c++类关于类静态成员和方法和类的普通成员和方法的关系以及区别
下面把静态属性(方法)称为类的属性(方法) ,普通属性(方法)称为对象的属性(方法)
调用类成员和属性的几种方法
/*
调用类成员和属性的几种方法:
类名::属性或方法名
对象.属性或对象名
*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cat{
public:
static int tot;
static void Comemet(){
tot=100;
}
static void Print(){
cout<<tot<<endl;
}
};
int Cat::tot=0;
int main()
{
Cat::Comemet();
Cat::Print();
cout<<Cat::tot<<endl;
Cat a;
a.Print();
a.Comemet();
cout<<a.tot<<endl;
return 0 ;
}
类和对象的方法和属性大的互相调用问题
- 公有私有保护同样适用类的属性和类的方法(为什么不呢?)
- 类的属性必须在主函数外进行初始化(必须初始化)
- 类方法和类属性不能和对象方法和对象属性重名。(会存在二义性的)
- 对象方法可访问类方法和类属性,类方法不能直接访问对象方法和属性( 只有制定一个对象才可访问对象的方法和属性)
/* 一 公有私有保护同样适用类的属性和类的方法 */
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cat{
private:
static int tot;
static void Comemet(){
tot=100;
}
};
int Cat::tot=0;/*编译*/
int main()
{
Cat::Comemet();/*编译失败 不能直接访问私有方法 */
cout<<Cat::tot<<endl;/*编译失败 不能访问直接直接私有成员 */
}
/* 二 类的属性必须在主函数外进行初始化 */
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cat{
private:
static int tot;
public:
static void Comemet(){
tot=100;
}
};
int Cat::tot=0;
int main()
{
return 0;
}
/* 三 类所属内的所有函数和变量都不允许重名(函数重载的函数不重名)*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cat{
private:
static int tot;
int tot;//编译失败 与Cat::tot冲突
public:
static void Comemet(){
tot=100;
}
static void Print(){
cout<<tot<<endl;
}
};
int Cat::tot=0;
int main()
{
return 0;
}
/*四 为了不产生二义性,所属的对象能访问直接类的内容*/
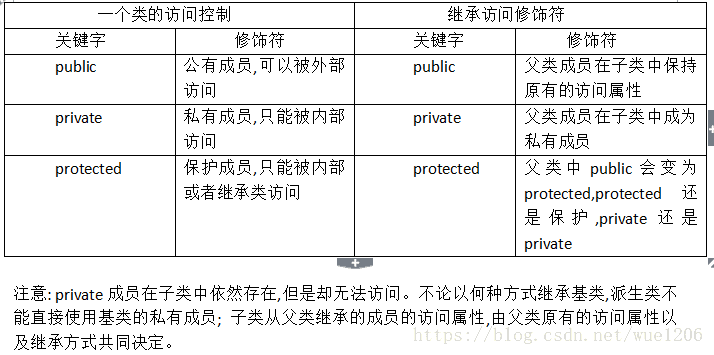
类的继承
派生类和父类不是友元关系。
故父类的私有成员不能被派生类访问
且父类的保护成员可以被派生类访问
且父类的共有成员可以被类外的访问
继承访问符作用如下所示