插入类排序:
将无序子序列中的一个或几个记录“插入”到有序序列中,从而增加记录的有序子序列的长度。
一趟直接插入排序的基本思想:
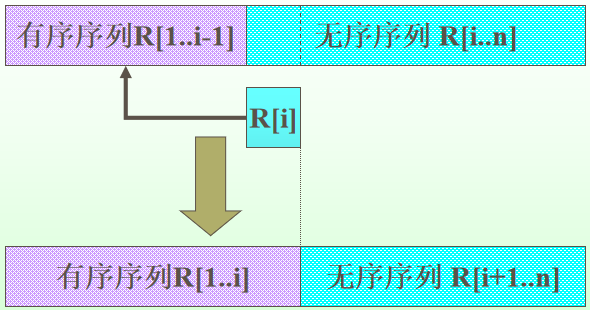
不同的具体实现方法导致不同的算法描述,以下描述三种插入排序算法:直接插入排序(基于顺序查找)、折半插入排序(基于折半查找)和希尔排序(基于逐趟缩小增量)。
1. 直接插入排序(Straight Insertion Sort)
1.1 思想
利用“顺序查找”实现“在R[1…i-1]中查找R[i]的插入位置”。基本操作是将一个记录插入到已经排好序的有序表中,从而得到一个新的。记录数增1的有序表。

1.2 实现
// 直接插入排序 数组长度+1 public static void InsertSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { if (a[i] < a[i-1]) { a[0] = a[i]; // 哨兵 int j; for (j = i-1; a[j] > a[0]; j--) { a[j+1] = a[j]; } // end for a[j+1] = a[0]; } // end if } // end for } // end InsertSort
1.3 复杂度分析
从空间上看,只需要一个记录的辅助空间,所以重点分析时间复杂度。最好情况下,即已经有序时,需要与前一项进行比较,共比较n-1次,不需要移动,所以时间复杂度为O(n)。最坏情况下,即完全逆序时,需要比较2+3+4+…+n=(n+2)(n-1)/2次,记录移动的次数也是最大值3+4+5+…+(n+1)=(n+4)(n-1)/2次。
对于随机的记录,根据概率相同的原则,平均比较和平均移动的次数约为n2/4次。因此,直接插入法时间复杂度为O(n2)。同样的时间复杂度,直接插入排序法比冒泡和简单选择排序的性能要好一些。
2. 折半插入排序
2.1 思想
因为R[1…i-1]是一个按关键字有序的有序序列,则可以利用折半查找实现“在R[1…i-1]中查找R[i]的插入位置”,如此实现的插入排序为折半插入排序。
2.2 实现
// 折半插入 public static void BInsertSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 2; i < length; i++) { a[0] = a[i]; int low = 1, high = i-1; while (low <= high) { int mid = low + (high - low)/2; if (a[0] < a[mid]) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } // end while for (int j = i -1; j >= high + 1; j--) { a[j + 1] = a[j]; } // end for a[high + 1] = a[0]; } // end for } // end BInsertSort
2.3 分析
关键字比较次数与待排序序列的初始状态无关,仅依赖于记录个数。在插入第i个记录时,需要经过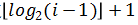 次关键字比较,才能确定它应该插入的位置。
次关键字比较,才能确定它应该插入的位置。
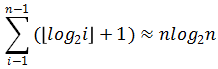
折半插入排序的记录移动次数与直接插入排序相同,依赖于记录的初始排序。时间复杂度为O(n2)。折半插入排序是一个稳定的排序方法。
3. 希尔排序(Shell Sort)
3.1 思想
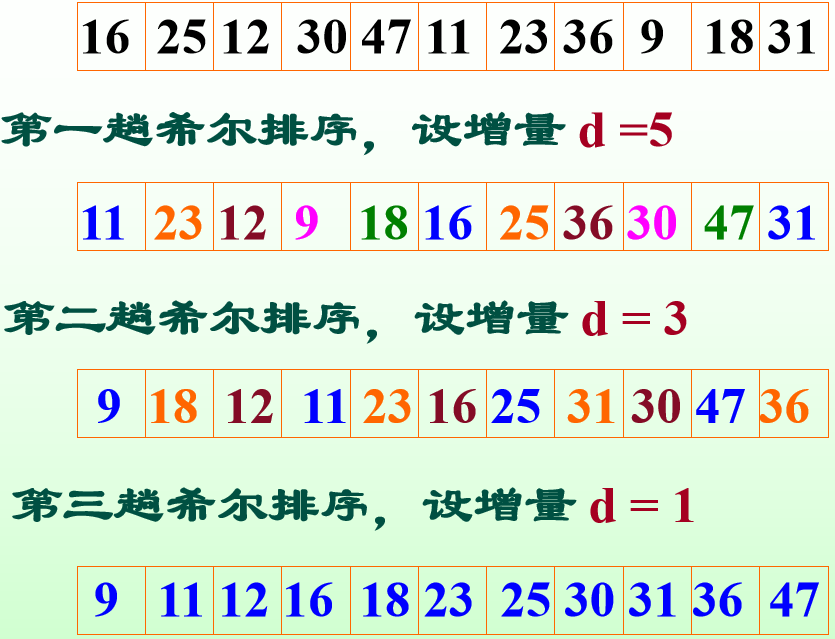
希尔排序又称为缩小增量排序。其基本思想为先将整个待排序记录序列分割成若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序,待整个序列中的记录基本有序时,再对全体记录进行一次直接插入排序。
基本有序:小的关键字基本在前面,大的关键字基本在后面,不大不小的基本在中间。
3.2算法
描述
|
1)选择一个步长序列 t1, t2, …, tk,其中 ti > ti+1,tk = 1; 2)按步长序列个数 k,对序列进行 k 趟排序; 3)每趟排序,根据对应的步长 ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为 m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅步长因子为 1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。 |
示例
实现
public static void ShellInsert(int[] a, int dk) { for (int i = dk+1; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i] < a[i-dk]) { a[0] = a[i]; int j; for (j = i - dk; (j > 0) && (a[0] > a[j]); j -= dk) { a[j+dk] = a[j]; } // end for a[j+dk] = a[0]; } // end if } // end for } // end ShellInsert public static void ShellSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; int dk = length/2; while (dk >= 1) { ShellInsert(a, dk); dk = dk/2; } // end while } // end ShellSort
3.3 复杂度
希尔排序的时效分析很难,关键字的比较次数与记录移动次数依赖于步长因子序列的选取。
特定情况下可以准确估算出关键码的比较次数和记录的移动次数。目前还没有人给出选取最好的步长因子序列的方法。步长因子序列可以有各种取法。但需要注意,最后一个步长因子必须为 1。一种改进方法是避免步长为偶数。
希尔排序方法是一个不稳定的排序方法。
4. 冒泡、简单选择、直接插入、折半插入、希尔排序和改进步长的希尔排序比较
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Date; /** * sort for Array * @author Administrator * */ public class Sort { // 非标准的冒泡排序,最简单的交换排序!(让每一个关键字,都和它后面的每一个关键字比较,如果大则交换) public static void BubbleSort1(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < length; j++) { if (a[i] > a[j]) { int obj = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = obj; } // end if } // end for } // end for } // end BubbleSort // 标准冒泡排序 public static void BubbleSort2(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) { for (int j = length - 2; j >= i; j--) { if (a[j] > a[j+1]) { int obj = a[j]; a[j] = a[j+1]; a[j+1] = obj; } // end if } // end for } // end for } // end BubbleSort public static void BubbleSort3(int[] a) { int length = a.length; boolean flag = true; // 用flag作为标记 for (int i = 0; (i < length - 1) && flag; i++) { flag = false; for (int j = length - 2; j >= i; j--) { if (a[j] > a[j+1]) { int obj = a[j]; a[j] = a[j+1]; a[j+1] = obj; flag = true; // 有数据交换则为true } // end if } // end for } // end for } // end BubbleSort // simple selection sort public static void SelectSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) { int min = i; for (int j = i+1; j < length; j++) { if (a[min] > a[j]) { min = j; } // end if } // end for if (i != min) { int obj = a[min]; a[min] = a[i]; a[i] = obj; } // end if } // end for } // end SelectSort // 直接插入排序 数组长度+1 public static void InsertSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { if (a[i] < a[i-1]) { a[0] = a[i]; // 哨兵 int j; for (j = i-1; a[j] > a[0]; j--) { a[j+1] = a[j]; } // end for a[j+1] = a[0]; } // end if } // end for } // end InsertSort // 折半插入 public static void BInsertSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; for (int i = 2; i < length; i++) { a[0] = a[i]; int low = 1, high = i-1; while (low <= high) { int mid = low + (high - low)/2; if (a[0] < a[mid]) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } // end while for (int j = i -1; j >= high + 1; j--) { a[j + 1] = a[j]; } // end for a[high + 1] = a[0]; } // end for } // end BInsertSort public static void ShellInsert(int[] a, int dk) { for (int i = dk+1; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i] < a[i-dk]) { a[0] = a[i]; int j; for (j = i - dk; (j > 0) && (a[0] < a[j]); j -= dk) { a[j+dk] = a[j]; } // end for a[j+dk] = a[0]; } // end if } // end for } // end ShellInsert public static void ShellSort(int[] a) { int length = a.length; int dk = (length - 1)/2; while (dk >= 1) { ShellInsert(a, dk); dk = dk/2; } // end while } // end ShellSort // 调整步长,使其不为偶数 public static void ShellSort2(int[] a) { int length = a.length; int dk = (length - 1)/2; dk = dk % 2 == 0 ? dk + 1 : dk; while (dk >= 1) { ShellInsert(a, dk); dk = dk/2; dk = dk % 2 == 0 ? dk + 1 : dk; } // end while } // end ShellSort public static void main(String[] args) { // 随机生成50000、50_0000的整数 int[] a = new int[500000+1]; a[0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = (int)(Math.random() * 500); //System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } //System.out.println(); // 保证各个排序算法使用的数据一样 int[] a2 = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length); int[] a3 = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length); int[] a4 = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length); int[] a5 = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length); int[] a6 = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length); Date d1 = new Date(); BubbleSort1(a); // 冒泡:最常用的初学实现 50000:795,801,781 500000:57843,57663,58525 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d1.getTime()); Date d2 = new Date(); SelectSort(a2); // 选择排序 50000:1128,1130,1019 500000:92676,93399,92440 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d2.getTime()); Date d3 = new Date(); InsertSort(a3); // 插入排序 50000:528,521,539 500000:53119,53948,53032 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d3.getTime()); Date d4 = new Date(); BInsertSort(a4); // 折半插入排序 50000:795,792,806 500000:83076,80211,79583 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d4.getTime()); Date d5 = new Date(); ShellSort(a5); // 希尔排序 50000:14,13,14 500000:84,82,78 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d5.getTime()); Date d6 = new Date(); ShellSort(a6); // 改进步长的希尔排序 50000:5,6,6 500000:69,72,71 System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - d6.getTime()); } // end main } // end Sort
对于随机序列来讲,简单选择排序效率最低,初学的冒泡排序与折半插入排序对于较小待排集合效率相当,比简单选择排序稍快,折半插入排序对于大待排序集合也很慢。希尔排序和改进步长的希尔排序效率很高。