网上的Linux PCI驱动教程基本就没有有用的。扯半天PCI配置空间就完了。但是PCI配置空间是最容易访问的,只是内核启动时扫描PCI设备时比较重要。对于PCI驱动,更常用的是PCI设备的IO空间和内存空间。
以前只知道在PCI设备的配置空间中,BAR0-BAR5能够读取到PCI设备的IO空间或地址空间的基址,但是如何区分这个BAR代表的到底是IO空间还是内存地址空间呢?
在PCI网卡的示例程序(pci-skeleton.c)中:
- pio_start = pci_resource_start(pdev, 0);
- pio_end = pci_resource_end(pdev, 0);
- pio_flags = pci_resource_flags(pdev, 0);
- pio_len = pci_resource_len(pdev, 0);
- mmio_start = pci_resource_start(pdev, 1);
- mmio_end = pci_resource_end(pdev, 1);
- mmio_flags = pci_resource_flags(pdev, 1);
- mmio_len = pci_resource_len(pdev, 1);
- /* make sure PCI base addr 0 is PIO */
- if (!(pio_flags & IORESOURCE_IO)) {
- dev_err(&pdev->dev, “region #0 not a PIO resource, aborting ”);
- rc = -ENODEV;
- goto err_out;
- }
- /* make sure PCI base addr 1 is MMIO */
- if (!(mmio_flags & IORESOURCE_MEM)) {
- dev_err(&pdev->dev, “region #1 not an MMIO resource, aborting ”);
- rc = -ENODEV;
- goto err_out;
- }
可以看到如果只写驱动程序的话,内核在扫描pci设备的时候早就把设备的BAR的属性识别好了。当然,到底有几个BAR,每个BAR到底是IO空间还是PCI地址空间可以直接问制作PCI设备的硬件工程师。
那么内核是如何获得这个flags呢?我跟了半天源码也没找到。只是知道,PCI总线规范规定直接读BAR,返回的是BAR空间基址。先写全1到BAR再 读,就能读取到BAR空间大小和属性。选最低的一位非0的,比如读到0xFFFFFF00,那个空间的大小就为0x100个Byte ,最后一位为0说明是地址区域,为1则这个BAR是IO空间。
此外,非常重要的一个概念是,BAR读取到的是PCI地址空间中的地址,不等同于CPU认识的内存地址。虽然在x86上如果没有开启IOMMU时,它们的值一般是相同的,但是对于其他构架的CPU如PowerPC就可以是不一样的。
所以正确的使用BAR空间的方法:
pciaddr=pci_resource_start(pdev,1);
if(pciaddr!=NULL)
{
ioremap(pciaddr,xx_SIZE);
}
错误的方法:
pci_read_config_dword(pdev,1,&pciaddr);
ioremap(pciaddr,xx_SIZE);
int container, group, device, i; struct vfio_group_status group_status = { .argsz = sizeof(group_status) }; struct vfio_iommu_type1_info iommu_info = { .argsz = sizeof(iommu_info) }; struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_map dma_map = { .argsz = sizeof(dma_map) }; struct vfio_device_info device_info = { .argsz = sizeof(device_info) }; /* Create a new container */ container = open("/dev/vfio/vfio", O_RDWR); if (ioctl(container, VFIO_GET_API_VERSION) != VFIO_API_VERSION) /* Unknown API version */ if (!ioctl(container, VFIO_CHECK_EXTENSION, VFIO_TYPE1_IOMMU)) /* Doesn't support the IOMMU driver we want. */ /* Open the group */ group = open("/dev/vfio/26", O_RDWR); /* Test the group is viable and available */ ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_STATUS, &group_status); if (!(group_status.flags & VFIO_GROUP_FLAGS_VIABLE)) /* Group is not viable (ie, not all devices bound for vfio) */ /* Add the group to the container */ ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_SET_CONTAINER, &container); /* Enable the IOMMU model we want */ ioctl(container, VFIO_SET_IOMMU, VFIO_TYPE1_IOMMU); /* Get addition IOMMU info */ ioctl(container, VFIO_IOMMU_GET_INFO, &iommu_info); /* Allocate some space and setup a DMA mapping */ dma_map.vaddr = mmap(0, 1024 * 1024, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, 0, 0); dma_map.size = 1024 * 1024; dma_map.iova = 0; /* 1MB starting at 0x0 from device view */ dma_map.flags = VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_READ | VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_WRITE; ioctl(container, VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA, &dma_map); /* Get a file descriptor for the device */ device = ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, "0000:06:0d.0"); /* Test and setup the device */ ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_INFO, &device_info); for (i = 0; i < device_info.num_regions; i++) { struct vfio_region_info reg = { .argsz = sizeof(reg) }; reg.index = i; ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_REGION_INFO, ®); /* Setup mappings... read/write offsets, mmaps * For PCI devices, config space is a region */ } for (i = 0; i < device_info.num_irqs; i++) { struct vfio_irq_info irq = { .argsz = sizeof(irq) }; irq.index = i; ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_IRQ_INFO, &irq); /* Setup IRQs... eventfds, VFIO_DEVICE_SET_IRQS */ } /* Gratuitous device reset and go... */ ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_RESET);
申请和映射了iommu的DMA内存。这些内存必须要给设备使用才有意义。因此首先获取VFIO的设备文件描述符;并通过设备的文件描述符获取设备的PCI BAR信息和IRQ信息。当然也可以对设备做复位操作 int device, i; struct vfio_device_info device_info = { .argsz = sizeof(device_info) }; /* Get a file descriptor for the device */ device = ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, "0000:06:0d.0"); /* Test and setup the device */ ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_INFO, &device_info); for (i = 0; i < device_info.num_regions; i++) { struct vfio_region_info reg = { .argsz = sizeof(reg) }; reg.index = i; ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_REGION_INFO, ®); /* Setup mappings... read/write offsets, mmaps * For PCI devices, config space is a region */ } for (i = 0; i < device_info.num_irqs; i++) { struct vfio_irq_info irq = { .argsz = sizeof(irq) }; irq.index = i; ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_IRQ_INFO, &irq); /* Setup IRQs... eventfds, VFIO_DEVICE_SET_IRQS */ } /* Gratuitous device reset and go... */ ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_RESET);
librte_eal/linux/eal/eal_vfio.h:27:#define RTE_VFIO_TYPE1 VFIO_TYPE1_IOMMU
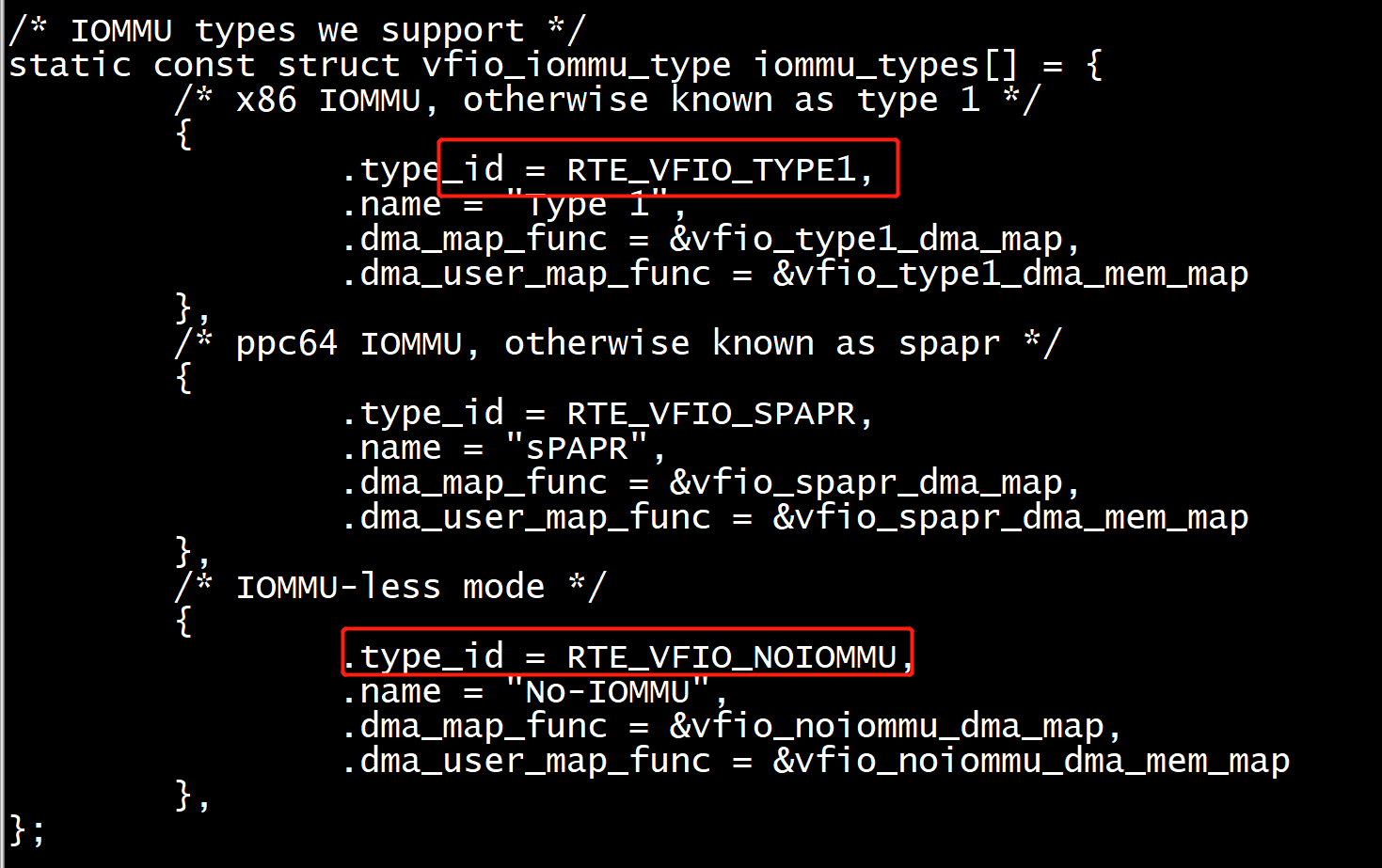
VFIO_SET_IOMMU
const struct vfio_iommu_type * vfio_set_iommu_type(int vfio_container_fd) { unsigned idx; for (idx = 0; idx < RTE_DIM(iommu_types); idx++) { const struct vfio_iommu_type *t = &iommu_types[idx]; int ret = ioctl(vfio_container_fd, VFIO_SET_IOMMU, t->type_id); if (!ret) { RTE_LOG(NOTICE, EAL, " using IOMMU type %d (%s) ", t->type_id, t->name); return t; } /* not an error, there may be more supported IOMMU types */ RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, " set IOMMU type %d (%s) failed, " "error %i (%s) ", t->type_id, t->name, errno, strerror(errno)); } /* if we didn't find a suitable IOMMU type, fail */ return NULL; }
dma_mem_map -------------VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMAstatic int vfio_type1_dma_mem_map(int vfio_container_fd, uint64_t vaddr, uint64_t iova, uint64_t len, int do_map) { struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_map dma_map; struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_unmap dma_unmap; int ret; if (do_map != 0) { memset(&dma_map, 0, sizeof(dma_map)); dma_map.argsz = sizeof(struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_map); dma_map.vaddr = vaddr; dma_map.size = len; dma_map.iova = iova; dma_map.flags = VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_READ | VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_WRITE; //VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA这个命令就是将iova通过IOMMU映射到vaddr对应的物理地址上去。 ret = ioctl(vfio_container_fd, VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA, &dma_map); if (ret) { /** * In case the mapping was already done EEXIST will be * returned from kernel. */ if (errno == EEXIST) { RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, " Memory segment is already mapped," " skipping"); } else { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " cannot set up DMA remapping," " error %i (%s) ", errno, strerror(errno)); return -1; } } } else { memset(&dma_unmap, 0, sizeof(dma_unmap)); dma_unmap.argsz = sizeof(struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_unmap); dma_unmap.size = len; dma_unmap.iova = iova; ret = ioctl(vfio_container_fd, VFIO_IOMMU_UNMAP_DMA, &dma_unmap); if (ret) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " cannot clear DMA remapping, error %i (%s) ", errno, strerror(errno)); return -1; } } return 0; }
static int vfio_pci_mmap(void *device_data, struct vm_area_struct *vma) { struct vfio_pci_device *vdev = device_data; struct pci_dev *pdev = vdev->pdev; unsigned int index; u64 phys_len, req_len, pgoff, req_start; int ret; index = vma->vm_pgoff >> (VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT - PAGE_SHIFT); if (vma->vm_end < vma->vm_start) return -EINVAL; if ((vma->vm_flags & VM_SHARED) == 0) return -EINVAL; if (index >= VFIO_PCI_ROM_REGION_INDEX) return -EINVAL; if (!(pci_resource_flags(pdev, index) & IORESOURCE_MEM)) return -EINVAL; phys_len = pci_resource_len(pdev, index); req_len = vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start; pgoff = vma->vm_pgoff & ((1U << (VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT - PAGE_SHIFT)) - 1); req_start = pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT; if (phys_len < PAGE_SIZE || req_start + req_len > phys_len) return -EINVAL; if (index == vdev->msix_bar) { /* * Disallow mmaps overlapping the MSI-X table; users don't * get to touch this directly. We could find somewhere * else to map the overlap, but page granularity is only * a recommendation, not a requirement, so the user needs * to know which bits are real. Requiring them to mmap * around the table makes that clear. */ /* If neither entirely above nor below, then it overlaps */ if (!(req_start >= vdev->msix_offset + vdev->msix_size || req_start + req_len <= vdev->msix_offset)) return -EINVAL; } /* * Even though we don't make use of the barmap for the mmap, * we need to request the region and the barmap tracks that. */ if (!vdev->barmap[index]) { ret = pci_request_selected_regions(pdev, 1 << index, "vfio-pci"); if (ret) return ret; vdev->barmap[index] = pci_iomap(pdev, index, 0); } vma->vm_private_data = vdev; vma->vm_flags |= VM_IO | VM_DONTEXPAND | VM_DONTDUMP; vma->vm_page_prot = pgprot_noncached(vma->vm_page_prot); vma->vm_pgoff = (pci_resource_start(pdev, index) >> PAGE_SHIFT) + pgoff; return remap_pfn_range(vma, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_pgoff, req_len, vma->vm_page_prot); }
vfio-pci与igb_uio映射硬件资源
DPDK(version 20.02)函数rte_pci_map_device用来映射pci device resource到用户态:
/* Map pci device, only reserve skeleton codes */
int
rte_pci_map_device(struct rte_pci_device *dev)
{
switch (dev->kdrv) {
case RTE_KDRV_VFIO:
pci_vfio_map_resource(dev);
break;
case RTE_KDRV_IGB_UIO:
pci_uio_map_resource(dev);
break;
}一 vfio-pci
当设备绑定到vfio-pci时,调用函数pci_vfio_map_resource
1.1 函数pci_vfio_map_resource
我们在此对函数pci_vfio_map_resource_primary的主要部分进行分析。
static int pci_vfio_map_resource_primary(struct rte_pci_device *dev) { struct vfio_device_info device_info = { .argsz = sizeof(device_info) }; char pci_addr[PATH_MAX] = {0}; int vfio_dev_fd; struct rte_pci_addr *loc = &dev->addr; int i, ret; struct mapped_pci_resource *vfio_res = NULL; struct mapped_pci_res_list *vfio_res_list = RTE_TAILQ_CAST(rte_vfio_tailq.head, mapped_pci_res_list); struct pci_map *maps; dev->intr_handle.fd = -1; #ifdef HAVE_VFIO_DEV_REQ_INTERFACE dev->vfio_req_intr_handle.fd = -1; #endif /* store PCI address string */ snprintf(pci_addr, sizeof(pci_addr), PCI_PRI_FMT, loc->domain, loc->bus, loc->devid, loc->function); ret = rte_vfio_setup_device(rte_pci_get_sysfs_path(), pci_addr, &vfio_dev_fd, &device_info); if (ret) return ret; /* allocate vfio_res and get region info */ vfio_res = rte_zmalloc("VFIO_RES", sizeof(*vfio_res), 0); if (vfio_res == NULL) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "%s(): cannot store vfio mmap details ", __func__); goto err_vfio_dev_fd; } memcpy(&vfio_res->pci_addr, &dev->addr, sizeof(vfio_res->pci_addr)); /* get number of registers (up to BAR5) */ vfio_res->nb_maps = RTE_MIN((int) device_info.num_regions, VFIO_PCI_BAR5_REGION_INDEX + 1); /* map BARs */ maps = vfio_res->maps; vfio_res->msix_table.bar_index = -1; /* get MSI-X BAR, if any (we have to know where it is because we can't * easily mmap it when using VFIO) */ ret = pci_vfio_get_msix_bar(vfio_dev_fd, &vfio_res->msix_table); if (ret < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s cannot get MSI-X BAR number! ", pci_addr); goto err_vfio_res; } /* if we found our MSI-X BAR region, check if we can mmap it */ if (vfio_res->msix_table.bar_index != -1) { int ret = pci_vfio_msix_is_mappable(vfio_dev_fd, vfio_res->msix_table.bar_index); if (ret < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Couldn't check if MSI-X BAR is mappable "); goto err_vfio_res; } else if (ret != 0) { /* we can map it, so we don't care where it is */ RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "VFIO reports MSI-X BAR as mappable "); vfio_res->msix_table.bar_index = -1; } } for (i = 0; i < (int) vfio_res->nb_maps; i++) { struct vfio_region_info *reg = NULL; void *bar_addr; ret = pci_vfio_get_region_info(vfio_dev_fd, ®, i); if (ret < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s cannot get device region info " "error %i (%s) ", pci_addr, errno, strerror(errno)); goto err_vfio_res; } /* chk for io port region */ ret = pci_vfio_is_ioport_bar(vfio_dev_fd, i); if (ret < 0) { free(reg); goto err_vfio_res; } else if (ret) { RTE_LOG(INFO, EAL, "Ignore mapping IO port bar(%d) ", i); free(reg); continue; } /* skip non-mmapable BARs */ if ((reg->flags & VFIO_REGION_INFO_FLAG_MMAP) == 0) { free(reg); continue; } /* try mapping somewhere close to the end of hugepages */ if (pci_map_addr == NULL) pci_map_addr = pci_find_max_end_va(); bar_addr = pci_map_addr; pci_map_addr = RTE_PTR_ADD(bar_addr, (size_t) reg->size); maps[i].addr = bar_addr; maps[i].offset = reg->offset; maps[i].size = reg->size; maps[i].path = NULL; /* vfio doesn't have per-resource paths */ ret = pci_vfio_mmap_bar(vfio_dev_fd, vfio_res, i, 0); if (ret < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s mapping BAR%i failed: %s ", pci_addr, i, strerror(errno)); free(reg); goto err_vfio_res; } dev->mem_resource[i].addr = maps[i].addr; free(reg); } if (pci_rte_vfio_setup_device(dev, vfio_dev_fd) < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s setup device failed ", pci_addr); goto err_vfio_res; } }
1.1.1 rte_vfio_setup_device
此函数的主要工作内容如下:
首先要获取device对应的iommu_group,找到iommu_group id, 并打开对应的字符设备
/* 此函数通过sys文件系统获取iommu_group的id号 */
int
rte_vfio_get_group_num(const char *sysfs_base,
const char *dev_addr, int *iommu_group_num)
/* 此函数打开字符设备/dev/vfio/{iommu_group},并返回字符设备句柄 */
int
rte_vfio_get_group_fd(int iommu_group_num)
{
struct vfio_config *vfio_cfg;
/* get the vfio_config it belongs to */
vfio_cfg = get_vfio_cfg_by_group_num(iommu_group_num);
vfio_cfg = vfio_cfg ? vfio_cfg : default_vfio_cfg;
return vfio_get_group_fd(vfio_cfg, iommu_group_num);
}
获取当前设备所属iommu_group的配置
struct vfio_config {
int vfio_enabled;
int vfio_container_fd;
int vfio_active_groups;
const struct vfio_iommu_type *vfio_iommu_type;
struct vfio_group vfio_groups[VFIO_MAX_GROUPS];
struct user_mem_maps mem_maps;
};
/* get the vfio_config it belongs to */
struct vfio_config *vfio_cfg;
vfio_cfg = get_vfio_cfg_by_group_num(iommu_group_num);
vfio_cfg = vfio_cfg ? vfio_cfg : default_vfio_cfg;
vfio_container_fd = vfio_cfg->vfio_container_fd;
user_mem_maps = &vfio_cfg->mem_maps;
? 将刚刚打开的字符设备添加到container中,并完成iommu的内存映射,在Intel架构中,调用函数vfio_type1_dma_map做映射,DPDK映射的内存有(看上去是所有DPDK管理的内存都做了映射)。。。。。
获取device fd及device info并返回。
/* get a file descriptor for the device */
*vfio_dev_fd = ioctl(vfio_group_fd, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, dev_addr);
/* test and setup the device */
ret = ioctl(*vfio_dev_fd, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_INFO, device_info);
================VFIO_GROUP_GET_STATUS VFIO_GROUP_SET_CONTAINER===============
rte_vfio_setup_device(const char *sysfs_base, const char *dev_addr, int *vfio_dev_fd, struct vfio_device_info *device_info) { struct vfio_group_status group_status = { .argsz = sizeof(group_status) }; struct vfio_config *vfio_cfg; struct user_mem_maps *user_mem_maps; int vfio_container_fd; int vfio_group_fd; int iommu_group_num; int i, ret; /* get group number */ ret = rte_vfio_get_group_num(sysfs_base, dev_addr, &iommu_group_num); /* if negative, something failed */ if (ret < 0) return -1; /* get the actual group fd */ vfio_group_fd = rte_vfio_get_group_fd(iommu_group_num); if (vfio_group_fd < 0) return -1; /* if group_fd == 0, that means the device isn't managed by VFIO */ if (vfio_group_fd == 0) { RTE_LOG(WARNING, EAL, " %s not managed by VFIO driver, skipping ", dev_addr); return 1; } /* * at this point, we know that this group is viable (meaning, all devices * are either bound to VFIO or not bound to anything) */ /* check if the group is viable */ ret = ioctl(vfio_group_fd, VFIO_GROUP_GET_STATUS, &group_status); /* get the vfio_config it belongs to */ vfio_cfg = get_vfio_cfg_by_group_num(iommu_group_num); vfio_cfg = vfio_cfg ? vfio_cfg : default_vfio_cfg; vfio_container_fd = vfio_cfg->vfio_container_fd; user_mem_maps = &vfio_cfg->mem_maps; /* check if group does not have a container yet */ if (!(group_status.flags & VFIO_GROUP_FLAGS_CONTAINER_SET)) { /* add group to a container */ ret = ioctl(vfio_group_fd, VFIO_GROUP_SET_CONTAINER, &vfio_container_fd); /* * pick an IOMMU type and set up DMA mappings for container * * needs to be done only once, only when first group is * assigned to a container and only in primary process. * Note this can happen several times with the hotplug * functionality. */ if (internal_config.process_type == RTE_PROC_PRIMARY && vfio_cfg->vfio_active_groups == 1 && vfio_group_device_count(vfio_group_fd) == 0) { const struct vfio_iommu_type *t; /* select an IOMMU type which we will be using */ t = vfio_set_iommu_type(vfio_container_fd); if (!t) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s failed to select IOMMU type ", dev_addr); close(vfio_group_fd); rte_vfio_clear_group(vfio_group_fd); return -1; } /* lock memory hotplug before mapping and release it * after registering callback, to prevent races */ rte_mcfg_mem_read_lock(); if (vfio_cfg == default_vfio_cfg) ret = t->dma_map_func(vfio_container_fd); else ret = 0; if (ret) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, " %s DMA remapping failed, error %i (%s) ", dev_addr, errno, strerror(errno)); close(vfio_group_fd); rte_vfio_clear_group(vfio_group_fd); rte_mcfg_mem_read_unlock(); return -1; } vfio_cfg->vfio_iommu_type = t; /* re-map all user-mapped segments */ rte_spinlock_recursive_lock(&user_mem_maps->lock); /* this IOMMU type may not support DMA mapping, but * if we have mappings in the list - that means we have * previously mapped something successfully, so we can * be sure that DMA mapping is supported. */ for (i = 0; i < user_mem_maps->n_maps; i++) { struct user_mem_map *map; map = &user_mem_maps->maps[i]; ret = t->dma_user_map_func( vfio_container_fd, map->addr, map->iova, map->len, 1); if (ret) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Couldn't map user memory for DMA: " "va: 0x%" PRIx64 " " "iova: 0x%" PRIx64 " " "len: 0x%" PRIu64 " ", map->addr, map->iova, map->len); rte_spinlock_recursive_unlock( &user_mem_maps->lock); rte_mcfg_mem_read_unlock(); return -1; } } rte_spinlock_recursive_unlock(&user_mem_maps->lock); /* register callback for mem events */ if (vfio_cfg == default_vfio_cfg) ret = rte_mem_event_callback_register( VFIO_MEM_EVENT_CLB_NAME, vfio_mem_event_callback, NULL); else ret = 0; /* unlock memory hotplug */ rte_mcfg_mem_read_unlock(); if (ret && rte_errno != ENOTSUP) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Could not install memory event callback for VFIO "); return -1; } if (ret) RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "Memory event callbacks not supported "); else RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "Installed memory event callback for VFIO "); } } /* get a file descriptor for the device */ *vfio_dev_fd = ioctl(vfio_group_fd, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, dev_addr); if (*vfio_dev_fd < 0) { /* if we cannot get a device fd, this implies a problem with * the VFIO group or the container not having IOMMU configured. */ RTE_LOG(WARNING, EAL, "Getting a vfio_dev_fd for %s failed ", dev_addr); close(vfio_group_fd); rte_vfio_clear_group(vfio_group_fd); return -1; } vfio_group_device_get(vfio_group_fd); return 0; }
1.1.2 pci_vfio_get_msix_bar
通过读取设备的PCI配置空间,读取的方法是通过上一步取得的设备句柄,获取msix的配置信息。并保存到vfio_res结构体中。
/* get MSI-X BAR, if any (we have to know where it is because we can't
* easily mmap it when using VFIO)
*/
ret = pci_vfio_get_msix_bar(vfio_dev_fd, &vfio_res->msix_table);
1.1.3 pci_vfio_get_region_info & pci_vfio_mmap_bar
获取设备的BAR REGION(寄存器,中断等信息),并完成寄存器的mmap映射,让用户态程序能够直接访问PCI设备的寄存器。
1.1.4 pci_rte_vfio_setup_device
这个函数首先设置中断,将第一个中断添加到系统的中断轮训链表去。
然后设置开启设备,并对设备复位。
static int
pci_rte_vfio_setup_device(struct rte_pci_device *dev, int vfio_dev_fd)
{
if (pci_vfio_setup_interrupts(dev, vfio_dev_fd) != 0) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Error setting up interrupts!
");
return -1;
}
/* set bus mastering for the device */
if (pci_vfio_set_bus_master(vfio_dev_fd, true)) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Cannot set up bus mastering!
");
return -1;
}
/*
* Reset the device. If the device is not capable of resetting,
* then it updates errno as EINVAL.
*/
if (ioctl(vfio_dev_fd, VFIO_DEVICE_RESET) && errno != EINVAL) {
RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Unable to reset device! Error: %d (%s)
",
errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
pci map mmap
pci_vfio_mmap_bar(int vfio_dev_fd, struct mapped_pci_resource *vfio_res, int bar_index, int additional_flags) { struct memreg { uint64_t offset; size_t size; } memreg[2] = {}; void *bar_addr; struct pci_msix_table *msix_table = &vfio_res->msix_table; struct pci_map *bar = &vfio_res->maps[bar_index]; if (bar->size == 0) { RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "Bar size is 0, skip BAR%d ", bar_index); return 0; } if (msix_table->bar_index == bar_index) { /* * VFIO will not let us map the MSI-X table, * but we can map around it. */ uint32_t table_start = msix_table->offset; uint32_t table_end = table_start + msix_table->size; table_end = RTE_ALIGN(table_end, PAGE_SIZE); table_start = RTE_ALIGN_FLOOR(table_start, PAGE_SIZE); /* If page-aligned start of MSI-X table is less than the * actual MSI-X table start address, reassign to the actual * start address. */ if (table_start < msix_table->offset) table_start = msix_table->offset; if (table_start == 0 && table_end >= bar->size) { /* Cannot map this BAR */ RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "Skipping BAR%d ", bar_index); bar->size = 0; bar->addr = 0; return 0; } memreg[0].offset = bar->offset; memreg[0].size = table_start; if (bar->size < table_end) { /* * If MSI-X table end is beyond BAR end, don't attempt * to perform second mapping. */ memreg[1].offset = 0; memreg[1].size = 0; } else { memreg[1].offset = bar->offset + table_end; memreg[1].size = bar->size - table_end; } RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, "Trying to map BAR%d that contains the MSI-X " "table. Trying offsets: " "0x%04" PRIx64 ":0x%04zx, 0x%04" PRIx64 ":0x%04zx ", bar_index, memreg[0].offset, memreg[0].size, memreg[1].offset, memreg[1].size); } else { memreg[0].offset = bar->offset; memreg[0].size = bar->size; } /* reserve the address using an inaccessible mapping */ bar_addr = mmap(bar->addr, bar->size, 0, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | additional_flags, -1, 0); if (bar_addr != MAP_FAILED) { void *map_addr = NULL; if (memreg[0].size) { /* actual map of first part */ map_addr = pci_map_resource(bar_addr, vfio_dev_fd, memreg[0].offset, memreg[0].size, MAP_FIXED); } /* if there's a second part, try to map it */ if (map_addr != MAP_FAILED && memreg[1].offset && memreg[1].size) { void *second_addr = RTE_PTR_ADD(bar_addr, (uintptr_t)(memreg[1].offset - bar->offset)); map_addr = pci_map_resource(second_addr, vfio_dev_fd, memreg[1].offset, memreg[1].size, MAP_FIXED); } if (map_addr == MAP_FAILED || !map_addr) { munmap(bar_addr, bar->size); bar_addr = MAP_FAILED; RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Failed to map pci BAR%d ", bar_index); return -1; } } else { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Failed to create inaccessible mapping for BAR%d ", bar_index); return -1; } bar->addr = bar_addr; return 0; }
pci_map_resource(void *requested_addr, int fd, off_t offset, size_t size, int additional_flags) { void *mapaddr; /* Map the PCI memory resource of device */ mapaddr = mmap(requested_addr, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | additional_flags, fd, offset); ----------------pci vfio mmap if (mapaddr == MAP_FAILED) { RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "%s(): cannot mmap(%d, %p, 0x%zx, 0x%llx): %s (%p) ", __func__, fd, requested_addr, size, (unsigned long long)offset, strerror(errno), mapaddr); } else RTE_LOG(DEBUG, EAL, " PCI memory mapped at %p ", mapaddr); return mapaddr; }
VFIO_DEVICE_GET_REGION_INFO

首先,利用mmap映射出1MB字节的虚拟空间,因为物理地址对于用户态不可见,只能通过虚拟地址访问物理空间。然后执行ioctl的VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA命令,传入参数主要包含vaddr及iova,其中iova代表的是设备发起DMA请求时要访问的地址,也就是IOMMU映射前的地址,vaddr就是mmap的地址。VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA命令会为虚拟地址vaddr找到物理页并pin住(因为设备DMA是异步的,随时可能发生,物理页面不能交换出去),然后找到Group对应的Contex Entry,建立页表项,页表项能够将iova地址映射成上面pin住的物理页对应的物理地址上去,这样对用户态程序完全屏蔽了物理地址,实现了用户空间驱动。IOVA地址的00x100000对应DRAM地址0x100000000x10100000,size为1024 * 1024。一句话概述,VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA这个命令就是将iova通过IOMMU映射到vaddr对应的物理地址上去。