• 公有继承(public)
公有继承在C++中是最常用的一种继承方式,我们先来看一个示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Father{ 4 public: 5 Father()=default; 6 void Father_show1(){ 7 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 8 } 9 protected: 10 void Father_show2(){ 11 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 12 } 13 private: 14 void Father_show3(){ 15 cout<<"调用Father类的private方法:Father_show3"<<endl; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Son:public Father{ 20 public: 21 Son()=default; 22 void Son_fun1(){ 23 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 24 Father_show1(); 25 Father_show2(); 26 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 27 } 28 protected: 29 void Son_fun2(){ 30 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 31 Father_show1(); 32 Father_show2(); 33 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 34 } 35 private: 36 void Son_fun3(){ 37 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 38 Father_show1(); 39 Father_show2(); 40 //Father_show3();//错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 41 } 42 }; 43 44 int main(){ 45 Son s; 46 s.Son_fun1(); //正确,只能调用对象的public方法 47 s.Father_show1(); 48 //s.Son_fun2(); //错误:不能调用对象的protected方法 49 //s.Father_show2(); 50 //s.Son_fun3(); //错误:不能调用对象的private方法 51 //s.Father_show3(); 52 return 0; 53 }

对公有继承的理解:
1.三种属性能力的强弱:public<protected<private
2.在C++的继承中,子类会继承父类中除构造函数和析构函数之外的所有成员(正所谓儿子无法继承父亲的生死) 。而公有继承(public)就相当于先将从父类那里继承的全部成员放到子类的public部分,如下:
1 class Son:public Father{ 2 /* 从Father类中继承的所有成员 3 public: 4 public: 5 void Father_show1(){ 6 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 7 } 8 protected: 9 void Father_show2(){ 10 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 11 } 12 private: 13 void Father_show1(){ 14 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 15 } 16 */ 17 public: 18 Son()=default; 19 void Son_fun1(){ 20 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 21 Father_show1(); 22 Father_show2(); 23 //Father_show3();//错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 24 } 25 protected: 26 void Son_fun2(){ 27 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 28 Father_show1(); 29 Father_show2(); 30 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 31 } 32 private: 33 void Son_fun3(){ 34 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 35 Father_show1(); 36 Father_show2(); 37 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 38 } 39 };
然后根据三种属性能力的强弱决定成员的属性在子类中究竟是public、protected还是private:
• Father_show1():在Father类中属于public方法,继承到子类Son后放在类的public部分,由于public=public,因此在子类Son中Father_show1()方法仍是public方法
• Father_show2():在Father类中属于protected方法,继承到子类Son后放在类的public部分,由于protected>public,因此子类Son中Father_show2()方法是protected方法
• Father_show3():在Father类中属于private方法,可以理解为“父亲的隐私”,继承到子类Son后放在类的public部分,由于private>public,因此子类Son中Father_show3()方法是private方法。然而正所谓“儿子即使继承了父亲的财产,也无法知晓父亲的隐私”,因此不管儿子以何种方式(public/protected/private)继承父亲的“财产”也无法利用父亲的“隐私”去进行“交易”,换句话说就是父类的private成员虽然可以被子类继承,但子类中的任何成员方法都不能在其函数体中调用这些从父类中继承而来的private成员。因此Son类中的成员方法不管其为与什么部分,都无法调用Father_show3
3.对象只能调用其public部分的成员,而不能调用protected和private部分的成员。因此上例中Son类的对象s可以调用方法Son_fun1()和方法Father_show1(),而无法调用方法Son_fun2()、Son_fun3()、Father_show2()和Father_show3()
• 保护继承(protected)
将上面的示例改为保护继承:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Father{ 4 public: 5 Father()=default; 6 void Father_show1(){ 7 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 8 } 9 protected: 10 void Father_show2(){ 11 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 12 } 13 private: 14 void Father_show3(){ 15 cout<<"调用Father类的private方法:Father_show3"<<endl; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Son:protected Father{ 20 public: 21 Son()=default; 22 void Son_fun1(){ 23 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 24 Father_show1(); 25 Father_show2(); 26 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 27 } 28 protected: 29 void Son_fun2(){ 30 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 31 Father_show1(); 32 Father_show2(); 33 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 34 } 35 private: 36 void Son_fun3(){ 37 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 38 Father_show1(); 39 Father_show2(); 40 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 41 } 42 }; 43 44 int main(){ 45 Son s; 46 s.Son_fun1(); //正确,只能调用对象的public方法 47 //s.Son_fun2(); //错误:不能调用对象的protected方法 48 //s.Father_show1(); 49 //s.Father_show2(); 50 //s.Son_fun3(); //错误:不能调用对象的private方法 51 //s.Father_show3(); 52 return 0; 53 }
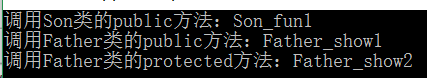
对保护继承的理解:
1.三种属性能力的强弱:public<protected<private
2.保护继承相当于先将从父类继承的所用成员都放在子类的protected部分:
1 class Son:public Father{ 2 /* 3 protected: 4 public: 5 void Father_show1(){ 6 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 7 } 8 protected: 9 void Father_show2(){ 10 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 11 } 12 private: 13 void Father_show1(){ 14 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 15 } 16 */ 17 public: 18 Son()=default; 19 void Son_fun1(){ 20 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 21 Father_show1(); 22 Father_show2(); 23 //Father_show3();//错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 24 } 25 protected: 26 void Son_fun2(){ 27 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 28 Father_show1(); 29 Father_show2(); 30 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 31 } 32 private: 33 void Son_fun3(){ 34 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 35 Father_show1(); 36 Father_show2(); 37 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 38 } 39 };
然后和公有继承一样,根据三种属性能力的强弱决定成员的属性在子类中究竟是public、protected还是private:
• 由于public<protected,因此方法Father_show1()在类Son中是protected方法
• 由于protected=protected,因此方法Father_show2()在类Son中是protected方法
• 就像在公有继承中分析的那样,Father_show3()在类Son中虽然是private方法,但Son类中的任何成员方法都不能在其函数体中调用方法Father_show3()
3.对象只能调用public部分的成员,此时方法Father_show1()是对象的protected方法,因此无法像公有继承那样再被显式调用了
• 私有继承
将上面的示例改为私有继承:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Father{ 4 public: 5 Father()=default; 6 void Father_show1(){ 7 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 8 } 9 protected: 10 void Father_show2(){ 11 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 12 } 13 private: 14 void Father_show3(){ 15 cout<<"调用Father类的private方法:Father_show3"<<endl; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class Son:private Father{ 20 public: 21 Son()=default; 22 void Son_fun1(){ 23 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 24 Father_show1(); 25 Father_show2(); 26 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 27 } 28 protected: 29 void Son_fun2(){ 30 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 31 Father_show1(); 32 Father_show2(); 33 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 34 } 35 private: 36 void Son_fun3(){ 37 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 38 Father_show1(); 39 Father_show2(); 40 //Father_show3(); //错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 41 } 42 }; 43 44 int main(){ 45 Son s; 46 s.Son_fun1(); //正确,只能调用对象的public方法
47 //s.Son_fun2(); //错误:不能调用对象的protected方法 48 //s.Son_fun3(); //错误:不能调用对象的private方法 49 //s.Father_show1(); 50 //s.Father_show2(); 51 //s.Father_show3(); 52 return 0; 53 }
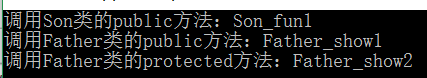
对私有继承的理解:
1.三种属性能力的强弱:public<protected<private
2.私有继承相当于先将从父类继承的所用成员都放在子类的private部分:
1 class Son:public Father{ 2 /* 3 private: 4 public: 5 void Father_show1(){ 6 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 7 } 8 protected: 9 void Father_show2(){ 10 cout<<"调用Father类的protected方法:Father_show2"<<endl; 11 } 12 private: 13 void Father_show1(){ 14 cout<<"调用Father类的public方法:Father_show1"<<endl; 15 } 16 */ 17 public: 18 Son()=default; 19 void Son_fun1(){ 20 cout<<"调用Son类的public方法:Son_fun1"<<endl; 21 Father_show1(); 22 Father_show2(); 23 //Father_show3();//错误:无法调用Father类的private方法 24 } 25 protected: 26 void Son_fun2(){ 27 cout<<"调用Son类的protected方法:Son_fun2"<<endl; 28 Father_show1(); 29 Father_show2(); 30 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 31 } 32 private: 33 void Son_fun3(){ 34 cout<<"调用Son类的private方法:Son_fun3"<<endl; 35 Father_show1(); 36 Father_show2(); 37 //Father_show3();//错误: 无法调用Father类的private方法 38 } 39 };
然后和公有继承一样,根据三种属性能力的强弱决定成员的属性在子类中究竟是public、protected还是private:
• 由于public<private,因此方法Father_show1()在类Son中是private方法,但类Son中的成员方法可以在函数体内调用该方法
• 由于private>protected,因此方法Father_show2()在类Son中是prijvate方法,但类Son中的成员方法可以在函数体内调用该方法
• 就像在公有继承中分析的那样,Father_show3()在类Son中虽然是private方法,但Son类中的任何成员方法都不能在其函数体中调用方法Father_show3()
3.对象只能调用public部分的成员,此时方法Father_show1()是对象的private方法,因此无法像公有继承那样再被显式调用了
QUESTION:保护继承(protected)和私有继承(private)有何不同?
ANSWER:在上面的例子中,我们发现保护继承方式和私有继承方式达到的效果完全一样,难道这两中继承方式没有任何区别吗?我们先来看一个例子:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class GrandFather{ //祖父类 4 public: 5 GrandFather()=default; 6 void GrandFather_show(){ 7 cout<<"调用GrandFather类的方法:GrandFather_show"<<endl; 8 } 9 }; 10 class Father:protected GrandFather{ //父类 11 public: 12 Father()=default; 13 }; 14 class Son:public Father{ //子类 15 public: 16 Son()=default; 17 void Son_show(){ 18 cout<<"调用Son类的方法:Son_show"<<endl; 19 GrandFather_show(); 20 } 21 }; 22 23 int main(){ 24 Son s; 25 s.Son_show(); 26 return 0; 27 }

我们发现上面的程序可以顺利运行。这是因为当Father类以保护方式(protected)继承GrandFather类时,GrandFather类中的公有方法GrandFather_show()会以protected方法的形式存在于类Father中,当类Son再以公有方式(public)继承类Father时,方法GrandFather_show()会仍以protected方法的形式存在与类Son中,由于一个类中的成员方法允许在其函数体内调用protected部分的成员,因此系统允许在Son类的成员方法Son_show()调用方法GrandFather_show(),从而使程序顺利运行。
现在我们将程序改为Father类以私有继承的方式继承GrandFather类:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class GrandFather{ //祖父类 4 public: 5 GrandFather()=default; 6 void GrandFather_show(){ 7 cout<<"调用GrandFather类的方法:GrandFather_show"<<endl; 8 } 9 }; 10 class Father:private GrandFather{ //父类 11 public: 12 Father()=default; 13 }; 14 class Son:public Father{ //子类 15 public: 16 Son()=default; 17 void Son_show(){ 18 cout<<"调用Son类的方法:Son_show"<<endl; 19 GrandFather_show(); 20 } 21 }; 22 23 int main(){ 24 Son s; 25 s.Son_show(); 26 return 0; 27 }
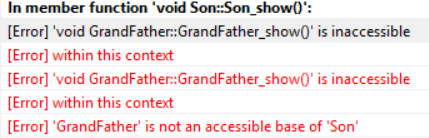
我们发现程序报错。这是因为当Father类以私有(private)继承GrandFather类时,GrandFather类中的公有方法GrandFather_show()会以private方法的形式存在于类Father中,换句话说方法GrandFather_show()变成了类Father的“隐私”;当类Son再以公有方式(public)继承类Father时,由于“儿子无法利用父亲的“隐私”进行交易”,因此无法在Son类中的任何成员方法中调用GrandFather_show()方法,包括Son_show()。此时如果我们将类Son中成员函数Son_show()中的语句“GrandFather();"注释掉,程序便可以重新顺利执行。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class GrandFather{ //祖父类 4 public: 5 GrandFather()=default; 6 void GrandFather_show(){ 7 cout<<"调用GrandFather类的方法:GrandFather_show"<<endl; 8 } 9 }; 10 class Father:private GrandFather{ //父类 11 public: 12 Father()=default; 13 }; 14 class Son:public Father{ 15 public: 16 Son()=default; 17 void Son_show(){ 18 cout<<"调用Son类的方法:Son_show"<<endl; 19 //GrandFather_show(); 20 } 21 }; 22 23 int main(){ 24 Son s; 25 s.Son_show(); 26 return 0; 27 }

•总结
| 父类中的访问属性 | 继承方式 | 子类中的访问属性 |
| private | public/protected/private | 不允许访问 |
| public | public | public |
| public | protected | protected |
| public | private | private |
| protected | public | protected |
| protected | protected | protected |
| protected | private | private |