这节讲什么是内联函数,为什么要使用内联函数?
当编译器发现某段代码在调用一个内联函数时,它不是去调用该函数,而是将该函数的代码,整段插入到当前位置。这样做的好处是省去了调用的过程,加快程序运行速度。(函数的调用过程,由于有前面所说的参数入栈等操作,所以总要多占用一些时间)。这样做的不好处:由于每当代码调用到内联函数,就需要在调用处直接插入一段该函数的代码,所以程序的体积将增大。拿生活现象比喻,就像电视坏了,通过电话找修理工来,你会嫌慢,于是干脆在家里养了一个修理工。这样当然是快了,不过,修理工住在你家可就要占地儿了。内联函数并不是必须的,它只是为了提高速度而进行的一种修饰。要修饰一个函数为内联型,使用如下格式:
inline 函数的声明或定义
简单一句话,在函数声明或定义前加一个 inline 修饰符。
inline int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a>b)? a : b;
}
内联函数的本质是,节省时间但是消耗空间。
二、inline函数的规则
(1)、一个函数可以自已调用自已,称为递归调用,含有递归调用的函数不能设置为inline;
(2)、使用了复杂流程控制语句:循环语句和switch语句,无法设置为inline;
(3)、由于inline增加体积的特性,所以建议inline函数内的代码应很短小。最好不超过5行。
(4)、inline仅做为一种“请求”,特定的情况下,编译器将不理会inline关键字,而强制让函数成为普通函数。出现这种情况,编译器会给出警告消息。
(5)、在你调用一个内联函数之前,这个函数一定要在之前有声明或已定义为inline,如果在前面声明为普通函数,而在调用代码后面才定义为一个inline函数,程序可以通过编译,但该函数没有实现inline。比如下面代码片段:
//函数一开始没有被声明为inline:
void foo();
//然后就有代码调用它:
foo();
//在调用后才有定义函数为inline:
inline void foo()
{
......
}
代码是的foo()函数最终没有实现inline;
(6)、为了调试方便,在程序处于调试阶段时,所有内联函数都不被实现。
三、使用内联函数时应注意以下几个问题:
(1) 在一个文件中定义的内联函数不能在另一个文件中使用。它们通常放在头文件中共享。
(2) 内联函数应该简洁,只有几个语句,如果语句较多,不适合于定义为内联函数。
(3) 内联函数体中,不能有循环语句、if语句或switch语句,否则,函数定义时即使有inline关键字,编译器也会把该函数作为非内联函数处理。
(4) 内联函数要在函数被调用之前声明。关键字inline 必须与函数定义体放在一起才能使函数成为内联,仅将inline 放在函数声明前面不起任何作用
内联函数的实现(一)
//File2.h
class Point
{
public:
Point(int x,int y);
~Point();
int GetX() const{return m_x;}
int GetY() const{return m_y;}
void SetX(int x){m_x = x;}
void SetY(int y){m_y = y;}
int GetArea() const;
private:
int m_x,m_y;
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//File1.cpp
#pragma hdrstop
#include <tchar.h>
#include<iomanip>
#include "File2.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#pragma argsused
Point::Point(int x,int y)
{
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
Point::~Point()
{
}
int Point::GetArea() const
{
int x = m_x*m_x;
int y = m_y*m_y;
return (x+y);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Point p(1,2);
cout<<p.GetX()<<setw(20)<<p.GetY()<<endl;
p.SetX(3);
p.SetY(4);
cout<<p.GetX()<<setw(20)<<p.GetY()<<endl;
cout<<p.GetArea()<<endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果如图

内联函数的复杂调用,内嵌其他的数据成员
//File2.h
#include<iostream> class Point { public: void setX(int x){m_x = x;} //内联函数 void setY(int y){m_y = y;} int GetX()const{return m_x;} int GetY()const{return m_y;} private: int m_x; //定义X坐标 int m_y; //定义Y坐标 }; class Rectangle { public: Rectangle(int top,int left,int bottom,int right); ~Rectangle(){} int GetTop()const{return m_top;} int GetLeft()const{return m_left;} int GetBottom()const{return m_bottom;} int GetRight()const{return m_right;} Point GetUpperLeft(){return m_upperleft;} Point GetLowerLeft(){return m_lowerleft;} Point GetUpperRight(){return m_upperright;} Point GetLowerRight(){return m_lowerright;} void SetUpperLeft(Point rt){m_upperleft = rt;} void SetLowerLeft(Point rt){m_lowerleft = rt;} void SetUpperRight(Point rt){m_upperright = rt;} void SetLowerRight(Point rt){m_lowerright = rt;} void SetTop(int top){m_top = top;} void SetLeft(int left){m_left = left;} void SetBottom(int bottom){m_bottom = bottom;} void SetRight(int right){m_right= right;} int GetArea() const; private: Point m_upperleft; Point m_upperright; Point m_lowerleft; Point m_lowerright; int m_top; int m_left; int m_bottom; int m_right; };
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------- //File1.cpp #pragma hdrstop #include <tchar.h> #include "File2.h" //--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #pragma argsused using namespace std; Rectangle::Rectangle(int top,int left,int bottom,int right) //定义矩形的四个点 { m_top = top; m_left = left; m_bottom = bottom; m_right = right; m_upperleft.setX(left); m_upperleft.setY(top); m_upperright.setX(right); m_upperright.setY(top); m_lowerleft.setX(left); m_lowerleft.setY(bottom); m_lowerright.setX(right); m_lowerright.setY(bottom); } int Rectangle::GetArea() const //计算矩形面积 { int Width = m_right- m_left; int Height = m_top - m_bottom; return(Width*Height); } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { Rectangle MyRectangle(100,20,50,80); int Area = MyRectangle.GetArea(); cout<<"Area:"<<Area<<endl; cout<< "左上角的坐标为:"<<MyRectangle.GetUpperLeft().GetX(); //获取矩形的左上角的坐标
getchar(); return 0; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
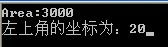
程序稍微难理解的是获取矩形的左上角坐标,程序调用MyRectangle.GetUpperLeft()方法的时候,其实是调用了File2.h文件中的GetUpperLeft()方法,该方法返回一个Point,而如果你想通过Point获取X坐标,需要调用GetX()方法。因此,为获得矩形左上角X坐标,对MyRectangle对象调用GetUpperLeft(),在对返回的值调用GetX().就获取的X的坐标