1、testRTSPClient简介
testRTSPClient是个简单的客户端实例,这个实例对rtsp数据交互作了详细的描述,其中涉及到rtsp会话的两个概念Source和Sink.
Source是生产数据,Sink是消费数据.
testRTSPClient非常简洁,除了接收服务端发送过来的数据,什么都没干,所以我们很方便在这个基础上改造,做我们自己的项目.
2、testRTSPClient编译,运行
在linux下编译运行更方便,鉴于我的电脑太渣,虚拟机跑起来费劲,就转到windows下来折腾.
在windows下只需要加载这一个文件就可以编译,我们以mediaServer为服务端,以testRTSPClient为客户端。
当然也可以用支持rtsp协议的摄像机或其他实体设备作为服务端。

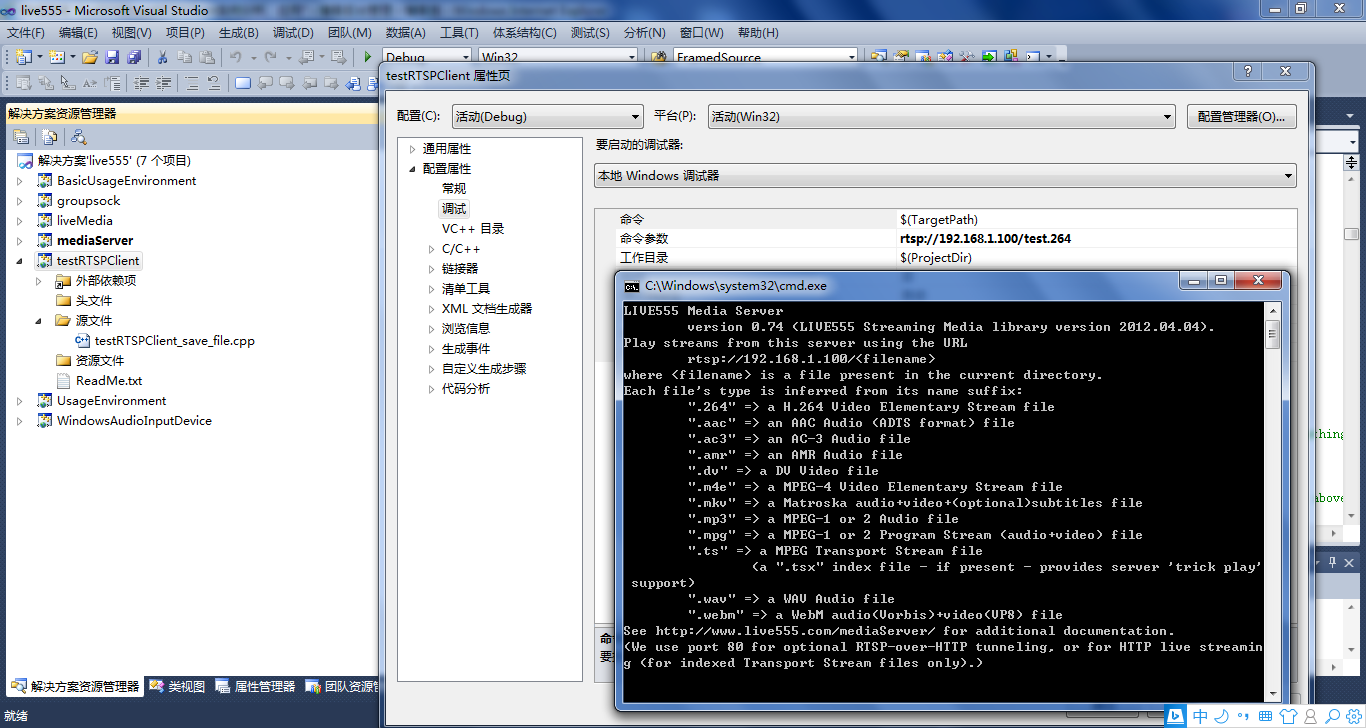
先启动mediaServer,然后在testRTSPClient项目的命令菜单里填入mediaServer 提示的IP, 再启动testRTSPClient即可。
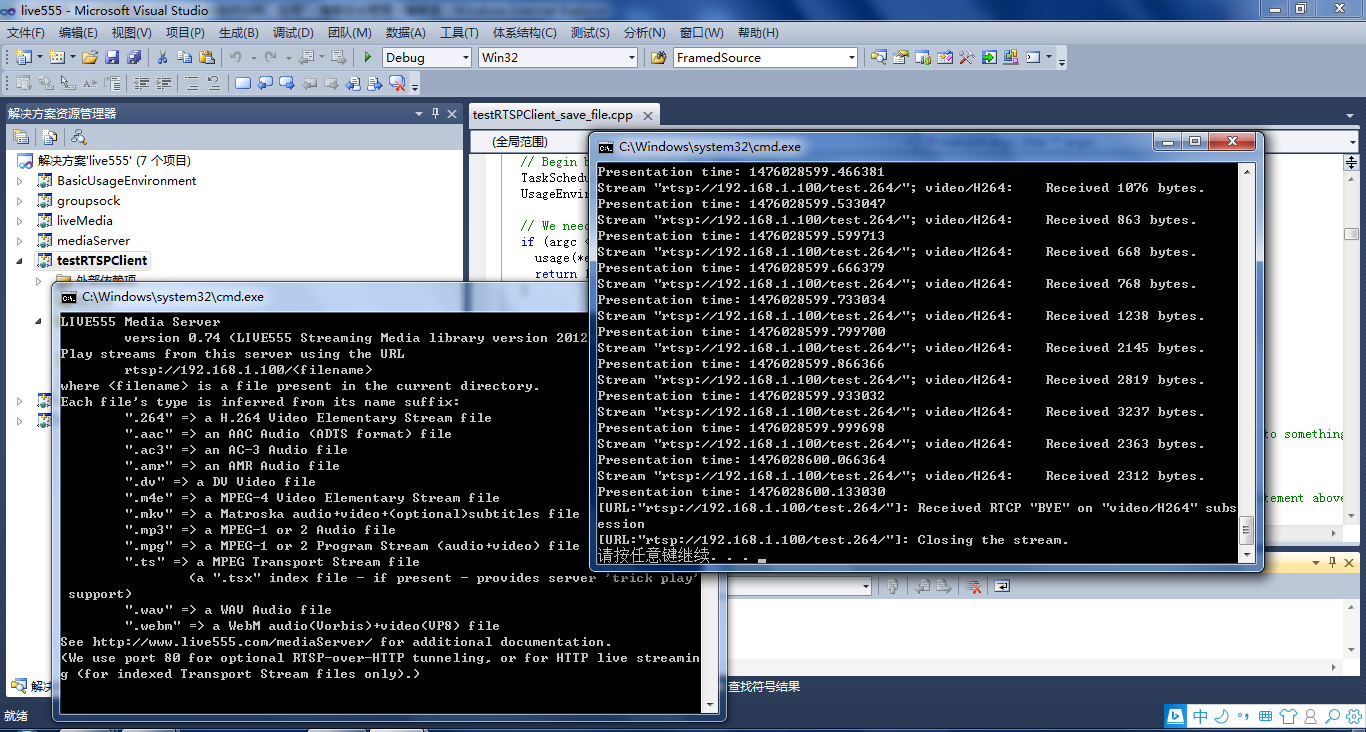
3、testRTSPClient核心代码解读
1)看代码之前可以大致浏览一下总体的框架,这位博主画了个流程图http://blog.csdn.net/smilestone_322/article/details/17297817
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream "" << fStreamId << ""; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ": Received " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ". Presentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "
";
#endif
// Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
}
Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen)
// Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
2)有网友在testRTSPClient基础上,把接收的数据写成h264文件了http://blog.csdn.net/occupy8/article/details/36426821
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(void* clientData, unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned durationInMicroseconds) {
DummySink* sink = (DummySink*)clientData;
sink->afterGettingFrame(frameSize, numTruncatedBytes, presentationTime, durationInMicroseconds);
}
// If you don't want to see debugging output for each received frame, then comment out the following line:
#define DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME 1
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream "" << fStreamId << ""; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ": Received " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ". Presentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "
";
#endif
//todo one frame
//save to file
if(!strcmp(fSubsession.mediumName(), "video"))
{
if(firstFrame)
{
unsigned int num;
SPropRecord *sps = parseSPropParameterSets(fSubsession.fmtp_spropparametersets(), num);
// For H.264 video stream, we use a special sink that insert start_codes:
struct timeval tv= {0,0};
unsigned char start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[0].sPropBytes, sps[0].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[1].sPropBytes, sps[1].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
delete [] sps;
firstFrame = False;
}
char *pbuf = (char *)fReceiveBuffer;
char head[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(head, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(fReceiveBuffer, frameSize, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
}
// Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
}
Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen)
// Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
testRTSPClient接收的fReceiveBuffer缓存没有起始码,start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};