"Virtual Machine Monitors: Current Technologies and Future Trends" by Rosenblum and Garfinkel
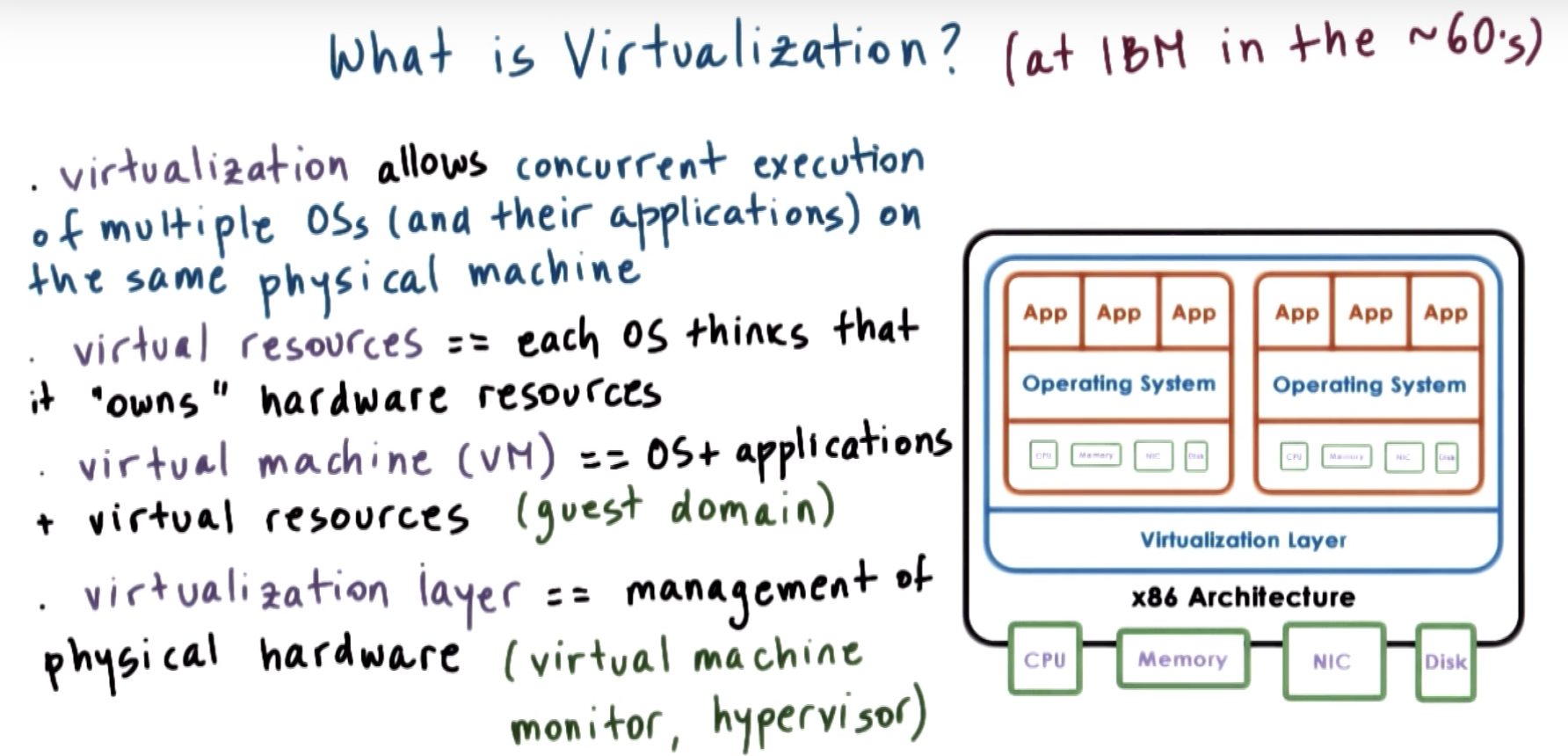
Defining Virtualization

1974 "Formal Requirements for Virtualizable Third Generation Architectures" by Popek and Goldberg
control means:
At last, the VMM (virtual machine monitor) is in complete control of the system resources.
This means that the virtual machine monitor has full control to make decisions, who access which resources and when,
and it can be relied upon to ensure safety and isolation among the VMs.
This doesnt mean that every single hardware access has to be inspected by VMM layer. Instead what this means is that the VMM determines if a particular VM is to be given direct hardware access.
And also, once those decisions are put in place, a VM can not change those policies, and potentially hurt other collocated VMs.

JVM is a language runtime which provides system services and portability to Java applications. It's very different than the underlying physical machine.
Virtual GB is just an emulator.
Quiz Help
Classical Definition of Visualization: Visualization (or a virtual machine) is an efficient, isolated duplicate of the machine.
Benefits of Virtualization



servers in data centers are underutilized. in fact the utilization rates were in average 20%.
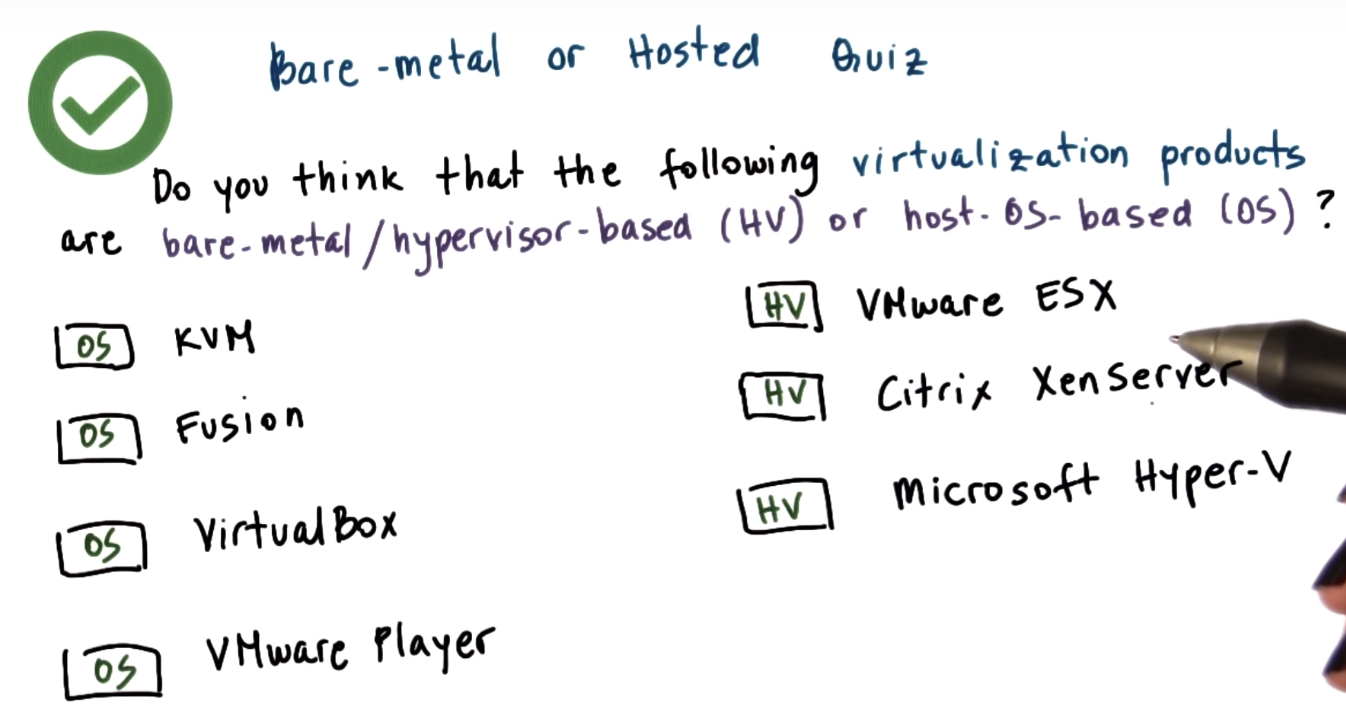
Virtualization Models Bare Metal
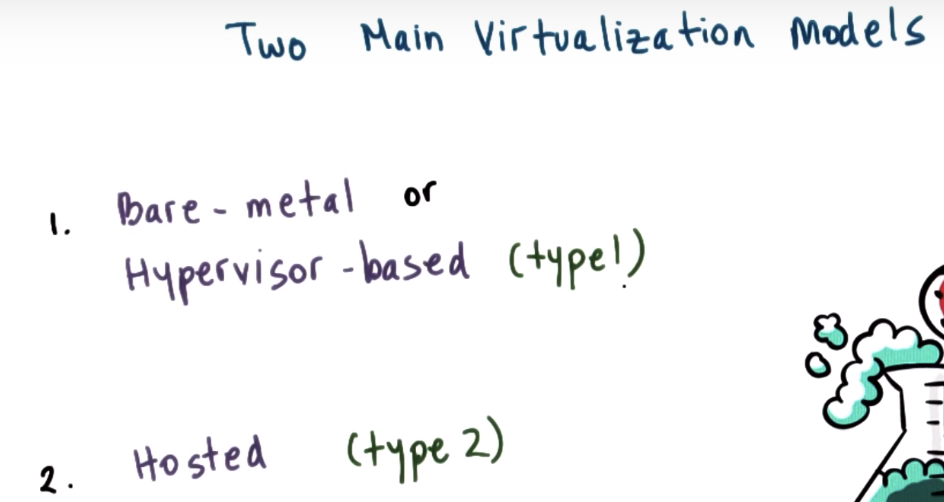
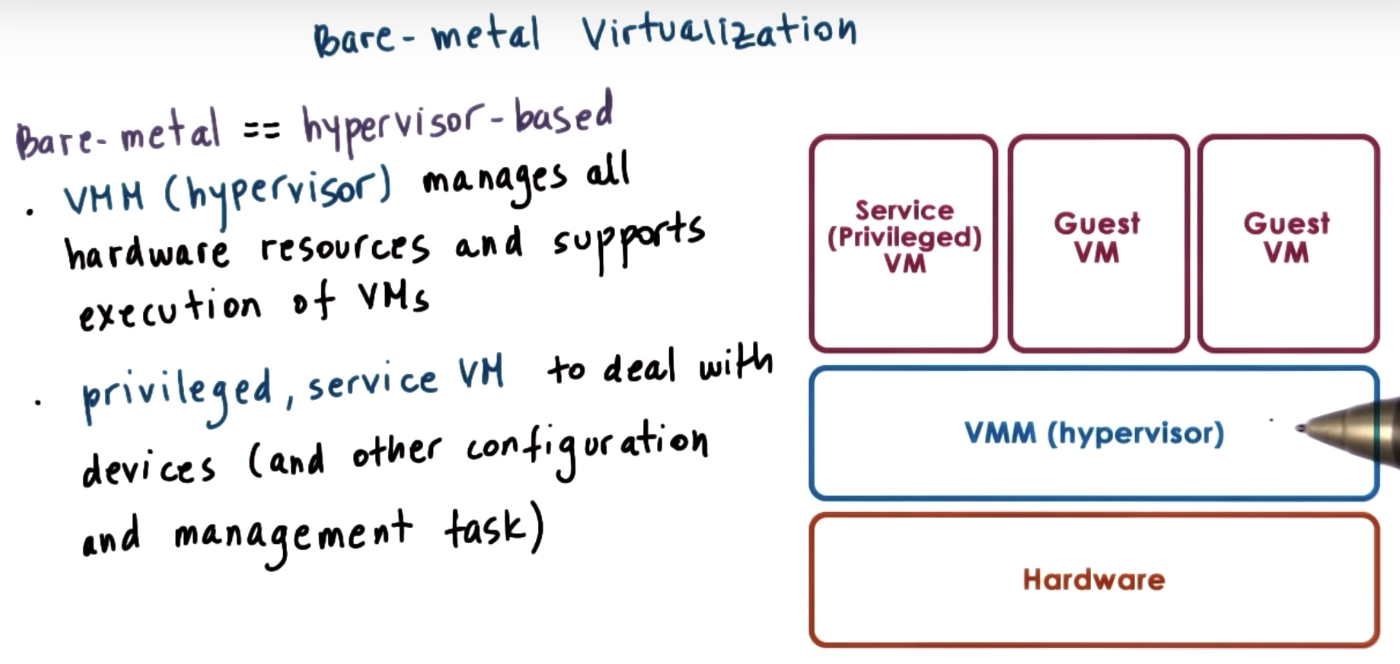

bare-metal => Guest VM is OS level
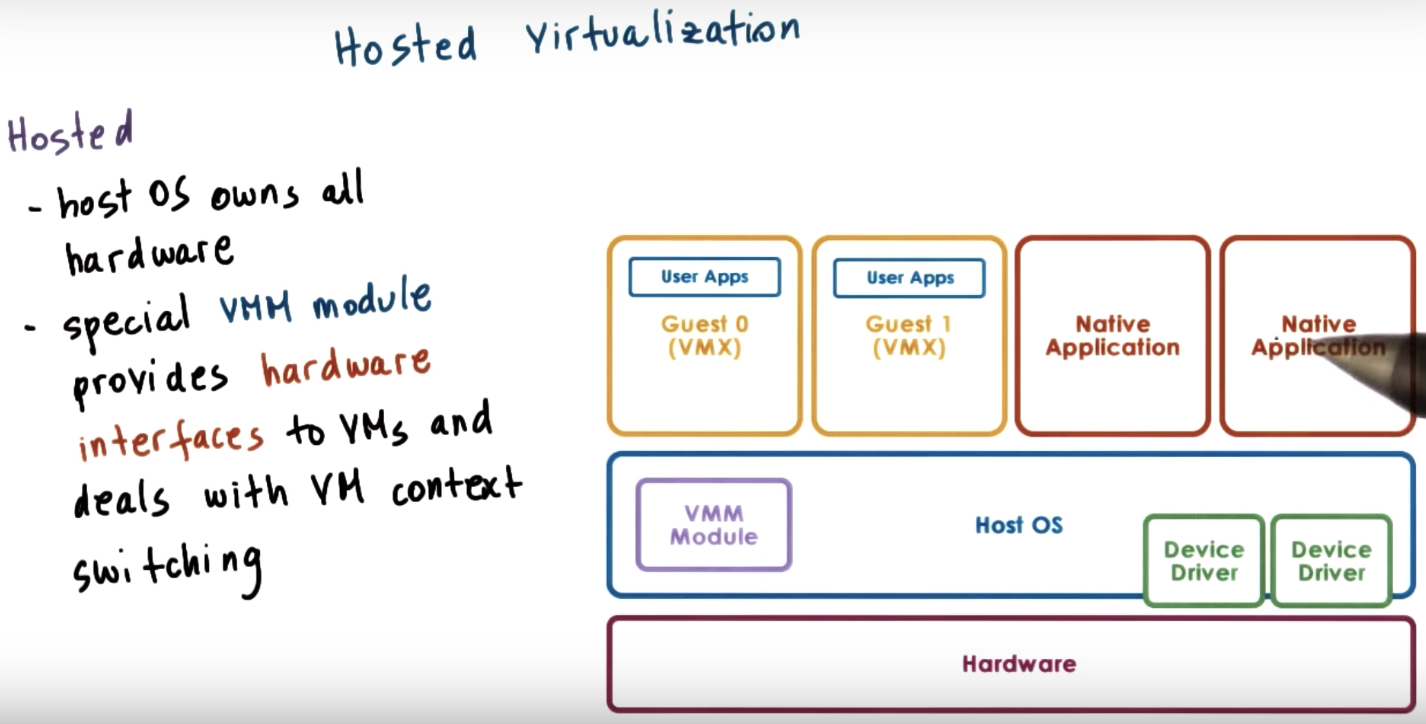
Hosted => application level
Virtualization Models Hosted

QEMU => hardware emulator
the goal of virtualization is to provide identical hardware.
the resoures that are available to the Guest VM are actually the exactly hardware resources from the physical platform,
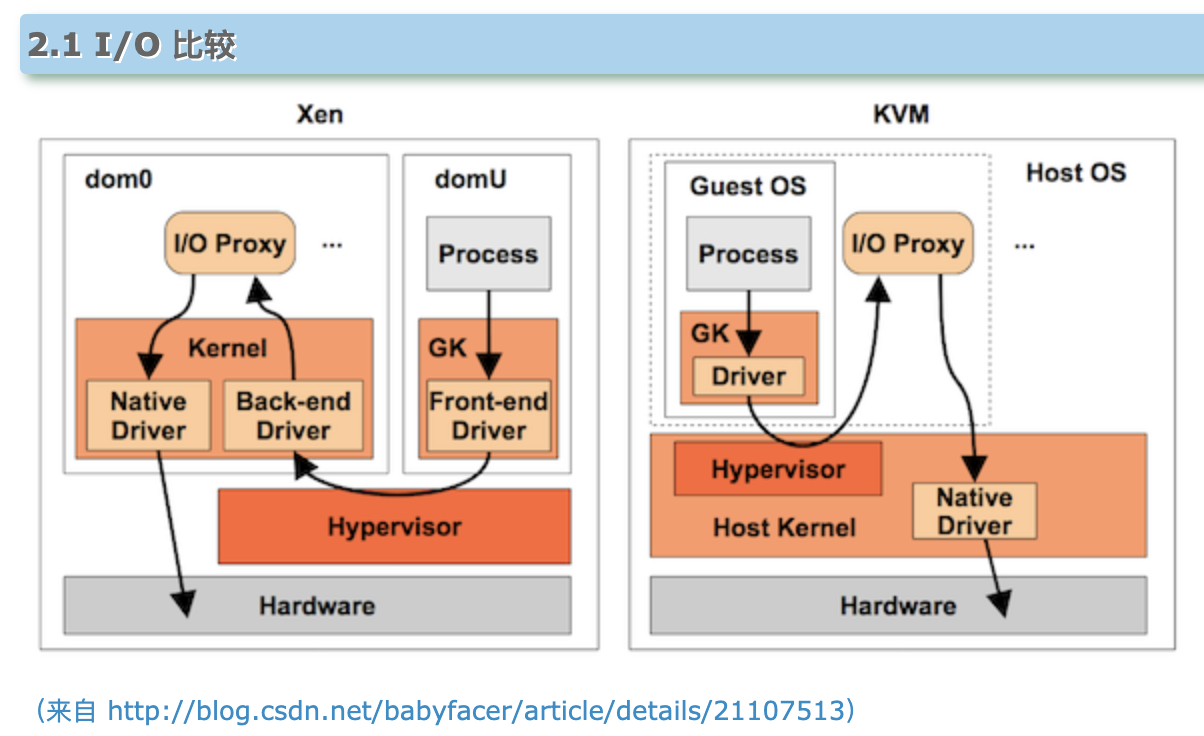
except that this virtualizer invenes during certain types of critical operations or specific instrutions relative to pass control to the KVM Module and the Host OS
One example of that would be any aspect of IO management, because all the support for the device drivers are handled as part of the Linux operating system.
KVM leverages the Linux community, it can quickly adapt to new devices, new security, bugs or similar things.
in fact, KVM was originally developed as a Linux module in order to allow regular use of Linux applications to take advantage of some of the virtualization related hardware
https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-differences-between-simulation-and-emulation


https://www.cnblogs.com/sammyliu/articles/4390371.html
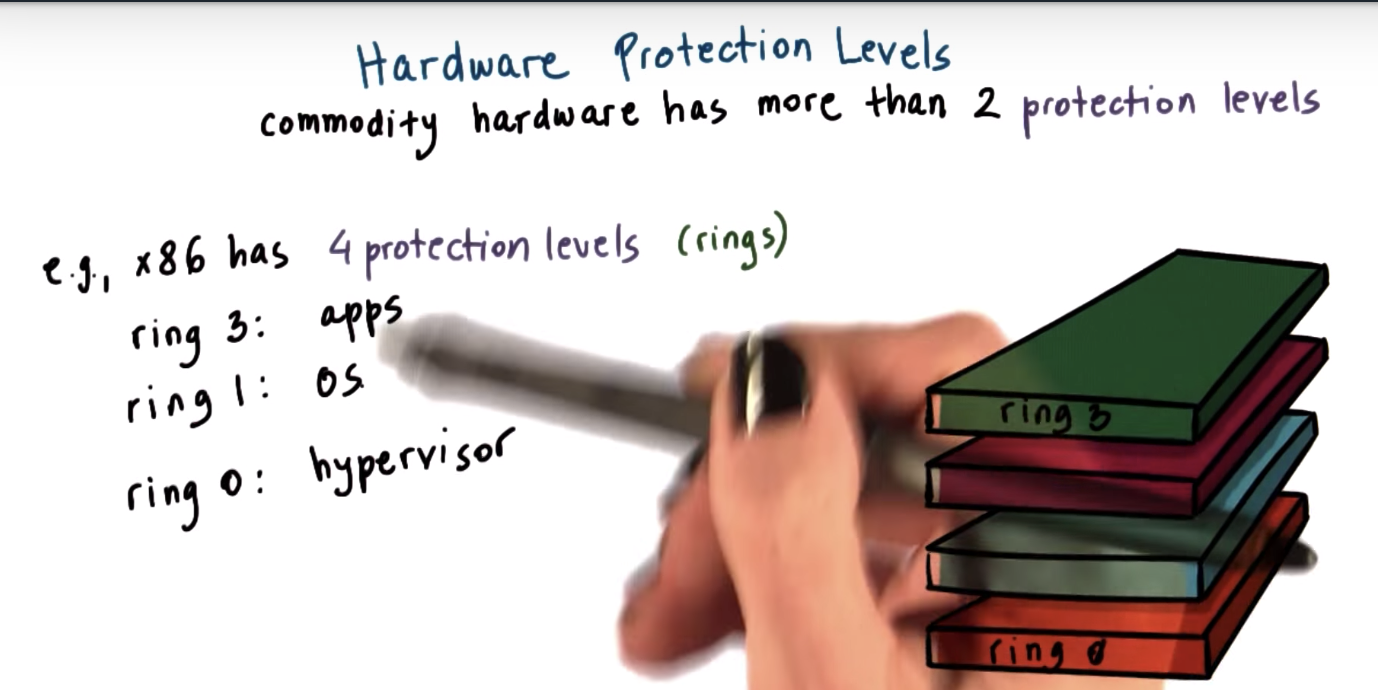
Hardware Protection Levels
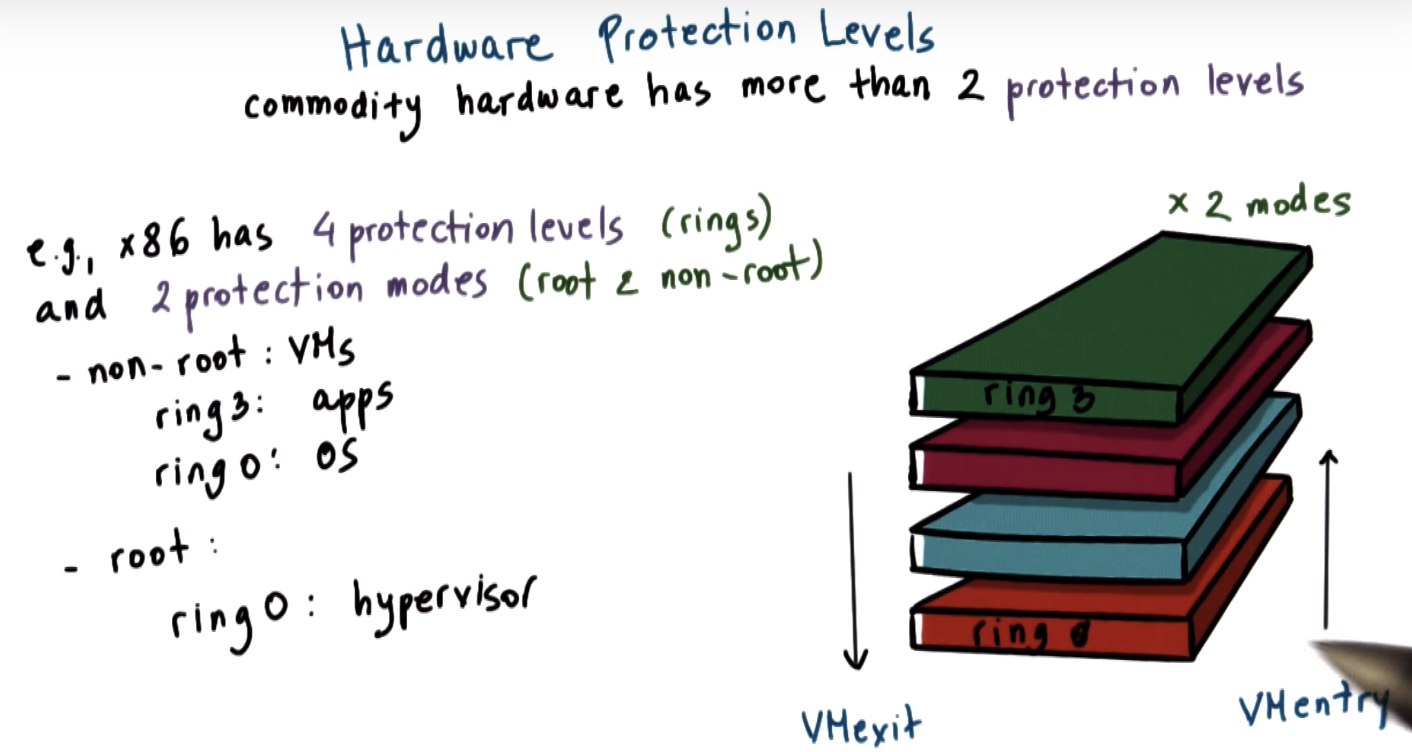
Processor Virtualization

x86 Virtualization in the Past


Binary Translation


the reason that this is done dynamically versus statically, so up front before any code is actually run, is because the exact execution sequence ay depend on the parameters that are available at runtime.
so it's input dependent. so you can not really do all of this in an efficient way statically up front.
or in some case you just cannot do it at all because you dont have the input parameters.
so then you dynamically capture these code blocks and then inspect them to see whether any of these 17 infamous instructions is about to be issued.
Paravirtualization

originally adapted and popularized by Xen
Open source verson Xen and Citrix Xen have diverged perhaps substantially over time.
BT and PV Quiz

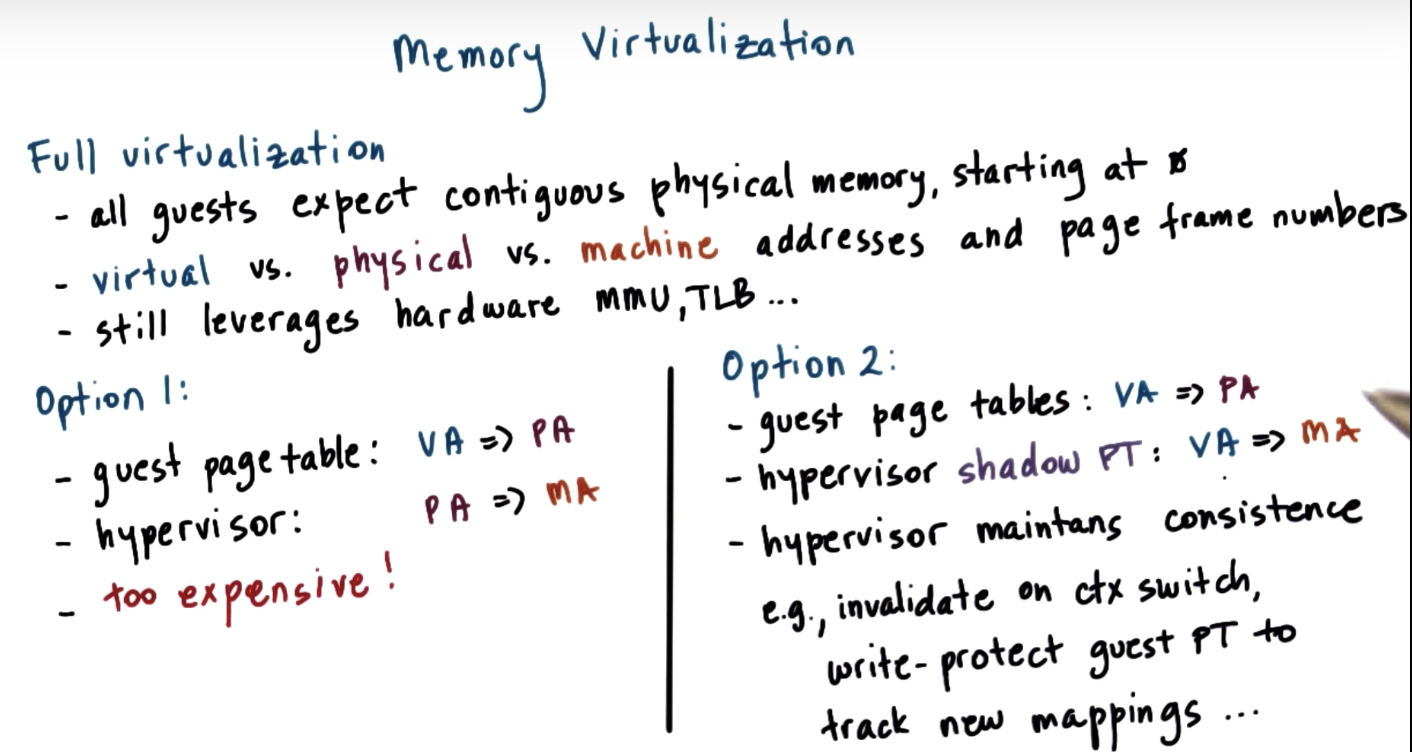
Memory Virtualization Full
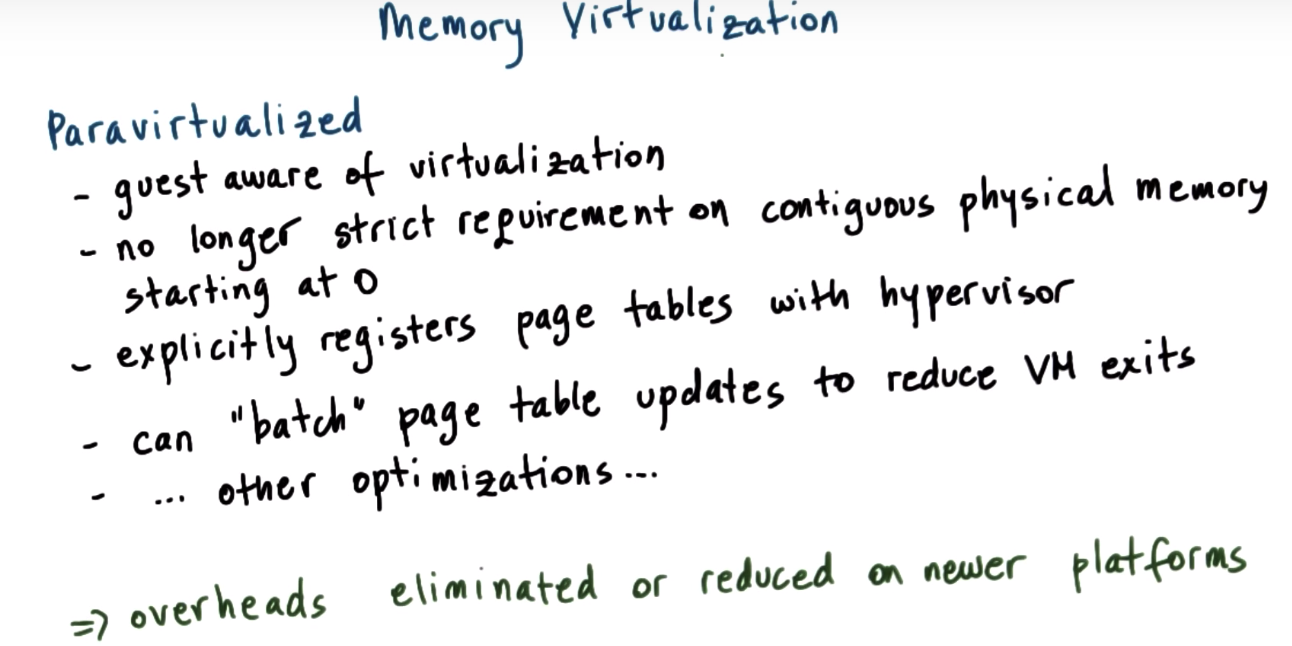
Memory Virtualization Paravirtualized
Device Virtualization
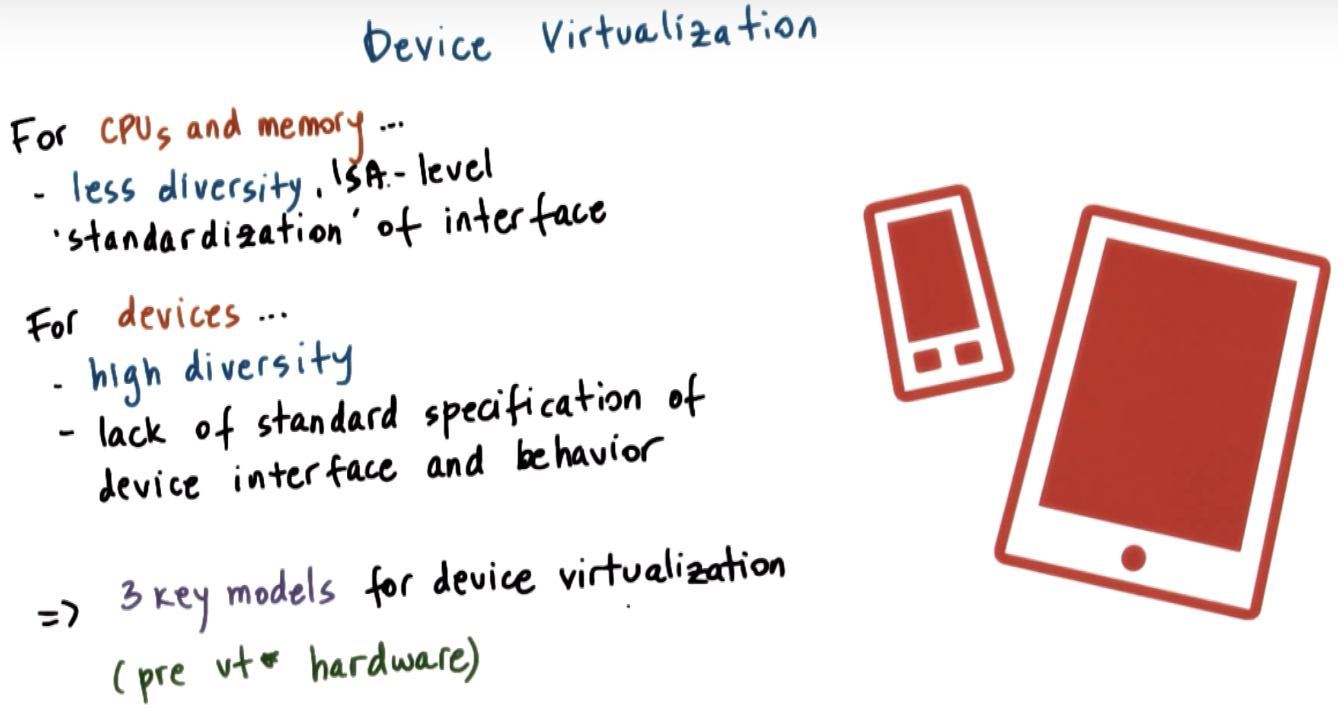
ISA => instruction set architecture => be standardized by hardware manufacturers
=> less complicated for CPU and memory because we only need to fit the specific ISA
Passthrough Model

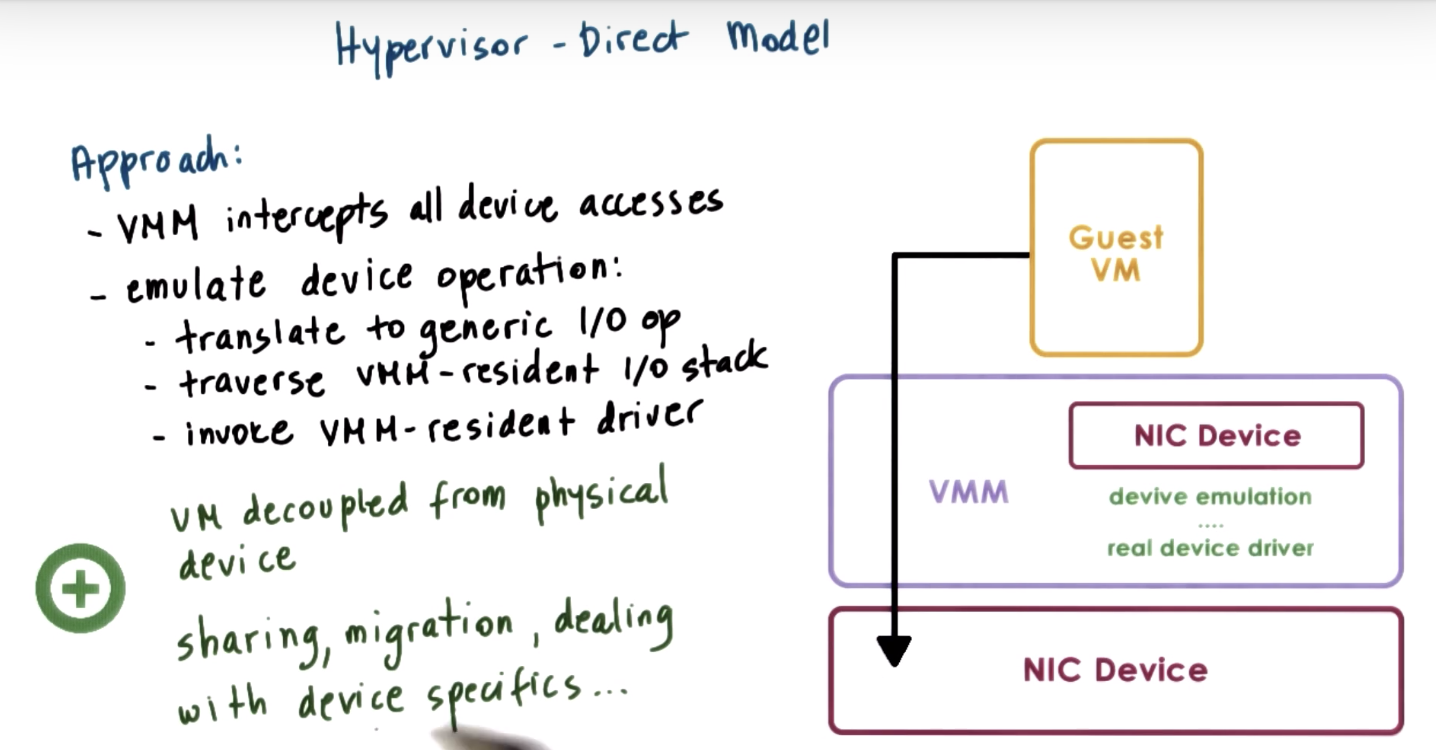
Hypervisor Direct Model

Split Device Driver Model

pass through => no supervision
hypervisor-directed => hypervisor in charge of translation
split device => VM is aware of the virtualization and adapts to the virtualizaiton.
Virtualization-related Hardware

clearly, there's some overheads that have to be incurred dut to virtualizaiton => virtualizaiton-friendly hardware => reduce number of bugs and ineffiency


With the split-device driver, all of the requests for device access are consolidated on the surface VM.
?????????
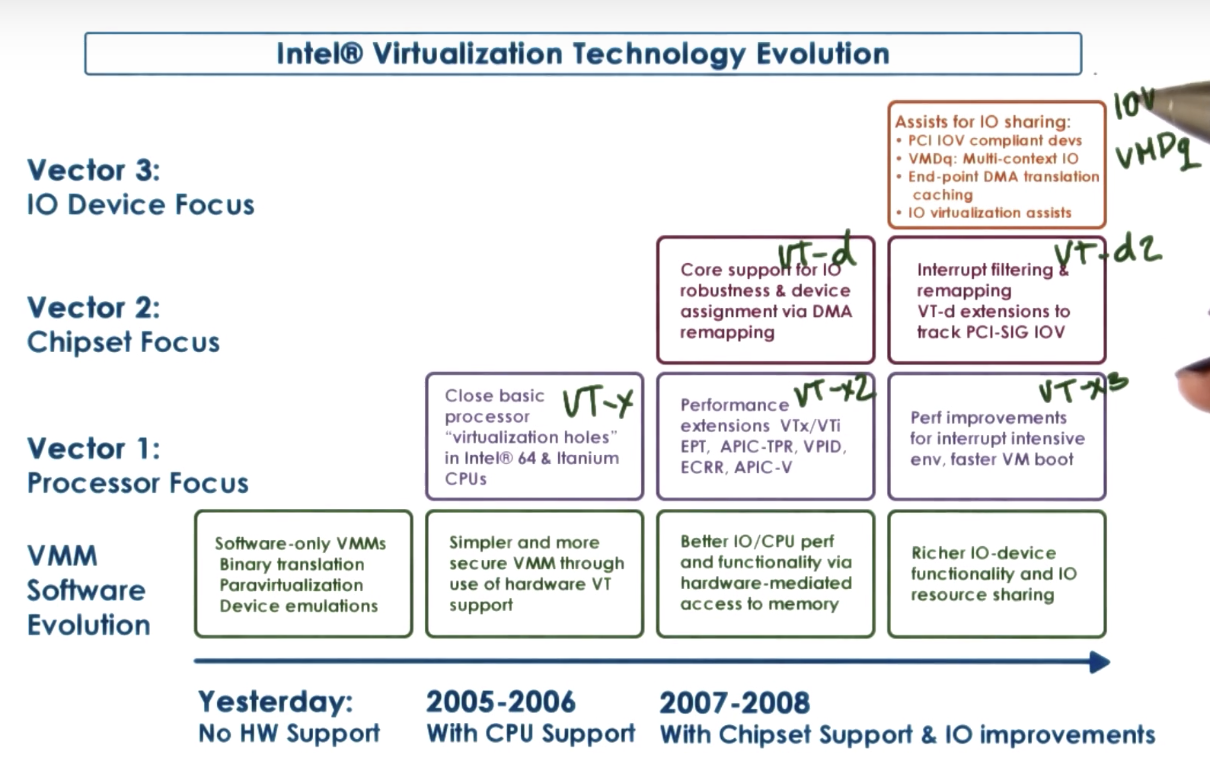
x86 VT Revolution