1. gdb调试

fun.c
#include <stdio.h> #include "head.h" int sum(int a, int b) { printf("welcome call %s, %d + %d = %d ",__FUNCTION__, a, b, a + b); return a + b; } int mul(int a, int b) { printf("welcome call %s, %d * %d = %d ", __FUNCTION__, a, b, a * b); return a * b; }
head.h
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int a, int b);
int mul(int a, int b);
main.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "head.h" typedef struct MyfunInfo { int fun_type; // 函数类型 int a; // 函数的第一个参数 int b; // 第二个参数 char funname[10]; // 函数名称 }MyfunInfo; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a = 2; int i = 0; int a1 = 10, b1 = 5; MyfunInfo funinfo[2]; char *Msg = "I will die !"; //Msg[0] = '1'; if (argc == 3) { a1 = atoi(argv[1]); b1 = atoi(argv[2]); funinfo[0].a = a1; funinfo[0].b = b1; funinfo[1].a = a1; funinfo[1].b = b1; } for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { printf("i===%d, LINE=%d ", i, __LINE__); if (i == 0) { funinfo[i].fun_type = 1; printf("begin call sum "); strcpy(funinfo[i].funname, "sum"); sum(funinfo[i].a, funinfo[i].b); } if (i == 1) { funinfo[i].fun_type = 2; //call mul printf("begin call mul "); strcpy(funinfo[i].funname, "mul"); mul(funinfo[i].a, funinfo[i].b); } } printf("say bye "); return 0; }

(-g是调试选项, 生成的app.out可调试)
2 启动gdb
gdb app.out

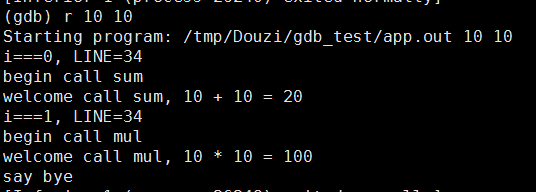
2.1 run (r) 启动
2.2 start 启动-停留在main函数,分步调试
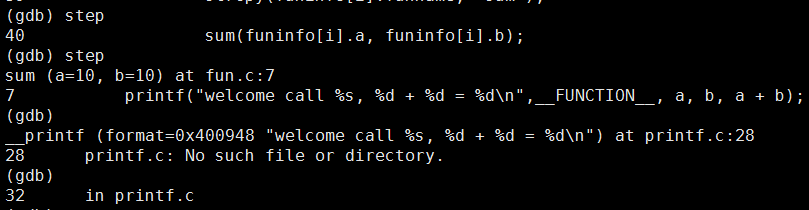
2.21 next(n):下一步

2.22 step(s):下一步, 可以进入函数内部, 但是库函数不能进
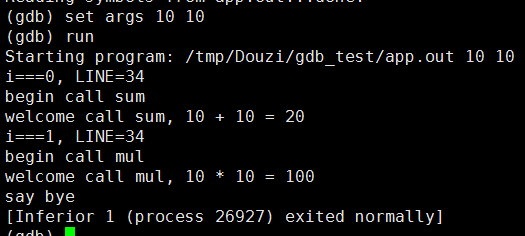
2.3 设置启动参数和设置变量值 set args parm1 parm2 ...
2.31 设置启动参数 set args parm1 parm2.....
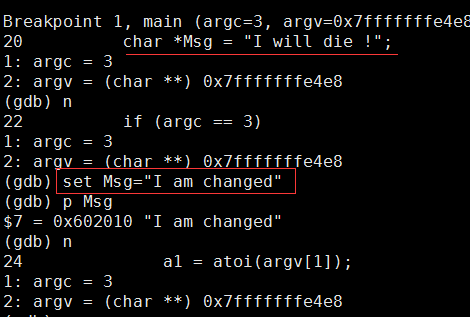
2.32 设置变量值
-
set argc=4
-
set argv[1]="12"
2.4 设置断点break (重要)
2.41 list查看代码
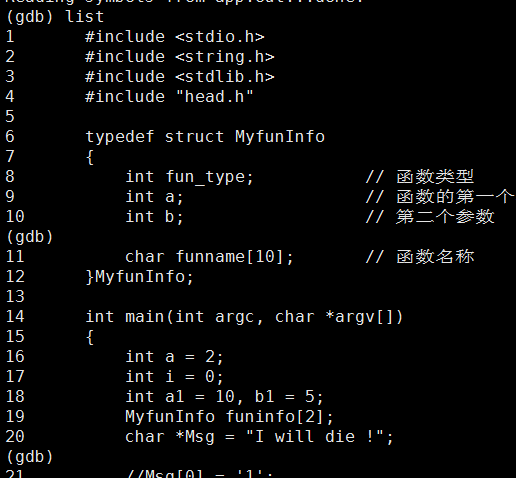
2.42 b 行号--主函数所在文件的行


2.43 b 函数名

2.44 b 文件名:行号

2.45 list 文件名:行号(默认10行)

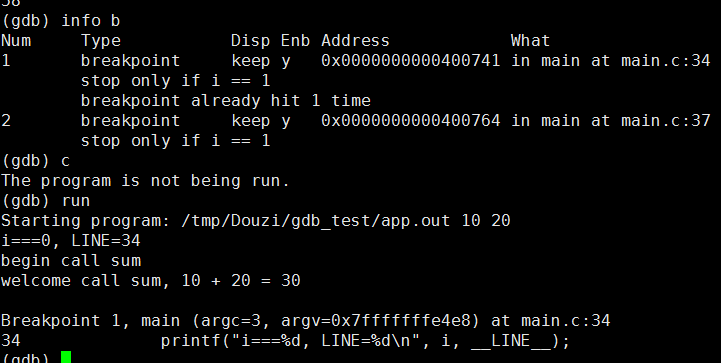
2.46 info b--显示全部断点
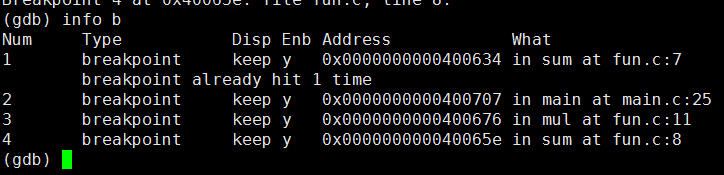
2.5 删除断点 del (d)

2.6 运行至下个断点 c
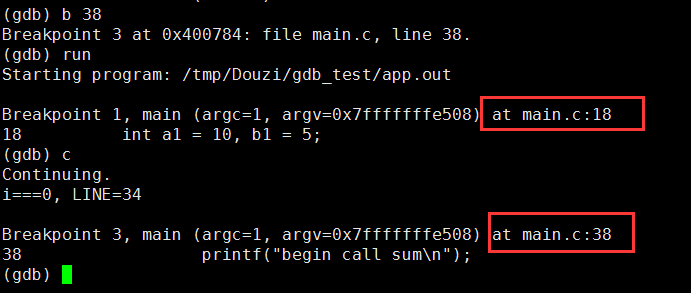
2.7 p 变量--打印变量

2.8 ptype--查看类型

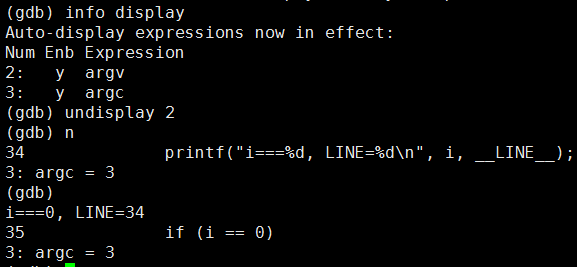
2.9 display 变量--用于追踪,查看变量具体何时变化
2.91 display 变量

2.92 undisplay 行号
3. 补充
3.1 设置条件断点


4. gdb跟踪core



注意:出现 段错误(核心已转储))
4.1 设置生成core:ulimit -c unlimited
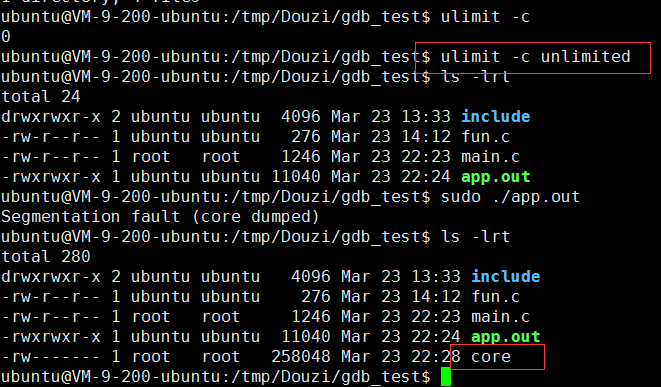

4.2 取消生成core:ulimit -c 0
4.3 设置core文件格式:/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
- 设置core
- 使用该命令修改文件(无法用vim): sudo echo "core-%e-%t" > /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern