String 的两种实例化方式
隐式实例化:直接赋值
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s == s2);
}
}
true

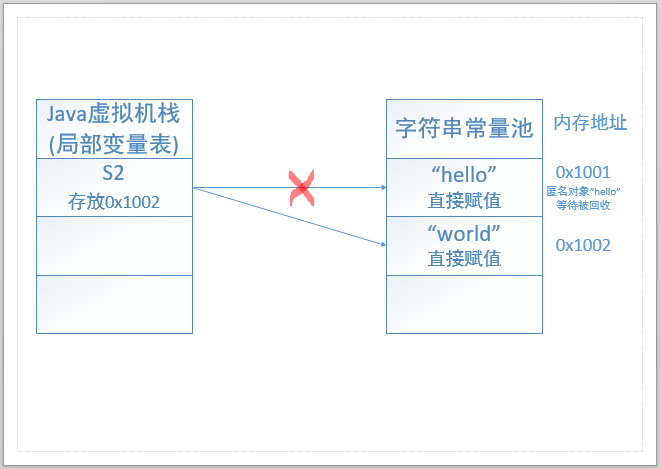
String 一般使用直接赋值的方式创建字符串。此时字符串是一个匿名对象,存放于位于堆的字符串常量池(String Table)中。匿名对象也是对象,就如同对象创建后,对象本身不可以改变,字符串也有不可变的特性,每次都将创建新的字符串。因为不可变,所以字符串可以称为字符串常量。
JVM 中设计字符串常量池是为了减少实例化重复的字符串,以节约新建时间和内存空间。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
System.out.println(s);
String s = "world";
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
hello
world
显式实例化:使用构造函数
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s==s2);
System.out.println(s==s3);
System.out.println(s2==s3);
}
}
false
false
false
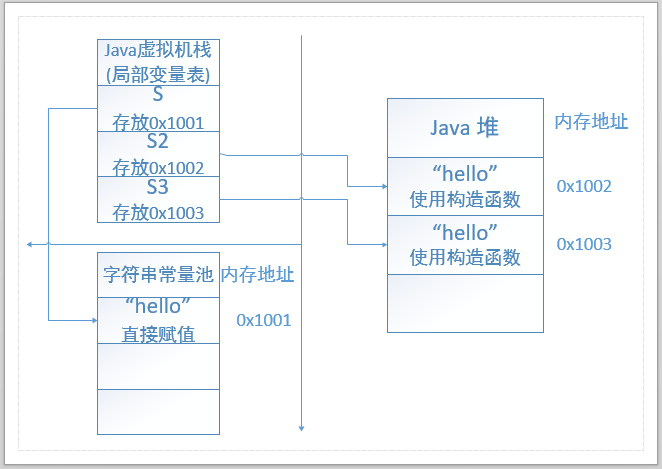
String 是一个类,可以使用构造函数创建字符串。
intern() 方法
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s2 == s2.intern());
System.out.println(s == s3.intern());
System.out.println(s2.intern() == s3.intern());
}
}
false
true
true
intern() 方法,复制字符串对象到字符串常量池,返回字符串(引用)。native() 方法
具体来说:JVM 会在字符串常量池中去比较是否有「等于(equals)」 此 String 对象的字符串,如果有,返回字符串引用,没有则将此 String 对象包含的字符串放入字符串常量池中,再返回引用
String 被 final 修饰。
- final 修饰类,类不能被继承
- 修饰方法,方法不能被重写
- 修饰字段,字段不能指向其他对象
字符串常量池和运行时常量池的关系
- 没有关系,运行时常量池存放运行 Class 文件的常量池表。
String 常用方法
转换为字符数组:toCharArray()
String string = "hello";
char[] array = string.toCharArray();
return new String(array);
获取指定字符
String string = "hello";
char c = string.charAt(0) // 'h'
格式化
String.format("%s %s %s", c1.name, c2.name, C.name)