(true); 32 if (!succeeded) { 33 throw new IllegalStateException("Job failed!"); 34 } 35 }
ParallelFPGrowthMapper.java
ParallelFPGrowthMapper中的setup方法将在map方法之前被运行。setup方法中调用了readFList方法。注意这里的readFList方法与之前分析的readFList方法参数不一样,所以是两个完全不同的方法。这里的readFList方法通过HadoopUtil.getCachedFiles(conf)来获取缓存文件flist,将其存储到fMap,其中item作为fMap的键,item在flist中的位置序号作为fMap的值,例如flist中的第一个item,其在fMap中将是<key=item, value=0>。这样做的原因是之后将fMap分Q个group时需要用到这个位置序号。在map方法中,输入是字节偏移量和事务数据库中的某一行数据。根据用户指定的分隔符splitter来切分数据。为了过滤非频繁项,通过fMap.containsKey(item)方法来查找该项是否存在于fList中。若存在,将其所对应的位置序号加入到itemSet,否则,将其丢弃。itemArr复制itemSet中的数据,并按照位置序号递增进行排序,即按照支持度递减进行排序。之后的for循环从itemArr的最后一个元素向前遍历,如果其所对应的groupID不在groups中,那么将初始化TransactionTree,将itemArr[0],itemArr[1],…,itemArr[j]存入该TransactionTree中。groupID的计算非常简单,将位置序号除以maxPerGroup即可。TransactionTree实现了Writable和Iterable<Pair<IntArrayList, Long>>接口,初始化TransactionTree时,构造方法将参数赋值给TransactionTree中的数据成员List<Pair<IntArrayList, Long>> transactionSet。这里Pair对象存储的两个元素分别是位置序号列表和1。
1 /** 2 * maps each transaction to all unique items groups in the transaction. mapper 3 * outputs the group id as key and the transaction as value 4 * 5 */ 6 public class ParallelFPGrowthMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,IntWritable,TransactionTree> { 7 8 private final OpenObjectIntHashMap<String> fMap = new OpenObjectIntHashMap<String>(); 9 private Pattern splitter; 10 private int maxPerGroup; 11 private final IntWritable wGroupID = new IntWritable(); 12 13 @Override 14 protected void map(LongWritable offset, Text input, Context context) 15 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 16 17 String[] items = splitter.split(input.toString()); 18 19 OpenIntHashSet itemSet = new OpenIntHashSet(); 20 21 for (String item : items) { 22 if (fMap.containsKey(item) && !item.trim().isEmpty()) { 23 itemSet.add(fMap.get(item)); 24 } 25 } 26 27 IntArrayList itemArr = new IntArrayList(itemSet.size()); 28 itemSet.keys(itemArr); 29 itemArr.sort(); 30 31 OpenIntHashSet groups = new OpenIntHashSet(); 32 for (int j = itemArr.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) { 33 // generate group dependent shards 34 int item = itemArr.get(j); 35 int groupID = PFPGrowth.getGroup(item, maxPerGroup); 36 37 if (!groups.contains(groupID)) { 38 IntArrayList tempItems = new IntArrayList(j + 1); 39 tempItems.addAllOfFromTo(itemArr, 0, j); 40 context.setStatus("Parallel FPGrowth: Generating Group Dependent transactions for: " + item); 41 wGroupID.set(groupID); 42 context.write(wGroupID, new TransactionTree(tempItems, 1L)); 43 } 44 groups.add(groupID); 45 } 46 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 51 super.setup(context); 52 53 int i = 0; 54 for (Pair<String,Long> e : PFPGrowth.readFList(context.getConfiguration())) { 55 fMap.put(e.getFirst(), i++); 56 } 57 58 Parameters params = 59 new Parameters(context.getConfiguration().get(PFPGrowth.PFP_PARAMETERS, "")); 60 61 splitter = Pattern.compile(params.get(PFPGrowth.SPLIT_PATTERN, 62 PFPGrowth.SPLITTER.toString())); 63 64 maxPerGroup = params.getInt(PFPGrowth.MAX_PER_GROUP, 0); 65 } 66 }
ParallelFPGrowthReducer.java
ParallelFPGrowthReducer的输入是<key=groupID, value={TransactionTree1, TransactionTree2, … , TransactionTreeN}>。setup方法获取了参数params,并且通过PFPGrowth.readFList(conf)方法获取了缓存文件flist,将频繁项存入featureReverseMap,将频繁项对应的支持度存入freqList。之前分析到ParallelFPGrowthMapper输出的TransactionTree其实是List<Pair<IntArrayList, Long>> transactionSet。在ParallelFPGrowthReducer内初始化了一个TransactionTree,虽然这个TransactionTree与之前的Transaction是同一个类,但是是一棵用二维数组实现的树。考虑到文章篇幅,建树的过程这里不作分析。假设已经建好了这棵树,cTree.generateFList方法遍历这棵树,返回Map<Integer, MutableLong> frequencyList。具体的遍历方法这里不作详细分析,提一下其调用过程:TransactionTree实现Iterator<Pair<IntArrayList, Long>>接口时重写了iterator方法,在generateFList方法中通过iterator方法生成一个迭代器来遍历整棵树。iterator方法返回的是TransactionTreeIterator对象。TransactionTreeIterator对象继承自AbstractIterator<Pair<IntArrayList, Long>>,实现了对TransactionTree进行遍历。localFList合并了generateFList的结果并按照支持度递减进行排序。生成频繁模式的方法有两种,用户可以自己选择来调用FPGrowthIds.generateTopKFrequentPatterns方法或者fpGrowth.generateTopKFrequentPatterns方法来生成频繁模式,本文将对后者进行分析。在ParallelFPGrowthReducer中还有一个IteratorAdapter类。它是设计模式中十分经典的适配器模式的具体应用,可以将两个不同类型的迭代器解耦。ParallelFPGrowthReducer的输出是<key=item, value={Top K Frequent Patterns}>。
1 /** 2 * takes each group of transactions and runs Vanilla FPGrowth on it and 3 * outputs the the Top K frequent Patterns for each group. 4 * 5 */ 6 public final class ParallelFPGrowthReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable,TransactionTree,Text,TopKStringPatterns> { 7 8 private final List<String> featureReverseMap = Lists.newArrayList(); 9 private final LongArrayList freqList = new LongArrayList(); 10 private int maxHeapSize = 50; 11 private int minSupport = 3; 12 private int numFeatures; 13 private int maxPerGroup; 14 private boolean useFP2; 15 16 private static final class IteratorAdapter implements Iterator<Pair<List<Integer>,Long>> { 17 private final Iterator<Pair<IntArrayList,Long>> innerIter; 18 19 private IteratorAdapter(Iterator<Pair<IntArrayList,Long>> transactionIter) { 20 innerIter = transactionIter; 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public boolean hasNext() { 25 return innerIter.hasNext(); 26 } 27 28 @Override 29 public Pair<List<Integer>,Long> next() { 30 Pair<IntArrayList,Long> innerNext = innerIter.next(); 31 return new Pair<List<Integer>,Long>(innerNext.getFirst().toList(), innerNext.getSecond()); 32 } 33 34 @Override 35 public void remove() { 36 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 37 } 38 } 39 40 @Override 41 protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<TransactionTree> values, Context context) throws IOException { 42 TransactionTree cTree = new TransactionTree(); 43 for (TransactionTree tr : values) { 44 for (Pair<IntArrayList,Long> p : tr) { 45 cTree.addPattern(p.getFirst(), p.getSecond()); 46 } 47 } 48 49 List<Pair<Integer,Long>> localFList = Lists.newArrayList(); 50 for (Entry<Integer,MutableLong> fItem : cTree.generateFList().entrySet()) { 51 localFList.add(new Pair<Integer,Long>(fItem.getKey(), fItem.getValue().toLong())); 52 } 53 54 Collections.sort(localFList, new CountDescendingPairComparator<Integer,Long>()); 55 56 if (useFP2) { 57 FPGrowthIds.generateTopKFrequentPatterns( 58 cTree.iterator(), 59 freqList, 60 minSupport, 61 maxHeapSize, 62 PFPGrowth.getGroupMembers(key.get(), maxPerGroup, numFeatures), 63 new IntegerStringOutputConverter( 64 new ContextWriteOutputCollector<IntWritable, TransactionTree, Text, TopKStringPatterns>(context), 65 featureReverseMap), 66 new ContextStatusUpdater<IntWritable, TransactionTree, Text, TopKStringPatterns>(context)); 67 } else { 68 FPGrowth<Integer> fpGrowth = new FPGrowth<Integer>(); 69 fpGrowth.generateTopKFrequentPatterns( 70 new IteratorAdapter(cTree.iterator()), 71 localFList, 72 minSupport, 73 maxHeapSize, 74 Sets.newHashSet(PFPGrowth.getGroupMembers(key.get(), 75 maxPerGroup, 76 numFeatures).toList()), 77 new IntegerStringOutputConverter( 78 new ContextWriteOutputCollector<IntWritable,TransactionTree,Text,TopKStringPatterns>(context), 79 featureReverseMap), 80 new ContextStatusUpdater<IntWritable,TransactionTree,Text,TopKStringPatterns>(context)); 81 } 82 } 83 84 @Override 85 protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 86 87 super.setup(context); 88 Parameters params = new Parameters(context.getConfiguration().get(PFPGrowth.PFP_PARAMETERS, "")); 89 90 for (Pair<String,Long> e : PFPGrowth.readFList(context.getConfiguration())) { 91 featureReverseMap.add(e.getFirst()); 92 freqList.add(e.getSecond()); 93 } 94 95 maxHeapSize = Integer.valueOf(params.get(PFPGrowth.MAX_HEAPSIZE, "50")); 96 minSupport = Integer.valueOf(params.get(PFPGrowth.MIN_SUPPORT, "3")); 97 98 maxPerGroup = params.getInt(PFPGrowth.MAX_PER_GROUP, 0); 99 numFeatures = featureReverseMap.size(); 100 useFP2 = "true".equals(params.get(PFPGrowth.USE_FPG2)); 101 }
TransactionTree.java
在分析fpGrowth.generateTopKFrequentPatterns方法之前,先来分析一下建树过程中使用的addPattern方法。下面的代码列出了TransactionTree的数据成员和addPattern方法。在addPattern方法中,首先从根节点开始与myList中的节点进行比较。childWithAttribute返回temp节点下的孩子节点中是否有和attributeValue名称相同的节点。如果没有,addCountMode置为false,将myList中剩余的节点添加到这棵树中;如果有,则通过addCount方法增加child节点的支持度。这一建树的思路与传统的FP-Growth中建树的思路完全一致。
1 private int[] attribute; //节点的名称属性 2 private int[] childCount; //对该节点的有多少个孩子节点进行计数 3 private int[][] nodeChildren; //二维数组,记录每一个节点的孩子节点 4 private long[] nodeCount; //当前节点的支持度计数 5 private int nodes; 6 private boolean representedAsList; //true表示以List形式展现,false表示以树的形式展现 7 private List<Pair<IntArrayList,Long>> transactionSet; 8 9 public int addPattern(IntArrayList myList, long addCount) { 10 int temp = ROOTNODEID; 11 int ret = 0; 12 boolean addCountMode = true; 13 for (int idx = 0; idx < myList.size(); idx++) { 14 int attributeValue = myList.get(idx); 15 int child; 16 if (addCountMode) { 17 child = childWithAttribute(temp, attributeValue); 18 if (child == -1) { 19 addCountMode = false; 20 } else { 21 addCount(child, addCount); 22 temp = child; 23 } 24 } 25 if (!addCountMode) { 26 child = createNode(temp, attributeValue, addCount); 27 temp = child; 28 ret++; 29 } 30 } 31 return ret; 32 }
FPGrowth.java
generateTopKFrequentPatterns方法的形参有transactionStream,frequencyList,minSupport,k,Collection<A> returnableFeatures,OutputCollector<A, List<Pair<List<A>, Long>>> output,Statusupdater updater。其中,transactionStream是根据当前key=groupID所对应的Pair<List<A>, Long>类型的values建立的cTree,这里Pair的第一项是位置序号,第二项是1;frequencyList是ParallelFPGrowthReducer中的localFList,其第一项是位置序号,第二项是支持度;Collection<A> returnableFeatures是当前key=group-id所包含的位置序号集合。
attributeIdMapping过滤了transactionStream中的非频繁项,并为频繁项分配新id,将其映射成<key=位置序号, value=id>。reverseMapping倒置了attributeIdMapping的映射关系。attributeFrequentcy记录了索引为id的项的支持度。对于returnableFeatures中的位置序号进行遍历,过滤非频繁项,returnFeatures记录了剩余的频繁项。之后调用generateTopKFrequentPatterns方法来构建本地的FP-tree和头表(Header-Table),并遍历FP-tree来输出频繁项。参考资料[1]详细分析了这一过程,这里不作进一步分析,需要注意到是在Mahout中FP-tree是以数组的形式存储。
1 /** 2 * Generate Top K Frequent Patterns for every feature in returnableFeatures 3 * given a stream of transactions and the minimum support 4 * 5 * @param transactionStream 6 * Iterator of transaction 7 * @param frequencyList 8 * list of frequent features and their support value 9 * @param minSupport 10 * minimum support of the transactions 11 * @param k 12 * Number of top frequent patterns to keep 13 * @param returnableFeatures 14 * set of features for which the frequent patterns are mined. If the 15 * set is empty or null, then top K patterns for every frequent item (an item 16 * whose support> minSupport) is generated 17 * @param output 18 * The output collector to which the the generated patterns are 19 * written 20 * @throws IOException 21 */ 22 public final void generateTopKFrequentPatterns(Iterator<Pair<List<A>,Long>> transactionStream, 23 Collection<Pair<A, Long>> frequencyList, 24 long minSupport, 25 int k, 26 Collection<A> returnableFeatures, 27 OutputCollector<A,List<Pair<List<A>,Long>>> output, 28 StatusUpdater updater) throws IOException { 29 30 Map<Integer,A> reverseMapping = Maps.newHashMap(); 31 Map<A,Integer> attributeIdMapping = Maps.newHashMap(); 32 33 int id = 0; 34 for (Pair<A,Long> feature : frequencyList) { 35 A attrib = feature.getFirst(); 36 Long frequency = feature.getSecond(); 37 if (frequency >= minSupport) { 38 attributeIdMapping.put(attrib, id); 39 reverseMapping.put(id++, attrib); 40 } 41 } 42 43 long[] attributeFrequency = new long[attributeIdMapping.size()]; 44 for (Pair<A,Long> feature : frequencyList) { 45 A attrib = feature.getFirst(); 46 Long frequency = feature.getSecond(); 47 if (frequency < minSupport) { 48 break; 49 } 50 attributeFrequency[attributeIdMapping.get(attrib)] = frequency; 51 } 52 53 log.info("Number of unique items {}", frequencyList.size()); 54 55 Collection<Integer> returnFeatures = Sets.newHashSet(); 56 if (returnableFeatures != null && !returnableFeatures.isEmpty()) { 57 for (A attrib : returnableFeatures) { 58 if (attributeIdMapping.containsKey(attrib)) { 59 returnFeatures.add(attributeIdMapping.get(attrib)); 60 log.info("Adding Pattern {}=>{}", attrib, attributeIdMapping 61 .get(attrib)); 62 } 63 } 64 } else { 65 for (int j = 0; j < attributeIdMapping.size(); j++) { 66 returnFeatures.add(j); 67 } 68 } 69 70 log.info("Number of unique pruned items {}", attributeIdMapping.size()); 71 generateTopKFrequentPatterns(new TransactionIterator<A>(transactionStream, 72 attributeIdMapping), attributeFrequency, minSupport, k, reverseMapping 73 .size(), returnFeatures, new TopKPatternsOutputConverter<A>(output, 74 reverseMapping), updater); 75 76 }
AggregatorMapper的输入是<key, value=TopKStringPatterns>,TopKStringPatterns是一个存储<Pair<List<String>,Long>>类型的列表,List<String>类型元素记录了每一个key=item对应的频繁模式,Long类型元素记录了支持度。
1 /** 2 * 3 * outputs the pattern for each item in the pattern, so that reducer can group them 4 * and select the top K frequent patterns 5 * 6 */ 7 public class AggregatorMapper extends Mapper<Text,TopKStringPatterns,Text,TopKStringPatterns> { 8 9 @Override 10 protected void map(Text key, TopKStringPatterns values, Context context) throws IOException, 11 InterruptedException { 12 for (Pair<List<String>,Long> pattern : values.getPatterns()) { 13 for (String item : pattern.getFirst()) { 14 List<Pair<List<String>,Long>> patternSingularList = Lists.newArrayList(); 15 patternSingularList.add(pattern); 16 context.setStatus("Aggregator Mapper:Grouping Patterns for " + item); 17 context.write(new Text(item), new TopKStringPatterns(patternSingularList)); 18 } 19 } 20 21 } 22 }
AggregatorReducer汇总了所有Key相同的item,然后按照支持度递减排序,最终输出Top K个频繁模式。
1 /** 2 * 3 * groups all Frequent Patterns containing an item and outputs the top K patterns 4 * containing that particular item 5 * 6 */ 7 public class AggregatorReducer extends Reducer<Text,TopKStringPatterns,Text,TopKStringPatterns> { 8 9 private int maxHeapSize = 50; 10 11 @Override 12 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<TopKStringPatterns> values, Context context) throws IOException, 13 InterruptedException { 14 TopKStringPatterns patterns = new TopKStringPatterns(); 15 for (TopKStringPatterns value : values) { 16 context.setStatus("Aggregator Reducer: Selecting TopK patterns for: " + key); 17 patterns = patterns.merge(value, maxHeapSize); 18 } 19 context.write(key, patterns); 20 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 25 super.setup(context); 26 Parameters params = new Parameters(context.getConfiguration().get("pfp.parameters", "")); 27 maxHeapSize = Integer.valueOf(params.get("maxHeapSize", "50")); 28 29 } 30 }
3. 讨论
并行化FP-Growth算法解决了大数据量时传统FP-Growth的性能瓶颈。除了并行化FP-Growth算法外,还有许多方法可以优化FP-Growth算法,比如并行化FP-Growth算法时考虑负载均衡,采用极大频繁项集和闭频繁项集表示频繁模式。
- 极大频繁项集
极大频繁项集是这样的频繁项集,它的直接超集都不是频繁的。极大频繁项集形成了可以导出所有频繁项集的最小项集集合,但是极大频繁项集却不包含它们子集的支持度信息。
- 闭频繁项集
如果项集的直接超集都不具有和它相同的支持度并且该项集的支持度大于或等于最小支持度阈值,则该项集是闭频繁项集。闭频繁项集提供了频繁项集的一种最小表示,该表示不丢失支持度信息。
4. 参考资料
[1] 关联分析:FP-Growth算法. Mark Lin. datahunter. 2014. [Link]
[2] PFP: Parallel FP-Growth for Query Recommendation. Haoyuan Li etc. RecSys '08 Proceedings of the 2008 ACM conference on Recommender systems. 2008. [PDF]