一、Bean的初始化和销毁
在我们的实际开发的时候,经常会遇到Bean在使用之前或之后做些必要的操作,Spring对Bean的生命周期操作提供了支持。在使用Java配置和注解配置下提供如下两种方式:
(1)Java配置的方式:使用 @Bean 的 initMethod 和 destroyMethod(相当于xml配置中的 init-method 和 destroy-method)。
(2)注解方式:利用JSR-250的 @PostContruct 和 @PreDestroy。
演示:
1.增加 JSR-250 支持。
<!-- JSR-250 支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jsr250-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
2.使用 @Bean 形式的Bean。
package com.ecworking.bean;
public class BeanWayService {
public void init(){
System.out.println("@Bean-init-method");
}
public BeanWayService() {
super();
System.out.println("初始化构造函数-BeanWayService");
}
private void destroy(){
System.out.println("@Bean-destroy-method");
}
}
3.使用JSR250形式的Bean。
package com.ecworking.bean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class JSR250WayService {
@PostConstruct // 在构造函数执行完之后执行
public void init(){
System.out.println("@JSR250-init-method");
}
public JSR250WayService() {
super();
System.out.println("初始化构造函数-JSR250WayService");
}
@PreDestroy // 在Bean销毁之前执行
private void destroy(){
System.out.println("@JSR250-destroy-method");
}
}
4.配置类。
package com.ecworking.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.ecworking.bean")
public class PrePostConfig {
// initMethod 和 destroyMethod 指定BeanWayService类的 init 和 destroy 方法在构造之后、Bean销毁之前执行
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")
BeanWayService beanWayService(){
return new BeanWayService();
}
@Bean
JSR250WayService jsr250WayService(){
return new JSR250WayService();
}
}
5.运行。
package com.ecworking.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrePostConfig.class);
BeanWayService beanWayService = context.getBean(BeanWayService.class);
JSR250WayService jsr250WayService = context.getBean(JSR250WayService.class);
context.close();
}
}
运行结果:

二、Profile
Prifile为不同环境下提供不同不同配置提供了支持(开发环境和生产环境下的配置肯定是不同的,例如,数据库的配置)。
1.通过设定Environment的 ActiveProfile来设定当前context需要使用的配置环境。在开发环境中使用@Profile注解类或方法,达到在不同环境下选择实例化不同的Bean。
2.通过设定jvm的spring.profile.active参数来设置配置环境。
3.Web项目设置在Servlet的context parameter中。
Servlet2.5及以下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.active</param-name>
<param-value>production</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
Servlet3.0及以上
public class WebInit implement WebApplicationInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext container) throws ServletException{ container.setInitParameter("spring.profiles.default", "dev"); } }
演示:
1.示例Bean。
package com.ecworking.profile; public class DemoBean { private String content; public DemoBean(String content) { this.content = content; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } }
2.profile配置。
package com.ecworking.profile; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; @Configuration public class ProfileConfig { @Bean @Profile("dev") // profile为dev时实例化devDemoBean public DemoBean devDemoBean(){ return new DemoBean("from dev profile"); } @Bean @Profile("prod") // profile为prod时实例化prodDemoBean public DemoBean prodDemoBean(){ return new DemoBean("from prod profile"); } }
3.运行。
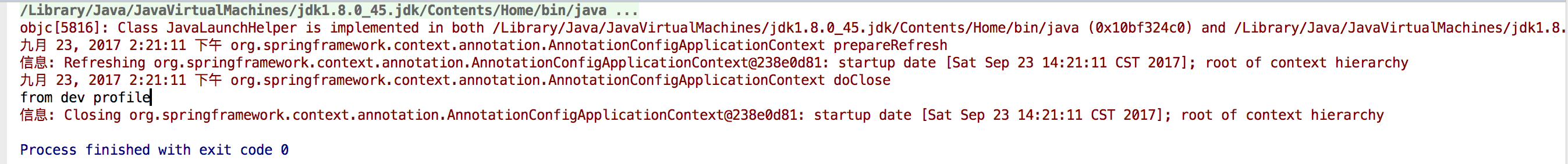
package com.ecworking.profile; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod"); //先将活动的Profile设置为prod。 context.register(ProfileConfig.class); //后注册Bean配置类,不然会报Bean未定义的错误。 context.refresh(); //刷新容器 DemoBean demoBean = context.getBean(DemoBean.class); System.out.println(demoBean.getContent()); context.close(); } }
运行结果:
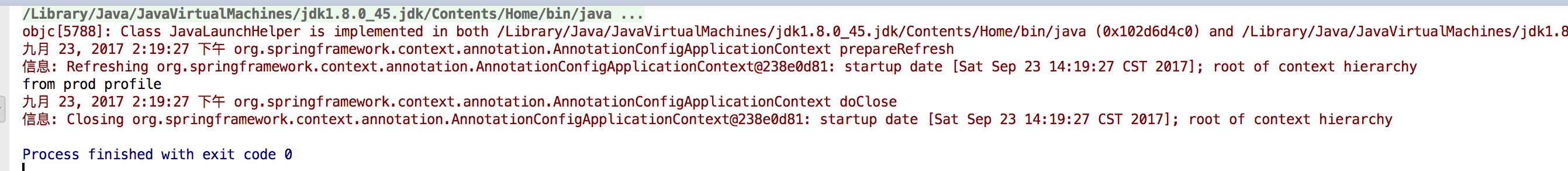
将 context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("prod") 改为 context.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev") 效果如下: