简介
线程池是什么?
- 打饭的阿姨们
- 前去吃饭的人们,任务
- 管理组件
线程池由三部分组成
- 执行队列,线程s
- 任务队列,任务s
- 管理组件
类似于
- 银行营业厅
- 食堂打饭
每个打饭的人都是一个线程
管理制度
参考链接
https://www.zhihu.com/question/27908489/answer/355105668
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1AT4y13791?from=search&seid=3536843546637261551
https://github.com/lizhenghn123/zl_threadpool (github点赞数较多)
线程池解决什么问题
- 解决任务处理。
- 阻塞IO。
- 解决线程创建于销毁的成本问题。
- 管理线程。
- 异步解耦的作用。
问题
- 如何增加线程
- 如何减少线程
- 增加与减少的策略
C的实现策略
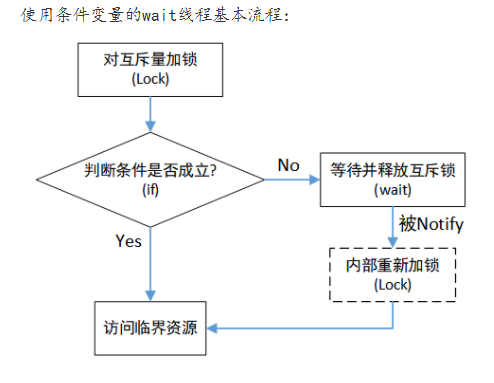
首先我们来认识这些多线程要用的pthread接口函数
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->jobs_mutex); // 对资源上锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->jobs_mutex); // 对资源解锁
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->jobs_cond); // 每调用一次,相当于P操作
pthread_cond_wait(&worker->pool->jobs_cond, &worker->pool->jobs_mutex); // 每调用一次相当于V操作
简单来说条件变量就是,许可证的发放,P相当于发了一张许可证,V相当于销毁了一张许可证,当没有许可证的时候pthread_cond_wait函数阻塞
pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void (start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
attr 如果为NULL表示的是默认的属性,start_routine表示函数指针,指向默认的线程函数,arg表示线程函数的唯一的参数
pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出线程,线程销毁操作
线程池实现源代码
code
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "timee.hh"
// B 站 线程池
// head insert
#define LL_ADD(item, list) do {
item->prev = NULL;
item->next = list;
if(list != NULL)
list->prev = item;
list = item;
} while(0)
#define LL_REMOVE(item, list) do {
if(item->prev != NULL) item->prev->next = item->next;
if(item->next != NULL) item->next->prev = item->prev;
if(list == item) list = item->next;
item->prev = item->next = NULL;
} while(0)
struct NWORKER{
pthread_t thread;
struct NMANAGER *pool;
int terminate;
struct NWORKER *prev;
struct NWORKER *next;
};
struct NJOB{
void (*func)(struct NJOB *job);
void *user_data;
struct NJOB *prev;
struct NJOB *next;
};
struct NMANAGER {
struct NWORKER *workers;
struct NJOB *jobs;
pthread_cond_t jobs_cond;
pthread_mutex_t jobs_mutex;
int thread_count;
int count;
pthread_mutex_t count_mutex;
};
typedef struct NMANAGER nThreadPool;
// static this file is valid
static void *nThreadCallback(void *arg) {
struct NWORKER *worker = (struct NWORKER*) arg;
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
while(worker->pool->jobs == NULL) {
if(worker->terminate) break;
// condition wait
pthread_cond_wait(&worker->pool->jobs_cond, &worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
}
if(worker->terminate){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
break;
}
struct NJOB *job = worker->pool->jobs;
LL_REMOVE(job, worker->pool->jobs);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
job->func((NJOB *)job);
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->pool->count_mutex);
worker->pool->count++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->count_mutex);
}
free(worker);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// Thread Pool Create
int nThreadPoolCreate(nThreadPool *pool, int numWorkers) {
if(numWorkers < 1) numWorkers = 1;
if(pool == NULL) return -1;
memset(pool, 0, sizeof(nThreadPool));
pthread_cond_t blank_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->jobs_cond, &blank_cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
pthread_mutex_t blank_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->jobs_mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
memcpy(&pool->count_mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
pool->count = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i<numWorkers; i++){
struct NWORKER *worker = (struct NWORKER*)malloc(sizeof(struct NWORKER));
if(worker == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return -2;
}
memset(worker, 0, sizeof(struct NWORKER));
worker->pool = pool;
int ret = pthread_create(&worker->thread, NULL, nThreadCallback, worker);
if(ret){
perror("pthread_create");
free(worker);
return -3;
}
LL_ADD(worker, pool->workers);
}
return 0;
}
// push job to pool
void nThreadPoolPush(nThreadPool *pool, struct NJOB *job) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
LL_ADD(job, pool->jobs);
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->jobs_cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
}
// destroy pool
int nThreadPoolDestroy(nThreadPool *pool){
struct NWORKER *worker = NULL;
for(worker = pool->workers; worker != NULL; worker = worker->next) {
worker->terminate = 1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->jobs_cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
return 0;
}
#if 1
// 0 --> 1000,
// task -->
void print(struct NJOB *job) {
printf("**%d**
", *(int *)(job->user_data));
for(int i = 0; i<10000; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 10000; j++);
}
int main() {
Timer<> timer;
timer.beginStage("START
");
nThreadPool *pool = new nThreadPool;
nThreadPoolCreate(pool, 16); // create 16 waiter
const int M = 100;
pool->thread_count = M;
NJOB t[M];
int num[M];
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
num[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0; i < M; i++){
t[i].func = print;
t[i].user_data = &num[i];
nThreadPoolPush(pool, &t[i]);
}
// wait all worker finish
bool check = false;
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->count_mutex);
if(pool->count == pool->thread_count){
check = true;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->count_mutex);
unsigned int microseconds = 1000;
usleep(microseconds);
if(check){
nThreadPoolDestroy(pool);
break;
}
}
timer.endStage("END
");
printf("
======
");
}
#endif
timee.hh 计时函数
#pragma once
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename TimeT = std::chrono::milliseconds>
class Timer{
public:
Timer() {
start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
}
size_t value() const {
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<TimeT>(now - start);
return (size_t) duration.count();
}
size_t reset() {
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<TimeT>(now - start);
start = now;
return (size_t) duration.count();
}
void beginStage(const std::string &name){
reset();
std::cout << name << " .. ";
std::cout.flush();
}
void endStage(const std::string &str = ""){
std::cout << "done. (took " << value() << " ms";
if(!str.empty()){
std::cout << ", " << str;
}
std::cout << ")" << std::endl;
}
private:
std::chrono::system_clock::time_point start;
};
基于查询法毕竟不太美观
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "timee.hh"
// Head insert
#define LL_ADD(node, head) do {
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = head;
if(head != NULL)
head->prev = node;
head = node;
} while(0)
#define LL_REMOVE(node, head) do {
if(node->prev != NULL) node->prev->next = node->next;
if(node->next != NULL) node->next->prev = node->prev;
if(head == node) head = node->next;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} while(0)
// 线程列表
struct NWORKER
{
pthread_t thread;
struct NMANAGER *pool;
int terminate;
struct NWORKER *prev;
struct NWORKER *next;
};
// 任务列表
struct NJOB
{
void (*func)(struct NJOB *job);
void *user_data;
struct NJOB *prev;
struct NJOB *next;
};
// 管理器
struct NMANAGER
{
struct NWORKER *workers;
struct NJOB *jobs;
unsigned int total_jobs;
unsigned int job_count; // 任务计数变量
pthread_mutex_t count_mutex;
pthread_cond_t end_cond;
pthread_mutex_t end_mutex;
pthread_cond_t jobs_cond;
pthread_mutex_t jobs_mutex; // 任何一个线程在干活之前都需要先获取锁
};
typedef struct NMANAGER nThreadPool;
// 定义线程所做的工作
static void *nThreadCallback(void *arg)
{
struct NWORKER *worker = (struct NWORKER*) arg;
while(1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex); // 干活之前先获取锁
while(worker->pool->jobs == NULL) { // 没有任务
if(worker->terminate) break;
// condition wait
pthread_cond_wait(&worker->pool->jobs_cond, &worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
}
if(worker->terminate){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
break;
}
// 从任务列表获取一个任务进行处理
struct NJOB *job = worker->pool->jobs;
LL_REMOVE(job, worker->pool->jobs);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->jobs_mutex);
job->func(job);
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->pool->count_mutex);
worker->pool->job_count++;
if (worker->pool->job_count == worker->pool->total_jobs) {
pthread_cond_signal(&worker->pool->end_cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->count_mutex);
}
free(worker);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// Thread Pool Create
int nThreadPoolCreate(nThreadPool *pool, int numWorkers)
{
if(numWorkers < 1) numWorkers = 1;
if(pool == NULL) return -1;
memset(pool, 0, sizeof(nThreadPool));
pthread_cond_t blank_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->jobs_cond, &blank_cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
memcpy(&pool->end_cond, &blank_cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
pthread_mutex_t blank_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->jobs_mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
memcpy(&pool->count_mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
memcpy(&pool->end_mutex, &blank_mutex, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
for(int i = 0; i<numWorkers; i++) {
struct NWORKER *worker = (struct NWORKER*)malloc(sizeof(struct NWORKER)); // 创建一个线程
if(worker == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return -2;
}
memset(worker, 0, sizeof(struct NWORKER));
worker->pool = pool; // 设置管理器
int ret = pthread_create(&worker->thread, NULL, nThreadCallback, worker);
if(ret){
perror("pthread_create");
free(worker);
return -3;
}
LL_ADD(worker, pool->workers); // 加入线程列表
}
return 0;
}
// push job to pool
void nThreadPoolPush(nThreadPool *pool, struct NJOB *job)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
LL_ADD(job, pool->jobs); // 新任务加入任务列表
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->jobs_cond); // 唤醒一个线程去处理
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->jobs_mutex); // 释放锁
}
// destroy pool
int nThreadPoolDestroy(nThreadPool *pool)
{
struct NWORKER *worker = NULL;
for(worker = pool->workers; worker != NULL; worker = worker->next) {
worker->terminate = 1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->jobs_cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->jobs_mutex);
return 0;
}
#if 1
void print(struct NJOB *job)
{
printf("**%d**
", *((int*)job->user_data));
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++);
}
int main()
{
Timer<> timer;
timer.beginStage("START
");
nThreadPool *pool = (nThreadPool *)malloc(sizeof(nThreadPool));
nThreadPoolCreate(pool, 16); // create 16 worker
#define JOB_COUNT 100
NJOB t[JOB_COUNT];
pool->total_jobs = JOB_COUNT;
pool->job_count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < JOB_COUNT; i++) {
t[i].func = print;
t[i].user_data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
(*(int*)t[i].user_data) = i;
nThreadPoolPush(pool, &t[i]);
}
if(pool->job_count != JOB_COUNT) {
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->end_cond, &pool->end_mutex);
printf("==>%d
", pool->job_count);
nThreadPoolDestroy(pool);
}
timer.endStage("END
");
}
#endif
image
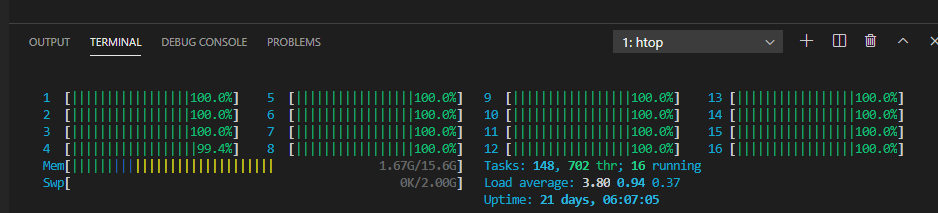
可以看到16个核心跑满了。
相当于一个资本家,对于自己手下的员工,让他不停歇的为你赚钱钱,开心~~
小节
C++的封装对于线程池的实现会更加优雅,但是线程池的C的时间更加粗糙,容易理解。
学了一天,发现,抄一样东西简单,让一样东西实用,理解他,有点点难,或许说我太菜了~~
编译命令
g++ threadpool.cc -lphtread