- Netty是在哪里检测线连接接入的?
- 新连接是怎样注册到NioEventLoop上的?
带着这两个问题,开始学习Netty的新连接接入是如何处理的。
一、检测新连接
- 检测新连接的入口方法是NioEventLoop的processSelectedKey()方法(详情见五)。
- 当读到是read或者Accept事件时会进入unsafe.read()方法。代码如下:
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
二、创建NioSocketChannel
- 由上一步进入unsafe(AbstractNioMessageChannel$NioMessageUnsafe)的read方法
-进入doReadMessages(readBuf)方法,可以看到
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
//创建java SocketChannel
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel().accept();
....
//将java SocketChannel包装成NioSocketChannel,并添加到buf中
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
....
NioSocketChannel的创建逻辑
- 将NioServerSocketChannel和本次连接的SocketChannel传入构造函数
- 创建相关配置config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket()),主要是禁用 Nagle算法。
setTcpNoDelay(true);
- 调用父类构造函数,传入SelectionKey.OP_READ事件
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
- 向上进入父类,设置为非阻塞 ch.configureBlocking(false)
ch.configureBlocking(false);
- 再向上进入父类,指定parent,id,unsafe和pipeChannel
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
new NioSocketChannel(this, ch)
- 判断是否继续下去allocHandle.continueReading()
@Override
public boolean continueReading() {
//默认为true
return config.isAutoRead() &&
//此处皆为0
attemptedBytesRead == lastBytesRead &&
//maxMessagePerRead默认为16
totalMessages < maxMessagePerRead &&
totalBytesRead < Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
如果是继续读下去,并且当前已经没有新连接到来就会跳出该循环。
三、分配线程及注册Selector
- 循环处理获取到的NioSocketChannel
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
此处的pipeLine为服务端启动时设置的DefaultChannelPipeLine,在init方法中我们向其添加了一个ServerBootstrapAcceptor。此处firefireChannelRead方法主要处理逻辑是在ServerBootStrap的channelRead方法中。进入该方法,主要做了以下三件事:
Tips:调用链是Head–ServerBootstrapAcceptor–Tail,还没看到,后续学习。
- 添加childHandler
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler),此处的childHandler是在服务端启动时设置:
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleNettyServerHandler());
}
});
- 设置options和 atrrs
拿到NioSocketChannel的NioSocketChannelConfig,将options和attrs设置。
for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
- 选择NioEventLoop并注册Selector
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
此处childGroup为ServerBootstrapAcceptor创建时传入的workerGroup。
进入register方法:
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
next()为chooser选择器的方法,循环选择group中的NioEventLoop。
跟随断点进入下:
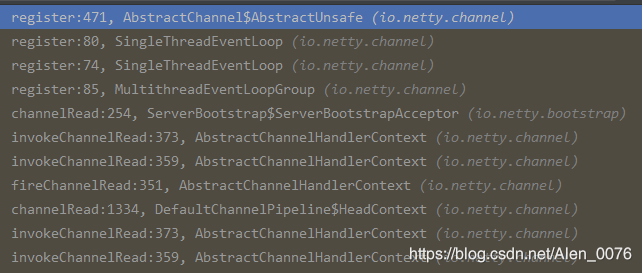
最终调用在:
//此处为Sever端线程,返回为false
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
//启动选择到的NioEventLoop线程,并注册该NioSocketChannel
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
....
}
最终调用到AbstractNioChannel的doRegister方法,注册Channel到Selector上:
//this即为当前封装的NioSocketChannel
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
四、向Selector注册事件读事件
接着上面的注册之后,有以下代码,刚NioSocketChannel已经注册完成,此处isAtIve为true
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
进入fireChannelActive方法
跟随断点进入:

最终进入AbstractChannel的doBeginRead方法:
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
此处的interestOps为NioSocketChannel创建时设置的:
//调用父类构造函数,传入SelectionKey.OP_READ事件
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}