本文讲讲一些纯技术的东西。并且讲讲一些原理性的东西,和一般的百度的文章不一致,如果你对序列化不清楚,绝对可以很有收获。
ok,我们先建一个控制台项目:

安装 Newtonsoft.Json 组件

ok,安装完成之后,我们来讲讲序列化的本质:
为什么需要序列化?
要理解这个问题很关键。很多事就会豁然开朗,与其讲为什么序列化,不如我们先来看看一个例子:
我们存储了一条字符串的数据到文件
我们可能会这么写
public static void SaveString(string str )
{
using(System.IO.StreamWriter sw = new System.IO.StreamWriter( "123.txt", false, Encoding.Default ))
{
sw.Write( str );
}
}
然后读取你存储的数据时候,会这么读
public static string ReadString( )
{
using (System.IO.StreamReader sr = new System.IO.StreamReader( "123.txt", Encoding.Default ))
{
return sr.ReadToEnd( );
}
}
其实这里的代码已经实现了最基本的序列化功能。如果你觉得存储string很简单,那么来存储一个int[]数组把。将整个数据存储到文件,然后读取加载
public static void SaveIntArray( int[] value )
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[value.Length * 4];
for (int i = 0; i < value.Length; i++)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes( value[i] ).CopyTo( buffer, i * 4 );
}
System.IO.File.WriteAllBytes( "1234.txt", buffer );
}
然后加载的步骤是
public static int[] ReadIntArray( )
{
byte[] buffer = System.IO.File.ReadAllBytes( "1234.txt" );
int[] value = new int[buffer.Length / 4];
for (int i = 0; i < value.Length; i++)
{
value[i] = BitConverter.ToInt32( buffer, i * 4 );
}
return value;
}
上述的两个示例展示了最基本的序列化和反序列化操作。我们实现序列化和反序列通常是用于写入文件,加载数据,发送到网络,从网络接收数据。
这个就是我们最大的需求了。
实际复杂的数据
比如我们有一串复杂的数据,需要写文件,或是收发网络,写文件和收发网络的本质是读写byte[]数组。而byte[]数组和string是几乎等效的,可以相互转换。很多的文件写入,或是网络收发都是支持支持string的
所以我们的序列化和反序列化的本质就是实际的数据和string的相互转换。
比如这个数据对象
public class Account
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public double Stature { get; set; }
}
要把这个数据对象转换成string,然后支持转换回来,应该怎么操作呢?
接下来就是干货了
XML序列化及,反序列化
直接上代码:
public class Account
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public double Stature { get; set; }
public string toXml( )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = new System.Xml.Linq.XElement( "Account" );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( UserName ), UserName );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Password ), Password );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Age ), Age.ToString() );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Phone ), Phone );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Stature ), Stature.ToString( ) );
return element.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByXml( string data )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = System.Xml.Linq.XElement.Parse( data );
UserName = element.Element( nameof( UserName ) ).Value;
Password = element.Element( nameof( Password ) ).Value;
Age = int.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Age ) ).Value );
Phone = element.Element( nameof( Phone ) ).Value;
Stature = double.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Stature ) ).Value );
}
}
我们改造一下就可以了,现在这个类支持了序列化及反序列了,我们看看控制台输出了什么?
static void Main( string[] args )
{
Account account = new Account( )
{
UserName = "张三",
Password = "123456",
Age = 25,
Phone = "12345678901",
Stature = 170.2d
};
Console.WriteLine( account.toXml( ) );
Console.ReadLine( );
}
看看控制台:
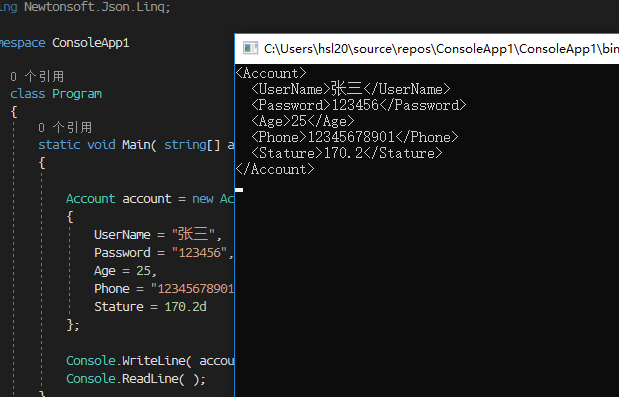
输出了我们想要的字符串信息。好了,接下来,我们看看JSON格式的数据
JSON序列化及反序列化
json因为库的方便性,所以不需要写多余的代码了
static void Main( string[] args )
{
Account account = new Account( )
{
UserName = "张三",
Password = "123456",
Age = 25,
Phone = "12345678901",
Stature = 170.2d
};
//Console.WriteLine( account.toXml( ) );
Console.WriteLine( JObject.FromObject( account ).ToString( ) );
Console.ReadLine( );
}
输出
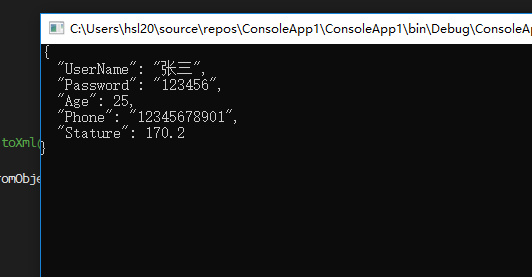
灵活的操作
现在有个小问题,密码部分的内容我不想支持序列化,或是换句话说,密码的信息在序列化的时候忽略。那么类改成下面即可
public class Account
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Newtonsoft.Json.JsonIgnore]
public string Password { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public double Stature { get; set; }
public string toXml( )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = new System.Xml.Linq.XElement( "Account" );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( UserName ), UserName );
//element.SetElementValue( nameof( Password ), Password );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Age ), Age.ToString() );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Phone ), Phone );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Stature ), Stature.ToString( ) );
return element.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByXml( string data )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = System.Xml.Linq.XElement.Parse( data );
UserName = element.Element( nameof( UserName ) ).Value;
//Password = element.Element( nameof( Password ) ).Value;
Age = int.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Age ) ).Value );
Phone = element.Element( nameof( Phone ) ).Value;
Stature = double.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Stature ) ).Value );
}
}
这样就忽略了密码的xml序列化和json的序列化
xml支持子元素和特性,内容存储上更加的丰富,json更加直接一点,内容精简一点,json也可以写成上述的xml灵活的方法,这样就支持任意格式对象的序列化和反序列化了。
public class Account
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Newtonsoft.Json.JsonIgnore]
public string Password { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public double Stature { get; set; }
public string toXml( )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = new System.Xml.Linq.XElement( "Account" );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( UserName ), UserName );
//element.SetElementValue( nameof( Password ), Password );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Age ), Age.ToString() );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Phone ), Phone );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Stature ), Stature.ToString( ) );
return element.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByXml( string data )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = System.Xml.Linq.XElement.Parse( data );
UserName = element.Element( nameof( UserName ) ).Value;
//Password = element.Element( nameof( Password ) ).Value;
Age = int.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Age ) ).Value );
Phone = element.Element( nameof( Phone ) ).Value;
Stature = double.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Stature ) ).Value );
}
public string toJson( )
{
JObject json = new JObject( );
//json.Add( nameof( Password ), new JValue( Password ) );
json.Add( nameof( UserName ), new JValue( UserName ) );
json.Add( nameof( Age ), new JValue( Age ) );
json.Add( nameof( Phone ), new JValue( Phone ) );
json.Add( nameof( Stature ), new JValue( Stature ) );
return json.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByJson(string data )
{
JObject json = JObject.Parse( data );
UserName = json[nameof( UserName )].Value<string>( );
//Password = json[nameof( Password )].Value<string>( );
Age = json[nameof( Age )].Value<int>( );
Phone = json[nameof( Phone )].Value<string>( );
Stature = json[nameof( Stature )].Value<double>( );
}
}
这样也能实现任意的序列化操作,甚至针对其中某个属性进行加密解密都可以。
性能对比(具体时间取决于电脑性能,我的cpu : i5-4590 内存 ddr3-1600)
两种序列化都有适合的场景,此处演示下序列化1W次的性能对比,看看性能差异
static void Main( string[] args )
{
Account account = new Account( )
{
UserName = "张三",
Password = "123456",
Age = 25,
Phone = "12345678901",
Stature = 170.2d
};
DateTime start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = account.toXml( );
;
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = JObject.FromObject( account ).ToString( );
;
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = account.toJson( );
;
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
Console.ReadLine( );
}
第一次运行:
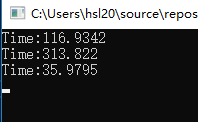
第二次运行:
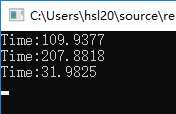
第三次运行:

接下来加上解析部分
{
Account account = new Account( )
{
UserName = "张三",
Password = "123456",
Age = 25,
Phone = "12345678901",
Stature = 170.2d
};
DateTime start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = account.toXml( );
Account account1 = new Account( );
account1.LoadByXml( value );
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = JObject.FromObject( account ).ToString( );
Account account1 = JObject.Parse( value ).ToObject<Account>( );
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
start = DateTime.Now;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
string value = account.toJson( );
Account account1 = new Account( );
account1.LoadByJson( value );
}
Console.WriteLine( "Time:" + (DateTime.Now - start).TotalMilliseconds );
Console.ReadLine( );
}
我们再来看看运行结果:
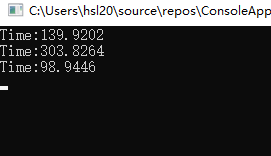
第二次运行结果:
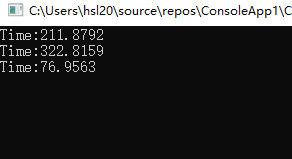
第三次结果:
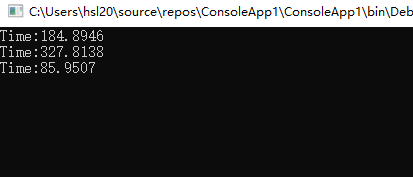
终极性能PK
如果我们自己来写json的序列化呢?
public class Account
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Newtonsoft.Json.JsonIgnore]
public string Password { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public double Stature { get; set; }
public string toXml( )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = new System.Xml.Linq.XElement( "Account" );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( UserName ), UserName );
//element.SetElementValue( nameof( Password ), Password );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Age ), Age.ToString() );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Phone ), Phone );
element.SetElementValue( nameof( Stature ), Stature.ToString( ) );
return element.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByXml( string data )
{
System.Xml.Linq.XElement element = System.Xml.Linq.XElement.Parse( data );
UserName = element.Element( nameof( UserName ) ).Value;
//Password = element.Element( nameof( Password ) ).Value;
Age = int.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Age ) ).Value );
Phone = element.Element( nameof( Phone ) ).Value;
Stature = double.Parse( element.Element( nameof( Stature ) ).Value );
}
public string toJson( )
{
JObject json = new JObject( );
//json.Add( nameof( Password ), new JValue( Password ) );
json.Add( nameof( UserName ), new JValue( UserName ) );
json.Add( nameof( Age ), new JValue( Age ) );
json.Add( nameof( Phone ), new JValue( Phone ) );
json.Add( nameof( Stature ), new JValue( Stature ) );
return json.ToString( );
}
public void LoadByJson(string data )
{
JObject json = JObject.Parse( data );
UserName = json[nameof( UserName )].Value<string>( );
//Password = json[nameof( Password )].Value<string>( );
Age = json[nameof( Age )].Value<int>( );
Phone = json[nameof( Phone )].Value<string>( );
Stature = json[nameof( Stature )].Value<double>( );
}
public string toMyJson( )
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder( );
sb.Append( "{" );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( $" "{nameof( UserName )}":" );
sb.Append( $""{ UserName.Replace( """, "\"" )}"," );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( $" "{nameof( Password )}":" );
sb.Append( $""{ Password.Replace( """, "\"" ) }"," );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( $" "{nameof( Age )}":" );
sb.Append( $"{Age}," );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( $" "{nameof( Phone )}":" );
sb.Append( $""{ Phone.Replace( """, "\"" )}"," );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( $" "{nameof( Stature )}":" );
sb.Append( $"{Stature}," );
sb.Append( Environment.NewLine );
sb.Append( "}" );
return sb.ToString( );
}
}
上述的方法 toMyJson 就是我们所写的一个方法名称,这个方法会主动进行序列化,里面也考虑了,如果字符串数据带有"的情况,需要进行替换 " 的情况,我们单独运行这个序列化的方法10000次
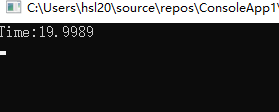
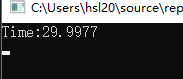
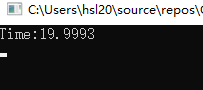
所以关于性能,可以大致做个参考
以上的结果只能参照一下,写法上大家可以根据自己的需求来选择,性能上肯定会有所差别的。感谢阅读:
