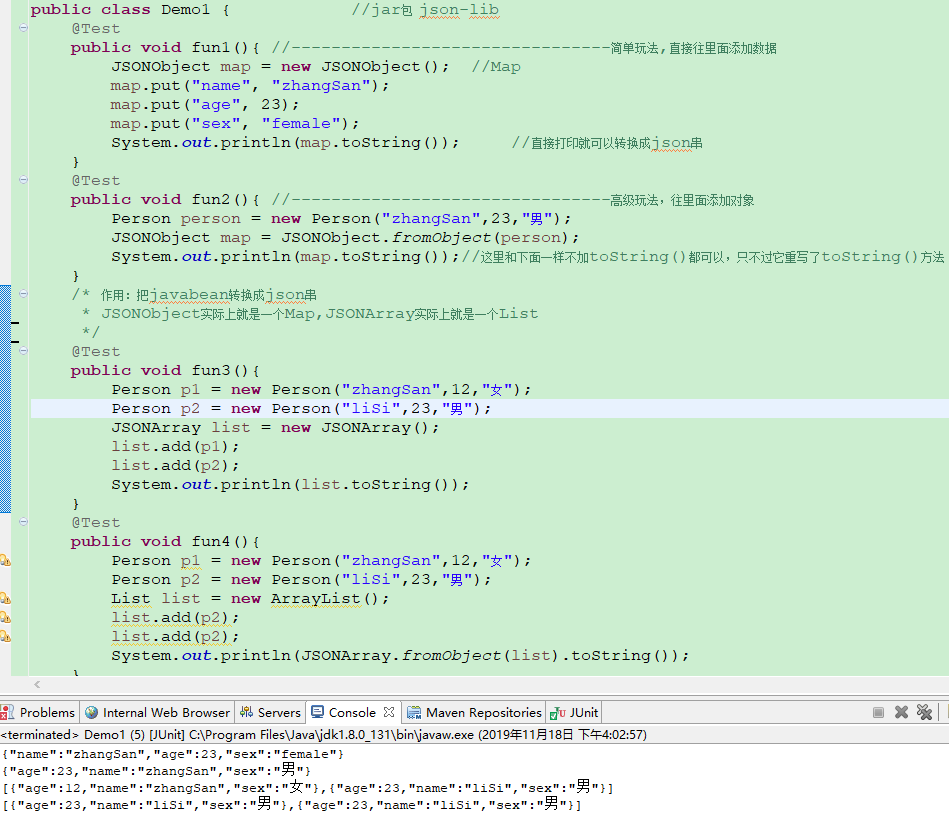
准备一个简单Person类
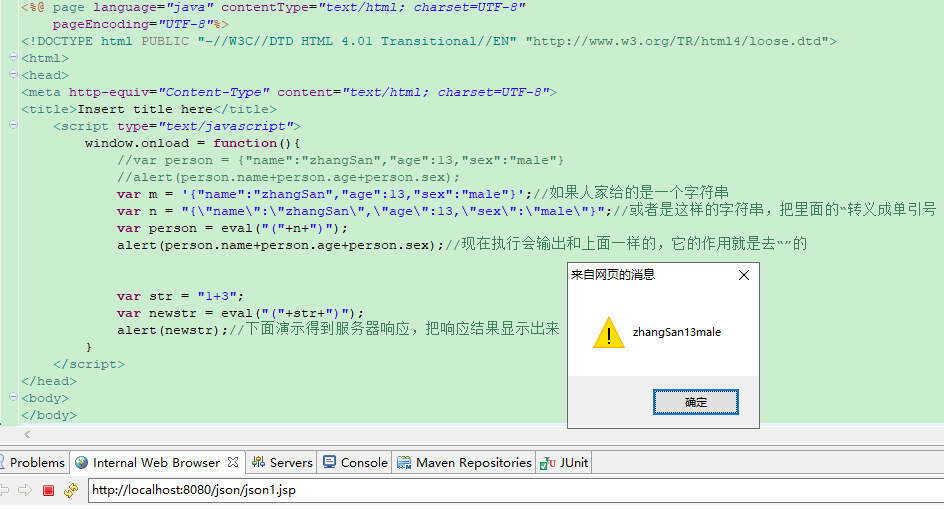
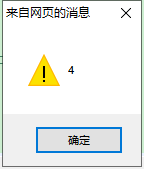
json1.jsp 测试结果两次alert
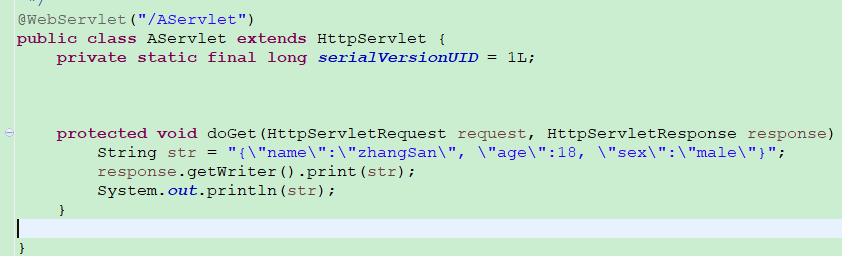
json2.jsp json2首先准备好一个servlet向浏览器发送字符串
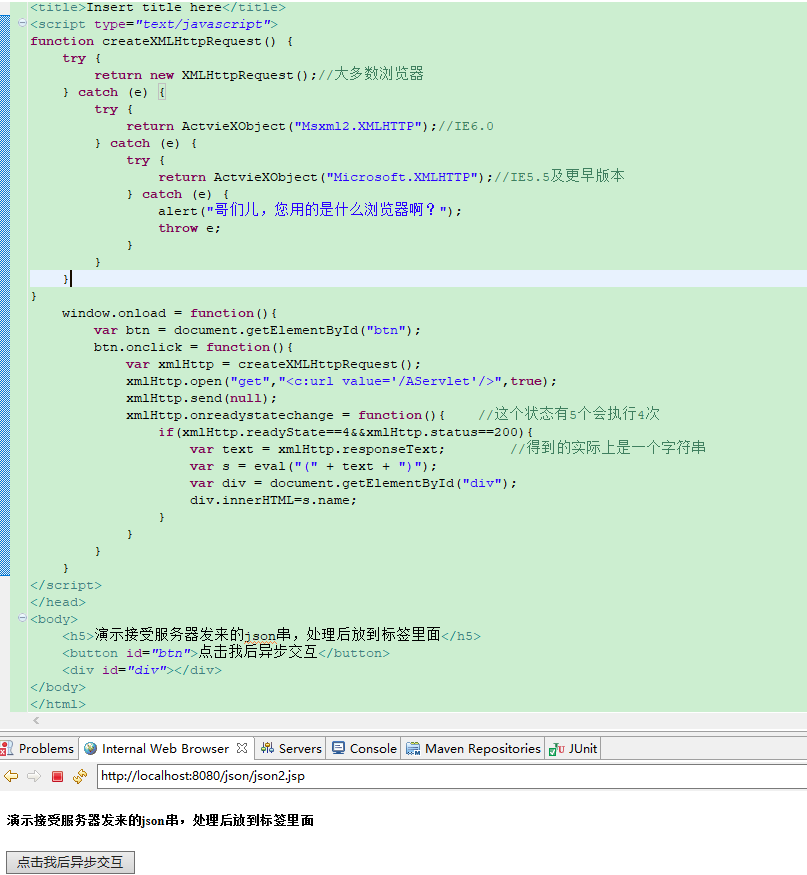
json3.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <title>My JSP 'json2.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> <script type="text/javascript"> function createXMLHttpRequest() { try { return new XMLHttpRequest();//大多数浏览器 } catch (e) { try { return ActvieXObject("Msxml2.XMLHTTP");//IE6.0 } catch (e) { try { return ActvieXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");//IE5.5及更早版本 } catch (e) { alert("哥们儿,您用的是什么浏览器啊?"); throw e; } } } } window.onload = function() { // 获取btn元素 var btn = document.getElementById("btn"); btn.onclick = function() {//给按钮的点击事件上添加监听 // 使用ajax得到服务器端响应,把结果显示到h3中 //1. 得到request var xmlHttp = createXMLHttpRequest(); //2. 连接 xmlHttp.open("GET", "<c:url value='/AServlet'/>", true); //3. 发送 xmlHttp.send(null); //4. 给xmlHttp的状态改变事件上添加监听 xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = function() { //双重判断 if(xmlHttp.readyState == 4 && xmlHttp.status == 200) { var text = xmlHttp.responseText;//它是一个json串 // 执行json串 var person = eval("(" + text + ")"); var s = person.name + ", " + person.age + ", " + person.sex; document.getElementById("h3").innerHTML = s; } }; }; }; </script> </head> <body> <%-- 点击按钮后,把服务器响应的数据显示到h3元素中 --%> <button id="btn">点击这里</button> <h1>JSON之HelloWorld</h1> <h3 id="h3"></h3> </body> </html>
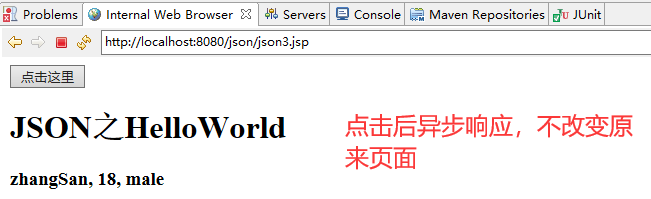
JsonObject
