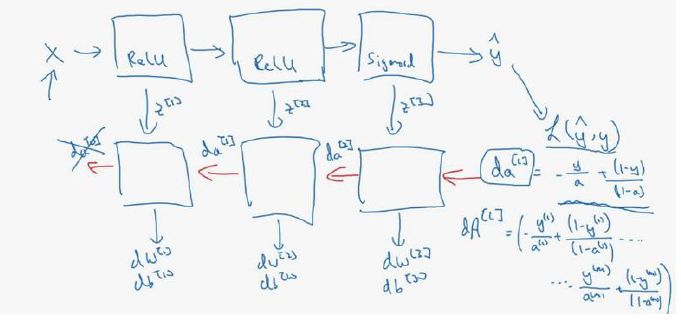
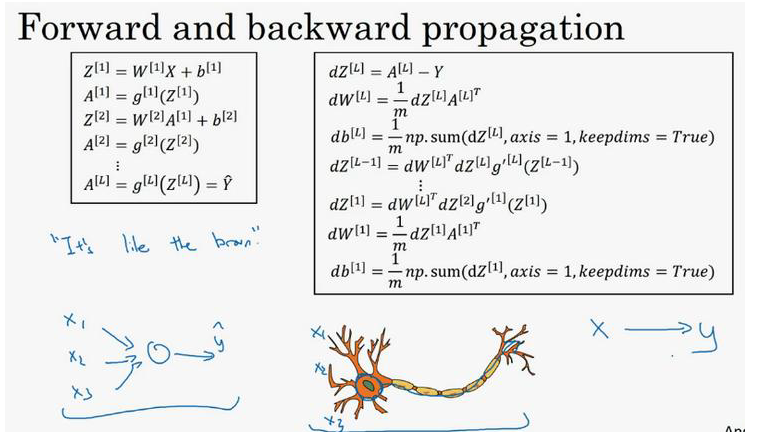
1.Forward and backward propagation:
- Forward propagation for layer L:
- Z[L]=W[L]A[L-1]+b[L]
- A[L]=g[L](Z[L])
- Backward propagation for layer L:
- dZ[L]=dA[L]*g'[L](Z[L])
- dW[L]=(1.0/m)dZ[L].A[L-1].T
- db[L]=(1.0/m)*np.sum(dZ[L],axis=1,keepdims=True)
- dA[L-1]=W'[L]dZ[L]
- 核对矩阵的维数(Getting your matrix dimensions right)
- w的维数是(下一层的维数,前一层的维数); W[L]:(n[L],n[L-1])
- b的维度是(下一层的维数,1),b[L]:(n[L],1);
- Z[L],A[L]的维度是(神经元个数,样本个数):(n[L],m)
- dW[L]和W[L]维度相同,db[L]和b[L]维度相同,dZ[L]和Z[L]维度相同,dA[L]和A[L]维度相同
2.搭建神经网络块(Building blocks of deep neural networks):
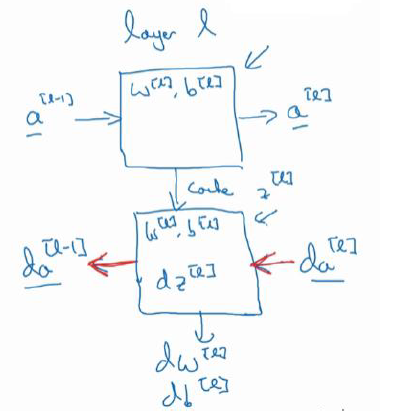
正向函数:输入A[L-1]、W[L]、b[L],输出A[L]并且缓存Z[L]
反向函数:输入dA[L]、Z[L]、W[L]、b[L],输出dA[L-1]、dW[L]、db[L]
3.参数与超参数
- 什么是超参数:
- learning rate(学习率)
- Iterations(梯度下降法循环的数量)
- L(隐藏层数目)
- n[L](隐藏层单元数目)
- choice of activation function(激活函数的选择)
- momentum、mini batch szie、regularization parameters 等等
4.编程实践:
激活函数:
import numpy as np def sigmoid(Z): """ Implements the sigmoid activation in numpy Arguments: Z -- numpy array of any shape Returns: A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Z cache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation """ A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z)) cache = Z return A, cache def relu(Z): """ Implement the RELU function. Arguments: Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shape Returns: A -- Post-activation parameter, of the same shape as Z cache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently """ A = np.maximum(0,Z) assert(A.shape == Z.shape) cache = Z return A, cache def relu_backward(dA, cache): """ Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit. Arguments: dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently Returns: dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z """ Z = cache dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object. # When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well. dZ[Z <= 0] = 0 assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape) return dZ def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache): """ Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit. Arguments: dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently Returns: dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z """ Z = cache s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z)) dZ = dA * s * (1-s) assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape) return dZ def tanh_backward(dA,cache): Z=cache dZ=dA*(1-np.power(np.tanh(Z),2)) assert(dZ.shape==Z.shape) return dZ
L层神经网络的编程实现
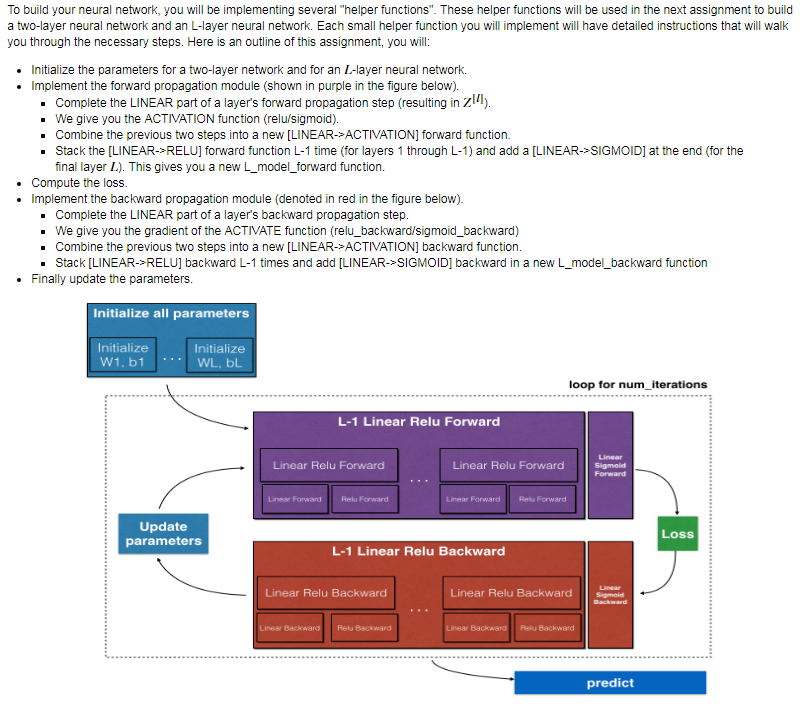
- Initialize Deep Neural Network parameters:
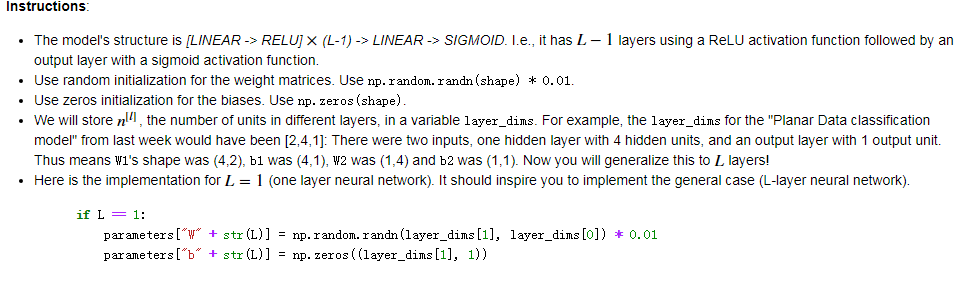
-
-
1 def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims): 2 """ 3 Arguments: 4 layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network 5 6 Returns: 7 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL": 8 Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) 9 bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1) 10 """ 11 np.random.seed(3) 12 parameters={} 13 L=len(layer_dims) 14 for l in range(1,L): 15 parameters['W'+str(l)]=np.random.randn(layer_dims[l],layer_dims[l-1])*0.01 16 parameters['b'+str(l)]=np.zeros((layer_dims[l],1)) 17 assert(parameters['W'+str(l)].shape==(layer_dims[l],layer_dims[l-1])) 18 assert(parameters['b'+str(l)].shape==(layer_dims[l],1)) 19 return parameters
-
-
- Forward propagation module:
- Linear Forward
- Linear_activation_forward:
- L-Layer Model
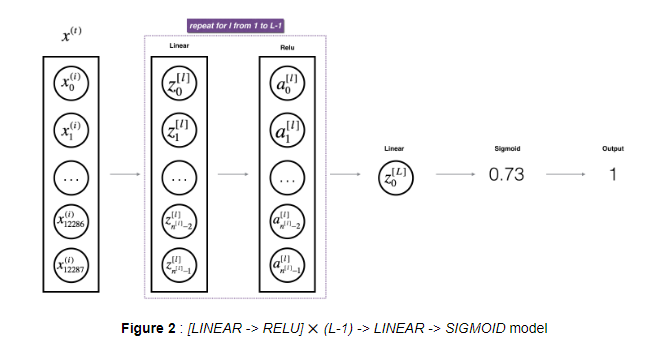
-
1 def linear_forward(A,W,b): 2 """ 3 Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation. 4 5 Arguments: 6 A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples) 7 W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer) 8 b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1) 9 10 Returns: 11 Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter 12 cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W" and "b" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently 13 """ 14 Z=np.dot(W,A)+b 15 assert(Z.shape==(W.shape[0],A.shape[1]) 16 linear_cache=(A,W,b) 17 return Z,cache 18 19 def linear_activation_forward(A_prev,W,b,activation): 20 """ 21 Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer 22 23 Arguments: 24 A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples) 25 W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer) 26 b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1) 27 activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu" 28 29 Returns: 30 A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value 31 cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache"; 32 stored for computing the backward pass efficiently 33 """ 34 if activation=='sigmoid': 35 Z,linear_cache=linear_forward(A_prev,W,b) 36 A,activation_cache=sigmoid(Z) 37 elif activation=='relu': 38 Z,linear_cache=linear_forward(A_prev,W,b) 39 A,activation_cache=relu(Z) 40 assert(A.shape==(W.shape[0],A_prev.shape[1])) 41 cache=(linear_cache,activation_cache) 42 return A,cache 43 44 def L_model_forward(X,parameters): 45 """ 46 Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation 47 48 Arguments: 49 X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) 50 parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep() 51 52 Returns: 53 AL -- last post-activation value 54 caches -- list of caches containing: 55 every cache of linear_activation_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-1) 56 """ 57 caches=[] 58 A=X 59 L=len(parameters)//2 60 for l in range(1,L): 61 A_prev=A 62 A,cache=linear_activation_forward(A_prev,parameters['W'+str(l)],parameters['b'+str(l)],'relu') 63 caches.append(cache) 64 A_prev=A 65 AL,cache=linear_activation_forward(A_prev,parameters['W'+str(L)],parameters['b'+str(L)],"sigmoid") 66 assert(AL.shape==(1,X.shape[1])) 67 return AL,caches
- Cost function:

-
1 def comput_cost(AL,Y): 2 """ 3 Implement the cost function defined by equation (7). 4 5 Arguments: 6 AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples) 8 9 Returns: 10 cost -- cross-entropy cost 11 """ 12 m=Y.shape[1] 13 cost=(-1.0/m)*(np.dot(Y,np.log(AL).T)+np.dot(1-Y,np.log(1-AL).T)) 14 cost=np.squeeze(cost) 15 asset(cost.shape==()) 16 return cost
- Backward propagation module
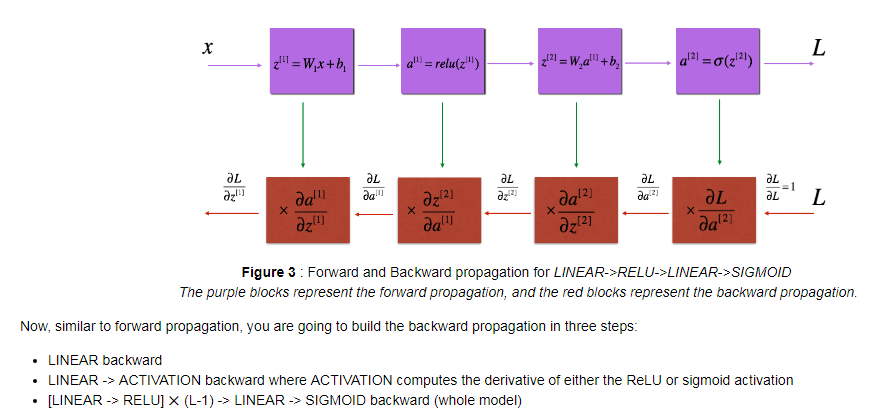
- Linear backward:
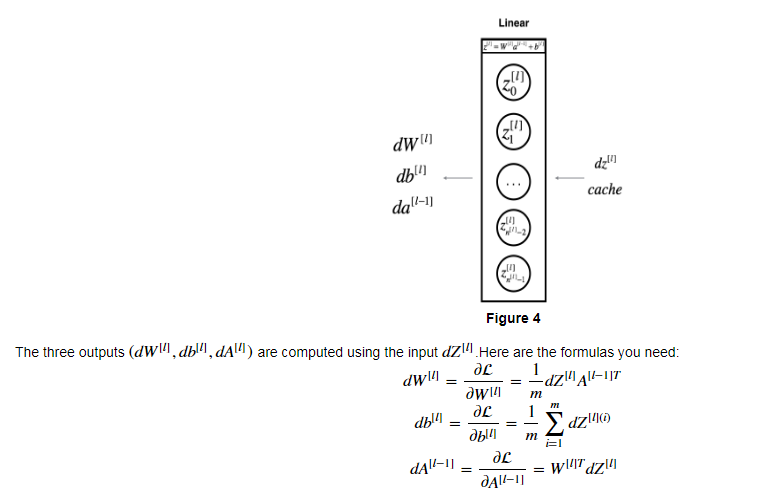
-
1 def linear_backward(dZ, cache): 2 """ 3 Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l) 4 5 Arguments: 6 dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l) 7 cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer 8 9 Returns: 10 dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev 11 dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W 12 db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b 13 """ 14 A_prev, W, b = cache 15 m = A_prev.shape[1] 16 17 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code) 18 dW = (1.0/m)*np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T) 19 db = (1.0/m)*np.sum(dZ,axis=1,keepdims=True) 20 dA_prev =np.dot(W.T,dZ) 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape) 24 assert (dW.shape == W.shape) 25 assert (db.shape == b.shape) 26 27 return dA_prev, dW, db
- Linear-Activation backward:

-
1 def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer. 4 5 Arguments: 6 dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l 7 cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently 8 activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu" 9 10 Returns: 11 dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev 12 dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W 13 db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b 14 """ 15 linear_cache, activation_cache = cache 16 17 if activation == "relu": 18 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 19 dZ = relu_backward(dA,activation_cache) 20 dA_prev, dW, db =linear_backward(dZ,linear_cache) 21 ### END CODE HERE ### 22 23 elif activation == "sigmoid": 24 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code) 25 dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA,activation_cache) 26 dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ,linear_cache) 27 ### END CODE HERE ### 28 29 return dA_prev, dW, db
- L-Model Backward:
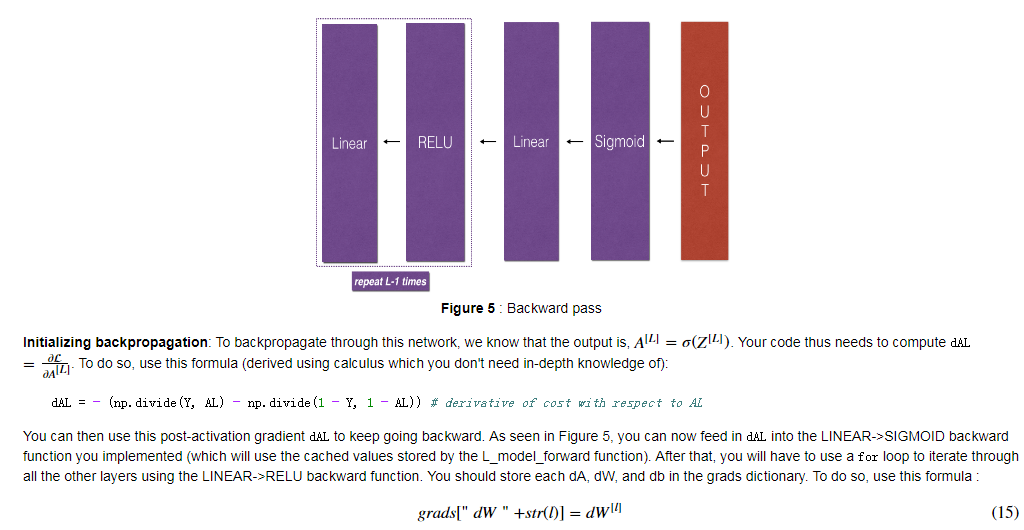
-
1 def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches): 2 """ 3 Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group 4 5 Arguments: 6 AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward()) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat) 8 caches -- list of caches containing: 9 every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2) 10 the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1]) 11 12 Returns: 13 grads -- A dictionary with the gradients 14 grads["dA" + str(l)] = ... 15 grads["dW" + str(l)] = ... 16 grads["db" + str(l)] = ... 17 """ 18 grads = {} 19 L = len(caches) # the number of layers 20 m = AL.shape[1] 21 Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL 22 23 # Initializing the backpropagation 24 ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code) 25 dAL = -(np.divide(Y,AL)-np.divide(1-Y,1-AL)) 26 ### END CODE HERE ### 27 28 # Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "dAL, current_cache". Outputs: "grads["dAL-1"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"] 29 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 30 current_cache =caches[-1] 31 grads["dA" + str(L-1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] =linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, "sigmoid") 32 ### END CODE HERE ### 33 34 # Loop from l=L-2 to l=0 35 for l in reversed(range(L-1)): 36 # lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients. 37 # Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)] 38 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines) 39 current_cache =caches[l] 40 dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp =linear_activation_backward(grads["dA"+str(l+1)], current_cache, "relu") 41 grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp 42 grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp 43 grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp 44 ### END CODE HERE ### 45 46 return grads
- Update Parameters

-
1 def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate): 2 """ 3 Update parameters using gradient descent 4 5 Arguments: 6 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters 7 grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward 8 9 Returns: 10 parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters 11 parameters["W" + str(l)] = ... 12 parameters["b" + str(l)] = ... 13 """ 14 15 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network 16 17 # Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop. 18 ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code) 19 for l in range(L): 20 parameters["W" + str(l+1)] -=learning_rate*grads["dW" + str(l+1)] 21 parameters["b" + str(l+1)] -= learning_rate*grads["db" + str(l+1)] 22 ### END CODE HERE ### 23 return parameters
- Linear Forward
5.深度神经网络的运用:
- Build Deep Learning model step:
- Initialize parameters / Define hyperparameters
- Loop for num_iterations:
- Forward propagation
- Compute cost function
- Backward propagation
- Update parameters (using parameters,and grads from backprop)
- Use trained parameters to predict labels

