9.JSP
9.0 前言
许多前辈说因为前后端分离,MVC已经实质上变成了MC,JSP已经没有学习的价值了。因此JSP的内容也只是粗浅的了解,甚至对于JSTL标签完全不去了解。
9.1 什么是JSP
Java Server Pages:Java服务器端页面,和Servlet一样,用于动态Web技术。
特点:
- 写JSP就像写HTML
- 区别:
- HTML只给用户提供静态的数据;
- JSP页面中可以嵌入Java代码,为用户提供动态数据;
9.2 JSP原理
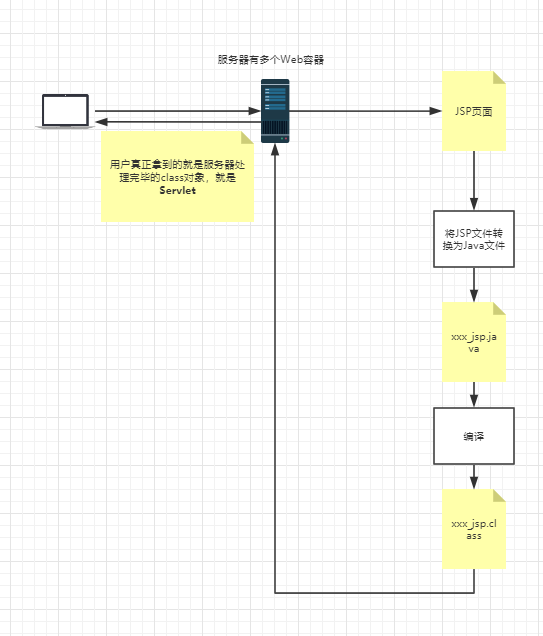
思路:JSP到底怎么执行的
-
代码层面没有任何问题
-
服务器内部工作
tomcat中有一个work目录;
IDEA使用Tomcat的会在IDEA的tomcat中生成一个work目录
C:Users用户名.IntelliJIdea2019.3system omcat任意一个项目workCatalinalocalhost�006_Seesion_warorgapachejsp
抑或是打开Tomcat的目录
TomcatworkCatalinalocalhostROOTorgapachejsp

可以发现页面转变成了Java程序
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet
JSP最终也会转换成一个Java类
打开index_jsp.java文件,可以发现该类继承org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
新建一个Maven,加入如下依赖,可以看HTTPJspBase的继承:
<dependency>
<groupId>tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>jasper-runtime</artifactId>
<version>5.5.23</version>
</dependency>

JSP本质上就是一个Servlet。再往下看:

可以看到,写JSP,后面是会转化为这种以前的程序员要做的繁琐的形式,JSP简化了这个流程。
再看大约第七十几行的位置:
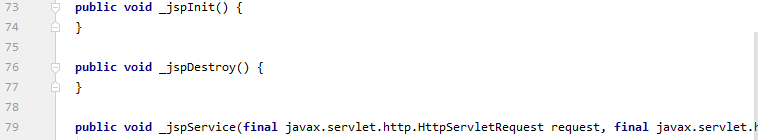
// 初始化
public void _jspInit() {
}
// 销毁
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
// JSPService
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response){...}
-
判断请求;
-
内置一些对象:
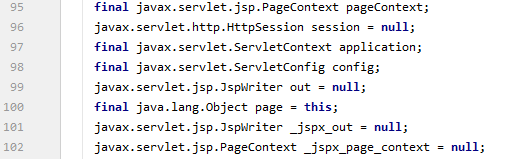
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; // 页面上下文 javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; // session final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; // applicationContext final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; // config javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; // out final java.lang.Object page = this; // page: 当前 javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null; // 暂时不管 javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null; // 暂时不管 HttpServletRequest request // 请求 HttpServletResponse reponse // 响应 -
输出页面前增加的代码:

response.setContentType("text/html"); //设置响应的页面类型 pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; -
以上的这些对象可以再JSP页面中用${....}直接使用:
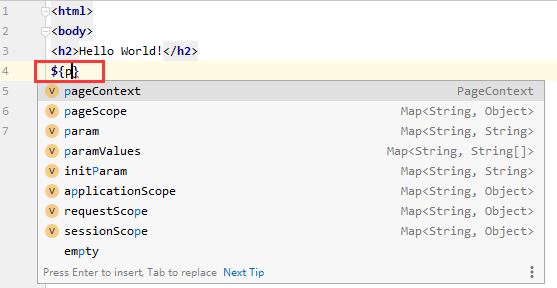
Hello JSP
创建一个Maven项目,模板是WebAPP。并在webapp目录下创建Hello.jsp
如下:

Hello.jsp代码如下:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/21
Time: 23:59
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String name = "duzhuan";
%>
name = <%= name %>
</body>
</html>
除14到17行外,其余都是IDEA自动创建的模板。
另附一推荐浏览:JSP页面中<%!%>与<%%>与<%=%>
配置好Tomcat,可以直接访问Hello.jsp查看效果:

这时去
C:Users用户名.IntelliJIdea2019.3system omcatUnnamed_JavaWeb_3workCatalinalocalhost�007_JSP_warorgapachejsp
查看情况(请注意用户名、Unnamed_JavaWeb_3的对应位置)
打开Hello_jsp.java

在JSP页面中:
- 只要是Java代码就会原封不动的输出
- 如果是HTML代码,就会转换为
out.write(....)这样格式输出到前端
9.3 JSP的基础语法
在9.2的项目里面操作,最终文件路径如下:
依赖
对9.2的项目的pom.xml添加如下依赖:
<!-- Servlet依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JSP依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL表达式的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- stadard标签库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
下面的本章内容仅有这几个依赖被使用。
前言
推荐链接Idea配置热部署,方便调试
9.3.1 JSP表达式
任何语言都有自己的语法,JSP作为java技术的一种应用,还有一些自己扩充的语法(了解即可,不必深入),同时JSP对Java所有的语法都支持。
<%-- 这是JSP的注释 --%>
<%= 变量或者表达式 %>
<%= new java.util.Date()%>
比如在webap目录下新建一个Fori.jsp,路径:
内容如下:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/22
Time: 2:15
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
out.println("<h1>"+sum+"</h1>");
%>
</body>
</html>
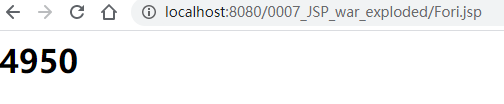
部署后访问Fori.jsp得到如下内容:
9.3.2 JSP脚本片段
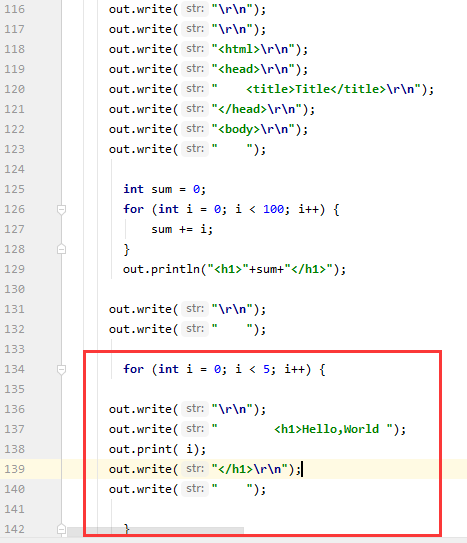
JSP可以做一些好玩的事情,将下面的脚本片段加入Fori.jsp里:
<%
for(int i = 0; i< 5; i++){
%>
<h1>Hello,World <%=i%> </h1>
<%
}
%>
重新部署,访问Fori.jsp里:

打开Fori_jsp.class可以看到这样的代码:
9.3.3 JSP声明
阅读Fori_jsp.class可以看出到目前为止的代码都是写在_jspService这个方法的try{}里面
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException{....}
那么怎么写在外面的代码,使用<%! %>
在Fori.jsp中添加如下代码:
<hr>
<%!
static {
System.out.println("Loading Servlet!");
}
private int globalVar = 0;
public void Saying(){
System.out.println("Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Heart's Club Band");
}
%>
重新部署到Tomcat,后台打印:

打开Fori_jsp.class可以找到如下代码:

JSP声明: 会被编译到JSP生成Java的类中。其他的就会被生成到jsp_Service方法中
9.4 JSP指令
9.4.1 错误页面
9.4.1.1 在jsp页面修改
-
各文件路径:
-
1.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/22
Time: 17:54
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int a = 1/ 0;
%>
</body>
</html>
很显然这是有错误的,当访问时会显示这样的页面:
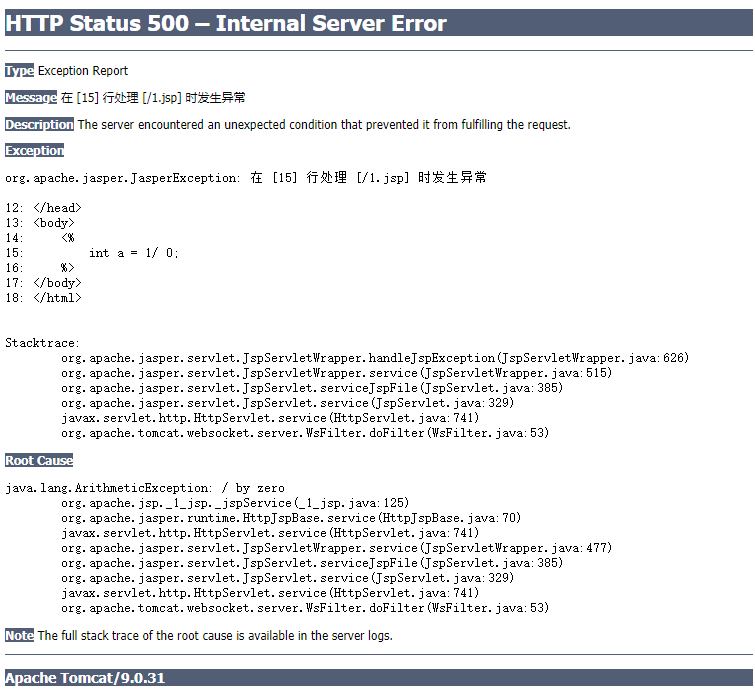
可以用JSP更换。
因此将1.jsp修改:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/22
Time: 17:54
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int a = 1/ 0;
%>
</body>
</html>
添加了<%@ page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %>这样就可以在发生错误的时候显示500.jsp这个页面。
- 500.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/22
Time: 19:20
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="img/500.jpg" alt="Error 500">
</body>
</html>
如果是访问1.jsp没有图,可试着将第14行修改为<img src="../img/500.jpg" alt="Error 500">。按照教程此处应为<img src="../img/500.jpg" alt="Error 500">,但这里实操的访问不到500.jpg这个图片,需改为500.jpg相对1.jsp的路径。如果是这种相对路径不一致的问题以后有方法解决,先不必纠结。
这里是由于JSP的静态引入的问题,通过看1.jsp的源码可以看到:
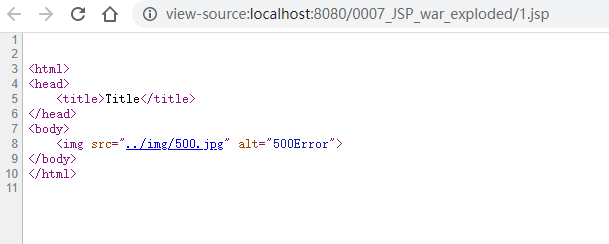
也就是说相当于直接把500.jsp的HTML的内容直接复制粘贴过来了。
JSP的问题就应该JSP解决,可以讲500.jsp的对应语句改为:
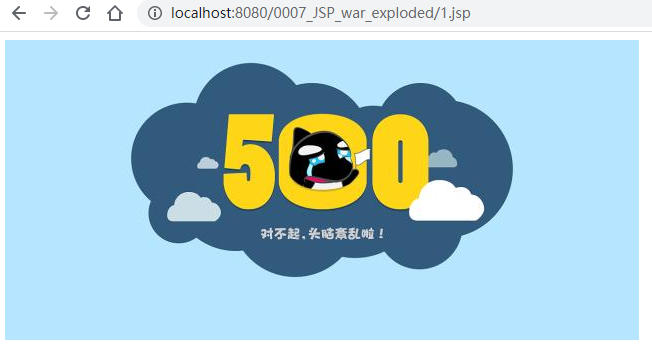
<img src="<%=request.getContextPath()%>/img/500.jpg" alt="500Error">
EL表达式,后面会讲到。
- 500.jpg是随便在网上找的一个500Error的图。
访问1.jsp,这个时候页面显示如下:
9.4.1.2 通过修改web.xml
很显然,上面的方式十分繁琐。至少比起这个方法,第一种方式需要在每个页面都写errorPage。
可以通过修改web.xml去做到同样效果:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0"
metadata-complete="true">
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error/404.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/error/500.jsp</location>
</error-page>
</web-app>
删掉1.jsp的<%@ page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %>
404.jsp随便的页面即可,例如:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/22
Time: 22:45
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error 404</h1>
</body>
</html>
重启Tomcat(非热部署,修改web.xml和Java代码需要重启Tomcat),访问1.jsp显示:

随便访问一个不存在的地址:

9.4.1.3 公共页

比如说B站的这个部分,每个页面都有。
这就是公共页。一般放在common文件夹里。下面是路径:
header.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/23
Time: 22:57
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Header</h1>
</body>
</html>
footer.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/23
Time: 22:57
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Footer</h1>
</body>
</html>
2.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/23
Time: 22:59
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%@include file="/common/footer.jsp"%>
<h1>网络主体</h1>
<%@include file="common/footer.jsp"%>
</body>
</html>
重新部署Tomcat,访问2.jsp,可以看到:
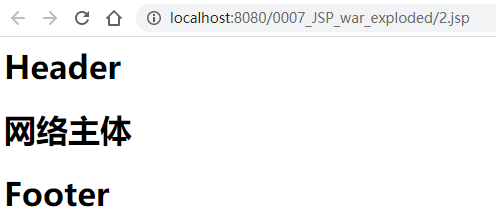
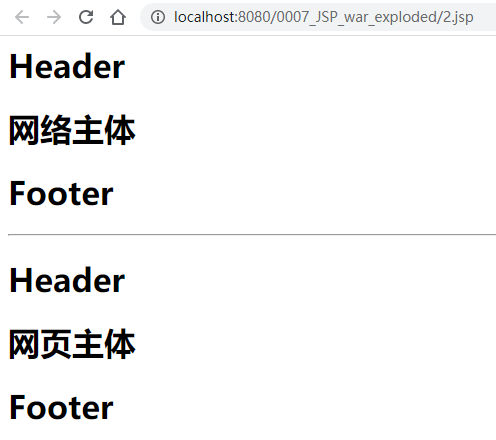
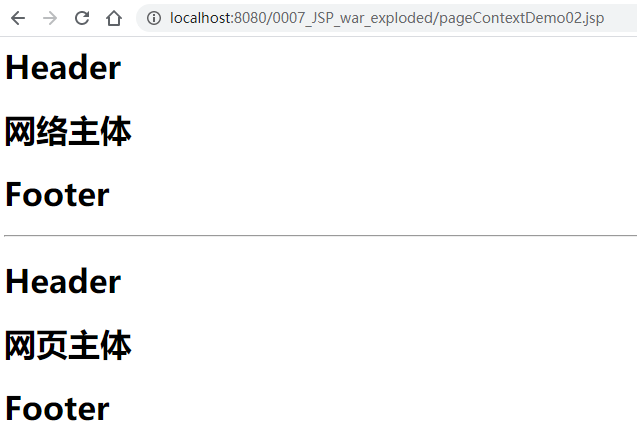
当然,也可以用jsp标签实现同样的效果。将2.jsp修改,只多了第18到23行:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/23
Time: 22:59
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%@include file="common/header.jsp"%>
<h1>网络主体</h1>
<%@include file="common/footer.jsp"%>
<hr>
<%-- JSP标签 --%>
<jsp:include page="/common/header.jsp"></jsp:include>
<h1>网页主体</h1>
<jsp:include page="/common/footer.jsp"></jsp:include>
</body>
</html>
虽然
重新部署后访问2.jsp看到:
打开它生成的_2_jsp.java文件,发现这几个语句:
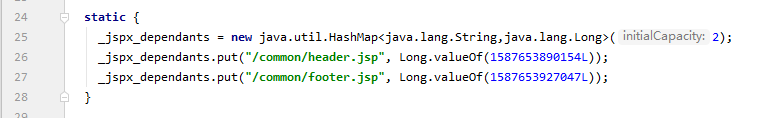
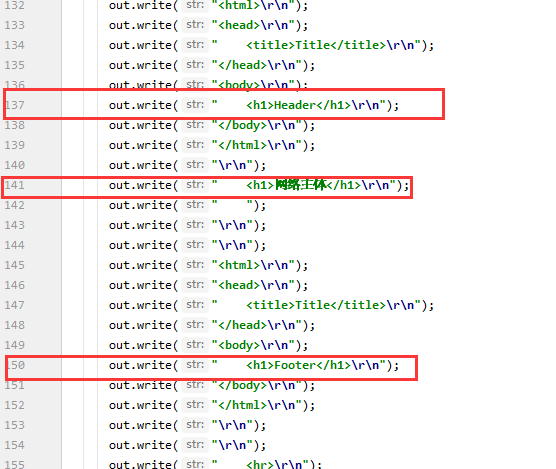
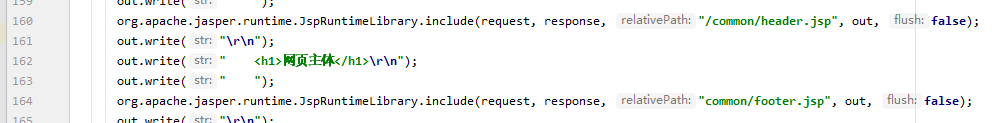
因此,<%@include%>会将两个页面合二为一(解释前面路径不对显示不出图片的问题),<jsp:include>拼接页面,本质上还是几个不同的页面。一般用<jsp:include>,更灵活(不过话说现在连JSP都没人用了......)。
9.5 JSP的9大内置对象及其作用域
9.5.1 内置对象
- PageContext 存东西
- Request 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application 【ServletContext】存东西
- config【ServletConfig】
- out
- page
- exception
在webapp目录下建一个pageContextDemo01.jsp的文件,内容如下:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/23
Time: 23:54
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
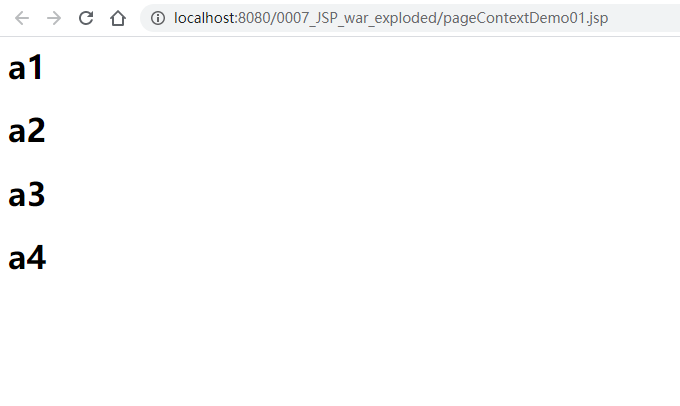
pageContext.setAttribute("name1","a1");
request.setAttribute("name2","a2");
session.setAttribute("name3","a3");
application.setAttribute("name4","a4");
%>
<%
// 取出值(此处代码会被原封不动转为java代码,应用//做注释)
// 为了学习,不直接取,而是通过寻找的方式来
String naem1 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem1");
String naem2 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem2");
String naem3 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem3");
String naem4 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem4");
String naem5 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem5");
%>
<%-- 使用EL表达式取 --%>
<h1>${name1}</h1>
<h1>${name2}</h1>
<h1>${name3}</h1>
<h1>${name4}</h1>
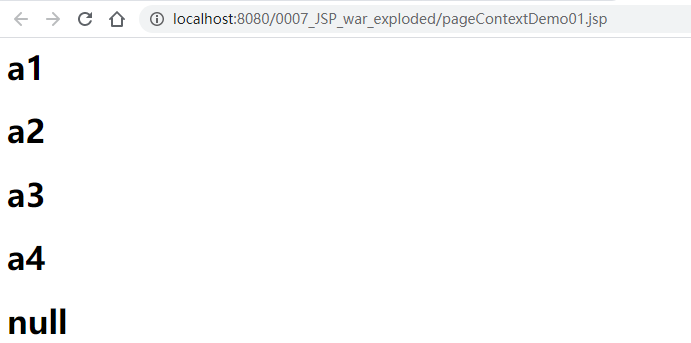
<%-- 下面这个值是不存在的 --%>
<h1>${name5}</h1>
</body>
</html>
重新部署Tomcat,访问pageContextDemo01.jsp可以看到:
若将第37行改为<h1><%= name5%></h1>的形式,重新部署后访问可以看到:
9.5.2 作用域
<%
// 保存的数据只在一个页面种有效
pageContext.setAttribute("name1","a1");
// 保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转发会携带这个页面
request.setAttribute("name2","a2");
// 保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
session.setAttribute("name3","a3");
// 保存的数据在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器
application.setAttribute("name4","a4");
%>
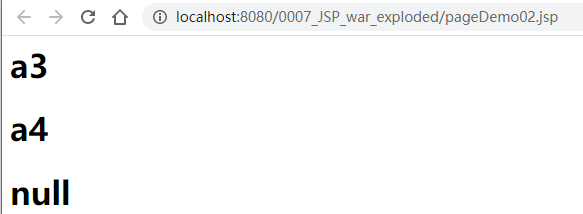
在webapp目录下创建pageDemo02.jsp,代码如下,只是从pageContextDemo01.jsp中复制粘贴了部分过来:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/24
Time: 0:27
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 取出值(此处代码会被原封不动转为java代码,应用//做注释)
// 为了学习,不直接取,而是通过寻找的方式来
String naem1 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem1");
String naem2 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem2");
String naem3 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem3");
String naem4 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem4");
String naem5 = (String) pageContext.findAttribute("naem5");
%>
<%-- 使用EL表达式取 --%>
<h1>${name1}</h1>
<h1>${name2}</h1>
<h1>${name3}</h1>
<h1>${name4}</h1>
<%-- 下面这个值是不存在的 --%>
<h1><%=naem5%></h1>
</body>
</html>
部署后访问pageDemo02.jsp可以看到(冷部署的话需要先访问pageContextDemo01.jsp赋值):
访问pageContext.setAttribute()的源码,发现有abstract public void setAttribute(String name, Object value, int scope);
去找到它的实现类:

有一段这样的代码:
public void setAttribute(String name, Object attribute, int scope) {
switch(scope) {
case 1:
this.mPage.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 2:
this.mRequest.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 3:
this.mSession.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 4:
this.mApp.put(name, attribute);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bad scope " + scope);
}
}
同时,PageContentImpl也继承了PageContent,打开,检索可以看到如下代码:
/**
* Page scope: (this is the default) the named reference remains available
* in this PageContext until the return from the current Servlet.service()
* invocation.
*/
public static final int PAGE_SCOPE = 1;
/**
* Request scope: the named reference remains available from the
* ServletRequest associated with the Servlet until the current request
* is completed.
*/
public static final int REQUEST_SCOPE = 2;
/**
* Session scope (only valid if this page participates in a session):
* the named reference remains available from the HttpSession (if any)
* associated with the Servlet until the HttpSession is invalidated.
*/
public static final int SESSION_SCOPE = 3;
/**
* Application scope: named reference remains available in the
* ServletContext until it is reclaimed.
*/
public static final int APPLICATION_SCOPE = 4;
这代表了可以自己规定某些东西的作用域(一般不建议这么玩)
在webapp目录下创建pageDemo03.jsp其代码如下:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/24
Time: 0:51
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("hello1","hello1",PageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
%>
</body>
</html>
其等价于session.setAttribute()。
JSP去获取值类似于JVM的双亲委派机制。
9.5.3 顺便内容-请求转发
在webapp目录下创建pageContentDemo02.jsp,内容如下:
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: HuangDekai
Date: 2020/4/24
Time: 2:12
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.forward("/2.jsp");
%>
</body>
</html>
重启Tomcat后访问pageContextDemo03.jsp结果如下:
相当于request.getRequestDispatcher('/2.jsp').forward(request,respond);
-
request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻,用户看完没用的
-
session: 客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如:购物车;Hystrix
-
application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据。