从Spring3.0,@Configuration用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含有一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法,这些方法将会被AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,初始化Spring容器。
注意:@Configuration注解的配置类有如下要求:
- @Configuration不可以是final类型;
- @Configuration不可以是匿名类;
- 嵌套的configuration必须是静态类。
一、用@Configuration加载spring
1.1、@Configuration配置spring并启动spring容器
1.2、@Configuration启动容器+@Bean注册Bean
1.3、@Configuration启动容器+@Component注册Bean
1.4、使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 注册 AppContext 类的两种方法
1.5、配置Web应用程序(web.xml中配置AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
二、组合多个配置类
2.1、在@configuration中引入spring的xml配置文件
2.2、在@configuration中引入其它注解配置
2.3、@configuration嵌套(嵌套的Configuration必须是静态类)
三、@EnableXXX注解
四、@Profile逻辑组配置
五、使用外部变量
一、@Configuation加载Spring方法
1.1、@Configuration配置spring并启动spring容器
@Configuration标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的<beans>,作用为:配置spring容器(应用上下文)
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class TestConfiguration { public TestConfiguration() { System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。"); } }
相当于:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.0.xsd" default-lazy-init="false"> </beans>
主方法进行测试:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件: // ApplicationContext context = new // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); } }
从运行主方法结果可以看出,spring容器已经启动了:

1.2、@Configuration启动容器+@Bean注册Bean,@Bean下管理bean的生命周期
@Bean标注在方法上(返回某个实例的方法),等价于spring的xml配置文件中的<bean>,作用为:注册bean对象
bean类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; public class TestBean { private String username; private String url; private String password; public void sayHello() { System.out.println("TestBean sayHello..."); } public String toString() { return "username:" + this.username + ",url:" + this.url + ",password:" + this.password; } public void start() { System.out.println("TestBean 初始化。。。"); } public void cleanUp() { System.out.println("TestBean 销毁。。。"); } }
配置类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; @Configuration public class TestConfiguration { public TestConfiguration() { System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。"); } // @Bean注解注册bean,同时可以指定初始化和销毁方法 // @Bean(name="testBean",initMethod="start",destroyMethod="cleanUp") @Bean @Scope("prototype") public TestBean testBean() { return new TestBean(); } }
主方法测试类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件: // ApplicationContext context = new // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); //获取bean TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); } }
结果:
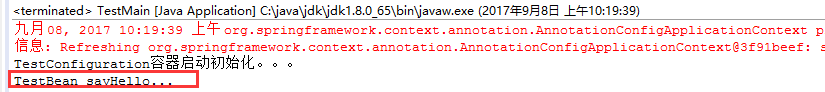
注:
(1)、@Bean注解在返回实例的方法上,如果未通过@Bean指定bean的名称,则默认与标注的方法名相同;
(2)、@Bean注解默认作用域为单例singleton作用域,可通过@Scope(“prototype”)设置为原型作用域;
(3)、既然@Bean的作用是注册bean对象,那么完全可以使用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Ripository等注解注册bean,当然需要配置@ComponentScan注解进行自动扫描。
@Bean下管理bean的生命周期
可以使用基于 Java 的配置来管理 bean 的生命周期。@Bean 支持两种属性,即 initMethod 和destroyMethod,这些属性可用于定义生命周期方法。在实例化 bean 或即将销毁它时,容器便可调用生命周期方法。生命周期方法也称为回调方法,因为它将由容器调用。使用 @Bean 注释注册的 bean 也支持 JSR-250 规定的标准 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注释。如果您正在使用 XML 方法来定义 bean,那么就应该使用 bean 元素来定义生命周期回调方法。以下代码显示了在 XML 配置中通常使用 bean 元素定义回调的方法。
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dxz.demo.configuration") public class TestConfiguration { public TestConfiguration() { System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。"); } //@Bean注解注册bean,同时可以指定初始化和销毁方法 @Bean(name="testBean",initMethod="start",destroyMethod="cleanUp") @Scope("prototype") public TestBean testBean() { return new TestBean(); } }
启动类:
public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); System.out.println(tb); TestBean tb2 = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb2.sayHello(); System.out.println(tb2); } }
结果:

分析:
结果中的1:表明initMethod生效
结果中的2:表明@Scope("prototype")生效
1.3、@Configuration启动容器+@Component注册Bean
bean类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; //添加注册bean的注解 @Component public class TestBean { private String username; private String url; private String password; public void sayHello() { System.out.println("TestBean sayHello..."); } public String toString() { return "username:" + this.username + ",url:" + this.url + ",password:" + this.password; } public void start() { System.out.println("TestBean 初始化。。。"); } public void cleanUp() { System.out.println("TestBean 销毁。。。"); } }
配置类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; @Configuration //添加自动扫描注解,basePackages为TestBean包路径 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dxz.demo.configuration") public class TestConfiguration { public TestConfiguration() { System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。"); } /*// @Bean注解注册bean,同时可以指定初始化和销毁方法 // @Bean(name="testNean",initMethod="start",destroyMethod="cleanUp") @Bean @Scope("prototype") public TestBean testBean() { return new TestBean(); }*/ }
主方法测试获取bean对象:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件: // ApplicationContext context = new // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); //获取bean TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); } }
sayHello()方法都被正常调用。
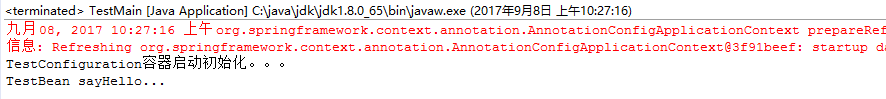
1.4、使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 注册 AppContext 类的两种方法
1.4.1、 配置类的注册方式是将其传递给 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 构造函数
public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); //获取bean TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); }
1.4.2、 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的register 方法传入配置类来注册配置类
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); ctx.register(AppContext.class) }
1.5、配置Web应用程序(web.xml中配置AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
过去,您通常要利用 XmlWebApplicationContext 上下文来配置 Spring Web 应用程序,即在 Web 部署描述符文件 web.xml 中指定外部 XML 上下文文件的路径。XMLWebApplicationContext 是 Web 应用程序使用的默认上下文类。以下代码描述了 web.xml 中指向将由 ContextLoaderListener 监听器类载入的外部 XML 上下文文件的元素。
<web-app> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>sampleServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> </servlet> ... </web-app>
现在,您要将 web.xml 中的上述代码更改为使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类。切记,XmlWebApplicationContext 是 Spring 为 Web 应用程序使用的默认上下文实现,因此您永远不必在您的web.xml 文件中显式指定这个上下文类。现在,您将使用基于 Java 的配置,因此在配置 Web 应用程序时,需要在web.xml 文件中指定 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类。上述代码将修改如下:
<web-app> <context-param> <param-name>contextClass</param-name> <param-value> org.springframework.web.context. support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext </param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> demo.AppContext </param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>sampleServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextClass</param-name> <param-value> org.springframework.web.context. support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext </param-value> </init-param> </servlet> ... </web-app>
以上修改后的 web.xml 现在定义了 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 上下文类,并将其作为上下文参数和 servlet 元素的一部分。上下文配置位置现在指向 AppContext 配置类。这非常简单。下一节将演示 bean 的生命周期回调和范围的实现。
1.6、@Configuation总结
@Configuation等价于<Beans></Beans>
@Bean等价于<Bean></Bean>
@ComponentScan等价于<context:component-scan base-package="com.dxz.demo"/>
二、组合多个配置类
2.1、在@configuration中引入spring的xml配置文件
package com.dxz.demo.configuration2; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource; @Configuration @ImportResource("classpath:applicationContext-configuration.xml") public class WebConfig { }
bean类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration2; public class TestBean2 { private String username; private String url; private String password; public void sayHello() { System.out.println("TestBean2 sayHello..."); } public String toString() { return "TestBean2 username:" + this.username + ",url:" + this.url + ",password:" + this.password; } public void start() { System.out.println("TestBean2 初始化。。。"); } public void cleanUp() { System.out.println("TestBean2 销毁。。。"); } }
测试类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration2; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(WebConfig.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件: // ApplicationContext context = new // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); // 获取bean TestBean2 tb = (TestBean2) context.getBean("testBean2"); tb.sayHello(); } }
结果:

2.2、在@configuration中引入其它注解配置
package com.dxz.demo.configuration2; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource; import com.dxz.demo.configuration.TestConfiguration; @Configuration @ImportResource("classpath:applicationContext-configuration.xml") @Import(TestConfiguration.class) public class WebConfig { }
测试类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration2; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import com.dxz.demo.configuration.TestBean; public class TestMain2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(WebConfig.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件: // ApplicationContext context = new // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); // 获取bean TestBean2 tb2 = (TestBean2) context.getBean("testBean2"); tb2.sayHello(); TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); } }
结果:
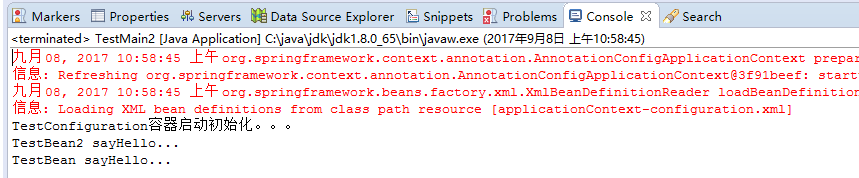
2.3、@configuration嵌套(嵌套的Configuration必须是静态类)
通过配置类嵌套的配置类,达到组合多个配置类的目的。但注意内部类必须是静态类。
上代码:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration3; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class TestBean { private String username; private String url; private String password; public void sayHello() { System.out.println("TestBean sayHello..."); } public String toString() { return "username:" + this.username + ",url:" + this.url + ",password:" + this.password; } public void start() { System.out.println("TestBean start"); } public void cleanUp() { System.out.println("TestBean destory"); } }
package com.dxz.demo.configuration3; public class DataSource { private String dbUser; private String dbPass; public String getDbUser() { return dbUser; } public void setDbUser(String dbUser) { this.dbUser = dbUser; } public String getDbPass() { return dbPass; } public void setDbPass(String dbPass) { this.dbPass = dbPass; } @Override public String toString() { return "DataSource [dbUser=" + dbUser + ", dbPass=" + dbPass + "]"; } }
配置类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration3; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dxz.demo.configuration3") public class TestConfiguration { public TestConfiguration() { System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。"); } @Configuration static class DatabaseConfig { @Bean DataSource dataSource() { return new DataSource(); } } }
启动类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration3; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContexts ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); //bean TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean"); tb.sayHello(); DataSource ds = (DataSource) context.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(ds); } }
结果:
TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。 TestBean sayHello... DataSource [dbUser=null, dbPass=null]
3、@EnableXXX注解
配合@Configuration使用,包括 @EnableAsync, @EnableScheduling, @EnableTransactionManagement, @EnableAspectJAutoProxy, @EnableWebMvc。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy---《spring AOP 之:@Aspect注解》
@EnableScheduling--《Spring 3.1新特性之二:@Enable*注解的源码,spring源码分析之定时任务Scheduled注解》
4、@Profile逻辑组配置
5、使用外部变量
1、@PropertySource + Environment,通过@PropertySource注解将properties配置文件中的值存储到Spring的 Environment中,Environment接口提供方法去读取配置文件中的值,参数是properties文件中定义的key值。
2、@PropertySource(PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer)+@Value