题目一
算法分类:并查集,DFS,Tarjan算法
原题:
How far away ?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)
Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Description
Input
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e5+5; 4 int s[maxn],height[maxn],val[maxn]; 5 int n,m; 6 inline int read(){ 7 register int x=0,f=1;char c=getchar(); 8 while(c<'0'||c>'9'){if(c=='-') f=-1;c=getchar();} 9 while(c>='0'&&c<='9') x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar(); 10 return x*f; 11 } 12 int find_set(int x){ 13 return x==s[x]?x:find_set(s[x]); 14 } 15 void init_set(){ 16 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 17 s[i] = i; 18 height[i]=0; 19 } 20 } 21 void union_set(int x1, int y1,int l){ //将联通的两个节点按秩合并 22 int x = find_set(x1); 23 int y = find_set(y1); 24 if (height[x] == height[y]) { 25 height[x] = height[x] + 1; 26 s[y1] = x1; 27 val[y1]=l; 28 } 29 else{ 30 if (height[x]<height[y]) s[x1]=y1,val[x1]=l; 31 else s[y1] = x1,val[y1]=l; 32 } 33 if(s[y1]==x1) { 34 int t=y1; 35 while(t!=s[t]){ 36 height[s[t]]=max(height[s[t]],height[t]+1); 37 t=s[t]; 38 } 39 } 40 else{ 41 int t=x1; 42 while(t!=s[t]){ 43 height[s[t]]=max(height[s[t]],height[t]+1); 44 t=s[t]; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 int main(){ 49 int t; 50 t=read(); 51 while(t--){ 52 n=read();m=read(); 53 n-=1; 54 init_set(); 55 while(n--){ 56 int x,y,v; 57 x=read(); 58 y=read(); 59 v=read(); 60 union_set(x,y,v); 61 } 62 while(m--){ 63 int x,y,k; 64 x=read();y=read(); 65 long long cnt=0; 66 if(height[y]>height[x]){ //将不在同一高度的两个节点移动至同一个高度 67 while(height[x]!=height[y]){ 68 cnt+=val[x]; 69 x=s[x]; 70 } 71 } 72 else if(height[y]<height[x]){ 73 while(height[y]!=height[x]){ 74 cnt+=val[y]; 75 y=s[y]; 76 } 77 } 78 else{} 79 if(x==y){ 80 printf("%lld ",cnt);continue; //如果两点已经重合,输出结果 81 } 82 else{ //将两点同时上移,直至两点重合 83 while(x!=y){ 84 cnt+=val[x]+val[y]; 85 x=s[x]; 86 y=s[y]; 87 } 88 } 89 printf("%lld ",cnt); 90 } 91 } 92 return 0; 93 }
虽然这道题目只有4e4的数据,并且给了两秒的时间,但是这样暴力的做法还是超时了。自己做了不少改进还是没有任何效果。所以这道题目得推翻一开始的做法重新来。
想了好久没有思路,后来通过几篇博客,了解到了Tarjan算法。
先来说一说Tarjan算法:
Tarjan算法实际上是一种离线算法。所谓离线,就是通过一次遍历一次性将所有询问结果进行计算并进行保存。最后不需要再回到图中计算直接输出结果。其时间复杂度为O(n+q);
n为所有节点的总个数,q为所有询问的个数。
Tarjin算法的基本流程大概是:
1.任选一个节点为根节点,以这个节点为起点
2.遍历该点u所有子节点v,并标记这些子节点v已被访问过。
3.若是v还有子节点,返回2,否则下一步。
4.将v的祖先记为u。
5.寻找与当前点u有询问关系的点v。若是v已经被访问过了,则可以确认u和v的最近公共祖先为v被合并到的父亲节点。如果v 没有被访问,则继续下一步操作
其实画一个图自己来手动模拟会显得更加直观
现在有这样一个图:
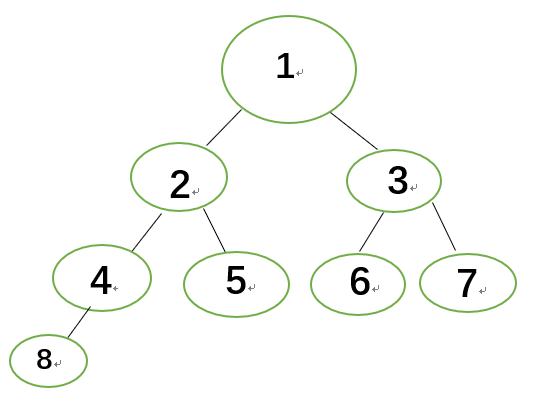
fa[1]=1,vis[1]=false 现在有两组点需要询问,要求这两个点的最近公共祖先
fa[2]=2,vis[2]=false 分别为点2和点4,点8与点5
fa[3]=3,vis[3]=false
fa[4]=4,vis[4]=false
fa[5]=5,vis[5]=false
fa[6]=6,vis[6]=false
fa[7]=7,vis[7]=false
fa[8]=8,vis[8]=false
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=40000+5; 4 struct Edge{ 5 int cnt,x[N],y[N],z[N],nxt[N],fst[N]; 6 void set(){ 7 cnt=0; 8 memset(x,0,sizeof x); 9 memset(y,0,sizeof y); 10 memset(z,0,sizeof z); 11 memset(nxt,0,sizeof nxt); 12 memset(fst,0,sizeof fst); 13 } 14 void add(int a,int b,int c){ 15 x[++cnt]=a; 16 y[cnt]=b; 17 z[cnt]=c; 18 nxt[cnt]=fst[a]; 19 fst[a]=cnt; 20 } 21 }e,q; 22 int T,n,m,from,to,dist,in[N],rt,dis[N],fa[N],ans[N]; 23 bool vis[N]; 24 void dfs(int rt){ 25 for (int i=e.fst[rt];i;i=e.nxt[i]){ 26 dis[e.y[i]]=dis[rt]+e.z[i]; 27 dfs(e.y[i]); 28 } 29 } 30 int getf(int k){ 31 return fa[k]==k?k:fa[k]=getf(fa[k]); 32 } 33 void LCA(int rt){ 34 for (int i=e.fst[rt];i;i=e.nxt[i]){ 35 LCA(e.y[i]); 36 fa[getf(e.y[i])]=rt; 37 } 38 vis[rt]=1; 39 for (int i=q.fst[rt];i;i=q.nxt[i]) 40 if (vis[q.y[i]]&&!ans[q.z[i]]) 41 ans[q.z[i]]=dis[q.y[i]]+dis[rt]-2*dis[getf(q.y[i])]; 42 } 43 int main(){ 44 scanf("%d",&T); 45 while (T--){ 46 q.set(),e.set(); 47 memset(in,0,sizeof in); 48 memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); 49 memset(ans,0,sizeof ans); 50 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 51 for (int i=1;i<n;i++) 52 scanf("%d%d%d",&from,&to,&dist),e.add(from,to,dist),in[to]++; 53 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 54 scanf("%d%d",&from,&to),q.add(from,to,i),q.add(to,from,i); 55 rt=0; 56 for (int i=1;i<=n&&rt==0;i++) 57 if (in[i]==0) 58 rt=i; 59 dis[rt]=0; 60 dfs(rt); 61 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 62 fa[i]=i; 63 LCA(rt); 64 for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) 65 printf("%d ",ans[i]); 66 } 67 return 0; 68 }
题目二
算法分类:递推DP,组合数
原题:HDU4489
The King’s Ups and Downs
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)
Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Description

or perhaps:

The king wants to know how many guards he needs so he can have a different up and down order at each changing of the guard for rest of his reign. To be able to do this, he needs to know for a given number of guards, n, how many different up and down orders there are:
For example, if there are four guards: 1, 2, 3,4 can be arrange as:
1324, 2143, 3142, 2314, 3412, 4231, 4132, 2413, 3241, 1423
For this problem, you will write a program that takes as input a positive integer n, the number of guards and returns the number of up and down orders for n guards of differing heights.
Input
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
1 c[1][0]=c[1][1]=1; 2 for(int i=2;i<=20;i++){ 3 c[i][0]=c[i][i]=1; 4 for(int j=1;j<i;j++){ 5 c[i][j]=c[i-1][j-1]+c[i-1][j]; 6 } 7 }
我们可以用两个dp数组,dp1和dp2分别表示以“高矮”结尾的方法数和以“矮高”开头的方法数。由于对于n个士兵排列的总方法数,以“高矮”和“矮高”开头的方法数各占总数的一半,同理以“高矮”结尾的方法数也一样。所以dp1[n]和dp2[n]都等于ans[n]的一半。
递推方程为:
ans[i]=dp1[j]*dp2[i-1-j]*c[i-1][j] (0<=j<i)
当然如果只用一个dp数组也是一样,
dp[i]=(dp[j]/2)*(dp[i-1-j]/2)*c[i-1][j] (0<=j<i)
这里n最大只有20,所以直接一次性打表把所有答案存下来,避免后面重复计算。注意答案的数值可能很大,所以要用long long。
上代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 ll c[22][22]; 5 ll dp1[25],dp2[25]; 6 #define scan(i) scanf("%d",&i) 7 int main(){ 8 int N;scan(N); 9 c[1][0]=c[1][1]=1; 10 for(int i=2;i<=20;i++){ 11 c[i][0]=c[i][i]=1; 12 for(int j=1;j<i;j++){ 13 c[i][j]=c[i-1][j-1]+c[i-1][j]; 14 } 15 } 16 dp1[1]=dp1[0]=dp2[0]=dp2[1]=1; 17 for(int i=2;i<=20;i++){ 18 ll t=0; 19 for(int j=0;j<i;j++){ 20 t+=dp1[j]*dp2[i-1-j]*c[i-1][j]; 21 } 22 dp1[i]=dp2[i]=t/2; 23 } 24 while(N--){ 25 int x,y; 26 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 27 if(y==1){ 28 printf("%d 1 ",x); 29 continue; 30 } 31 ll ans=dp1[y]*2; 32 printf("%d %lld ",x,ans); 33 } 34 return 0; 35 }
题目三
题目来源:CF#552(div3)
G题:数论
G. Minimum Possible LCM
You are given an array aa consisting of nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an .
Your problem is to find such pair of indices i,ji,j (1≤i<j≤n1≤i<j≤n ) that lcm(ai,aj)lcm(ai,aj) is minimum possible.
lcm(x,y)lcm(x,y) is the least common multiple of xx and yy (minimum positive number such that both xx and yy are divisors of this number).
The first line of the input contains one integer nn (2≤n≤1062≤n≤106 ) — the number of elements in aa .
The second line of the input contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤1071≤ai≤107 ), where aiai is the ii -th element of aa .
Print two integers ii and jj (1≤i<j≤n1≤i<j≤n ) such that the value of lcm(ai,aj)lcm(ai,aj) is minimum among all valid pairs i,ji,j . If there are multiple answers, you can print any.
5
2 4 8 3 6
1 2
5
5 2 11 3 7
2 4
6
2 5 10 1 10 2
1 4
题意:
给出n个数,要求输出最小公倍数最大的两个数的下标
知识补充:GCD和LCM:
GCD即最大公约数,求最大公约数有多种方法,常见的有质因数分解法、短除法、辗转相除法、更相减损法。
algorithm库里有函数__gcd()
欧几里得(辗转相除法):
1 int gcd(int a,int b) 2 3 { 4 5 if(b==0) return a; 6 7 return gcd(b,a%b); 8 9 } 10 11 12 13 14 int gcd(int x,int y){return y==0?x:GCD(x%y)}
更相减损术:
1 while(!(a%2) && !(b%2)) 2 { 3 a = a/2; 4 b = b/2; 5 } 6 while(a != b) 7 { 8 if(a>b){ 9 a = a-b; 10 }else{ 11 b = b-a; 12 } 13 }
stein算法:Stein算法只有整数的移位和加减法。原理如下:
- 若a和b都是偶数,则记录下公约数2,然后都除2(即右移1位);
- 若其中一个数是偶数,则偶数除2,因为此时2不可能是这两个数的公约数了
- 若两个都是奇数,则a = |a-b|,b = min(a,b),因为若d是a和b的公约数,那么d也是|a-b|和min(a,b)的公约数。
1 int SteinGCD(int a, int b) { 2 if (a < b) { int t = a; a = b; b = t; } 3 if (b == 0) return a; 4 if ((a & 1) == 0 && (b & 1) == 0) 5 return SteinGCD(a >> 1, b >> 1) << 1; 6 else if ((a & 1) == 0 && (b & 1) != 0) 7 return SteinGCD(a >> 1, b); 8 else if ((a & 1) != 0 && (b & 1) == 0) 9 return SteinGCD(a, b >> 1); 10 else 11 return SteinGCD(a - b, b); 12 }
LCM即最小公倍数
有如下公式 LCM(a,b)*GCD(a,b)=a*b;通过分解分解质因数可以很容易的证明。
1 int GCD(int x,int y){ 2 3 return !y?x:GCD(y,x%y); 4 5 } 6 7 int LCM(int x,int y){ 8 9 return x*y/GCD(x,y); 10 11 }
题解:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int maxn=1e7+10; 5 int n,v; 6 int pos[maxn]; 7 ll ans; 8 int ai,aj; 9 int main(){ 10 scanf("%d",&n); 11 ans=1e18; 12 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 13 scanf("%d",&v); 14 if(pos[v]&&ans>v) 15 ans=v,ai=pos[v],aj=i; 16 pos[v]=i; 17 } 18 for(ll i=1;i<maxn;i++) 19 { 20 ll first=-1; 21 for(ll j=i;j<maxn;j+=i) 22 { 23 if(pos[j]) 24 { 25 if(first==-1)first=j; 26 else 27 { 28 if(ans>first*j/i) 29 ans=first*j/i,ai=pos[first],aj=pos[j]; 30 break; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 if(ai>aj){ 36 int temp=ai; 37 ai=aj; 38 aj=temp; 39 } 40 printf("%d %d ",ai,aj); 41 return 0; 42 }
E题:
There are nn students standing in a row. Two coaches are forming two teams — the first coach chooses the first team and the second coach chooses the second team.
The ii -th student has integer programming skill aiai . All programming skills are distinct and between 11 and nn , inclusive.
Firstly, the first coach will choose the student with maximum programming skill among all students not taken into any team, and kk closest students to the left of him and kk closest students to the right of him (if there are less than kk students to the left or to the right, all of them will be chosen). All students that are chosen leave the row and join the first team. Secondly, the second coach will make the same move (but all students chosen by him join the second team). Then again the first coach will make such move, and so on. This repeats until the row becomes empty (i. e. the process ends when each student becomes to some team).
Your problem is to determine which students will be taken into the first team and which students will be taken into the second team.
The first line of the input contains two integers nn and kk (1≤k≤n≤2⋅1051≤k≤n≤2⋅105 ) — the number of students and the value determining the range of chosen students during each move, respectively.
The second line of the input contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤n1≤ai≤n ), where aiai is the programming skill of the ii -th student. It is guaranteed that all programming skills are distinct.
Print a string of nn characters; ii -th character should be 1 if ii -th student joins the first team, or 2 otherwise.
5 2 2 4 5 3 1
11111
5 1 2 1 3 5 4
22111
7 1 7 2 1 3 5 4 6
1121122
5 1 2 4 5 3 1
21112
In the first example the first coach chooses the student on a position 33 , and the row becomes empty (all students join the first team).
In the second example the first coach chooses the student on position 44 , and the row becomes [2,1][2,1] (students with programming skills [3,4,5][3,4,5] join the first team). Then the second coach chooses the student on position 11 , and the row becomes empty (and students with programming skills [1,2][1,2] join the second team).
In the third example the first coach chooses the student on position 11 , and the row becomes [1,3,5,4,6][1,3,5,4,6] (students with programming skills [2,7][2,7] join the first team). Then the second coach chooses the student on position 55 , and the row becomes [1,3,5][1,3,5] (students with programming skills [4,6][4,6] join the second team). Then the first coach chooses the student on position 33 , and the row becomes [1][1] (students with programming skills [3,5][3,5] join the first team). And then the second coach chooses the remaining student (and the student with programming skill 11 joins the second team).
In the fourth example the first coach chooses the student on position 33 , and the row becomes [2,1][2,1] (students with programming skills [3,4,5][3,4,5] join the first team). Then the second coach chooses the student on position 11 , and the row becomes empty (and students with programming skills [1,2][1,2] join the second team).
题意:
现有n个人排成一队,两个教练轮流从队中挑选最高的人以及最高的人左边k个人和右边k个人,现在需要你求出每个人分别被哪一个教练挑选走。
题解:
这条题目其实就是一条模拟题,唯一要说的就是如何快速找到当前队中存在的最大值,以及最大值所对应的位置。
用一个check数组保存每一个值的状态,这样在寻找最大值的时候,可以从n开始,如果这个值已经被用过了,就减一再判断,直到找到当前未用的最大值。然后用position数组保存每一个值的下标,方便索引。
代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=2e5+5; 4 int n,k,x; 5 struct node{ 6 int val; 7 int id; 8 node *pre; 9 node *next; 10 }; 11 node p[maxn]; 12 int ans[maxn]; 13 int position[maxn]; 14 bool check[maxn]; 15 inline void build(){ 16 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 17 scanf("%d",&x); 18 p[i].val=x; 19 p[i].id=i; 20 p[i].pre=&p[i-1];p[i].next=&p[i+1]; 21 if(i==1)p[i].pre=NULL; 22 if(i==n)p[i].next=NULL; 23 position[x]=i; 24 } 25 return; 26 } 27 int main(){ 28 scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); 29 build(); 30 int ma=n; 31 int an=1; 32 while(ma!=0){ 33 check[ma]=true; 34 ans[position[ma]]=an; 35 int po=position[ma]; 36 int k1=k;int k2=k; 37 int p1=po,p2=po; 38 while(k1--){ 39 if(p[po].next==NULL)break; 40 int v=p[po].next->val; 41 check[v]=true; 42 ans[position[v]]=an; 43 p1=p[po].next->id; 44 p[po].next=p[po].next->next; 45 } 46 while(k2--){ 47 if(p[po].pre==NULL)break; 48 int v=p[po].pre->val; 49 check[v]=true; 50 ans[position[v]]=an; 51 p2=p[po].pre->id; 52 p[po].pre=p[po].pre->pre; 53 } 54 if(p[p1].next!=NULL)p1=p[p1].next->id; 55 else p1=n+1; 56 if(p[p2].pre!=NULL)p2=p[p2].pre->id; 57 else p2=0; 58 if(p1<=n&&p2>=1){ 59 p[p1].pre=&p[p2]; 60 p[p2].next=&p[p1]; 61 } 62 if(p1<=n&&p2<1)p[p1].pre=NULL; 63 if(p1>n&&p2>=1)p[p2].next=NULL; 64 if(an==1)an=2;else an=1; 65 while(check[ma])ma--; 66 } 67 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 68 printf("%d",ans[i]); 69 return 0; 70 }