substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)方法在jdk 6和jdk 7中的实现是不同的。了解他们的区别可以帮助你更好的使用他。为简单起见,后文中用substring()代表substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)方法。
substring() 的作用
substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)方法截取字符串并返回其[beginIndex,endIndex-1]范围内的内容。
String x = "abcdef";
x = x.substring(1,3);
System.out.println(x);
输出内容:
bc
调用substring()时发生了什么?
你可能知道,因为x是不可变的,当使用x.substring(1,3)对x赋值的时候,它会指向一个全新的字符串:
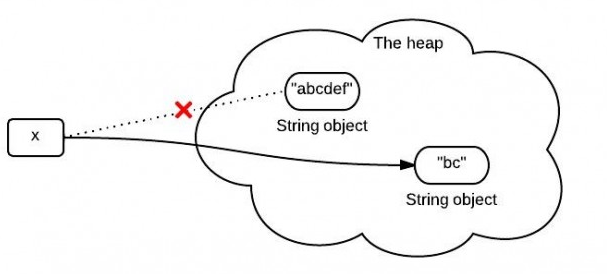
然而,这个图不是完全正确的表示堆中发生的事情。因为在jdk6 和 jdk7中调用substring时发生的事情并不一样。
JDK 6中的substring
String是通过字符数组实现的。在jdk 6 中,String类包含三个成员变量:char value[], int offset,int count。他们分别用来存储真正的字符数组,数组的第一个位置索引以及字符串中包含的字符个数。
当调用substring方法的时候,会创建一个新的string对象,但是这个string的值仍然指向堆中的同一个字符数组。这两个对象中只有count和offset 的值是不同的。
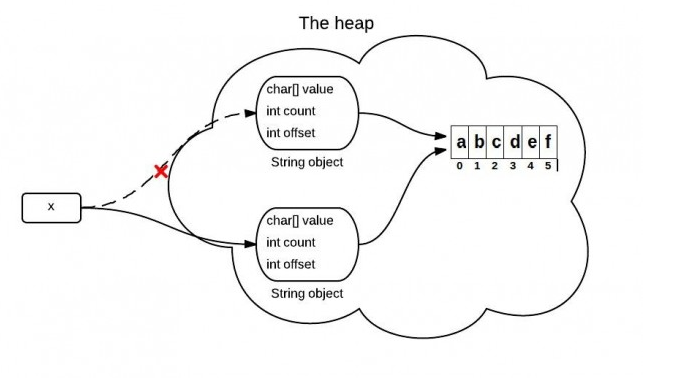
下面是证明上说观点的Java源码中的关键代码:
//JDK 6 String(int offset, int count, char value[]) { this.value = value; this.offset = offset; this.count = count; } public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) { //check boundary return new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex, value); }
JDK 6中的substring导致的问题
如果你有一个很长很长的字符串,但是当你使用substring进行切割的时候你只需要很短的一段。这可能导致性能问题,因为你需要的只是一小段字符序列,但是你却引用了整个字符串(因为这个非常长的字符数组一直在被引用,所以无法被回收,就可能导致内存泄露)。在JDK 6中,一般用以下方式来解决该问题,原理其实就是生成一个新的字符串并引用他。
x = x.substring(x, y) + ""
JDK 7 中的substring
上面提到的问题,在jdk 7中得到解决。在jdk 7 中,substring方法会在堆内存中创建一个新的数组。

Java源码中关于这部分的主要代码如下:
//JDK 7 public String(char value[], int offset, int count) { //check boundary this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset + count); } public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) { //check boundary int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex; return new String(value, beginIndex, subLen); }
来自:http://www.hollischuang.com/archives/1232