Controller接收各种形式的传参:
RequestMapping()包含三部分信息:
表单传参:
1、表单action请求
1:参数名称和顺序都要和表单字段名称一致,直接接收(适合字段较少的)
<from id="viewForm" action="view/first"> <input id="roleName" type="text" name="roleName"/> <input id="roleNum" type="text" name="roleNum"/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </from> |
@RequestMapping("/first") public String findName(String roleName,String roleNum){ System.out.println(roleName); System.out.println(roleNum); return "index.jsp"; } |
2:表单中多个字段和一个POJO中属性名称完全对应,则可以对象入参,也不需要注解
@RequestMapping("/add") public String addUser(User user){ System.out.println(user.getName()); return "index.jsp"; } |
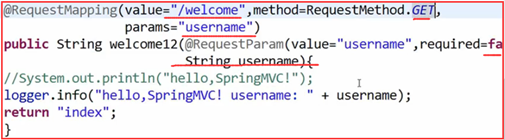
3:使用RequestParam注解,表单中的变量名和controller接收中的变量名不一致!
<from id="viewForm" action="view/first"> <input id="roleName" type="text" name="roleName"/> <input id="roleNum" type="text" name="roleNum"/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </from> |
@RequestMapping("/first") public String findName(@RequestParam("roleName")String roleName,String roleNum){ System.out.println(roleName); System.out.println(roleNum); return "index.jsp"; } |
或者写成@RequestParam(value="roleName",required=false)
2、表单序列化ajax请求
JS代码:
$("#commit").click(function(){ alert("jingru ajax2"); var param = $("#commit").serialize(); $.ajax({ url:"json", data:param, type:"post", dataType:"json", success:function(result){ alert(result.msg1); $("#josnview").text(result.msg1); }, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); }); |
Html代码:
<from id="viewForm"> <input id="roleName" type="text" name="roleName"/> <input id="roleNum" type="text" name="roleNum"/> <input id="commit" type="button" value="提交"/> </from> |
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public String findJson(String roleName, String roleNum){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); String str1 = roleName; String str2 = roleNum; System.out.println("roleName="+roleName +"roleNum="+roleNum ); map.put("msg1", str1 + str2 +"你好"); return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
此种方法验证时候,序列化的data无法传到controller中,待解决…
URL传参
4:RESTFul风格,它将只支持http的GET请求。
$("#json").click(function(){ var param ={}; param.gname = "gname"; param.gid = "gid"; $.ajax({ url:"json/"+true, data:param, type:"GET", dataType:"json", success:function(result){ $("#josnview").text(result.msg1); }, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); }); |
@RequestMapping(value="/json/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String findJson(@RequestParam(value="gname")String name, @RequestParam(value="gid",required=false)String ps, @PathVariable(value="id")Boolean id){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("msg1", name+ps+"你好"+id); return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
注意:一定要是GET请求。@PathVariable注解允许接收参数为String,Integer,Boolean等!
传递JSON参数
1:原生ajax
A: Javascript监听浏览器网页事件(点击,提交,更改等)
B: 创建Ajax引擎对象


C: 配置请求对象的信息

Open()方法还可以设置是否异步req.open( "GET", url, true );
注意:如果是GET请求,则send(null); 如果使用POST请求,就一定要设置请求头,并send(data):
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-u;rlencoded; charset=gb2312");
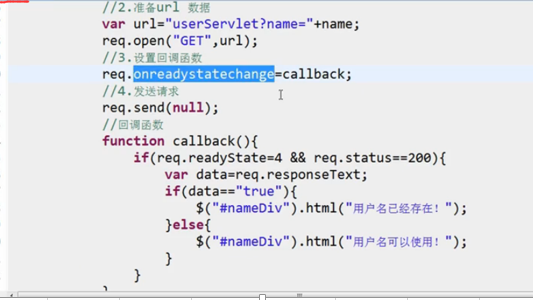
设置响应超时,在send()之前:
xhr.open(); xhr.ontimeout = function(){ alert('request timeout'); } |
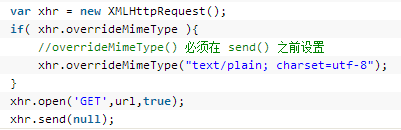
overrideMimeType()方法。
用于重写XHR响应的MIME类型。这对服务器与客户端使用不同编码类型时非常有用。例如在以前如果浏览器使用UTF-8而服务器返回了GBK格式的数据时可能会遇到乱码。而现在就可以用overrideMimeType来解决。
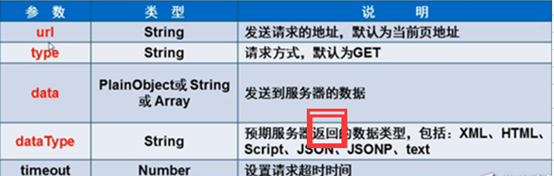
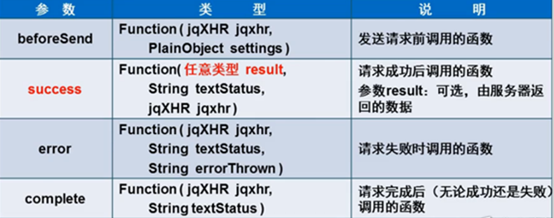
2.$.ajax()方法
可以定义请求失败时的回调函数。$.get() , $.post(),$.getJSON() 则不可以。

1、基本类型入参
Js代码:
$("#json").click(function(){ alert("jingru ajax2"); var param = {}; param.name="1"; param.ps="2"; $.ajax({ url:"json", data:param, type:"post", async:true, dataType:"json", //一般都会预期返回JSON字符串 success:function(result){ alert(result); $("#josnview").text(result.msg); }, error:function(){ alert("回调失败"); } }); }); |
Controller代码
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public String findJson(@RequestParam(value="name")String name, @RequestParam(value="ps",required=false)String ps){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("msg", name+ps+"你好"); return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public Map<String,Object> findJson( @RequestParam(value="name")String name, @RequestParam(value="ps",required=false)String ps){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("msg", name+ps+"你好"); return map; } |
2、基本类型的Bean入参
定义一个Bean
public class Goods implements Serializable {
//商品名称 private String gname; private Integer gid; @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd") private Date gtime; private BigDecimal[] nums; //省略get()/set()方法……
} |
Js代码:
$("#json").click(function(){ alert("jingru ajax2"); var param = {}; param.gname = "gname"; param.gid = 2; $.ajax({ url:"json", data:param, type:"post", async:true, dataType:"json", success:function(result){ alert(result); $("#josnview").text(result.msg); }, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); }); |
Controller代码
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public String findJson(Goods goods){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("msg", goods.getGname()+goods.getGid()+"你好"); System.out.println("name="+goods.getGname()+goods.getGid());
return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
3、@requestBody 处理Bean中属性有数组
@requestBody注解常用来处理contentType不是默认的application/x-www-form-urlcoded编码的内容,比如说:application/json或者是application/xml等。一般情况下来说常用其来处理application/json类型。通过@requestBody可以将请求体中的JSON字符串绑定到相应的bean上,当然,也可以将其分别绑定到对应的字符串上。@requestBody User user 这种形式会将JSON字符串中的值赋予user中对应的属性上需要注意的是,JSON字符串中的key必须对应user中的属性名,否则是请求不过去的。
@RequestBody接收的是一个Json对象的字符串,而不是一个Json对象。然而在ajax请求往往传的都是Json对象,后来发现用 JSON.stringify(data)的方式就能将对象变成字符串。同时ajax请求的时候也要指定dataType: "json",contentType:"application/json" 这样就可以轻易的将一个对象或者List传到Java端,使用@RequestBody即可绑定对象或者List.
JS代码:
$("#json").click(function(){ alert("jingru ajax2"); var param = {}; param.gname = "gname"; param.gid = 2; param.nums = [2.12,3.54,3.67]; $.ajax({ url:"json", data:JSON.stringify(param), //json对象转换为字符串 type:"post", async:true, contentType:"application/json;charset=utf-8", //必须 dataType:"json", success:function(result){ alert(result); $("#josnview").text(result.msg);
}, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); }); |
Bean代码不变:
public class Goods implements Serializable {
//商品名称 private String gname; private Integer gid; @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd") private Date gtime; private BigDecimal[] nums; //省略set()/get()方法 } |
Controller代码: //contentType:"application/json",必须添加该注解
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public String findJson(@RequestBody Goods goods){ //List list = new ArrayList(); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); BigDecimal[] nums = goods.getNums(); if(nums.length>0){ map.put("msg", nums[0]+goods.getGname()+goods.getGid()+"你好"); }else{ System.out.println("nums.length==0"); } return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
4、@requestBody 处理json格式的数组
传递JSON对象,controller用Bean接收!
传递JSON数组,controller用List<Object>接收!
传递JSON对象数组,controller用List<Bean>接收!
JS代码:
$("#json").click(function(){ alert("jingru ajax2"); var param = ["nihao",3.54,true]; $.ajax({ url:"json", data:JSON.stringify(param), type:"post", async:true, contentType:"application/json;charset=utf-8", dataType:"json", success:function(result){ alert(result.msg1+ result.msg2+ result.msg3); $("#josnview").text(result.msg1); }, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); });
|
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("/json") @ResponseBody public String findJson(@RequestBody List<Object> list){ //List list = new ArrayList(); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); //BigDecimal[] nums = goods.getNums(); if(list.size()>0){ map.put("msg1", list.get(0)+"你好"); map.put("msg2", list.get(1)+"你好"); map.put("msg3", list.get(2)+"你好"); }else{ System.out.println("nums.length==0"); } return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
保存并获取属性参数
@RequestAttribute/@SeesionAttribute
获取http请求的属性值,并传递给controller!(类似于@RequestParam)
JSP代码:
<% request.setAttribute("id" , 1L); request.getRequestDispatcher("./attribute/request.do").forward(request,response); %> |
Conreoller代码
@RequestMapping("/request") Public ModelAndView reqAttr(@RequestAttribute(name="id",required=false)Long id){ …..return mv; } |
@SeesionAttribute的用法一模一样
@SessionAttributes
只能标注在类上面,不能标注在方法上。当执行完controller之后,响应的模型的属性将会被保存在session中。这样不需要侵入式的servletAPI来设置session属性了!
URL请求:/attribute/sessionAttributes.do?user_id=1
Controller代码:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/ attribute") @SessionAttributes( name={"user_id"} , type={User.class} ) public Class AttributeController{
@RequestMapping("/ sessionAttributes") Public ModelAndView sessionAttr(Long user_id){ ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); User user = userService.getUser(user_id); mv.addObject("user",user); //根据类型名,session将保存User mv.addObject("user_id",user_id); //根据属性名,session将保存user_id mv.setView("anotherJSP"); return mv; }} |
在下一个jsp页面anotherJSP中可以直接从session中获取user和user_id
@CookieValue的使用
注意客户端禁用coookie的情况!
Js代码:
//设置cookie function setCookie(c_name,value,expiredays) { var exdate=new Date() exdate.setDate(exdate.getDate()+expiredays) document.cookie=c_name+ "=" +escape(value)+ ((expiredays==null) ? "" : ";expires="+exdate.toGMTString()) }
$(function(){ setCookie("cookie_name1","cookiename1",null); setCookie("cookie_name2","cookiename2",null);
$("#json").click(function(){ var param ={}; param.gname = "gname"; param.gid = "gid"; $.ajax({ url:"json/"+true, data:param, type:"GET", dataType:"json", success:function(result){ alert(result.msg1); $("#josnview").text(result.msg1); }, error:function(){ alert("huidiao失败"); } }); }); }); |
Controller代码
@RequestMapping(value="/json/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String findJson(@RequestParam(value="gname")String name, @RequestParam(value="gid",required=false)String ps, @PathVariable(value="id")Boolean id, @CookieValue(value="cookie_name1",required=true,defaultValue="mycookie")String cookie1, @CookieValue(value="cookie_name2",required=true,defaultValue="mycookie")String cookie2){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>(); map.put("msg1", name+ps+"你好"+id+cookie1+cookie2); return JSON.toJSONString(map); } |
注意:required属性默认就是true,在客户端禁用cookie或者找不到对应的cookie的时候:
会自动按照defaultValue输出,此时如果没哟定义defaultValue则请求会报错。所以为了安全,最好定义defaultValue!
@RquestHeader
获取请求头的一些信息。请求头的常见信息如下:
User-Agent
直接在方法里面使用注解获取:
@RequestHeader(value="User-Agdddent",required=false,defaultValue="header")String aencoding |
Mybatis的SQL查询
1 无参数
没有入参,只能为查询语句,并且是返回多条记录!(可以用list集合和map集合接收)
多条记录返回List<Bean>/嵌套Map集合
Dao接口代码:
public List<User> queryUser(); |
Mapper.xml代码:
<resultMap id="allUser" type="User"> <result property="userid" column="userID" /> <result property="userrole" column="userRole" /> <result property="username" column="userName" /> <result property="pwd" column="pwd" /> <result property="address" column="address" /> <result property="phone" column="phone" /> <result property="email" column="email" /> <result property="sex" column="sex" /> <result property="birthday" column="birthday" /> <result property="hdpicpath" column="hdpicpath" /> <result property="wkpicpath" column="wkpicpath" /> </resultMap>
<!-- 查询所哟的用户--> <select id="queryUser" resultMap="allUser" > |
@MapKey("id")
Map<Long, Map<String,Object>> getUserValueMap();
单条记录返回Bean/Map
@MapKey("id")
Map<Long, UserInfo> getUserInfoMap();
2 单独几个参数
单独几个参数的时候,在接口方法处需要加注解@Param("参数名"),参数名以便在sql中按顺序引用。一个参数时候,可以省略(最好加上)
返回影响行数int
增删改语句默认返回影响的行数int,xml中可以不写返回值类型。
多条记录返回List<User>/嵌套的Map集合
注意:
1:多参数入参,所以不用在xml中写入参类型,类型是不统一的。
2:Sql中参数引用的时候要和传参的顺序一致!
3:返回多条记录却制定resultType="Bean"是会报错的!
必须用resultMap或者resultType="map集合"!
用list接收的情况:
/* * 查询满足条件的所有用户 */ @MapKey("id") public List<User> queryUser(@Param("sex")String sex, @Param("userRole")Integer userRole, @Param("userName")String userName); |
<resultMap id="allUser" type="User"> <result property="userid" column="userID" /> <result property="userrole" column="userRole" /> <result property="username" column="userName" /> <result property="pwd" column="pwd" /> <result property="address" column="address" /> <result property="phone" column="phone" /> <result property="email" column="email" /> <result property="sex" column="sex" /> <result property="birthday" column="birthday" /> <result property="hdpicpath" column="hdpicpath" /> <result property="wkpicpath" column="wkpicpath" /> </resultMap>
<!-- 查询所哟的用户--> <select id="queryUser" resultMap="allUser" > select * from `user` where sex = #{sex} and userRole = #{userRole} and userName = #{userName} </select> |
单条记录返回Bean或者Map集合
3 Bean入参
一个Bean入参
一个Bean入参的时候需要指定parametersType(类的完全限定名,或者配置别名)(经过验证,不指定parametersType也是可以的)。
sql语句获取参数的时候直接用#{属性名}即可。参数之间没有顺序要求。
复合Bean入参
多个Bean的入参必须加上@Param("类名称"),在sql中用各自的类名称.属性引用,多个Bean没法定义parametersType,顾省略。(这个可以用于连表查询的情况!)
4 Map入参
1:单Map入参和单Bean入参一样的,在接口方法处不用@Param注解,则在sql语句里面直接用#{key}获取value。parametersType="Map"可以指定(代码可读性高),也可以不指定。
2:如果是多个Map一起入参,在接口方法处必须加@Param("别名"),在sql语句中用
#{别名.key}获取value
5 List入参
List入参常常和动态sql《foreach》组合用。因为list中的个数未知!
<!--List:forech中的collection属性类型是List,collection的值必须是:list,item的值可以随意,Dao接口中参数名字随意 --> |
占位符#和$的区别
动态SQL
什么是动态SQL? |
foreach
使用场景:
- 相同的参数用在in()的括号里面。
- 相同的几个对象用于批量插入或者更新。
foreach标签 |
1: 数组入参
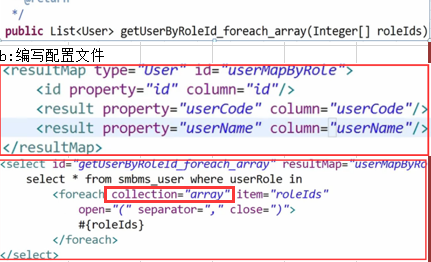
2:List入参
A:list里面的参数是一个字段
DAO接口:
public List<User> queryUser(List<String> pwd); |
Mapper.xml
<resultMap id="allUser" type="User"> <result property="userid" column="userID" /> <result property="userrole" column="userRole" /> <result property="username" column="userName" /> <result property="pwd" column="pwd" /> <result property="address" column="address" /> <result property="phone" column="phone" /> <result property="email" column="email" /> <result property="sex" column="sex" /> <result property="birthday" column="birthday" /> <result property="hdpicpath" column="hdpicpath" /> <result property="wkpicpath" column="wkpicpath" /> </resultMap>
<!-- 查询所哟的用户--> <select id="queryUser" resultMap="allUser" > select * from `user` where pwd in <foreach collection="list" item="pwd" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{pwd} </foreach> </select> |
Controller代码:
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); List<String> pwd = new ArrayList<>(); pwd.add("123"); pwd.add("456"); pwd.add("134"); pwd.add("135"); pwd.add("111"); list = userService.queryUser(pwd); |
B:list里面的参数是一个对象(批量插入数据)
插入之后返回主键
接口代码:
/* * 批量插入用户 */ public int queryUser(List<User> user); |
Mapper.xml文件:
<!-- 插入几个用户,并返回各自的主键--> <insert id="queryUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="userid"> insert into `user`(userName,pwd,address,phone,email,sex,userRole)values <foreach collection="list" item="user" open="(" separator="),(" close=")"> #{user.username},#{user.pwd},#{user.address},#{user.phone},#{user.email},#{user.sex},#{user.userrole} </foreach> </insert> |
Controller代码:
User u1 = new User(); u1.setAddress("成都市后山区"); u1.setEmail("ndihao@qq.com"); u1.setPhone("8765421"); u1.setPwd("987"); u1.setSex("女"); u1.setUserrole(0); u1.setUsername("zhs"); //同理new u2,u3 userInput.add(u1); userInput.add(u2); userInput.add(u3);
int a = userService.queryUser(userInput); //返回影响的行数 int b1 = u1.getUserid();//插入成功后主键回填到指定的userid字段 int b2 = u2.getUserid(); int b3 = u3.getUserid(); |
useGeneratedKeys="true"是用JDBC的statement对象的getGeneratedKeys()获取主键。
keyProperty:仅在insert、update才使用,定义主键回填到哪个字段,复合主键用(,)隔开,不能和keyColumn同时使用
keyColumn: 仅在insert、update才使用.(在postgreSQL中是必须的),不能和keyProperty同时使用
statementType: STATEMENT / PREPARED / CALLABLE 分别使用Statement,PreparedStatement,CallableStatement
批量更新
Dao接口文件:经过测试,批量修改成功,但是主键返回失败
/* * 批量修改用户 */ public int queryUser(List<User> user); |
Mapper.xml文件:
<!-- 插入几个用户,并返回各自的主键--> <update id="queryUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="userid"> UPDATE `user` SET pwd = CASE userName <foreach collection="list" item="user" open="" separator="" close=""> WHEN #{user.username} THEN #{user.pwd} </foreach> END WHERE userName IN <foreach collection="list" item="user" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{user.username} </foreach> </update> |
Controller代码:
User u1 = new User(); u1.setPwd("2090"); u1.setUsername("56789");
User u2 = new User(); u2.setPwd("2091"); u2.setUsername("11111"); //将username=11111的人的pwd修改为2091
User u3 = new User(); u3.setPwd("2092"); u3.setUsername("8888"); //将username=8888的人的pwd修改为2092
userInput.add(u1); userInput.add(u2); userInput.add(u3);
int a = userService.queryUser(userInput); int b1 = u1.getUserid(); int b2 = u2.getUserid(); int b3 = u3.getUserid(); |
If (test)
常用于判断
choose/when/otherwise
存在 1=1的弊端!
<select id="getEmpByChoose" resultType="Emp" parameterType="Emp"> select * from emp where 1 = 1 <choose> <when test="job != null"> and job = #{job} </when> <when test="deptno != null"> and deptno = #{deptno} </when> <otherwise> and mgr = #{mgr} </otherwise> </choose> </select> |
trim/where/set
where + if 可以解决 where 1=1的弊端
<select id="getMaxDepartId" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="java.lang.String"> SELECT MAX(DEPART_ID) FROM T_P_DEPART <where> <if test="_parameter!=null and _parameter!=''"> AND DEPART_PID = #{departId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> <if test="_parameter==null or _parameter==''"> AND DEPART_PID IS NULL </if> </where> </select> |
trim+ if 标签也可以解决 where 1=1 的弊端
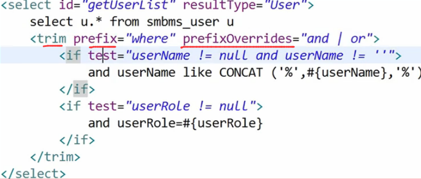
Set的使用:
<update id="updateEmpBySet" parameterType="Emp"> update emp <set> <if test="ename != null and ename != ''"> ename = #{ename}, </if> <if test="job != null and job != ''"> job = #{job}, </if> </set> where empno = #{empno} </update> |
bing
主要用于字符串拼接!
Mysql用concat()拼接,oracle用"||"拼接。所以不能共用同一sql语句。
Bing标签可以将传入的变量先拼接好,这样就可以在sql其它位置引用。
<selet resultType="" > <bing name="pattern_username" value=" '%' + username + '%' " /> Select * from tablename where username like #{ pattern_username } </select> |
<ResulMap /> 、 连表查询
resultMap标签:
resultMap的基本配置项 |
resultMap的属性: |
Ident表和user表联查:
存在外键关联的(需要作为查询结果返回的)pojo定义:
public class Indent implements Serializable { private Integer indentid;//订单编号 private String userid;//用户编号 private String indentime;//下单时间 private String indentstatu;//订单状态 private List<User> userlist; //存在外键关联 private List<T_status> statuslist; //存在外键关联 |
mapper文件resultMap编写:
<resultMap type="Indent" id="indentlist"> <id property="indentid" column="indentId"/> <result property="userid" column="userId"/> <result property="indentstatu" column="indentStatu"/> <result property="indenttime" column="indentTime"/> <collection property="userlist" ofType="User"> <id property="userid" column="userId"/> 填写外键 <result property="address" column="address"/> <result property="username" column="userName"/> <result property="phone" column="phone"/> </collection> <collection property="statuslist" ofType="T_status" resultMap="statuslist"/> </resultMap>
<!-- 分页显示订单记录 --> <select id="getAllIndent" resultMap="indentlist"> SELECT i.indentId,u.userName,u.phone,u.address,s.statusName FROM `user` u INNER JOIN indent i ON u.userId=i.userId INNER JOIN t_status s ON s.indentStatu=i.indentStatu LIMIT #{usecurrentPage},3 </select> |